A single security breach can erase months of SEO progress overnight. When Google flags your site as compromised, organic traffic drops by an average of 95% within hours. Your rankings vanish. Your brand reputation suffers. Recovery takes weeks or months.
Website security and SEO are inseparable in modern search. Google actively penalizes hacked sites, rewards secure connections, and uses trust signals to determine rankings. For business owners investing in organic growth, ignoring security creates catastrophic risk.
This guide covers everything you need to protect your SEO investment: how security affects rankings, common threats that destroy organic performance, essential protective measures, audit processes, and recovery strategies when things go wrong.
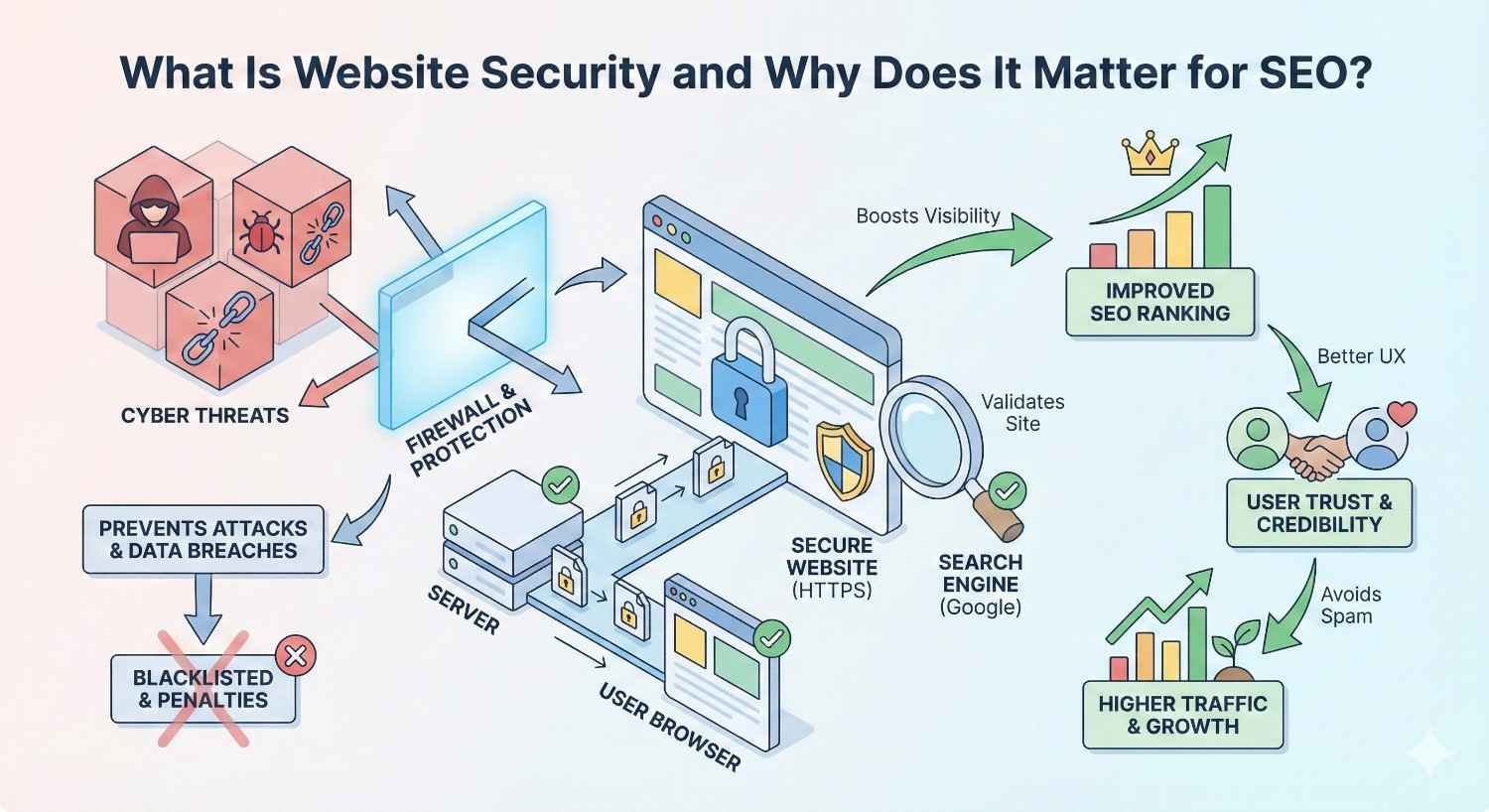
What Is Website Security and Why Does It Matter for SEO?
Website security encompasses all measures protecting your site from unauthorized access, data breaches, malware infections, and malicious attacks. For SEO purposes, security extends beyond protecting data. It directly influences how search engines evaluate, rank, and display your site in results.
Google’s mission centers on delivering safe, trustworthy results. When your site poses risks to users, Google responds by suppressing your visibility, displaying warnings, or removing you from the index entirely. Security failures don’t just threaten your data. They threaten your entire organic traffic channel.
Defining Website Security in the Context of Search Visibility
Search-focused website security means protecting the elements that search engines evaluate when determining rankings and user safety. This includes your SSL certificate status, server response integrity, content authenticity, and protection against code injections that could harm visitors.
From an SEO perspective, security vulnerabilities create multiple ranking problems. Malware infections trigger Safe Browsing warnings that block users from accessing your site. Spam injections pollute your indexed pages with irrelevant or harmful content. Server compromises can redirect your traffic to malicious destinations.
The connection runs deeper than penalties. Secure sites load faster because they’re not burdened with malicious scripts. They maintain consistent uptime because they’re protected against attacks. They preserve their backlink equity because they’re not flagged as dangerous by referring domains.
How Google Evaluates Site Trustworthiness
Google assesses trustworthiness through multiple security-related signals. The most visible is HTTPS status. Sites without valid SSL certificates receive explicit warnings in Chrome and ranking disadvantages in search results.
Beyond HTTPS, Google’s Safe Browsing technology continuously scans the web for compromised sites. When detected, your site receives warnings that appear before users can access your content. These warnings devastate click-through rates and signal to Google that your site shouldn’t rank prominently.
Google also evaluates behavioral signals that security issues influence. High bounce rates from security warnings, short session durations from compromised user experiences, and declining engagement metrics all feed into ranking algorithms. A security problem creates a cascade of negative signals that compound over time.
How Website Security Directly Impacts Search Rankings
Security isn’t a peripheral SEO concern. It’s a core ranking factor with documented, measurable effects on organic performance. Understanding these connections helps you prioritize security investments alongside content and link building efforts.
HTTPS as a Confirmed Google Ranking Signal
Google confirmed HTTPS as a ranking signal in 2014 and has strengthened its importance since. While initially described as a lightweight signal, HTTPS has become a baseline expectation. Sites without it face both ranking disadvantages and user trust barriers.
Chrome displays “Not Secure” warnings for HTTP sites, particularly those with forms or login fields. This warning alone reduces conversion rates and increases bounce rates. Users have learned to associate the padlock icon with safety. Its absence creates immediate friction.
The ranking impact extends beyond the direct signal. HTTPS enables HTTP/2 protocol, which improves page speed. Faster sites rank better and provide superior user experiences. The security investment delivers compounding SEO benefits.
Core Web Vitals and Security Performance Correlation
Security measures and Core Web Vitals performance are interconnected. Malware infections typically inject additional scripts that slow page rendering. Compromised servers struggle to deliver content efficiently. Security plugins and firewalls, when properly configured, actually improve performance by blocking malicious requests before they consume resources.
Largest Contentful Paint suffers when malicious scripts compete for rendering priority. First Input Delay increases when injected code blocks the main thread. Cumulative Layout Shift worsens when unauthorized elements load unpredictably.
Clean, secure sites maintain consistent performance baselines. They’re not fighting against hidden processes or unauthorized code execution. This stability translates directly into better Core Web Vitals scores and the ranking benefits they provide.
User Experience Signals Affected by Security Issues
Security problems create measurable user experience degradation that search engines detect through behavioral signals. When users encounter security warnings, they bounce immediately. When sites load slowly due to malware, users abandon sessions. When content appears compromised, users don’t engage.
These behavioral patterns feed into Google’s understanding of content quality. High bounce rates signal that users aren’t finding value. Short dwell times suggest content doesn’t meet expectations. Low pages-per-session indicate poor engagement.
Security issues create a negative feedback loop. Poor security leads to poor user experience, which leads to poor behavioral signals, which leads to lower rankings, which leads to less traffic and fewer opportunities to demonstrate value. Breaking this cycle requires addressing the root security problems.
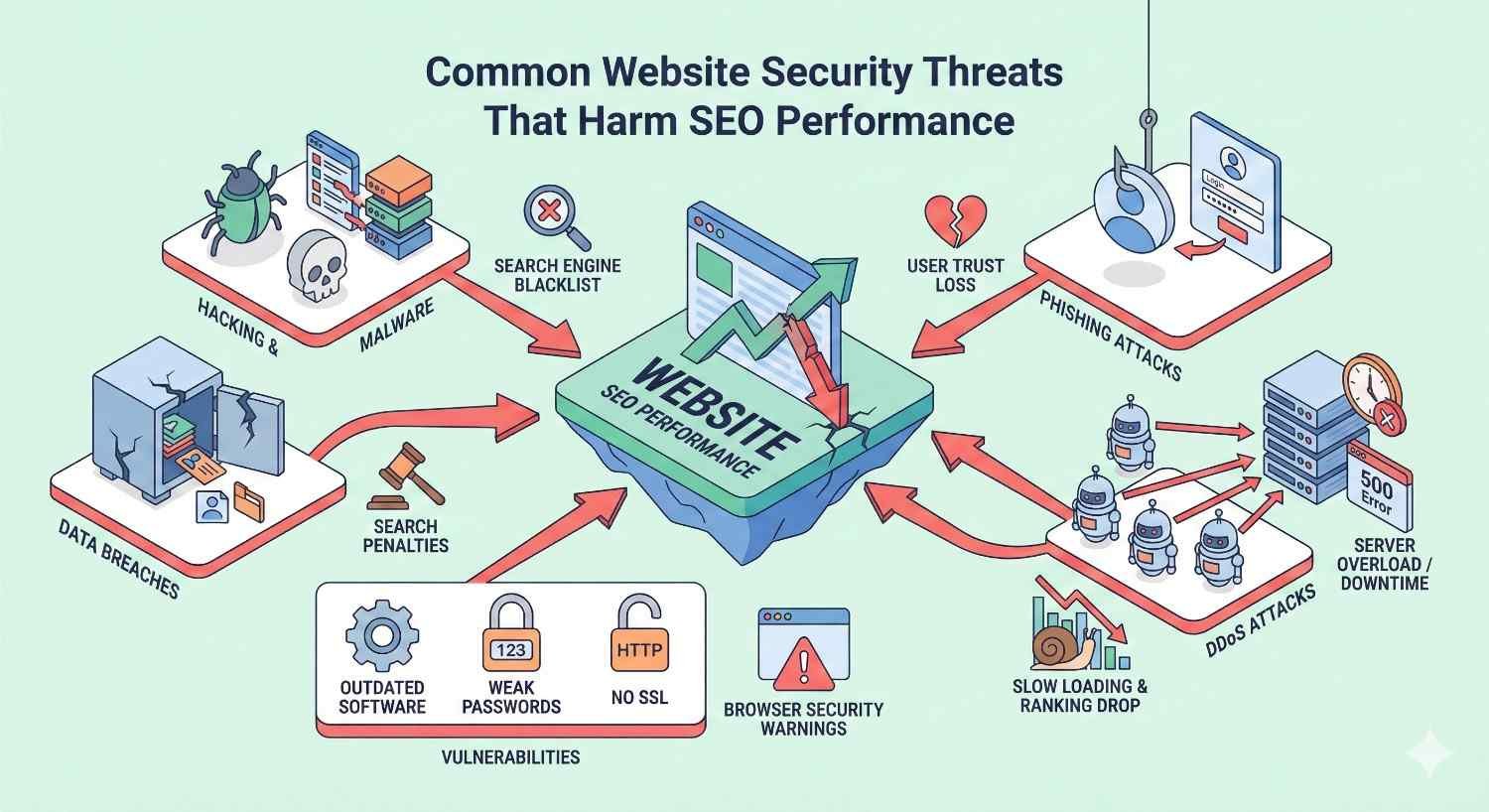
Common Website Security Threats That Harm SEO Performance
Understanding specific threats helps you recognize vulnerabilities and prioritize protective measures. Each threat type creates distinct SEO consequences requiring different remediation approaches.
Malware Infections and Google Blacklisting
Malware infections represent the most severe SEO threat. When Google detects malware on your site, it adds you to the Safe Browsing blacklist. Users attempting to visit see full-page warnings stating your site may harm their computer. Traffic drops to near zero.
Common malware types include drive-by download scripts that attempt to install software on visitor devices, cryptocurrency miners that hijack visitor processing power, and redirect scripts that send users to malicious destinations. Each type triggers blacklisting and ranking penalties.
Recovery from malware blacklisting requires complete remediation, verification through Google Search Console, and a review request. The process typically takes one to four weeks even after you’ve cleaned the infection. During this period, your organic traffic remains suppressed.
Phishing Attacks and Safe Browsing Warnings
Phishing attacks use your site to host fake login pages or forms designed to steal user credentials. Attackers often create hidden directories containing convincing replicas of banking, email, or social media login pages.
Google’s Safe Browsing identifies these pages and flags your entire domain as deceptive. The warning prevents users from accessing any page on your site, not just the phishing content. Your legitimate pages become inaccessible through organic search.
Phishing content often goes undetected by site owners because it’s hidden in obscure directories. Regular security scans and file integrity monitoring are essential for early detection before Google flags your domain.
SEO Spam Injections and Cloaked Content
SEO spam injections represent a particularly insidious threat because they’re designed to be invisible to site owners while visible to search engines. Attackers inject hidden links, doorway pages, or cloaked content that only appears when Googlebot visits.
These injections serve multiple purposes for attackers. They may redirect your PageRank to their sites through hidden links. They may create thousands of spam pages targeting pharmaceutical, gambling, or adult keywords. They may use your domain authority to rank their content.
The SEO damage is severe. Your site becomes associated with spam content in Google’s index. Your rankings for legitimate keywords decline as spam pages dilute your topical relevance. Manual actions may be applied, requiring formal reconsideration requests.
DDoS Attacks and Site Downtime Impact
Distributed Denial of Service attacks overwhelm your server with traffic, making your site inaccessible to legitimate users and search engine crawlers. While the direct ranking impact of brief downtime is minimal, extended or repeated outages create significant SEO problems.
When Googlebot encounters repeated access failures, it reduces crawl frequency. New content isn’t indexed promptly. Updates to existing pages aren’t reflected in search results. Your site’s freshness signals deteriorate.
Extended downtime also affects user behavioral signals. Users who can’t access your site from search results bounce immediately. If this pattern continues, Google interprets it as a quality signal and adjusts rankings accordingly.
Negative SEO Through Hacked Backlinks
Attackers sometimes compromise your site specifically to manipulate your backlink profile. They may inject hidden outbound links to their properties, effectively stealing your link equity. They may create spam pages that attract toxic backlinks, polluting your profile.
More sophisticated attacks involve using your compromised site to build links to competitors’ negative SEO targets. Your domain becomes associated with link schemes, potentially triggering algorithmic penalties or manual actions.
Monitoring your backlink profile for unexpected changes helps detect these attacks early. Sudden spikes in outbound links or incoming links from irrelevant sources often indicate compromise.
Google’s Security Requirements and Penalties
Google enforces security standards through both algorithmic adjustments and manual actions. Understanding these enforcement mechanisms helps you appreciate the stakes and prioritize compliance.
Manual Actions for Hacked Sites
When Google’s systems detect that your site has been compromised, they may issue a manual action. This appears in Google Search Console with specific details about the detected problem. Manual actions result in immediate ranking suppression or complete removal from search results.
Common manual action categories include “Hacked site” for general compromises, “User-generated spam” when attackers exploit comment or forum systems, and “Spammy structured markup” when schema is manipulated to display false information.
Resolving manual actions requires fixing the underlying security issue, documenting your remediation efforts, and submitting a reconsideration request. Google’s team manually reviews your request, which typically takes several days to several weeks.
Safe Browsing Warnings and Traffic Loss
Safe Browsing warnings operate independently from manual actions. They’re triggered automatically when Google’s scanning systems detect malware, phishing, or unwanted software on your site. The warnings appear in Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and other browsers that use Google’s Safe Browsing data.
The traffic impact is immediate and severe. Users see full-page interstitial warnings requiring them to actively choose to proceed. Most users don’t. Studies indicate that Safe Browsing protects over 5 billion devices daily, meaning your warning reaches virtually all potential visitors.
Removing Safe Browsing warnings requires cleaning your site and requesting a review through Search Console. Google typically processes these reviews within 72 hours, though complex cases may take longer.
Index Removal and Recovery Timelines
In severe cases, Google removes compromised sites from the index entirely. This goes beyond ranking suppression. Your pages simply don’t appear in search results at all. The removal may be partial, affecting only compromised sections, or complete, affecting your entire domain.
Recovery timelines vary based on the severity of the compromise and the completeness of your remediation. Simple malware infections with thorough cleanup may recover within one to two weeks. Complex compromises involving thousands of spam pages may require three to six months for full recovery.
The recovery process isn’t just about removing the security warning. It’s about rebuilding the trust signals and ranking positions you lost. Even after Google lifts penalties, your rankings don’t automatically return to previous levels. You must re-earn those positions through continued SEO efforts.
Essential Website Security Measures for SEO Protection
Proactive security measures prevent the ranking disasters described above. Each measure addresses specific vulnerability categories and contributes to overall site trustworthiness.
SSL/TLS Certificate Implementation
SSL/TLS certificates encrypt data transmitted between your server and visitors’ browsers. They’re required for HTTPS, which is both a ranking signal and a user trust indicator. Implementation is straightforward and often free through services like Let’s Encrypt.
Proper implementation requires more than installing a certificate. You must redirect all HTTP traffic to HTTPS, update internal links to use HTTPS, ensure third-party resources load over HTTPS, and configure HSTS headers to prevent downgrade attacks.
Certificate maintenance matters for SEO. Expired certificates trigger browser warnings that devastate traffic. Misconfigured certificates create mixed content warnings that undermine trust. Automated renewal and monitoring prevent these issues.
Web Application Firewall (WAF) Setup
Web Application Firewalls filter malicious traffic before it reaches your server. They block common attack patterns including SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and brute force login attempts. This protection prevents many compromises before they occur.
WAFs also improve performance by blocking bot traffic that consumes server resources. Legitimate crawlers like Googlebot pass through while malicious bots are blocked. This ensures your server resources serve real users and search engines efficiently.
Cloud-based WAF solutions like Cloudflare, Sucuri, and AWS WAF provide protection without requiring server-level configuration. They’re particularly valuable for sites on shared hosting where server access is limited.
Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Scanning
Automated vulnerability scanning identifies security weaknesses before attackers exploit them. These scans check for outdated software, known vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and suspicious file changes.
Scanning frequency should match your risk profile. High-traffic sites handling sensitive data should scan daily. Smaller sites may scan weekly. All sites should scan after any significant changes to code, plugins, or configurations.
Comprehensive audits go beyond automated scanning. They include manual review of access logs, user permissions, third-party integrations, and security configurations. Annual professional security audits are worthwhile investments for sites where organic traffic drives significant revenue.
Secure Hosting and Server Configuration
Your hosting environment forms the foundation of site security. Shared hosting creates risks because other sites on the same server may be compromised. Managed hosting and VPS solutions provide better isolation and security controls.
Server configuration hardening includes disabling unnecessary services, restricting file permissions, configuring secure PHP settings, and implementing proper access controls. These configurations prevent many common attack vectors.
Hosting providers vary significantly in their security practices. Evaluate providers based on their security certifications, incident response procedures, backup policies, and track record. The cheapest hosting often proves most expensive when security failures destroy your organic traffic.
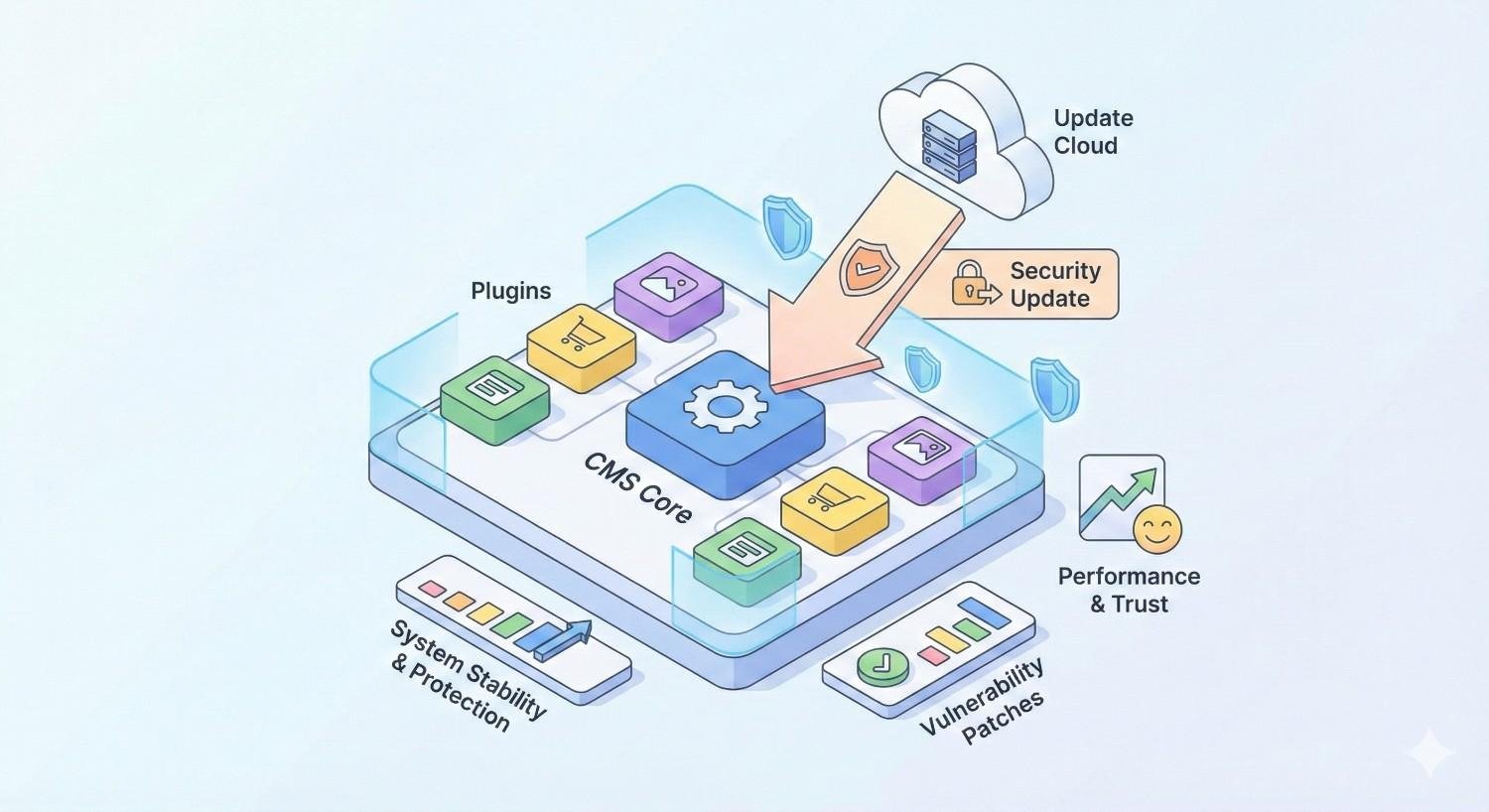
CMS and Plugin Security Updates
Content management systems and their plugins represent the most common attack vector for website compromises. Outdated WordPress installations, vulnerable plugins, and abandoned themes create exploitable weaknesses.
Update discipline is essential. Enable automatic updates for minor releases. Apply major updates promptly after testing. Remove unused plugins and themes entirely rather than just deactivating them.
Plugin selection matters for security. Choose plugins from reputable developers with active maintenance histories. Check update frequency, support responsiveness, and security track records before installing. Fewer, well-maintained plugins are safer than many questionable ones.
Access Control and Authentication Protocols
Weak authentication enables unauthorized access that leads to all other security problems. Strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and limited user permissions form the foundation of access security.
Implement the principle of least privilege. Users should have only the permissions necessary for their roles. Admin access should be limited to those who genuinely need it. Regular access audits identify and remove unnecessary permissions.
Login security measures include limiting failed login attempts, implementing CAPTCHA for repeated failures, using unique usernames rather than “admin,” and monitoring login activity for suspicious patterns.
How to Audit Your Website for Security and SEO Issues
Regular audits identify problems before they cause ranking damage. Effective audits combine automated tools with manual review processes.
Google Search Console Security Reports
Google Search Console provides direct insight into how Google perceives your site’s security status. The Security Issues report shows any detected malware, hacked content, or social engineering problems.
Check this report weekly at minimum. When issues appear, they require immediate attention. The report provides specific details about detected problems and affected URLs, guiding your remediation efforts.
Search Console also shows manual actions in a separate report. Review both reports regularly. The absence of current issues doesn’t guarantee security. It means Google hasn’t detected problems yet.
Third-Party Security Scanning Tools
External scanning tools provide perspectives that internal monitoring misses. They scan your site as an outside attacker would, identifying vulnerabilities visible from the public internet.
Popular scanning tools include Sucuri SiteCheck for malware detection, Qualys SSL Labs for certificate analysis, and OWASP ZAP for vulnerability assessment. Using multiple tools provides comprehensive coverage since each has different detection strengths.
Paid security services offer continuous monitoring with immediate alerts. For sites where organic traffic drives significant revenue, the investment in real-time monitoring pays for itself by enabling rapid response to emerging threats.
Backlink Profile Analysis for Spam Detection
Your backlink profile can reveal security compromises that other scans miss. Sudden increases in outbound links may indicate injected spam. Unexpected incoming links from irrelevant or malicious sites may indicate your site is being used in attack campaigns.
Regular backlink audits using tools like Ahrefs, Semrush, or Moz identify anomalies requiring investigation. Look for links you didn’t build, anchor text you didn’t create, and referring domains that don’t make sense for your niche.
When you identify suspicious backlink activity, investigate the source. If your site has been compromised to create these links, security remediation is required. If external sites are linking to you maliciously, disavow files may be appropriate.
Technical SEO Audit Integration
Security audits should integrate with broader technical SEO audits. Many security issues manifest as technical SEO problems. Spam injections create indexation bloat. Malware affects page speed. Compromises cause redirect chains.
When conducting technical SEO audits, include security checkpoints. Verify SSL configuration. Check for unexpected indexed pages. Review server response codes for anomalies. Examine robots.txt and sitemap for unauthorized changes.
This integrated approach ensures security issues don’t hide in plain sight as “technical SEO problems.” The root cause matters. Fixing symptoms without addressing underlying security vulnerabilities leads to recurring issues.
Recovering SEO Rankings After a Security Breach
Despite best efforts, breaches occur. Effective recovery minimizes ranking damage and accelerates return to normal organic performance.
Identifying and Removing Malicious Code
Complete malware removal requires systematic identification of all compromised files. Partial cleanup leaves backdoors that attackers use to reinfect your site. Thorough removal is essential for lasting recovery.
Start by identifying the infection vector. How did attackers gain access? Vulnerable plugins, weak passwords, and compromised hosting accounts are common entry points. Understanding the vector prevents reinfection.
Use file integrity monitoring to identify changed files. Compare current files against known clean versions. Remove or restore all modified files. Check database tables for injected content. Review user accounts for unauthorized additions.
Submitting Reconsideration Requests to Google
After cleaning your site, request Google’s review through Search Console. For manual actions, use the reconsideration request feature. For Safe Browsing warnings, use the security issues review request.
Effective reconsideration requests document your remediation thoroughly. Explain what happened, what you found, what you fixed, and what you’ve implemented to prevent recurrence. Vague requests receive vague responses or rejections.
Be patient but persistent. Initial requests sometimes fail if Google’s review finds remaining issues. Address any feedback provided and resubmit. Most legitimate cleanup efforts eventually succeed with thorough documentation.
Rebuilding Trust Signals and Authority
Penalty removal doesn’t automatically restore rankings. The trust signals and authority you built before the breach were damaged. Rebuilding requires renewed effort across all SEO channels.
Content freshness signals help demonstrate active site management. Update key pages with current information. Publish new content on your regular schedule. Show Google that your site is actively maintained and monitored.
Link building may require outreach to sites that removed links during your compromise. Some referring domains automatically remove links to flagged sites. Rebuilding these relationships restores lost link equity.
Realistic Recovery Timelines and Expectations
Full SEO recovery from security breaches typically takes three to six months for moderate incidents. Severe compromises involving thousands of spam pages or extended blacklisting may require six to twelve months for complete recovery.
Recovery isn’t linear. You may see rapid initial improvement as penalties lift, followed by slower progress as you rebuild authority. Some keywords recover faster than others based on competition levels and the specific damage incurred.
Set realistic expectations with stakeholders. Security incidents have real costs measured in lost traffic, revenue, and recovery effort. These costs justify ongoing security investments that prevent future incidents.
Website Security Tools and Solutions Comparison
Choosing appropriate security tools depends on your site’s size, complexity, and risk profile. Understanding available options helps you make informed investment decisions.
Free vs. Paid Security Plugins
Free security plugins provide basic protection suitable for low-risk sites. They typically include firewall rules, login security, and basic malware scanning. Popular free options include Wordfence (WordPress), Sucuri Security, and iThemes Security.
Paid versions add features critical for higher-risk sites. Real-time threat intelligence updates protection against emerging attacks. Priority support ensures rapid assistance during incidents. Advanced scanning detects sophisticated malware that free versions miss.
The cost difference between free and paid security is minimal compared to the cost of a security incident. For sites generating meaningful revenue through organic traffic, paid security tools represent sound investments.
Managed Security Services Overview
Managed security services handle security monitoring and response on your behalf. They provide continuous monitoring, immediate incident response, and expert remediation when problems occur.
Services like Sucuri, SiteLock, and Cloudflare offer managed security packages. These typically include WAF protection, malware scanning, incident response, and cleanup guarantees. Pricing varies based on site size and service level.
Managed services make sense when you lack internal security expertise or time for ongoing monitoring. The cost is predictable, and you gain access to security professionals who handle incidents daily.
Enterprise vs. SME Security Requirements
Enterprise sites face different security challenges than small business sites. Higher traffic volumes attract more attacks. Larger codebases contain more potential vulnerabilities. Regulatory requirements may mandate specific security controls.
Enterprise security typically requires dedicated security personnel, comprehensive logging and monitoring, incident response procedures, and regular penetration testing. These investments are proportional to the business value at risk.
SME sites can achieve adequate security with managed services, quality hosting, disciplined updates, and regular audits. The key is matching security investment to actual risk rather than either over-investing or ignoring security entirely.
Website Security Best Practices by Platform
Different platforms present different security challenges. Platform-specific best practices address the unique vulnerabilities each system presents.
WordPress Security for SEO
WordPress powers over 40% of websites, making it the most targeted CMS. Its popularity means attackers develop specialized tools for WordPress exploitation. Security requires WordPress-specific measures.
Essential WordPress security includes keeping core, themes, and plugins updated; using security plugins like Wordfence or Sucuri; implementing strong authentication; choosing reputable themes and plugins; and using quality hosting with WordPress-specific protections.
WordPress-specific vulnerabilities often involve plugins. Audit your plugin list regularly. Remove anything unused. Research security histories before installing new plugins. Consider premium plugins from established developers for critical functionality.
Shopify and E-commerce Security Considerations
E-commerce sites face heightened security requirements due to payment processing and customer data handling. Shopify handles much of this security at the platform level, but store owners retain responsibilities.
Shopify’s managed platform provides SSL, PCI compliance, and infrastructure security. Store owners must secure their admin access, vet third-party apps carefully, and protect customer data they export or store externally.
For SEO purposes, Shopify’s security foundation is solid. Focus on app security, as vulnerable apps can compromise your store. Review app permissions carefully and remove apps you no longer use.
Custom CMS and Headless Architecture Security
Custom-built sites and headless architectures require security expertise that platform users can rely on vendors to provide. Every security control must be implemented deliberately.
Headless architectures separate frontend and backend, creating multiple attack surfaces. API security becomes critical. Authentication between services must be robust. Each component requires independent security consideration.
Custom sites benefit from security frameworks and libraries rather than building security from scratch. OWASP guidelines provide comprehensive security standards. Regular security audits by qualified professionals identify vulnerabilities that internal teams miss.
Building a Long-Term Security and SEO Strategy
Sustainable organic growth requires integrating security into ongoing SEO operations rather than treating it as a separate concern.
Integrating Security into Technical SEO Workflows
Security checks should be standard components of technical SEO audits. Every crawl should verify SSL status. Every indexation review should check for spam pages. Every performance analysis should consider security tool overhead.
When planning site changes, include security review in the process. New plugins require security vetting. Server migrations require security configuration verification. Redesigns require security testing before launch.
This integration ensures security doesn’t become an afterthought addressed only after problems occur. Proactive security maintenance is far less costly than reactive incident response.
Ongoing Monitoring and Incident Response Planning
Continuous monitoring enables rapid response to emerging threats. Automated alerts for security issues, uptime monitoring, and anomaly detection provide early warning of problems.
Incident response plans document procedures for handling security events. Who is notified? What are the immediate containment steps? How is remediation verified? Who communicates with stakeholders? Having these answers ready before incidents occur enables faster, more effective response.
Test your incident response procedures periodically. Simulated incidents reveal gaps in your plans and ensure team members understand their roles. The time to discover procedural problems is during testing, not during actual incidents.
Measuring Security ROI Through Organic Performance
Security investments are justified through risk reduction and performance maintenance. Quantifying this ROI helps secure ongoing budget for security measures.
Track security-related metrics alongside SEO metrics. Monitor uptime percentages, security scan results, blocked attack attempts, and incident frequency. Correlate these with organic traffic trends to demonstrate the relationship between security investment and traffic stability.
Calculate the cost of potential incidents. Estimate traffic loss from a week of blacklisting. Calculate revenue impact from that traffic loss. Compare against security tool and service costs. This analysis typically shows security investments delivering strong returns.
Conclusion
Website security and SEO are fundamentally connected. Google rewards secure, trustworthy sites with better rankings and penalizes compromised sites with warnings, suppressed visibility, and index removal. Protecting your organic traffic requires protecting your site.
The security measures outlined here represent essential investments for any site depending on organic traffic. SSL implementation, regular updates, security monitoring, and incident response planning form the foundation of sustainable SEO performance.
We help businesses build and protect their organic growth through comprehensive SEO services that include technical security considerations. Contact White Label SEO Service to discuss how we can strengthen both your security posture and your search visibility.
Frequently Asked Questions About Website Security and SEO
Does HTTPS improve Google rankings?
Yes, HTTPS is a confirmed Google ranking signal. While it’s considered a lightweight factor compared to content quality and backlinks, HTTPS has become a baseline expectation. Sites without it face ranking disadvantages and user trust barriers from browser warnings.
Can a hacked website recover its SEO rankings?
Yes, hacked websites can recover their rankings, but recovery takes time and effort. After cleaning the infection and having Google remove warnings, expect three to six months for moderate incidents to fully recover. Severe compromises may require longer.
How long does it take to remove a Google security warning?
Google typically processes security review requests within 72 hours for straightforward cases. Complex situations involving extensive compromise may take longer. The review only succeeds if you’ve completely remediated the security issue.
What are the signs my website has been compromised?
Common signs include unexpected redirects, new pages you didn’t create, modified files, new user accounts, Google Search Console security alerts, sudden traffic drops, and warnings when visiting your site. Regular monitoring helps detect these signs early.
How often should I audit my website for security issues?
Automated security scans should run at least weekly for most sites. High-traffic sites or those handling sensitive data should scan daily. Comprehensive manual audits should occur quarterly, with professional penetration testing annually for high-value sites.
What security tools do I need for my website?
Essential tools include an SSL certificate, a web application firewall, a security plugin appropriate for your CMS, and uptime monitoring. Additional tools like malware scanners, backup solutions, and vulnerability scanners add important protection layers.
How much does website security cost?
Basic security using free tools and standard SSL costs nothing beyond hosting. Comprehensive security with premium plugins, managed WAF services, and professional monitoring typically costs $20 to $500 monthly depending on site size and requirements. This investment is minimal compared to the cost of security incidents.



