Technical SEO audit tools identify the hidden infrastructure problems preventing your website from ranking. These specialized platforms crawl your site like search engines do, exposing crawlability errors, indexation issues, page speed problems, and structural flaws that silently drain organic traffic.
Without proper technical foundations, even exceptional content struggles to reach its audience. Broken links, slow load times, and misconfigured robots.txt files create barriers between your pages and search engine crawlers.
This guide covers the best technical SEO audit tools available, essential features to evaluate, step-by-step audit processes, and how to choose the right solution for your business size and budget.
What Are Technical SEO Audit Tools?
Technical SEO audit tools serve a specific function in the broader SEO ecosystem. They focus exclusively on the infrastructure and code-level elements that affect how search engines discover, crawl, render, and index your website.
Definition and Core Purpose
Technical SEO audit tools are software platforms designed to analyze website architecture, server configurations, HTML markup, and performance metrics that influence search engine accessibility. Their core purpose is identifying technical barriers preventing optimal crawling and indexing.
These tools simulate how Googlebot and other search engine crawlers interact with your site. They check HTTP status codes, analyze page load performance, validate structured data implementation, and map internal linking structures.
The primary output is an actionable report highlighting errors, warnings, and optimization opportunities. Issues are typically categorized by severity, helping teams prioritize fixes that deliver the greatest ranking impact.
Unlike manual audits, these tools can analyze thousands of URLs in minutes. They detect problems humans would miss, such as redirect chains buried deep in site architecture or orphan pages with no internal links pointing to them.
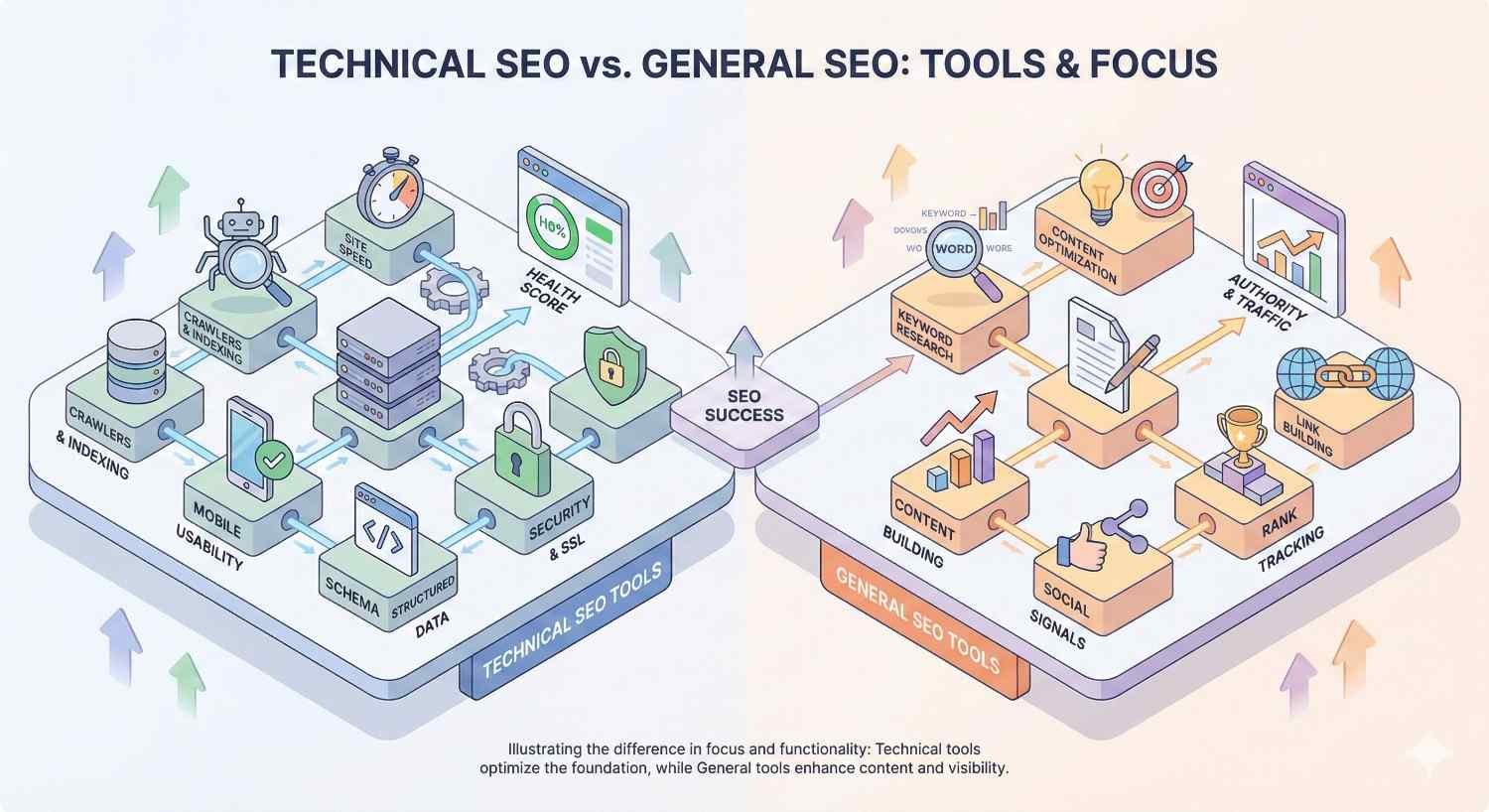
How Technical SEO Tools Differ from General SEO Tools
General SEO platforms like Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Moz offer broad functionality spanning keyword research, backlink analysis, rank tracking, and competitor intelligence. Technical SEO tools focus narrowly on infrastructure health.
The distinction matters for resource allocation. General SEO tools answer questions like “What keywords should I target?” and “Who links to my competitors?” Technical tools answer “Can Google actually crawl and index my pages correctly?”
Screaming Frog, for example, excels at deep crawl analysis but offers no keyword research capabilities. Google Search Console provides indexation data directly from Google but lacks the competitive analysis features found in all-in-one platforms.
Many businesses need both categories. General tools inform content and link building strategy. Technical tools ensure that strategy can actually succeed by removing infrastructure obstacles.
The overlap exists in enterprise platforms. SEMrush and Ahrefs include site audit modules alongside their broader toolsets. However, dedicated technical tools often provide deeper analysis, more configuration options, and specialized features like log file analysis.
Why Technical SEO Audits Matter for Organic Growth
Technical SEO forms the foundation of search visibility. Content quality and backlink profiles matter enormously, but they cannot compensate for fundamental crawling and indexing failures.
Impact on Crawlability and Indexation
Search engines allocate a crawl budget to each website based on site authority and server capacity. Technical issues waste this budget on low-value pages, redirect chains, and error pages.
When Googlebot encounters slow server responses, it reduces crawl frequency. When it finds thousands of duplicate pages, it may deprioritize crawling your important content entirely.
Indexation problems are equally damaging. Pages blocked by robots.txt, returning noindex tags, or suffering from canonicalization errors never appear in search results regardless of their quality.
Google’s documentation confirms that crawl budget optimization becomes critical for sites exceeding several thousand URLs. Technical audits identify exactly where crawl budget is being wasted.
Common crawlability issues include:
- Blocked resources preventing proper page rendering
- Infinite crawl spaces from faceted navigation
- Soft 404 errors that waste crawl budget
- Excessive redirect chains slowing crawl efficiency
Connection to Site Performance and User Experience
Page speed directly influences both rankings and user behavior. Google’s Core Web Vitals became ranking factors in 2021, making performance optimization a technical SEO priority.
Technical audit tools measure Largest Contentful Paint, First Input Delay, and Cumulative Layout Shift across your entire site. They identify specific resources causing slowdowns, from unoptimized images to render-blocking JavaScript.
Mobile usability represents another critical intersection. With mobile-first indexing, Google primarily uses the mobile version of your site for ranking decisions. Technical audits reveal mobile-specific issues like viewport configuration errors, touch target sizing problems, and content parity gaps between mobile and desktop versions.
User experience signals feed back into rankings. High bounce rates from slow pages, poor mobile experiences, or confusing navigation patterns indicate quality problems to search algorithms.
How Technical Issues Affect Rankings and Revenue
The connection between technical SEO and revenue is direct and measurable. Pages that cannot be indexed generate zero organic traffic. Slow pages convert at lower rates than fast ones.
Research from Portent found that conversion rates drop by an average of 4.42% for each additional second of load time. A site loading in one second converts at nearly three times the rate of a site loading in five seconds.
Indexation failures represent complete revenue loss from affected pages. If your highest-value product pages are accidentally noindexed, that traffic and those sales simply disappear.
Technical debt compounds over time. Small issues accumulate into major problems. A few redirect chains become hundreds. Duplicate content from one parameter becomes thousands of variations. Regular audits prevent this accumulation.
The ROI calculation for technical SEO is straightforward. Fixing a crawlability issue that was blocking 20% of your pages from indexation can increase organic traffic by 20% or more, with corresponding revenue impact.
Key Features to Look for in Technical SEO Audit Tools
Not all technical SEO tools offer the same capabilities. Understanding essential features helps you select tools matching your specific needs and technical complexity.
Site Crawling and Error Detection
The foundation of any technical SEO tool is its crawler. Quality crawlers should:
- Handle JavaScript rendering to see pages as Googlebot does
- Respect or override robots.txt for complete analysis
- Support authentication for staging environments
- Allow custom extraction of specific page elements
- Scale to handle sites with millions of URLs
Error detection should cover HTTP status codes comprehensively. Beyond basic 404 errors, tools should identify soft 404s, redirect loops, server errors, and timeout issues.
The best crawlers provide configuration options for crawl speed, URL filtering, and custom user agents. This flexibility allows auditing specific site sections or simulating different crawler behaviors.
Page Speed and Core Web Vitals Analysis
Performance analysis should integrate real user data from Chrome User Experience Report alongside lab-based testing. This combination reveals both actual user experiences and specific optimization opportunities.
Look for tools that:
- Measure all three Core Web Vitals metrics
- Identify specific resources causing performance issues
- Provide page-level and site-wide performance data
- Track performance trends over time
- Offer actionable recommendations for improvement
Integration with Google PageSpeed Insights API adds value by providing Google’s own performance assessments directly within the audit workflow.
Mobile-Friendliness Testing
Mobile testing should go beyond basic viewport checks. Comprehensive mobile analysis includes:
- Touch target sizing and spacing
- Font legibility on small screens
- Content parity between mobile and desktop
- Mobile-specific rendering issues
- Viewport configuration validation
Tools should flag mobile usability errors that could trigger Google’s mobile-friendliness penalties or create poor user experiences affecting engagement metrics.
Structured Data and Schema Validation
Schema markup helps search engines understand page content and can enable rich results in SERPs. Technical tools should:
- Detect all structured data on each page
- Validate markup against Schema.org specifications
- Identify errors preventing rich result eligibility
- Flag missing required properties
- Test markup against Google’s rich results requirements
The difference between valid schema and schema that actually qualifies for rich results matters. Tools should distinguish between technical validity and practical eligibility.
XML Sitemap and Robots.txt Analysis
Sitemap analysis should verify:
- All important pages are included
- No blocked or redirecting URLs appear
- Sitemap size stays within limits
- Last modified dates are accurate
- Sitemap index files are properly structured
Robots.txt analysis should identify overly restrictive rules, syntax errors, and conflicts between robots.txt directives and other signals like meta robots tags.
Cross-referencing sitemaps against crawl data reveals discrepancies. Pages in sitemaps but not found during crawling indicate potential issues. Pages found during crawling but missing from sitemaps represent optimization opportunities.
Internal Linking and Site Architecture Mapping
Internal link analysis reveals how authority flows through your site and how easily users and crawlers can reach important pages. Key metrics include:
- Click depth from homepage to each page
- Internal link distribution across pages
- Orphan pages with no internal links
- Internal link anchor text patterns
- Site architecture visualization
Tools should identify pages with excessive click depth, which may struggle to rank due to reduced crawl priority and PageRank dilution.
Log File Analysis Capabilities
Log file analysis shows actual crawler behavior rather than simulated crawling. This data reveals:
- Which pages Googlebot actually visits
- Crawl frequency for different site sections
- Server response times during real crawls
- Wasted crawl budget on low-value URLs
- Crawl patterns and trends over time
Not all technical SEO tools include log file analysis. Those that do provide insights impossible to obtain through standard crawling alone.
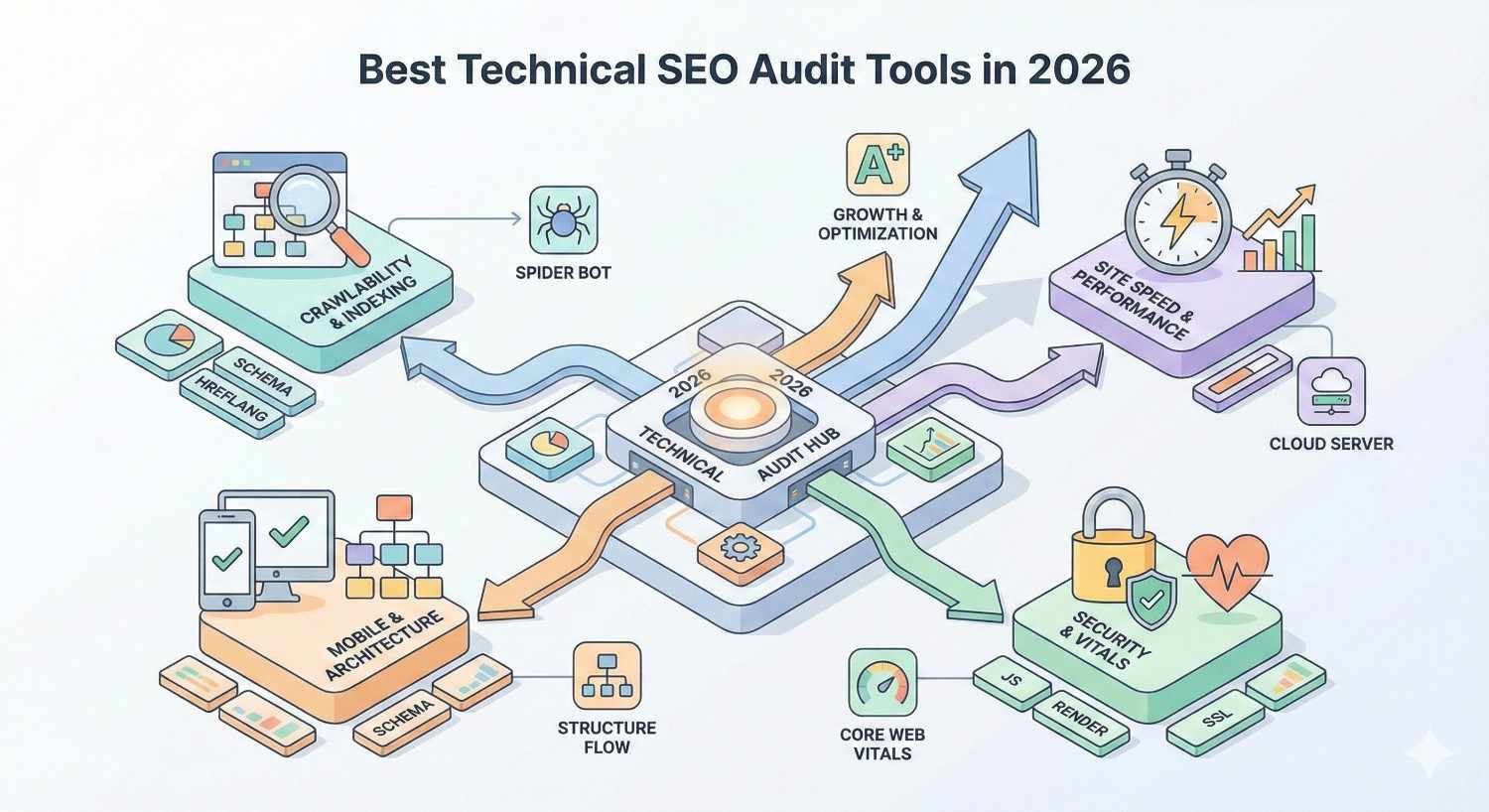
Best Technical SEO Audit Tools in 2026
The technical SEO tool landscape includes specialized crawlers, all-in-one platforms with audit modules, and free tools from Google itself. Each serves different use cases and budgets.
Screaming Frog SEO Spider
Screaming Frog remains the industry standard for technical SEO professionals. This desktop-based crawler offers unmatched depth and flexibility for site analysis.
Key strengths:
- Crawls up to 500 URLs free, unlimited with license
- JavaScript rendering via Chrome integration
- Custom extraction using XPath, CSS selectors, or regex
- Integration with Google Analytics, Search Console, and PageSpeed Insights
- Log file analysis module
- Extensive export and reporting options
Best for: SEO professionals, agencies, and technical teams needing granular control over crawl configuration and data extraction.
Pricing: Free for up to 500 URLs. Annual license costs approximately $259 for unlimited crawling.
The learning curve is steeper than cloud-based alternatives, but the depth of analysis justifies the investment for serious technical SEO work.
Sitebulb
Sitebulb combines powerful crawling with exceptional visualization and prioritized recommendations. It translates technical data into actionable insights more effectively than most competitors.
Key strengths:
- Intuitive visualizations of site architecture
- Prioritized hints explaining issue impact
- PDF reporting suitable for client delivery
- JavaScript crawling capabilities
- Accessibility auditing features
Best for: Agencies needing client-ready reports and SEO professionals who prefer visual data presentation.
Pricing: Cloud and desktop options available. Desktop licenses start around $13.50 per month when billed annually.
Sitebulb excels at making technical SEO accessible to less technical team members while still providing depth for experts.
Ahrefs Site Audit
Ahrefs Site Audit integrates technical analysis into the broader Ahrefs platform. This integration allows correlating technical issues with ranking and traffic data.
Key strengths:
- Scheduled crawls with change monitoring
- JavaScript rendering
- Integration with Ahrefs’ backlink and keyword data
- Health score tracking over time
- Pre-configured issue categories
Best for: Teams already using Ahrefs who want technical auditing within their existing workflow.
Pricing: Included with Ahrefs subscriptions starting at $99 per month.
The audit module is comprehensive but less configurable than dedicated tools like Screaming Frog. The value lies in integration with Ahrefs’ broader dataset.
SEMrush Site Audit
SEMrush Site Audit offers similar integration benefits within the SEMrush ecosystem. The tool emphasizes ease of use and actionable recommendations.
Key strengths:
- Thematic reports grouping related issues
- Crawlability, HTTPS, and performance categories
- Integration with SEMrush’s other tools
- Scheduled crawls and email alerts
- Comparison with previous crawls
Best for: Marketing teams using SEMrush as their primary SEO platform.
Pricing: Included with SEMrush subscriptions starting at $139.95 per month.
SEMrush provides clear explanations of each issue type, making it accessible for teams without deep technical expertise.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console provides data directly from Google about how it sees your site. No third-party tool can replicate this authoritative perspective.
Key strengths:
- Actual indexation status from Google
- Core Web Vitals data from real users
- Mobile usability reports
- Manual action notifications
- URL inspection for individual pages
- Completely free
Best for: Every website. Search Console is essential regardless of what other tools you use.
Limitations: Cannot crawl your site on demand. Data reflects Google’s crawling schedule. Limited historical data retention.
Search Console should be your first stop for understanding indexation issues. Third-party tools complement but cannot replace this direct Google data.
DeepCrawl (Lumar)
Lumar, formerly DeepCrawl, targets enterprise websites with millions of pages. The platform emphasizes scalability, automation, and integration with development workflows.
Key strengths:
- Handles extremely large sites efficiently
- API access for custom integrations
- Automated monitoring and alerts
- Integration with CI/CD pipelines
- Detailed JavaScript analysis
Best for: Enterprise organizations with large, complex websites and dedicated technical SEO resources.
Pricing: Custom pricing based on site size and features. Generally positioned as a premium enterprise solution.
Lumar’s strength is managing technical SEO at scale, including integration with development processes to catch issues before deployment.
Moz Pro Site Crawl
Moz Pro includes site crawling within its broader SEO platform. The tool prioritizes accessibility and clear issue explanations.
Key strengths:
- Weekly automated crawls
- Issue prioritization by impact
- Integration with Moz’s domain authority metrics
- Clear, jargon-free explanations
- Campaign-based organization
Best for: Teams new to technical SEO who need guidance on issue prioritization and resolution.
Pricing: Included with Moz Pro subscriptions starting at $99 per month.
Moz’s crawl depth and configuration options are more limited than specialized tools, but the platform excels at making technical SEO approachable.
ContentKing (Real-Time Auditing)
ContentKing takes a fundamentally different approach by monitoring sites continuously rather than running periodic crawls. This real-time monitoring catches issues immediately.
Key strengths:
- 24/7 monitoring with instant alerts
- Change tracking and audit trails
- No scheduled crawls needed
- Immediate notification of critical issues
- Historical change data
Best for: High-traffic sites where issues cause immediate revenue impact, and teams needing to track changes across large sites.
Pricing: Based on pages monitored. Plans start around $89 per month for smaller sites.
ContentKing is particularly valuable for sites with frequent content changes or multiple contributors where issues can be introduced at any time.
Free vs Paid Technical SEO Audit Tools
Budget constraints are real, especially for startups and small businesses. Understanding what free tools can and cannot do helps allocate resources effectively.
Best Free Technical SEO Tools
Several powerful options cost nothing:
Google Search Console provides authoritative indexation data, Core Web Vitals reports, and mobile usability analysis directly from Google. Every site should use it.
Screaming Frog (free version) crawls up to 500 URLs with most features available. Sufficient for small sites and learning the tool before purchasing.
Google PageSpeed Insights analyzes individual page performance with specific recommendations. Limited to one URL at a time but provides detailed diagnostics.
Bing Webmaster Tools offers similar functionality to Search Console for Bing’s index. Also includes SEO reports and site scan features.
Chrome DevTools enables manual inspection of page elements, network requests, and performance metrics. Essential for diagnosing specific issues.
Rich Results Test validates structured data against Google’s requirements for rich result eligibility.
These free tools can handle basic technical SEO needs for small sites. The limitation is scale and automation rather than capability.
When to Invest in Paid Tools
Paid tools become necessary when:
- Your site exceeds 500 URLs
- You need scheduled, automated crawls
- JavaScript rendering is required for accurate analysis
- You manage multiple client sites
- Log file analysis is needed
- You require detailed reporting for stakeholders
- Time savings justify the cost
The calculation is straightforward. If a $259 annual Screaming Frog license saves 10 hours of manual work per month, it pays for itself quickly at any reasonable hourly rate.
Paid tools also reduce error risk. Manual audits miss issues that automated crawlers catch consistently. The cost of missing a critical technical problem often exceeds annual tool subscriptions.
Tool Comparison by Budget and Business Size
Bootstrapped startups and small sites (under 500 pages):
- Google Search Console (free)
- Screaming Frog free version
- Google PageSpeed Insights
- Total cost: $0
Growing businesses (500-10,000 pages):
- Google Search Console (free)
- Screaming Frog licensed ($259/year)
- Optional: Sitebulb for reporting ($162/year)
- Total cost: $259-$421/year
Agencies managing multiple clients:
- Screaming Frog ($259/year)
- Sitebulb for client reports ($324/year for agency license)
- Ahrefs or SEMrush for broader SEO needs ($1,188-$1,679/year)
- Total cost: $1,771-$2,262/year
Enterprise (100,000+ pages):
- Lumar for scale and automation (custom pricing)
- ContentKing for real-time monitoring (custom pricing)
- Google Search Console (free)
- Total cost: $10,000-$50,000+/year depending on site size
Match tool investment to business impact. A site generating $1 million annually in organic revenue can easily justify enterprise tooling. A local business blog cannot.
How to Conduct a Technical SEO Audit Step-by-Step
A systematic approach ensures comprehensive coverage and prioritized action. Follow these steps for thorough technical analysis.
Step 1: Crawl Your Website
Begin by crawling your entire site with a tool like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb. Configure the crawl appropriately:
- Enable JavaScript rendering if your site uses client-side rendering
- Set an appropriate crawl speed to avoid server strain
- Include or exclude subdomains based on your site structure
- Consider crawling as both Googlebot desktop and mobile
For large sites, start with a sample crawl of key sections before committing to a full crawl that might take hours.
Export the crawl data for analysis. Key reports include all URLs, response codes, page titles, meta descriptions, H1 tags, and canonical tags.
Step 2: Identify Indexation Issues
Cross-reference your crawl data with Google Search Console’s index coverage report. Look for discrepancies between pages you want indexed and pages Google has actually indexed.
Check for:
- Pages returning noindex tags that should be indexed
- Important pages blocked by robots.txt
- Canonical tags pointing to wrong URLs
- Pages excluded due to duplicate content detection
- Crawl errors preventing indexation
Prioritize fixing indexation issues on high-value pages first. A blocked product category page matters more than a blocked tag archive.
Step 3: Analyze Site Speed and Core Web Vitals
Use Google Search Console’s Core Web Vitals report for site-wide performance data based on real user experiences. This shows which URLs pass or fail each metric.
Supplement with PageSpeed Insights analysis of key page templates. Focus on:
- Homepage
- Main category or service pages
- Product or article templates
- Landing pages for paid campaigns
Identify common issues across templates. Fixing a render-blocking script on your article template improves performance for every article, not just one page.
Step 4: Check Mobile Usability
Review Search Console’s mobile usability report for flagged issues. Common problems include:
- Text too small to read
- Clickable elements too close together
- Content wider than screen
- Viewport not configured
Test representative pages using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test. Verify that mobile and desktop versions contain the same content, as Google uses mobile-first indexing.
Step 5: Review URL Structure and Redirects
Analyze your crawl data for redirect issues:
- Redirect chains (A redirects to B redirects to C)
- Redirect loops
- Internal links pointing to redirecting URLs
- Mixed HTTP/HTTPS content
- Inconsistent trailing slash handling
Clean URL structures use consistent patterns, avoid parameters when possible, and include relevant keywords. Identify URLs that deviate from your preferred structure.
Step 6: Audit Internal Links and Site Architecture
Map your site’s internal linking structure. Identify:
- Orphan pages with no internal links
- Pages with excessive click depth from homepage
- Uneven internal link distribution
- Broken internal links
- Internal links using redirects
Visualize site architecture to understand how authority flows. Important pages should be reachable within three clicks from the homepage and should receive internal links from related content.
Step 7: Validate Structured Data
Test structured data implementation using Google’s Rich Results Test and Schema Markup Validator. Check that:
- Schema types match page content
- Required properties are present
- No errors prevent rich result eligibility
- Markup is present on all appropriate pages
Common issues include missing required fields, incorrect data types, and markup that doesn’t match visible page content.
Step 8: Prioritize and Fix Issues
Not all issues deserve equal attention. Prioritize based on:
Critical (fix immediately):
- Pages blocked from indexing that should rank
- Severe Core Web Vitals failures on key pages
- Broken functionality affecting user experience
- Security issues
High priority (fix within 2 weeks):
- Redirect chains on high-traffic pages
- Missing or incorrect canonical tags
- Duplicate content issues
- Mobile usability errors
Medium priority (fix within 1 month):
- Suboptimal internal linking
- Minor structured data errors
- Non-critical page speed improvements
- URL structure inconsistencies
Low priority (ongoing maintenance):
- Minor broken links to external sites
- Optimization opportunities rather than errors
- Nice-to-have improvements
Create a prioritized action plan with specific tasks, owners, and deadlines. Track progress and re-crawl after fixes to verify resolution.
How to Choose the Right Technical SEO Tool for Your Business
Different organizations have different needs. The best tool depends on your site size, team expertise, budget, and workflow requirements.
For Small Businesses and Startups
Small businesses typically need simplicity and affordability over advanced features. Recommended approach:
Essential (free):
- Google Search Console for indexation monitoring
- Google PageSpeed Insights for performance checks
- Screaming Frog free version for periodic crawls
Optional upgrade:
- Screaming Frog license when exceeding 500 pages
- Sitebulb if you need clearer visualizations
Focus on mastering free tools before investing in paid options. Most small business technical SEO needs can be met without significant tool investment.
For Agencies Managing Multiple Clients
Agencies need efficiency, scalability, and professional reporting. Key requirements:
- Ability to manage multiple projects
- White-label or customizable reports
- Scheduled crawls and monitoring
- Team collaboration features
Recommended stack:
- Screaming Frog for deep technical analysis
- Sitebulb for client-facing reports
- Ahrefs or SEMrush for broader SEO data
- ContentKing for clients requiring real-time monitoring
The investment in proper tooling pays off through time savings and improved client deliverables. Budget $2,000-$5,000 annually for a comprehensive agency toolkit.
For Enterprise Websites
Enterprise sites face unique challenges: massive scale, complex architectures, multiple stakeholders, and integration requirements.
Key needs:
- Handling millions of URLs efficiently
- API access for custom integrations
- Integration with development workflows
- Granular access controls
- Detailed audit trails
Recommended approach:
- Lumar for scalable crawling and monitoring
- ContentKing for real-time change detection
- Custom dashboards pulling from multiple data sources
- Integration with CI/CD pipelines for pre-deployment testing
Enterprise technical SEO often requires dedicated resources and custom solutions beyond off-the-shelf tools.
For In-House Marketing Teams
In-house teams need tools that balance capability with usability. Not everyone on the team will be a technical SEO specialist.
Key considerations:
- Learning curve and ease of use
- Integration with existing marketing tools
- Clear prioritization and recommendations
- Collaboration features
Recommended approach:
- SEMrush or Ahrefs if already using for other SEO tasks
- Sitebulb for teams wanting dedicated technical analysis
- Google Search Console as the foundation
Choose tools that match your team’s technical comfort level. A powerful tool that nobody uses provides no value.
Common Technical SEO Issues Found During Audits
Understanding frequent problems helps you know what to look for and how to fix issues when found.
Duplicate Content and Canonicalization Errors
Duplicate content occurs when substantially similar content exists at multiple URLs. Common causes include:
- HTTP and HTTPS versions both accessible
- WWW and non-WWW versions both accessible
- URL parameters creating duplicate pages
- Pagination without proper handling
- Print-friendly page versions
Canonical tags tell search engines which version to index. Errors include:
- Missing canonical tags
- Self-referencing canonicals on duplicate pages
- Canonical tags pointing to non-existent URLs
- Conflicting signals between canonical and other directives
Fix by implementing consistent canonical tags, using 301 redirects for true duplicates, and configuring URL parameters in Search Console.
Broken Links and 404 Errors
Broken links create poor user experiences and waste crawl budget. They occur when:
- Pages are deleted without redirects
- URLs are changed without updating internal links
- External sites remove linked content
- Typos exist in link URLs
Audit tools identify broken links automatically. Prioritize fixing:
- Internal broken links (you control these)
- Broken links on high-traffic pages
- Broken links to important external resources
Implement redirects for removed pages that had external backlinks or significant traffic.
Slow Page Load Times
Page speed issues stem from various causes:
- Unoptimized images (wrong format, excessive size)
- Render-blocking JavaScript and CSS
- Excessive HTTP requests
- Slow server response times
- No browser caching
- Uncompressed resources
Each issue requires different solutions. Image optimization might involve converting to WebP format and implementing lazy loading. JavaScript issues might require code splitting or deferring non-critical scripts.
Focus on Core Web Vitals metrics: LCP under 2.5 seconds, FID under 100 milliseconds, and CLS under 0.1.
Missing or Incorrect Hreflang Tags
Hreflang tags tell search engines which language and regional versions of pages to show different users. Errors include:
- Missing hreflang on international pages
- Incorrect language or region codes
- Missing return links (page A references B, but B doesn’t reference A)
- Hreflang pointing to non-existent pages
- Conflicting hreflang and canonical signals
Hreflang implementation is notoriously error-prone. Use validation tools and audit regularly if you have international content.
Orphan Pages and Crawl Depth Problems
Orphan pages have no internal links pointing to them. Search engines may never discover these pages, and even if they do, the lack of internal links signals low importance.
Crawl depth measures how many clicks from the homepage are required to reach a page. Pages buried deep in site architecture receive less crawl priority and PageRank.
Fix by:
- Adding internal links to orphan pages from relevant content
- Restructuring navigation to reduce click depth
- Creating hub pages that link to related content
- Reviewing and updating XML sitemaps
JavaScript Rendering Issues
Modern websites often rely heavily on JavaScript. Problems occur when:
- Content loads only after JavaScript execution
- Search engines cannot execute JavaScript correctly
- Critical content is hidden behind user interactions
- JavaScript errors prevent page rendering
Test using Google’s URL Inspection tool to see how Googlebot renders your pages. Compare rendered HTML to source HTML to identify content that requires JavaScript.
Solutions include server-side rendering, dynamic rendering for crawlers, or ensuring critical content exists in initial HTML.
How Long Does a Technical SEO Audit Take?
Audit duration varies significantly based on site complexity and audit depth. Setting realistic expectations helps with planning and resource allocation.
Factors That Affect Audit Duration
Site size: A 100-page site crawls in minutes. A million-page site might take days.
Technical complexity: JavaScript-heavy sites require rendering, which slows crawling. Complex architectures need more analysis time.
Audit scope: A focused crawlability audit takes less time than a comprehensive audit covering performance, accessibility, and international SEO.
Tool capabilities: Enterprise tools handle large sites faster than desktop applications with limited resources.
Analysis depth: Running a crawl takes hours. Analyzing results, prioritizing issues, and creating recommendations takes days or weeks.
Team expertise: Experienced technical SEOs work faster and identify issues that less experienced auditors might miss.
Realistic Timelines by Website Size
Small sites (under 500 pages):
- Crawl time: 15-30 minutes
- Analysis and recommendations: 4-8 hours
- Total audit: 1-2 days
Medium sites (500-10,000 pages):
- Crawl time: 1-4 hours
- Analysis and recommendations: 1-3 days
- Total audit: 3-5 days
Large sites (10,000-100,000 pages):
- Crawl time: 4-24 hours
- Analysis and recommendations: 1-2 weeks
- Total audit: 2-3 weeks
Enterprise sites (100,000+ pages):
- Crawl time: 1-7 days
- Analysis and recommendations: 2-4 weeks
- Total audit: 4-6 weeks
These timelines assume a single auditor. Larger teams can parallelize work and reduce total duration.
Technical SEO Audit Checklist
Use this checklist to ensure comprehensive audit coverage:
Crawlability
- Robots.txt allows crawling of important content
- No critical pages blocked by noindex
- XML sitemap exists and is submitted to Search Console
- Sitemap contains only indexable, canonical URLs
- No infinite crawl spaces from parameters or facets
- Server responds quickly to crawler requests
Indexation
- Important pages are indexed in Google
- Canonical tags are correctly implemented
- No unintended duplicate content issues
- Pagination uses appropriate markup
- Parameter handling is configured in Search Console
Site Architecture
- Important pages are within 3 clicks of homepage
- No orphan pages lacking internal links
- Internal links use descriptive anchor text
- Navigation is crawlable (not JavaScript-dependent)
- Breadcrumbs are implemented correctly
Technical Performance
- Core Web Vitals pass on key templates
- Images are optimized and use modern formats
- CSS and JavaScript are minified and compressed
- Browser caching is configured
- No render-blocking resources delay content
Mobile
- Site passes mobile-friendly test
- Mobile and desktop content parity exists
- Touch targets are appropriately sized
- Viewport is correctly configured
Security
- HTTPS is implemented site-wide
- No mixed content warnings
- HTTP redirects to HTTPS
- Security headers are configured
Structured Data
- Schema markup is present on appropriate pages
- Markup validates without errors
- Required properties are included
- Markup matches visible page content
International (if applicable)
- Hreflang tags are correctly implemented
- Return links exist for all hreflang references
- Language and region codes are valid
- No conflicts between hreflang and canonical
When to Hire an SEO Agency for Technical Audits
Not every organization has the expertise or resources for comprehensive technical SEO. Knowing when to seek help prevents wasted effort and missed opportunities.
Signs You Need Professional Help
Declining organic traffic without obvious cause: If traffic drops and you cannot identify why, technical issues may be the culprit. Professional auditors know where to look.
Major site changes planned: Migrations, redesigns, and platform changes carry significant technical SEO risk. Expert guidance prevents costly mistakes.
Complex technical architecture: JavaScript frameworks, headless CMS implementations, and enterprise-scale sites require specialized expertise.
Lack of internal expertise: If nobody on your team understands technical SEO, attempting complex fixes risks making problems worse.
Competitive pressure: If competitors are outranking you despite inferior content, technical advantages may explain the gap.
Resource constraints: Even if you have expertise, you may lack time. Outsourcing audits frees internal resources for implementation.
What to Expect from a Professional Technical SEO Audit
A quality professional audit should include:
Comprehensive crawl analysis covering all aspects of technical SEO, not just surface-level checks.
Prioritized recommendations explaining which issues matter most and why, with clear severity ratings.
Specific fix instructions that developers can implement without additional research.
Baseline metrics documenting current state for measuring improvement after fixes.
Executive summary translating technical findings into business impact for stakeholders.
Follow-up support to answer questions during implementation and verify fixes work correctly.
Expect to pay $2,000-$10,000 for a thorough professional audit depending on site size and complexity. Enterprise audits may cost significantly more.
Beware of audits that simply export tool reports without analysis. The value is in expert interpretation and prioritization, not raw data.
Conclusion: Building Sustainable Organic Growth Through Technical SEO
Technical SEO audit tools transform invisible infrastructure problems into actionable optimization opportunities. From crawlability and indexation to Core Web Vitals and structured data, these platforms reveal the foundation issues that determine whether your content can actually reach its audience.
The right tool depends on your specific situation. Small sites can accomplish significant improvements with free options like Google Search Console and Screaming Frog’s free tier. Growing businesses benefit from licensed tools offering automation and scale. Enterprise organizations require platforms built for complexity and integration.
We help businesses build sustainable organic growth through comprehensive technical SEO audits and ongoing optimization at White Label SEO Service. Our team identifies the infrastructure issues limiting your search visibility and implements fixes that deliver measurable traffic and revenue improvements. Contact us for a professional technical SEO audit that goes beyond surface-level checks to uncover the opportunities your competitors are missing.
Frequently Asked Questions About Technical SEO Audit Tools
What is the best free technical SEO audit tool?
Google Search Console is the most valuable free technical SEO tool because it provides actual indexation data directly from Google. Screaming Frog’s free version offers comprehensive crawling for sites under 500 pages. Together, these tools cover most small business technical SEO needs without any cost.
How often should I audit my website for technical SEO?
Conduct comprehensive technical SEO audits quarterly for most websites. High-traffic sites or those with frequent content changes benefit from monthly audits. Set up continuous monitoring with tools like ContentKing or scheduled crawls to catch issues between full audits.
Can I do a technical SEO audit without tools?
Manual technical SEO audits are possible but impractical for any site beyond a few pages. You can manually check robots.txt, view page source for meta tags, and test individual URLs. However, identifying issues across hundreds or thousands of pages requires automated crawling tools.
What’s the difference between a technical SEO audit and a full SEO audit?
Technical SEO audits focus specifically on infrastructure: crawlability, indexation, site speed, and code-level issues. Full SEO audits also cover content quality, keyword targeting, backlink profiles, and competitive positioning. Technical audits are one component of comprehensive SEO analysis.
Do technical SEO tools work for all CMS platforms?
Yes, technical SEO audit tools work with any CMS because they analyze the output (HTML, server responses) rather than the underlying platform. WordPress, Shopify, custom builds, and headless CMS implementations all produce crawlable websites that these tools can analyze.
How much do technical SEO audit tools cost?
Costs range from free to enterprise pricing. Google Search Console costs nothing. Screaming Frog licenses cost $259 annually. All-in-one platforms like Ahrefs and SEMrush start around $99-$140 monthly. Enterprise solutions like Lumar use custom pricing based on site size and features.
Can technical SEO tools replace an SEO expert?
Technical SEO tools identify issues but cannot replace expert judgment for prioritization, strategy, and implementation. Tools report that you have 500 redirect chains. Experts determine which ones matter, why they occurred, and how to fix them without creating new problems. Tools and expertise work together.



