SaaS SEO services combine technical optimization, content strategy, and authority building specifically designed for software companies seeking sustainable organic growth. Unlike traditional SEO approaches, these specialized services address the unique challenges of subscription-based business models, complex buyer journeys, and highly competitive software markets.
For founders, marketing managers, and growth teams at software companies, understanding SaaS SEO is no longer optional. With customer acquisition costs rising across paid channels, organic search represents one of the most scalable and cost-effective paths to predictable revenue growth.
This guide covers everything from foundational strategies and keyword research to realistic timelines, pricing models, and provider selection. You will learn how to build a comprehensive SEO roadmap that connects directly to pipeline and revenue.

What Are SaaS SEO Services?
SaaS SEO services represent a specialized discipline within search engine optimization, tailored specifically for software-as-a-service companies. These services go beyond generic optimization tactics to address the distinct challenges that software businesses face in organic search.
Definition of SaaS SEO Services
SaaS SEO services encompass the strategic and technical activities designed to improve organic search visibility for software companies. This includes technical website optimization, content creation aligned with the software buyer journey, link building within the technology ecosystem, and performance measurement tied to subscription metrics.
The core objective differs from traditional SEO. Rather than simply driving traffic, SaaS SEO focuses on attracting qualified prospects who match ideal customer profiles and have genuine intent to evaluate or purchase software solutions. This requires deep understanding of how software buyers research, compare, and ultimately select products.
Professional SaaS SEO providers typically offer comprehensive service packages that include technical audits, keyword strategy development, content production, link acquisition, and ongoing performance optimization. The best providers understand both search engine mechanics and SaaS business fundamentals.
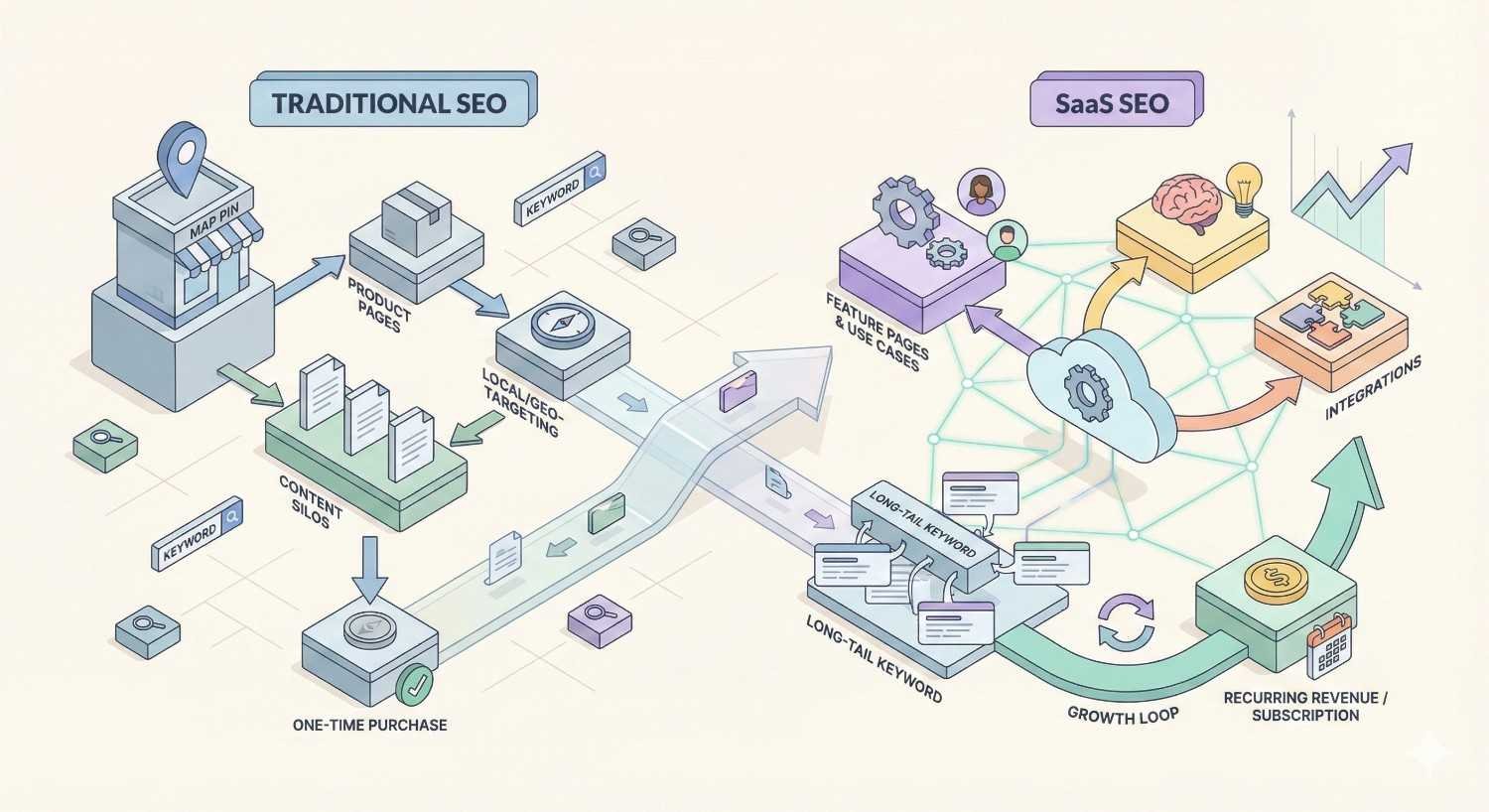
How SaaS SEO Differs from Traditional SEO
Traditional SEO often focuses on broad traffic acquisition and general visibility improvements. SaaS SEO requires a fundamentally different approach because software companies operate under unique business constraints and opportunities.
The subscription revenue model changes everything. A single organic visitor who converts to a paying customer might generate thousands of dollars in lifetime value. This means SaaS SEO must prioritize quality over quantity, targeting users with genuine purchase intent rather than maximizing raw traffic numbers.
Software products also have complex feature sets that create extensive keyword opportunities. A project management tool might rank for hundreds of feature-specific queries, integration searches, comparison terms, and use case variations. Traditional businesses rarely have this depth of product-related search demand.
The competitive landscape presents another distinction. SaaS markets often feature well-funded competitors with substantial content marketing budgets. Winning in organic search requires sophisticated strategies that combine technical excellence, content depth, and strategic link building.
Core Components of Software Company SEO
Effective SaaS SEO rests on four interconnected pillars that must work together for sustainable results.
Technical SEO forms the foundation. Software websites often use JavaScript frameworks, dynamic content, and complex application architectures that require specialized optimization approaches. Without solid technical fundamentals, content and link building efforts deliver diminished returns.
Content strategy drives organic visibility expansion. This includes product-focused pages, educational resources, comparison content, and thought leadership that addresses questions throughout the buyer journey. Content must demonstrate genuine expertise while targeting commercially valuable search queries.
Link building establishes domain authority within the software ecosystem. SaaS companies have unique link building opportunities through integration partnerships, software directories, industry publications, and technology communities. Strategic link acquisition accelerates ranking improvements and competitive positioning.
Analytics and measurement connect SEO activities to business outcomes. SaaS SEO requires tracking beyond traffic and rankings to include trial signups, demo requests, pipeline contribution, and ultimately revenue attribution from organic channels.
Why SaaS Companies Need Specialized SEO Services
Generic SEO approaches consistently underperform for software companies. The unique characteristics of SaaS businesses demand specialized expertise and tailored strategies.
The Unique SaaS Buyer Journey
Software purchasing decisions follow a distinct pattern that differs significantly from traditional product purchases. Understanding this journey is essential for effective SEO strategy.
The research phase extends longer than most industries. According to Gartner research, B2B buyers spend only 17% of their time meeting with potential suppliers. The majority of their journey happens through independent research, much of it through search engines.
Software buyers typically progress through awareness, consideration, and decision stages with specific information needs at each point. During awareness, they search for solutions to problems they are experiencing. In consideration, they compare options and evaluate features. At decision, they seek validation through reviews, case studies, and pricing information.
Effective SaaS SEO maps content to each stage of this journey. Top-of-funnel content captures problem-aware searchers. Middle-funnel content helps prospects evaluate solutions. Bottom-funnel content converts researchers into trial users or demo requests.
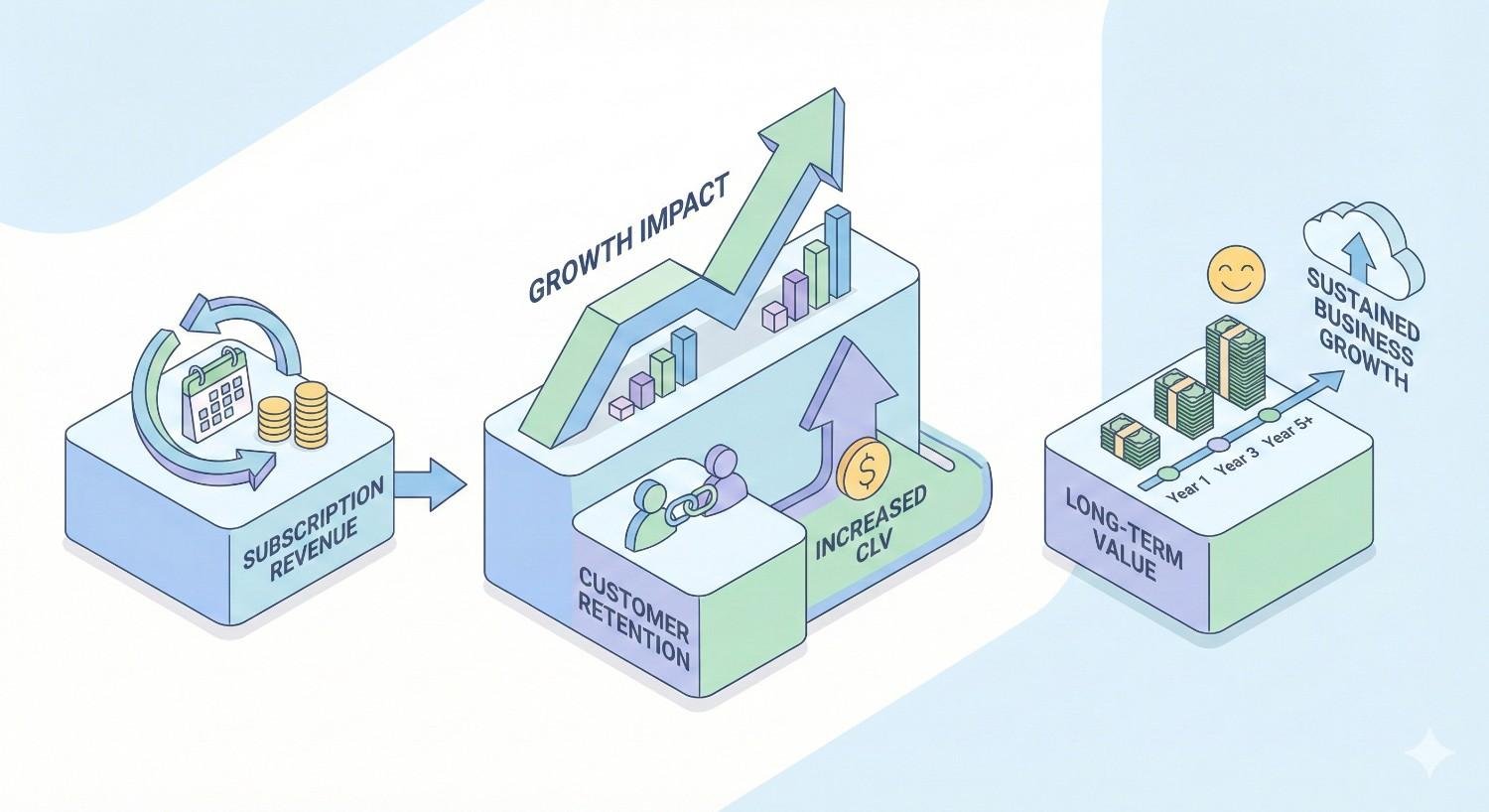
Subscription Revenue and Customer Lifetime Value Impact
The subscription business model fundamentally changes how SEO value should be calculated. A single organic conversion can generate substantial recurring revenue over months or years.
Consider a B2B SaaS product with $200 monthly pricing and 24-month average customer lifetime. Each organic conversion represents $4,800 in lifetime value. This dramatically changes the acceptable cost per acquisition and the investment justification for SEO.
Customer lifetime value also means that SEO investments compound over time. Unlike paid advertising where traffic stops when spending stops, organic rankings continue generating conversions month after month. The cumulative value of sustained organic visibility creates significant competitive advantages.
This economic reality makes SEO particularly attractive for SaaS companies seeking to reduce customer acquisition costs while building sustainable growth channels. The upfront investment in SEO pays dividends across the entire customer lifetime.
Competitive Landscape in Software Markets
Software markets have become intensely competitive, with well-funded companies investing heavily in organic search visibility. Standing out requires strategic sophistication and sustained execution.
Most software categories feature established players with substantial domain authority and content libraries. New entrants cannot simply publish a few blog posts and expect to compete. Winning requires comprehensive strategies that address technical foundations, content depth, and authority building simultaneously.
The competitive intensity also means that generic SEO tactics produce minimal results. Software companies need strategies specifically designed for their market dynamics, including competitor analysis, keyword gap identification, and differentiated positioning.
Specialized SaaS SEO services provide the expertise needed to compete effectively. Providers with software industry experience understand the competitive landscape and can develop strategies that create genuine differentiation in organic search.
Key Benefits of SEO for Software Companies
Investing in SEO delivers multiple strategic advantages for software companies beyond simple traffic increases. Understanding these benefits helps justify investment and set appropriate expectations.
Sustainable Organic Traffic Growth
Organic search traffic compounds over time in ways that paid channels cannot match. Each piece of content that ranks continues generating visitors indefinitely, creating cumulative growth effects.
Unlike paid advertising where traffic correlates directly with spending, organic traffic builds on previous investments. A blog post published today might generate traffic for years. Feature pages that rank well continue attracting prospects without ongoing costs.
This compounding effect becomes particularly powerful as content libraries expand. Software companies with hundreds of ranking pages generate substantial traffic volumes that would cost millions in paid advertising to replicate.
The sustainability of organic traffic also provides business stability. Companies overly dependent on paid channels face significant risk if advertising costs increase or platform policies change. Organic traffic provides a stable foundation that reduces overall marketing risk.
Reduced Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC)
Customer acquisition cost represents one of the most critical metrics for SaaS businesses. SEO offers a path to significantly lower CAC compared to paid channels.
Paid advertising costs have increased substantially across major platforms. WordStream data shows average cost-per-click in the software industry exceeds $3.80, with competitive terms reaching $50 or more. These costs make paid acquisition increasingly challenging for companies without substantial budgets.
Organic traffic, once established, has minimal marginal cost. The investment in SEO is largely upfront, with ongoing costs for content production and optimization. As organic traffic grows, the effective cost per visitor decreases dramatically.
For SaaS companies focused on unit economics, SEO represents one of the most efficient paths to sustainable growth. The combination of lower acquisition costs and higher lifetime value creates favorable economics that support long-term profitability.
Brand Authority and Trust Building
Ranking prominently in search results builds brand credibility in ways that paid placements cannot replicate. Users inherently trust organic results more than advertisements.
When prospects search for solutions and consistently find your content ranking highly, they develop positive brand associations. This visibility establishes your company as a legitimate player in the market, particularly important for newer companies competing against established brands.
Content that ranks well also demonstrates expertise. Educational resources, comprehensive guides, and thought leadership content that achieves organic visibility signals genuine knowledge and authority in your domain.
This trust-building effect extends beyond direct conversions. Prospects who discover your brand through organic search often return later through direct visits or branded searches. The initial organic touchpoint creates awareness that influences future purchasing decisions.
Long-Term ROI vs. Paid Advertising
The return on investment profile for SEO differs fundamentally from paid advertising. Understanding this difference is essential for appropriate resource allocation.
Paid advertising delivers immediate results but requires continuous spending. The moment you stop paying, traffic stops. This creates a linear relationship between investment and results with no compounding benefits.
SEO requires upfront investment before results materialize, but those results persist and compound over time. A comprehensive SEO program might take 6-12 months to show significant results, but the traffic generated continues for years.
When calculated over multi-year timeframes, SEO typically delivers superior ROI compared to paid channels. The initial investment period is followed by extended periods of high-value traffic at minimal marginal cost.
For SaaS companies planning for long-term growth rather than short-term metrics, SEO represents a strategic investment that builds lasting competitive advantages.
Essential SaaS SEO Strategies for 2025-2026
Effective SaaS SEO requires integrated strategies that address product visibility, content development, and technical foundations. The most successful software companies combine multiple approaches for comprehensive organic growth.
Product-Led SEO Strategy
Product-led SEO focuses on creating organic visibility for your software’s features, use cases, and competitive positioning. This approach captures high-intent searchers actively evaluating solutions.
Feature Page Optimization
Individual feature pages represent high-value SEO opportunities that many software companies underutilize. Each significant feature can target specific search queries from prospects seeking that capability.
Effective feature pages go beyond simple descriptions. They explain the problem the feature solves, demonstrate how it works, show real-world applications, and address common questions. This depth satisfies both user intent and search engine quality signals.
Feature pages should target specific keyword variations including “[feature] software,” “how to [accomplish task],” and “[feature] for [industry/use case].” This captures searchers at various stages of awareness and intent.
Internal linking between feature pages and related content strengthens topical authority. Creating content clusters around major features signals comprehensive expertise to search engines while providing users with complete information.
Use Case and Solution Pages
Use case pages target searchers looking for solutions to specific problems or applications within particular industries. These pages often capture highly qualified traffic from prospects with clear purchase intent.
Effective use case pages address specific scenarios where your software provides value. A project management tool might create pages for “marketing team project management,” “software development workflow,” or “agency client management.” Each page targets distinct audience segments with tailored messaging.
Solution pages take a similar approach but focus on problem categories rather than applications. Pages targeting “how to improve team collaboration” or “reducing project delays” capture problem-aware searchers who may not yet know specific solutions exist.
Both page types should include relevant case studies, specific feature highlights, and clear calls to action. The goal is converting research-stage visitors into trial users or demo requests.
Integration and Comparison Pages
Integration pages capture searchers looking for software that works with tools they already use. These pages often have high commercial intent and relatively low competition.
Creating pages for each significant integration your software supports targets queries like “[your product] [integration partner] integration” and “connect [tool A] with [tool B].” These searches indicate active evaluation and strong purchase intent.
Comparison pages address searchers directly comparing your software against competitors. While these pages require careful positioning, they capture bottom-funnel traffic from prospects making final decisions.
Effective comparison pages provide honest, balanced assessments while highlighting your genuine advantages. Overly promotional comparison content damages credibility and fails to satisfy user intent.
Content-Led Growth Strategy
Content marketing drives organic visibility expansion beyond product-focused pages. A strategic content approach addresses the full buyer journey while building topical authority.
Bottom-of-Funnel Content Optimization
Bottom-funnel content targets searchers ready to make purchasing decisions. This includes pricing pages, case studies, testimonials, and implementation guides.
Pricing pages often rank for high-intent queries like “[product] pricing” and “[product] cost.” Optimizing these pages for search visibility captures prospects in final evaluation stages.
Case studies and success stories target searches for “[product] reviews,” “[product] case study,” and industry-specific validation queries. These pages provide social proof while capturing organic traffic.
Implementation and onboarding content addresses concerns about adoption complexity. Pages explaining setup processes, integration steps, and time-to-value help convert hesitant prospects.
Middle-of-Funnel Educational Content
Middle-funnel content helps prospects evaluate solutions and understand their options. This includes comparison guides, buying guides, and educational resources about solution categories.
Buying guides targeting queries like “how to choose [software category]” or “what to look for in [solution type]” capture prospects actively researching options. These guides should provide genuine value while naturally positioning your solution.
Educational content explaining concepts, methodologies, and best practices establishes expertise while attracting qualified audiences. A CRM company might create content about sales processes, customer relationship management strategies, and pipeline optimization.
This content type builds trust and familiarity before prospects reach decision stages. Visitors who find valuable educational content often return when ready to evaluate specific solutions.
Top-of-Funnel Awareness Content
Top-funnel content captures broader audiences who may not yet recognize their need for your solution. This content builds brand awareness and creates entry points into your marketing funnel.
Problem-focused content addresses challenges your target audience faces. A time tracking software company might create content about productivity improvement, remote team management, or project estimation accuracy.
Industry trends, research reports, and thought leadership content attracts audiences interested in your domain. While these visitors may not convert immediately, they enter your awareness and nurturing systems.
Top-funnel content requires careful balance. The content must provide genuine value to rank well, but should also create natural pathways toward your solution. Overly promotional top-funnel content fails to satisfy informational intent.

Technical SEO Foundation for SaaS Websites
Technical SEO ensures search engines can effectively crawl, index, and rank your website. Software company websites often present unique technical challenges that require specialized attention.
Site Architecture and URL Structure
Logical site architecture helps both users and search engines understand your content organization. Clear hierarchies signal topical relationships and distribute link equity effectively.
URL structures should reflect content hierarchy and include relevant keywords. Product pages, feature pages, and content categories should have consistent, descriptive URL patterns.
Faceted navigation, common in software products with multiple features and use cases, requires careful handling to prevent duplicate content and crawl budget waste. Proper canonicalization and parameter handling ensure search engines index the right pages.
Internal linking architecture should connect related content and guide users through logical journeys. Strategic internal links strengthen topical clusters and help important pages accumulate authority.
Core Web Vitals and Page Speed
Page experience signals directly impact rankings and user engagement. Core Web Vitals measure loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) measures loading speed for the main content element. Software websites should target LCP under 2.5 seconds for optimal performance.
First Input Delay (FID) and Interaction to Next Paint (INP) measure interactivity responsiveness. Complex software interfaces may require optimization to meet performance thresholds.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) measures visual stability during page load. Dynamic content loading, common in software applications, can cause layout shifts that harm user experience and rankings.
JavaScript SEO Considerations
Many SaaS websites use JavaScript frameworks like React, Vue, or Angular that create specific SEO challenges. Search engines have improved JavaScript rendering, but issues persist.
Server-side rendering or static site generation ensures content is immediately available to search engine crawlers. Client-side only rendering can delay or prevent proper indexing.
Dynamic content loading requires careful implementation to ensure search engines can access all important content. Lazy loading, infinite scroll, and AJAX content updates need SEO-friendly implementations.
JavaScript-heavy sites should use Google Search Console’s URL Inspection tool to verify how Googlebot renders pages. Differences between rendered and source HTML can indicate indexing problems.
International SEO for Global SaaS
Software companies serving global markets need international SEO strategies to capture traffic across regions and languages.
Hreflang implementation tells search engines which language and regional versions to show different users. Proper hreflang prevents duplicate content issues and ensures users see appropriate content.
URL structures for international content can use subdirectories (/es/, /de/), subdomains (es.example.com), or country-code domains (example.es). Each approach has tradeoffs for implementation complexity and SEO signal consolidation.
Content localization goes beyond translation. Effective international SEO adapts content for local markets, including regional terminology, local examples, and market-specific positioning.
SaaS Keyword Research and Topic Clustering
Strategic keyword research forms the foundation of effective SaaS SEO. Understanding what your target audience searches for and how to organize content around those topics drives sustainable organic growth.
Identifying High-Intent SaaS Keywords
High-intent keywords indicate searchers with genuine interest in evaluating or purchasing software solutions. These keywords typically deliver the highest conversion rates and business value.
Product-category keywords like “[software type] software” or “best [solution category]” capture prospects actively seeking solutions. These terms often have high competition but justify the investment due to conversion potential.
Feature-specific keywords target searchers looking for particular capabilities. Terms like “[specific feature] tool” or “software with [capability]” indicate clear functional requirements.
Problem-solution keywords capture searchers describing challenges your software addresses. Understanding how prospects articulate their problems reveals valuable keyword opportunities.
Competitor and comparison keywords indicate active evaluation. Searches for “[competitor] alternatives” or “[product A] vs [product B]” represent bottom-funnel opportunities.
Building Topic Clusters for Software Products
Topic clusters organize content around central themes, signaling comprehensive expertise to search engines while providing users with complete information resources.
Each cluster centers on a pillar page covering a broad topic comprehensively. Supporting content addresses specific subtopics in greater depth, linking back to the pillar page.
For software companies, natural clusters form around product categories, use cases, industries served, and problem domains. A marketing automation platform might build clusters around email marketing, lead nurturing, campaign management, and marketing analytics.
Cluster architecture should reflect how your target audience thinks about topics. User research and search data reveal natural groupings and relationships between concepts.
Internal linking within clusters strengthens topical signals. Every piece of cluster content should link to the pillar page and relevant supporting content, creating clear topical associations.
Competitor Keyword Gap Analysis
Analyzing competitor keyword rankings reveals opportunities to capture traffic they currently own. Gap analysis identifies terms where competitors rank but you do not.
Tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, and Moz provide competitor keyword data showing ranking positions, traffic estimates, and keyword difficulty. This data reveals both opportunities and competitive challenges.
Prioritize gaps based on business value, not just traffic volume. A keyword driving 100 highly qualified visitors may be more valuable than one driving 10,000 unqualified visitors.
Gap analysis also reveals content types that perform well in your market. If competitors rank with comparison guides, case studies, or tool roundups, similar content formats may work for your site.
Search Intent Mapping for SaaS Funnels
Search intent describes what users actually want when they enter a query. Mapping intent to funnel stages ensures content satisfies user needs while supporting business objectives.
Informational intent indicates users seeking knowledge or understanding. These searches often use question formats or broad topic terms. Content should educate and build awareness.
Commercial investigation intent indicates users researching options before purchase. These searches often include comparison terms, “best” modifiers, or review-seeking language. Content should help evaluation while positioning your solution.
Transactional intent indicates users ready to take action. These searches often include brand names, pricing terms, or action words like “buy,” “signup,” or “demo.” Content should facilitate conversion.
Navigational intent indicates users seeking specific pages or brands. These searches typically include brand names or specific product terms. Ensuring your pages rank for branded queries protects against competitor interception.
On-Page SEO for SaaS Websites
On-page optimization ensures individual pages communicate relevance and value to both search engines and users. Effective on-page SEO combines technical elements with user experience considerations.
Optimizing SaaS Landing Pages
Landing pages for software products require specific optimization approaches that balance SEO requirements with conversion objectives.
Title tags should include primary keywords while compelling clicks from search results. For product pages, formats like “[Product Name]: [Primary Benefit] | [Brand]” balance keyword targeting with brand building.
Header structures should use H1 tags for primary page topics and H2-H6 tags for logical content hierarchy. Headers should include relevant keywords naturally while accurately describing section content.
Body content should comprehensively address the topic while naturally incorporating target keywords and semantic variations. Keyword density matters less than topical completeness and natural language usage.
Above-the-fold content should immediately communicate value propositions and include primary keywords. Users and search engines both prioritize content that appears first on the page.
Meta Tags and Schema Markup for Software
Meta tags and structured data help search engines understand page content and display rich results in search listings.
Meta descriptions should summarize page content in 150-160 characters while including target keywords and compelling users to click. While not a direct ranking factor, meta descriptions significantly impact click-through rates.
Schema markup provides structured data that search engines use for rich results. Software-relevant schema types include Product, SoftwareApplication, Organization, FAQ, and HowTo.
SoftwareApplication schema can display ratings, pricing, and operating system compatibility directly in search results. This enhanced visibility can significantly improve click-through rates for product pages.
FAQ schema enables question-and-answer content to appear as expandable results in search listings. This format captures additional SERP real estate and addresses common user questions directly.
Internal Linking Architecture
Strategic internal linking distributes page authority, establishes topical relationships, and guides users through your site. Effective internal linking is one of the most underutilized SEO tactics.
Link from high-authority pages to important pages you want to rank. Homepage links, popular blog posts, and frequently visited pages pass significant authority through internal links.
Use descriptive anchor text that includes relevant keywords. Generic anchors like “click here” or “learn more” waste opportunities to signal page topics to search engines.
Create logical linking paths that match user journeys. A visitor reading about a problem should find natural links to solution content, feature pages, and conversion opportunities.
Audit internal links regularly to identify orphaned pages, broken links, and opportunities to strengthen important pages. Tools like Screaming Frog and Sitebulb automate internal link analysis.
Conversion-Focused SEO Elements
SEO and conversion optimization should work together, not compete. Pages can rank well while also converting visitors effectively.
Clear calls to action should appear throughout content without disrupting user experience. CTAs should match user intent and funnel stage, offering appropriate next steps.
Social proof elements like testimonials, customer logos, and case study references build trust while adding relevant content. These elements can include keywords naturally while supporting conversion.
Page speed directly impacts both rankings and conversion rates. Google research shows that as page load time increases from 1 to 3 seconds, bounce probability increases by 32%.
Mobile optimization ensures pages perform well across devices. With mobile-first indexing, mobile experience directly impacts rankings even for desktop searches.
Link Building Strategies for SaaS Companies
Link building remains essential for competitive rankings in software markets. SaaS companies have unique opportunities to build authority through industry relationships and content assets.
Digital PR and Thought Leadership
Digital PR generates high-quality links through media coverage, expert contributions, and newsworthy content. This approach builds both links and brand visibility.
Original research and data studies attract links from publications seeking credible sources. Software companies can leverage product data, user surveys, or industry analysis to create linkable research assets.
Expert commentary on industry trends positions company leaders as authoritative sources. Journalists and bloggers regularly seek expert perspectives for articles, creating natural link opportunities.
Newsworthy announcements including funding rounds, major partnerships, and significant product launches can generate coverage and links from technology publications.
Building relationships with journalists and industry analysts creates ongoing opportunities. Regular, helpful engagement establishes your company as a reliable source for future coverage.
SaaS-Specific Link Building Tactics
Software companies have unique link building opportunities that other industries cannot access. Leveraging these opportunities efficiently builds relevant, high-quality backlinks.
Integration Partner Link Building
Integration partnerships create natural link opportunities that benefit both parties. Partners typically link to integration documentation, co-marketing content, and marketplace listings.
Integration marketplace listings on platforms like Salesforce AppExchange, HubSpot Marketplace, or Slack App Directory provide authoritative links while driving referral traffic.
Co-created content with integration partners, including joint webinars, case studies, and how-to guides, generates links from partner websites while reaching new audiences.
Technical documentation for integrations often earns links from developers and users seeking implementation guidance. Comprehensive, helpful documentation attracts natural links over time.
Software Directory and Review Site Links
Software directories and review platforms provide authoritative links while influencing purchase decisions. Maintaining optimized profiles across relevant platforms supports both SEO and sales.
Major platforms like G2, Capterra, TrustRadius, and GetApp allow company profiles with website links. Complete, optimized profiles improve visibility within these platforms while providing valuable backlinks.
Industry-specific directories relevant to your software category often have lower competition and highly targeted audiences. Identifying and claiming profiles on niche directories builds relevant link portfolios.
Review generation strategies that encourage satisfied customers to leave reviews improve directory visibility while building social proof. Higher ratings and more reviews typically improve directory rankings and click-through rates.
Guest Posting on Industry Publications
Contributing content to industry publications builds authority while earning contextual backlinks. Quality guest posts demonstrate expertise to new audiences.
Identify publications your target audience reads and that accept contributor content. Technology publications, industry blogs, and business media often welcome expert contributions.
Pitch topics that provide genuine value to the publication’s audience. Self-promotional content rarely gets accepted, while genuinely helpful content builds relationships for ongoing opportunities.
Guest post links should appear naturally within content, not forced into author bios. Contextual links within article body carry more SEO value than bio links.
Building Domain Authority for Software Brands
Domain authority develops through consistent link building, quality content, and technical excellence over time. There are no shortcuts, but strategic approaches accelerate progress.
Focus on earning links from relevant, authoritative sources rather than pursuing volume. A single link from a respected technology publication provides more value than dozens of low-quality directory links.
Create linkable assets that naturally attract backlinks over time. Tools, calculators, templates, and comprehensive guides earn links as people discover and reference them.
Monitor competitor backlink profiles to identify link opportunities they have accessed. If competitors have links from specific publications or directories, similar opportunities likely exist for your company.
Disavow toxic links that could harm your site. Low-quality, spammy, or irrelevant links can negatively impact rankings. Regular backlink audits identify links that should be disavowed.
SaaS SEO Timelines and Realistic Expectations
Understanding realistic timelines helps set appropriate expectations and maintain commitment through the initial investment period. SEO results develop gradually but compound significantly over time.
Month-by-Month SEO Timeline for SaaS
While every situation differs, general patterns emerge for SaaS SEO programs. Understanding typical timelines helps with planning and expectation setting.
Months 1-2: Foundation and audit phase. Technical issues are identified and prioritized. Keyword research and content strategy development begin. Quick wins are identified and implemented.
Months 3-4: Technical fixes are implemented. Initial content production begins. Link building outreach starts. Early ranking movements may appear for lower-competition terms.
Months 5-6: Content library expands. Link building gains momentum. Rankings improve for target keywords. Traffic increases become measurable.
Months 7-9: Compound effects begin appearing. Multiple pages rank for target terms. Organic traffic shows consistent growth. Conversion optimization refines based on data.
Months 10-12: Significant traffic and ranking improvements materialize. ROI becomes clearly measurable. Strategy refinements based on performance data. Expansion into additional keyword opportunities.
Year 2 and beyond: Compounding growth continues. Topical authority strengthens. Competitive positions solidify. SEO becomes a primary growth channel.
Factors That Influence Ranking Speed
Multiple factors affect how quickly SEO efforts produce results. Understanding these factors helps set realistic expectations for specific situations.
Domain authority and history significantly impact timeline. Established domains with existing authority see faster results than new domains starting from zero.
Competition level in target keywords affects difficulty and timeline. Highly competitive terms require more time and resources than lower-competition opportunities.
Content quality and comprehensiveness influence ranking speed. Exceptional content that clearly exceeds competitors can rank faster than merely adequate content.
Technical foundation affects how quickly search engines can crawl and index improvements. Sites with significant technical issues may see delayed results until those issues are resolved.
Link building velocity and quality impact authority growth. Consistent acquisition of quality links accelerates ranking improvements.
Early Wins vs. Long-Term Growth Milestones
Balancing quick wins with long-term strategy maintains momentum while building sustainable growth. Both elements are essential for successful SEO programs.
Early wins typically come from technical fixes, low-competition keywords, and optimization of existing content. These improvements can show results within weeks rather than months.
Long-competition keywords, new content development, and authority building require sustained effort over months. These investments deliver larger returns but require patience.
Effective SEO programs pursue both simultaneously. Quick wins demonstrate progress and build stakeholder confidence while long-term investments develop sustainable competitive advantages.
Celebrate early wins while maintaining focus on strategic objectives. Short-term results should not distract from the larger goal of building dominant organic visibility.
Setting KPIs and Success Metrics
Clear KPIs enable progress tracking and demonstrate SEO value to stakeholders. Metrics should connect SEO activities to business outcomes.
Traffic metrics including organic sessions, new users, and pageviews show visibility growth. Segment by landing page type to understand which content drives results.
Ranking metrics track positions for target keywords over time. Focus on keywords with business value rather than vanity metrics.
Engagement metrics including bounce rate, time on page, and pages per session indicate content quality and relevance. Poor engagement may indicate intent mismatch or content issues.
Conversion metrics connect traffic to business outcomes. Track trial signups, demo requests, and other conversion events from organic traffic.
Revenue metrics attribute pipeline and closed revenue to organic channels. This requires proper attribution setup but provides the clearest ROI demonstration.
Measuring SaaS SEO Performance and ROI
Effective measurement connects SEO activities to business outcomes. Proper tracking and attribution enable data-driven optimization and stakeholder communication.
Essential SaaS SEO Metrics and KPIs
SaaS SEO measurement requires metrics that reflect both search performance and business impact. Tracking the right metrics enables informed decision-making.
Organic traffic growth shows overall visibility improvement. Track month-over-month and year-over-year changes to identify trends and seasonality.
Keyword rankings for target terms indicate competitive positioning. Track rankings for high-value keywords while monitoring overall keyword portfolio growth.
Click-through rate from search results indicates title and description effectiveness. Low CTR despite good rankings suggests optimization opportunities.
Organic conversion rate measures how effectively traffic converts to desired actions. Compare against other channels and track changes over time.
Customer acquisition cost from organic channels enables comparison against paid alternatives. Calculate by dividing SEO investment by organic customer acquisitions.
Attribution Models for Organic Traffic
Attribution determines how credit for conversions is assigned across touchpoints. Proper attribution reveals organic search’s true contribution to revenue.
Last-click attribution assigns full credit to the final touchpoint before conversion. This model often undervalues organic search, which frequently initiates journeys completed through other channels.
First-click attribution assigns credit to the initial touchpoint. This model better reflects organic search’s role in awareness and discovery.
Linear attribution distributes credit equally across all touchpoints. This provides balanced perspective but may not reflect actual influence.
Position-based attribution assigns higher weight to first and last touchpoints. This model often provides the most realistic view of organic search contribution.
Data-driven attribution uses machine learning to assign credit based on actual conversion patterns. This approach requires sufficient data volume but provides the most accurate attribution.
Connecting SEO to Revenue and Pipeline
Demonstrating SEO’s revenue impact requires connecting organic traffic to pipeline and closed deals. This connection justifies investment and guides strategy.
Implement proper tracking to identify organic traffic sources for leads and opportunities. UTM parameters, CRM integration, and marketing automation enable this tracking.
Calculate pipeline contribution by summing opportunity values from organic sources. Track this metric monthly to show SEO’s impact on sales pipeline.
Measure closed revenue attributed to organic channels. This provides the clearest ROI calculation and demonstrates SEO’s business value.
Compare organic customer lifetime value against other channels. Organic customers often have higher retention and lifetime value due to stronger initial intent.
Reporting Frameworks for Stakeholders
Effective reporting communicates SEO progress and value to different audiences. Tailor reports to stakeholder interests and decision-making needs.
Executive reports should focus on business outcomes: revenue, pipeline, and ROI. Include trend lines showing progress over time and comparison against targets.
Marketing team reports include tactical metrics: traffic, rankings, and conversions. Provide enough detail to inform optimization decisions.
Technical reports for development teams focus on implementation status, technical issues, and performance metrics. Include specific recommendations and priorities.
Regular reporting cadence maintains visibility and accountability. Monthly reports work for most stakeholders, with quarterly deep-dives for strategic review.
How Much Do SaaS SEO Services Cost?
Understanding SEO pricing helps with budgeting and provider evaluation. Costs vary significantly based on scope, provider type, and competitive requirements.
SaaS SEO Pricing Models Explained
SEO providers use several pricing models, each with different implications for scope, flexibility, and value.
Monthly retainer models charge fixed fees for ongoing services. Retainers typically range from $3,000 to $25,000+ monthly for SaaS companies, depending on scope and provider caliber.
Project-based pricing charges fixed fees for defined deliverables. This model works well for specific initiatives like technical audits, content projects, or site migrations.
Hourly consulting charges for time spent on SEO activities. Rates typically range from $150 to $500+ per hour depending on expertise level.
Performance-based pricing ties fees to results achieved. While appealing in theory, this model creates misaligned incentives and is generally avoided by reputable providers.
Hybrid models combine elements of different approaches. A common structure includes a base retainer plus project fees for specific initiatives.
Factors That Affect SEO Service Pricing
Multiple factors influence SEO pricing beyond simple service scope. Understanding these factors helps evaluate proposals and set realistic budgets.
Competitive intensity in your market affects required investment. Highly competitive software categories require more resources to achieve meaningful results.
Current website condition impacts initial investment needs. Sites with significant technical issues or thin content require more upfront work.
Growth objectives influence scope and timeline. Aggressive growth targets require larger investments than maintenance-focused programs.
Provider expertise and reputation affect pricing. Agencies with proven SaaS experience and strong track records command premium rates.
Geographic location of the provider influences pricing. Agencies in major markets typically charge more than those in lower-cost regions.
Budgeting for SEO as a SaaS Company
Appropriate SEO budgets depend on company stage, growth objectives, and competitive requirements. General guidelines help with initial planning.
Early-stage startups might allocate $2,000-5,000 monthly for foundational SEO work. This covers basic technical optimization, initial content development, and limited link building.
Growth-stage companies typically invest $5,000-15,000 monthly for comprehensive programs. This enables sustained content production, active link building, and ongoing optimization.
Enterprise SaaS companies often invest $15,000-50,000+ monthly for competitive markets. This supports large-scale content operations, aggressive link building, and dedicated resources.
Budget allocation should reflect strategic priorities. Companies prioritizing organic growth should invest accordingly, while those focused on other channels may allocate less.
Plan for sustained investment over 12-24 months minimum. SEO requires consistent effort over time to produce meaningful results.
In-House SEO vs. SaaS SEO Agency: Which Is Right for You?
Choosing between in-house teams and agency partnerships depends on company stage, resources, and strategic priorities. Both approaches have distinct advantages.
Pros and Cons of In-House SEO Teams
Building internal SEO capabilities provides control and integration but requires significant investment and expertise development.
Advantages of in-house teams: Deep product and market knowledge enables highly relevant content and strategy. Internal teams understand nuances that external partners may miss.
Direct integration with product, engineering, and marketing teams enables faster implementation and better coordination.
Institutional knowledge accumulates over time, building lasting capabilities that remain with the company.
Disadvantages of in-house teams: Recruiting experienced SaaS SEO talent is challenging and expensive. Senior SEO professionals command $80,000-150,000+ salaries plus benefits.
Single points of failure create risk. If your SEO person leaves, capabilities may leave with them.
Limited perspective from working on one site can lead to blind spots. Agencies see patterns across many clients.
Keeping skills current requires ongoing investment in training and tools.
Benefits of Partnering with a SaaS SEO Agency
Agency partnerships provide expertise and scalability without the overhead of building internal teams.
Advantages of agency partnerships: Access to specialized expertise across technical SEO, content, and link building. Agencies employ specialists in each discipline.
Scalable resources can expand or contract based on needs. Agencies can deploy additional resources for major initiatives.
Diverse experience from working with multiple clients provides broader perspective and proven playbooks.
Established processes and tools reduce ramp-up time and improve efficiency.
Disadvantages of agency partnerships: Less deep product knowledge than internal teams. Agencies require onboarding and ongoing communication to stay aligned.
Divided attention across multiple clients may limit responsiveness. Ensure clear expectations for communication and turnaround.
Potential for misaligned incentives if agency priorities differ from your goals. Choose partners with transparent practices.
Hybrid Models and When to Use Them
Many successful SaaS companies combine internal resources with agency support. Hybrid models capture benefits of both approaches.
Internal SEO leadership with agency execution works well for companies wanting strategic control with scalable implementation. An internal SEO manager directs strategy while agencies handle content production and link building.
Agency strategy with internal execution suits companies with content and development resources but lacking SEO expertise. Agencies provide direction while internal teams implement.
Specialized agency support for specific functions allows companies to build internal capabilities gradually. Agencies might handle link building while internal teams manage content and technical SEO.
The right model depends on your specific situation, resources, and growth stage. Many companies evolve their approach as they scale.
How to Choose the Right SaaS SEO Service Provider
Selecting the right SEO partner significantly impacts results. Thorough evaluation helps identify providers who can deliver meaningful outcomes.
Questions to Ask Potential SEO Partners
Asking the right questions reveals provider capabilities, approach, and fit. These questions help evaluate potential partners effectively.
Experience questions: What experience do you have with SaaS companies specifically? Ask for relevant examples and results.
Can you share case studies from software companies similar to ours? Look for demonstrated success in comparable situations.
Who would work on our account, and what is their background? Understand the actual team, not just sales representatives.
Process questions: How do you approach SaaS keyword research and strategy development? Look for sophisticated understanding of software buyer journeys.
What does your typical engagement timeline look like? Ensure expectations align with realistic SEO timelines.
How do you measure and report on results? Confirm they track metrics that matter to your business.
Collaboration questions: How do you work with internal marketing and product teams? Look for collaborative approaches rather than siloed execution.
What do you need from us to be successful? Understand resource requirements and expectations.
How do you handle communication and project management? Ensure their processes match your preferences.
Red Flags and Warning Signs to Avoid
Certain warning signs indicate providers who may not deliver results or could potentially harm your site. Avoid providers exhibiting these behaviors.
Guaranteed rankings for specific keywords indicate either dishonesty or willingness to use risky tactics. No legitimate provider can guarantee specific ranking positions.
Vague or evasive answers about methods, team members, or past results suggest potential problems. Reputable providers are transparent about their approaches.
Extremely low pricing compared to market rates often indicates inexperience, offshore outsourcing, or corner-cutting that produces poor results.
Emphasis on vanity metrics like traffic volume without connection to business outcomes suggests misaligned priorities.
Reluctance to provide references or case studies may indicate lack of successful client relationships.
Long-term contracts with difficult exit terms protect the provider rather than the client. Reputable agencies earn continued business through results.
Evaluating Case Studies and Track Records
Case studies and references provide evidence of provider capabilities. Evaluate these materials critically to assess fit.
Look for case studies from companies similar to yours in size, market, and challenges. Success with enterprise software companies may not translate to early-stage startups.
Verify claimed results when possible. Ask for references you can contact directly to confirm case study accuracy.
Understand the context behind results. What was the starting point? What resources were invested? What timeline produced the results?
Ask about challenges and failures, not just successes. How providers handle difficulties reveals their problem-solving capabilities and honesty.
Request references from current clients, not just past successes. Current client satisfaction indicates ongoing service quality.
Common SaaS SEO Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Learning from common mistakes helps avoid costly errors. These pitfalls frequently undermine SaaS SEO efforts.
Ignoring Technical SEO Fundamentals
Technical issues can completely undermine content and link building investments. Addressing technical foundations first ensures other efforts produce results.
Crawlability problems prevent search engines from discovering and indexing content. JavaScript rendering issues, blocked resources, and poor site architecture create invisible barriers to ranking.
Site speed problems harm both rankings and user experience. Software websites with complex functionality often have performance issues that require dedicated optimization.
Mobile experience issues impact rankings through mobile-first indexing. Ensure your site performs well across devices, not just desktop.
Duplicate content from URL parameters, pagination, or content syndication dilutes ranking signals. Proper canonicalization and parameter handling prevent these issues.
Targeting Wrong Keywords and Intent Mismatch
Keyword selection mistakes waste resources on traffic that does not convert. Strategic keyword targeting focuses efforts on valuable opportunities.
Chasing high-volume keywords without considering intent attracts visitors who are not potential customers. A keyword with 10,000 monthly searches but informational intent may produce fewer conversions than a 500-search commercial keyword.
Ignoring long-tail opportunities leaves valuable traffic to competitors. Specific, lower-volume keywords often have higher conversion rates and lower competition.
Failing to map keywords to funnel stages creates content gaps. Ensure coverage across awareness, consideration, and decision stages.
Not updating keyword strategy as markets evolve allows competitors to capture emerging opportunities. Regular keyword research identifies new trends and shifting search behavior.
Neglecting Product-Market Fit in Content
Content that does not resonate with target audiences fails regardless of SEO optimization. Alignment between content and audience needs is essential.
Generic content that could apply to any software company fails to differentiate. Content should reflect your specific product, positioning, and target customers.
Ignoring customer language and terminology creates disconnect. Use the words and phrases your customers actually use, not internal jargon.
Failing to address real customer problems produces content that ranks but does not convert. Understand and address the actual challenges your customers face.
Not involving product and customer-facing teams in content development misses valuable insights. These teams understand customer needs better than marketing alone.
Expecting Immediate Results
Unrealistic timeline expectations lead to premature strategy changes or abandoned efforts. Understanding SEO timelines maintains commitment through the investment period.
SEO typically requires 6-12 months to show significant results. Expecting major improvements in weeks or a few months sets up disappointment.
Changing strategies before they have time to work prevents any approach from succeeding. Give strategies adequate time before evaluating and adjusting.
Comparing SEO timelines to paid advertising creates unfair expectations. Paid delivers immediate but temporary results; SEO delivers delayed but lasting results.
Not celebrating incremental progress undermines team morale. Recognize improvements in rankings, traffic, and engagement even before major results materialize.
SaaS SEO Case Studies: Real Results and Learnings
Examining real-world examples illustrates how SaaS SEO strategies produce results. These patterns inform strategy development and expectation setting.
B2B SaaS SEO Success Story
A B2B project management software company demonstrates typical SaaS SEO progression and results.
Starting situation: The company had a functional website but minimal organic visibility. Monthly organic traffic was under 5,000 sessions, with few rankings for target keywords.
Strategy implemented: Comprehensive technical audit and fixes addressed crawlability and performance issues. Content strategy focused on product-led pages for features and use cases, plus educational content for the project management topic cluster. Link building targeted integration partners and industry publications.
Timeline and results: Months 1-3 focused on technical fixes and content planning. Months 4-6 saw initial content production and early ranking improvements. By month 9, organic traffic had grown to 25,000 monthly sessions. At month 12, traffic exceeded 50,000 sessions with strong conversion rates.
Key success factors: Patient investment through the initial period, comprehensive technical foundation, and content aligned with buyer journey stages.
B2C Software Company Growth Example
A consumer productivity app illustrates SEO success in B2C software markets.
Starting situation: The app had strong product-market fit but relied heavily on paid acquisition. Organic traffic was minimal despite a quality product.
Strategy implemented: Content strategy targeted problem-aware searchers looking for productivity solutions. Feature pages optimized for specific use cases. App store optimization complemented website SEO.
Timeline and results: Content production began immediately with focus on high-intent keywords. By month 6, several articles ranked on page one for target terms. Month 12 saw organic traffic contributing 30% of new user signups, significantly reducing overall CAC.
Key success factors: Focus on conversion-oriented content rather than just traffic, integration of website SEO with app store optimization, and consistent content production.
Key Takeaways and Patterns
Common patterns emerge across successful SaaS SEO programs. These patterns inform strategy development.
Technical foundations matter. Every successful case study began with addressing technical issues that could undermine other efforts.
Content aligned with buyer journey produces results. Successful programs create content for each funnel stage rather than focusing only on top-of-funnel traffic.
Patience and consistency are essential. Results compound over time, but only with sustained effort through the initial investment period.
Integration with broader marketing amplifies results. SEO works best when coordinated with product marketing, sales enablement, and other channels.
Measurement and optimization improve outcomes. Tracking results and adjusting based on data produces better outcomes than set-and-forget approaches.
Future of SaaS SEO: Trends and Predictions
Understanding emerging trends helps prepare for future changes. These developments will shape SaaS SEO strategy in coming years.
AI and Machine Learning Impact on SaaS SEO
Artificial intelligence is transforming both search engines and SEO practices. Adapting to these changes maintains competitive positioning.
Search engines increasingly use AI to understand content quality, relevance, and user satisfaction. This makes genuine expertise and helpful content more important than technical optimization tricks.
AI content generation tools create both opportunities and challenges. While AI can assist content production, search engines are developing capabilities to identify and potentially devalue purely AI-generated content.
AI-powered search features like Google’s AI Overviews change how users interact with search results. Optimizing for these features requires structured, authoritative content that AI systems can confidently cite.
Personalization through AI means different users may see different results for the same query. Building broad topical authority becomes more important than optimizing for specific keyword variations.
Voice Search and Conversational Queries
Voice search and conversational interfaces are changing how people search. Adapting content for these patterns captures emerging traffic.
Voice searches tend to be longer and more conversational than typed queries. Content should address natural language questions, not just keyword phrases.
Featured snippets and direct answers become more important as voice assistants read results aloud. Structuring content to provide clear, concise answers improves voice search visibility.
Local and immediate-need queries dominate voice search. SaaS companies may see less direct impact, but understanding voice patterns informs overall content strategy.
Conversational AI interfaces like ChatGPT are becoming search alternatives for some users. Creating content that AI systems can accurately cite and reference maintains visibility across platforms.
Zero-Click Searches and SERP Evolution
Search result pages increasingly provide answers directly, reducing clicks to websites. Adapting to this reality maintains organic value.
Featured snippets, knowledge panels, and AI overviews answer many queries without requiring clicks. Winning these positions provides visibility even without traffic.
Brand building becomes more important as direct-answer features reduce informational traffic. Users who see your brand in search results may later search directly for your company.
Bottom-funnel and transactional queries maintain click-through rates better than informational queries. Focusing on high-intent keywords protects against zero-click erosion.
Diversifying traffic sources reduces dependence on any single channel. While SEO remains valuable, building presence across multiple platforms provides stability.
Getting Started with SaaS SEO Services
Taking action on SEO requires clear first steps and prioritization. These starting points help launch effective SEO programs.
SEO Audit: Your First Step
Comprehensive audits reveal current status and prioritize improvements. Starting with an audit ensures efforts address the most impactful issues.
Technical audits identify crawlability, indexation, and performance issues. Tools like Screaming Frog, Sitebulb, and Google Search Console reveal technical problems.
Content audits assess existing content quality, coverage, and optimization. Identify gaps, underperforming content, and optimization opportunities.
Backlink audits evaluate current link profile quality and identify toxic links. Tools like Ahrefs and Moz provide backlink analysis capabilities.
Competitive audits reveal how competitors approach SEO and identify opportunities. Understanding competitive positioning informs strategy development.
Building Your SaaS SEO Roadmap
Strategic roadmaps prioritize activities and set realistic timelines. Effective roadmaps balance quick wins with long-term investments.
Prioritize technical fixes that could block other efforts. Address crawlability, indexation, and major performance issues first.
Identify quick-win content opportunities. Existing content that could rank with optimization, low-competition keywords, and conversion page improvements often produce fast results.
Plan sustained content development aligned with keyword strategy. Map content production to target keywords and funnel stages.
Establish link building processes for ongoing authority development. Identify partnership opportunities, content promotion channels, and outreach targets.
Set milestones and checkpoints for progress evaluation. Regular review enables strategy adjustment based on results.
Quick Wins to Implement Today
Immediate actions can produce results while longer-term strategies develop. These quick wins provide early momentum.
Optimize title tags and meta descriptions for key pages. Improved titles and descriptions can increase click-through rates within days.
Fix obvious technical issues identified in Google Search Console. Addressing crawl errors and indexation problems removes barriers to ranking.
Add internal links from high-authority pages to important target pages. Strategic internal linking can improve rankings relatively quickly.
Update and expand thin content on important pages. Adding depth to existing content often produces faster results than creating new pages.
Claim and optimize profiles on relevant software directories. These quick wins provide links and visibility while longer-term strategies develop.
Conclusion
SaaS SEO services provide software companies with sustainable paths to organic growth, reduced customer acquisition costs, and lasting competitive advantages. The strategies, timelines, and measurement approaches covered in this guide equip you to make informed decisions about SEO investment and execution.
Success requires patience, strategic focus, and consistent execution over time. The compounding nature of SEO means that investments made today continue generating returns for years, making it one of the most valuable long-term growth channels available to software companies.
At White Label SEO Service, we help SaaS companies build comprehensive organic growth programs that connect directly to revenue and pipeline. Contact us to discuss how specialized SaaS SEO services can accelerate your company’s growth trajectory.
Frequently Asked Questions About SaaS SEO Services
How long does SaaS SEO take to show results?
Most SaaS companies see meaningful results within 6-12 months of consistent SEO effort. Early improvements in rankings and traffic often appear by months 4-6, with significant business impact typically materializing by month 9-12. Competitive markets may require longer timelines.
What’s the difference between SaaS SEO and regular SEO?
SaaS SEO addresses the unique characteristics of software businesses including subscription revenue models, complex buyer journeys, and technical website architectures. It focuses on metrics like customer lifetime value and trial conversions rather than just traffic, and leverages SaaS-specific opportunities like integration partnerships and software directories.
Can SEO work for early-stage SaaS startups?
Yes, SEO can be highly effective for early-stage startups, though strategy should match resources and timeline expectations. Startups can focus on lower-competition keywords, build foundational content, and establish technical best practices. Early SEO investment compounds over time, providing advantages as the company scales.
How do I measure SEO ROI for my software company?
Calculate SEO ROI by tracking organic traffic conversions through your funnel to closed revenue. Implement proper attribution to credit organic touchpoints, then compare attributed revenue against SEO investment. Include both direct conversions and assisted conversions where organic search played a role in the customer journey.
What SEO tools do SaaS companies need?
Essential tools include Google Search Console and Google Analytics for performance tracking, keyword research tools like Semrush or Ahrefs for strategy development, technical audit tools like Screaming Frog for site analysis, and rank tracking tools for monitoring progress. Most companies also benefit from content optimization tools and backlink analysis platforms.
Should SaaS companies focus on SEO or paid ads first?
The optimal approach depends on timeline and resources. Paid advertising delivers immediate results but requires ongoing spending. SEO requires upfront investment but produces lasting results. Many successful SaaS companies run both simultaneously, using paid for immediate needs while building organic visibility for long-term sustainability.
What makes a SaaS SEO agency different from a general SEO agency?
SaaS-specialized agencies understand software buyer journeys, subscription business models, and technical challenges specific to software websites. They have experience with SaaS metrics, understand how to connect SEO to pipeline and revenue, and know how to leverage SaaS-specific opportunities like integration partnerships and software review platforms.



