Broken links silently drain your SEO performance, waste crawl budget, and frustrate users who hit dead ends on your site. Every 404 error represents lost link equity, missed conversions, and a signal to search engines that your site may not be well-maintained.
This technical debt accumulates faster than most website owners realize. A single URL change can cascade into dozens of broken internal links, while external sites linking to your deleted pages represent authority you’re no longer capturing.
This guide walks you through the complete broken link audit process, from detection to resolution, plus prevention strategies that keep your site healthy long-term.
What Are Broken Links? (And Why They Matter for SEO)
A broken link points to a destination that no longer exists or returns an error. When users or search engine crawlers click these links, they encounter error pages instead of the expected content. This creates friction across your entire digital presence.
Broken links aren’t just technical inconveniences. They represent real business impact through lost traffic, diminished authority, and degraded user experience. Understanding the different types helps you prioritize fixes effectively.
Types of Broken Links
Internal broken links occur within your own website. These happen when you link from one page on your site to another page that no longer exists. A blog post linking to a deleted product page creates an internal broken link. These are entirely within your control to fix.
External broken links (outbound) point from your site to other websites. When you cite a source, reference a tool, or link to a partner and that destination disappears, you’ve created an external broken link. While you can’t control other sites, you’re responsible for maintaining your outbound links.
Incoming broken links (backlinks) are links from other websites pointing to pages on your site that no longer exist. These represent the most significant SEO opportunity loss. Other sites linked to your content, passing authority and referral traffic, but that value now hits a dead end.
How Broken Links Impact Your Website
SEO performance and rankings suffer when broken links accumulate. Search engines interpret excessive 404 errors as a quality signal. While Google states that 404s themselves don’t directly hurt rankings, the lost link equity and poor user signals certainly do. Pages that previously received authority through internal links lose that support when links break.
User experience and engagement decline measurably. Users who encounter broken links lose trust in your site. Research from Nielsen Norman Group confirms that error pages create frustration and increase bounce rates. Each broken link is a potential customer walking away.
Crawl budget waste becomes significant for larger sites. Search engines allocate limited resources to crawl your site. Every request spent on a 404 page is a request not spent discovering or re-crawling your valuable content. For sites with thousands of pages, this inefficiency compounds.
Link equity loss represents perhaps the most damaging long-term impact. When external sites link to your content and that page returns a 404, you capture none of that authority. Internal links that pointed to deleted pages no longer distribute PageRank through your site architecture.
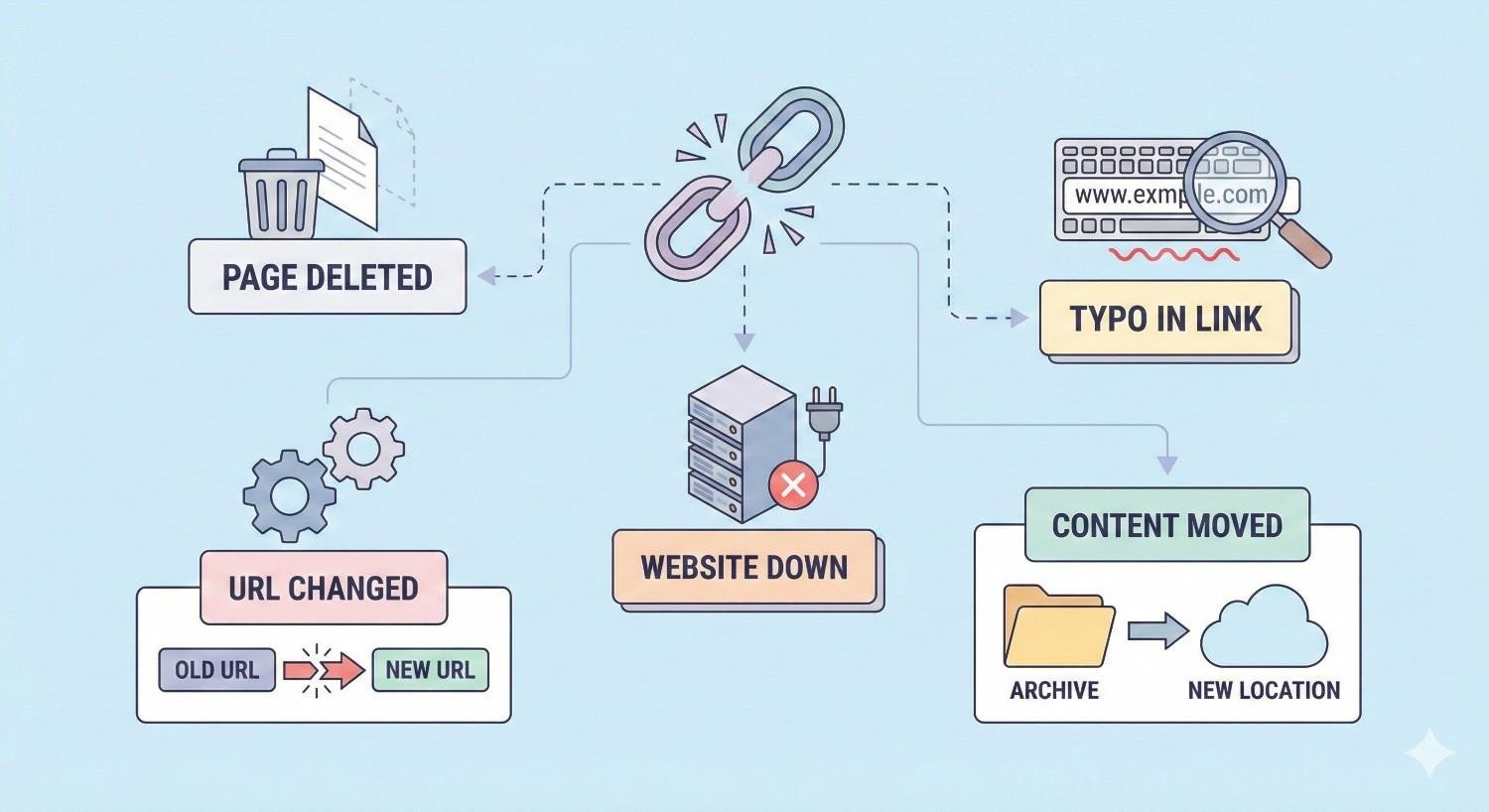
Common Causes of Broken Links
Understanding why broken links occur helps you prevent them. Most broken links stem from predictable scenarios that proper processes can address.
Internal Causes
Page deletions without redirects create the majority of internal broken links. When you remove a product, archive a blog post, or consolidate pages, every internal link pointing to that URL breaks instantly. The fix is simple but often overlooked: implement redirects before or immediately after deletion.
URL structure changes during site redesigns or platform updates break existing links. Changing from /blog/post-title to /articles/post-title invalidates every link using the old structure. URL changes require comprehensive redirect mapping.
CMS migrations frequently generate broken links. Moving from WordPress to Shopify, or any platform transition, often changes URL patterns. Without careful planning, hundreds or thousands of links can break simultaneously.
Manual linking errors happen during content creation. Typos in URLs, incorrect copy-paste operations, or linking to staging environments instead of production all create broken links from the start.
External Causes
Third-party site changes are outside your control but affect your content. When you link to a resource and that site restructures, your outbound link breaks. Industry statistics pages, tool documentation, and news articles frequently move or disappear.
Domain expirations eliminate entire websites. Companies go out of business, projects get abandoned, and domains lapse. Any links you’ve built to those destinations become broken.
Content removals happen when other sites delete specific pages. A study you cited gets retracted, a product you referenced gets discontinued, or a company removes a resource. The domain still exists, but your specific link target is gone.
How to Audit Broken Links on Your Website
A systematic audit identifies all broken links across your site. The process involves selecting appropriate tools, running comprehensive crawls, categorizing findings, and prioritizing fixes based on impact.
Step 1: Choose Your Broken Link Audit Tool
Google Search Console provides free broken link data directly from Google’s perspective. Navigate to Pages > Not Found to see URLs Google attempted to crawl but couldn’t access. This shows what Google actually encounters, though it may not catch every broken link on your site.
Screaming Frog SEO Spider offers the most comprehensive crawling for technical SEO. The free version crawls up to 500 URLs, sufficient for smaller sites. Configure it to check response codes and identify all 4xx and 5xx errors. It shows both the broken URL and every page linking to it.
Ahrefs Site Audit combines crawling with backlink data. This reveals not just internal broken links but also broken backlinks from external sites. The integration with their backlink database makes it particularly valuable for link equity recovery.
Semrush Site Audit provides similar functionality with detailed issue explanations. It categorizes broken links by severity and provides fix recommendations. The interface suits teams who need clear prioritization.
Other specialized tools include Sitebulb for visual crawl analysis, DeepCrawl for enterprise sites, and browser extensions like Check My Links for quick page-level checks.
Step 2: Run a Comprehensive Site Crawl
Crawl configuration settings determine what your audit captures. Enable JavaScript rendering if your site uses client-side navigation. Include external link checking to find broken outbound links. Set appropriate crawl delays to avoid overwhelming your server.
Crawl depth and scope should cover your entire site. Start from your homepage and allow the crawler to follow all internal links. For large sites, you may need to crawl in sections or increase memory allocation. Ensure the crawler accesses all important sections including blog archives, product categories, and resource libraries.
What to look for in crawl results includes any URL returning 4xx or 5xx status codes. Pay attention to the “inlinks” count showing how many pages link to each broken URL. High inlink counts indicate widely-linked pages that need immediate attention.
Step 3: Identify and Categorize Broken Links
404 errors (Not Found) indicate the URL doesn’t exist on the server. This is the most common broken link type. The page was either deleted, moved without a redirect, or never existed at the linked URL.
410 errors (Gone) explicitly communicate that content was intentionally removed and won’t return. This is actually preferable to 404 for permanently deleted content, as it tells search engines to stop checking.
500 errors (Server errors) indicate technical problems rather than missing content. These require developer investigation. The page may exist but fail to load due to code errors, database issues, or server configuration problems.
Redirect chains and loops aren’t technically broken links but cause similar problems. A redirect chain occurs when URL A redirects to B, which redirects to C. Each hop loses link equity and slows page loading. Redirect loops occur when redirects create a circular path, making the destination unreachable.
Step 4: Export and Prioritize Your Broken Links
Priority by traffic impact focuses on pages that received significant organic traffic before breaking. Check Google Analytics historical data for URLs now returning 404s. High-traffic pages deserve immediate redirects to capture that demand.
Priority by link equity addresses pages with valuable backlinks. Use Ahrefs or similar tools to identify broken URLs that have external links pointing to them. These represent authority you’re currently losing.
Priority by user journey importance considers where broken links appear. A broken link on your homepage or main navigation affects every visitor. Broken links in checkout flows or lead generation paths directly impact conversions.
Creating your fix priority list combines these factors. Export your broken link data to a spreadsheet. Add columns for traffic, backlinks, and page importance. Score each broken link and sort by total priority. This gives you a clear action sequence.
Step 5: Audit Broken Backlinks
Using Ahrefs for broken backlink analysis reveals external links pointing to your 404 pages. Navigate to Site Explorer > Best by Links > add a 404 filter. This shows pages that other sites link to but no longer exist on your site. Each represents recoverable link equity.
Using Google Search Console shows some broken backlink data under Links > Top linked pages. Cross-reference this with your 404 list. Pages appearing in both reports have external links hitting dead ends.
Identifying reclamation opportunities means evaluating which broken backlinks are worth recovering. A link from a high-authority site to a deleted blog post justifies recreating that content or redirecting to a relevant alternative. Low-quality links to irrelevant pages may not warrant action.
How to Fix Broken Links: Step-by-Step Solutions
Fixing broken links requires different approaches depending on the link type and your available options. The goal is always to preserve user experience and link equity.
Fixing Internal Broken Links
Option 1: Implement 301 redirects when equivalent content exists elsewhere. If you deleted a product page but have a similar product, redirect the old URL to the new one. If you consolidated blog posts, redirect old URLs to the combined article. This preserves link equity and sends users to relevant content.
Option 2: Update the link URL when the destination simply moved. If your team page changed from /about/team to /company/team, update all internal links to use the new URL. This is cleaner than relying on redirects for internal navigation.
Option 3: Remove the broken link when no relevant destination exists. If you linked to a discontinued service with no replacement, removing the link entirely may be appropriate. Update the surrounding content to make sense without the link.
Option 4: Restore deleted content when the original page had significant value. If you accidentally deleted a high-performing blog post or removed a page that still receives traffic, restoring it may be the best solution. Check backups or cached versions.
Fixing Broken External Links (Outbound)
Replace with updated URL when the destination simply moved. Many sites restructure without proper redirects. Search for the content on the destination site and update your link to the new location.
Find alternative resource when the original is truly gone. If you cited a study that’s no longer available, find another credible source making the same point. Update your content to reference the new source.
Use archived version (Wayback Machine) for historically important references. The Internet Archive often has cached versions of deleted pages. Link to the archived version when the original content’s specific wording or data matters.
Remove if no longer relevant when the link added minimal value. If you linked to a tool that no longer exists and alternatives aren’t worth mentioning, simply remove the link and adjust your content accordingly.
Fixing Broken Backlinks (Incoming Links)
Set up 301 redirects to relevant pages to capture link equity from external sites. If other sites link to your deleted /ultimate-guide-seo page, redirect it to your current comprehensive SEO resource. The linking sites don’t need to update anything.
Recreate deleted content when backlinks point to valuable topics you no longer cover. If you removed a popular resource that earned significant links, consider recreating it. The backlinks already exist; you just need to provide the destination.
Reach out to linking sites as a secondary approach. Contact webmasters and request they update their links to your current URL. This is time-intensive but creates cleaner link profiles. Prioritize high-authority sites.
Leverage broken link building opportunities by identifying what content earned those links. Understanding why sites linked to your deleted content helps you create better content that earns new links.
Implementing 301 Redirects Correctly
When to use 301 vs 302 redirects depends on permanence. Use 301 (permanent) redirects when the old URL will never return. Use 302 (temporary) redirects only for genuinely temporary situations like A/B tests or maintenance. For broken link fixes, 301 is almost always correct.
How to implement redirects (by platform) varies by your technology stack. In WordPress, plugins like Redirection or Yoast handle redirects through the admin interface. For Apache servers, add rules to your .htaccess file. Nginx uses the server configuration file. Shopify, Squarespace, and other platforms have built-in redirect management.
Redirect mapping best practices ensure accuracy at scale. Create a spreadsheet with old URLs in one column and new destinations in another. Verify each mapping makes semantic sense. Test redirects after implementation. Document your redirect logic for future reference.
Avoiding redirect chains requires checking existing redirects before adding new ones. If URL A already redirects to B, and you need to redirect B to C, update the original redirect so A goes directly to C. Tools like Screaming Frog identify existing chains.
Tools for Finding and Fixing Broken Links
The right tools make broken link management efficient. Your choice depends on site size, budget, and technical requirements.
Free Broken Link Checker Tools
Google Search Console remains essential for any website. It shows crawl errors from Google’s perspective, identifies pages with 404 status, and reveals which URLs Google attempted to access. The data comes directly from Google’s crawlers, making it authoritative for SEO purposes.
Screaming Frog (free version) crawls up to 500 URLs with full functionality. For small sites, this provides comprehensive broken link detection including response codes, redirect chains, and inlink analysis. The limitation is purely on crawl size.
Dead Link Checker offers simple online checking without software installation. Enter your URL and it crawls your site looking for broken links. Useful for quick checks but lacks the depth of desktop tools.
W3C Link Checker validates links according to web standards. It’s thorough but slow, making it better suited for smaller sites or specific page checks rather than full site audits.
Premium SEO Tools for Broken Link Audits
Ahrefs Site Audit combines crawling with their extensive backlink database. This integration reveals not just broken internal links but broken backlinks from external sites. Pricing starts at $99/month with Site Audit included in all plans.
Semrush Site Audit provides detailed issue categorization and fix recommendations. The interface clearly prioritizes issues by impact. Plans including Site Audit start at $129.95/month.
Moz Pro includes site crawling with their Link Explorer data. The integration helps identify broken links with significant link equity. Pro plans start at $99/month.
Sitebulb offers visual crawl analysis that makes complex site structures understandable. The visualization helps identify patterns in broken links. Desktop licenses start at $13.50/month.
Tool Comparison and Recommendations
Best for small websites is the combination of Google Search Console plus Screaming Frog free version. This covers Google’s perspective and provides detailed crawl data without cost. For sites under 500 pages, this combination handles most needs.
Best for enterprise sites is Ahrefs or Semrush combined with Screaming Frog paid version. Large sites need the unlimited crawling of paid tools plus the backlink integration of enterprise SEO platforms. The investment pays off in efficiency and completeness.
Best for ongoing monitoring is a platform with scheduled crawling and alerts. Ahrefs, Semrush, and Sitebulb all offer automated crawl scheduling. Set weekly or monthly crawls with email notifications when new broken links appear.
Preventing Broken Links: Best Practices
Prevention costs less than remediation. Implementing proper processes stops broken links before they occur.
Implement a Redirect Strategy Before Making Changes
Plan redirects before deleting or moving any page. Create a redirect map as part of your content removal or URL change process. Never delete a page that has internal links, external backlinks, or organic traffic without a redirect in place.
Make redirect planning a required step in your content workflow. Before any page deletion gets approved, someone must document where that URL will redirect and implement the redirect before removal.
Use Relative URLs for Internal Links
Relative URLs like /blog/post-title adapt automatically to domain changes. Absolute URLs like https://example.com/blog/post-title break if your domain changes or you move between staging and production environments.
While both work for established sites, relative URLs reduce one category of broken link risk. They’re particularly valuable during development and for sites that may change domains.
Set Up Automated Monitoring
Scheduled crawls catch broken links before they accumulate. Configure your SEO tool to crawl weekly or monthly depending on how frequently your site changes. More dynamic sites need more frequent monitoring.
Alert configurations notify you immediately when problems appear. Set thresholds for new 404 errors that trigger email notifications. This enables rapid response before broken links impact users or rankings.
Regular GSC checks should be part of your routine. Review the Pages report in Google Search Console at least monthly. This shows what Google actually encounters, which may differ from your internal crawl data.
Maintain a Link Inventory
Document your important internal links, especially those in navigation, footers, and high-traffic pages. When you need to change URLs, this inventory shows you exactly what needs updating.
Track your most-linked content so you know which pages require extra care before modification. A page with 50 internal links needs more careful handling than one with 2.
Create a Pre-Launch Checklist for Site Changes
Before any significant site update, run through a broken link prevention checklist. This includes crawling the staging environment, mapping all URL changes, implementing redirects, and testing after launch.
Document this checklist and require sign-off before major changes go live. The few minutes spent checking prevents hours of broken link cleanup later.
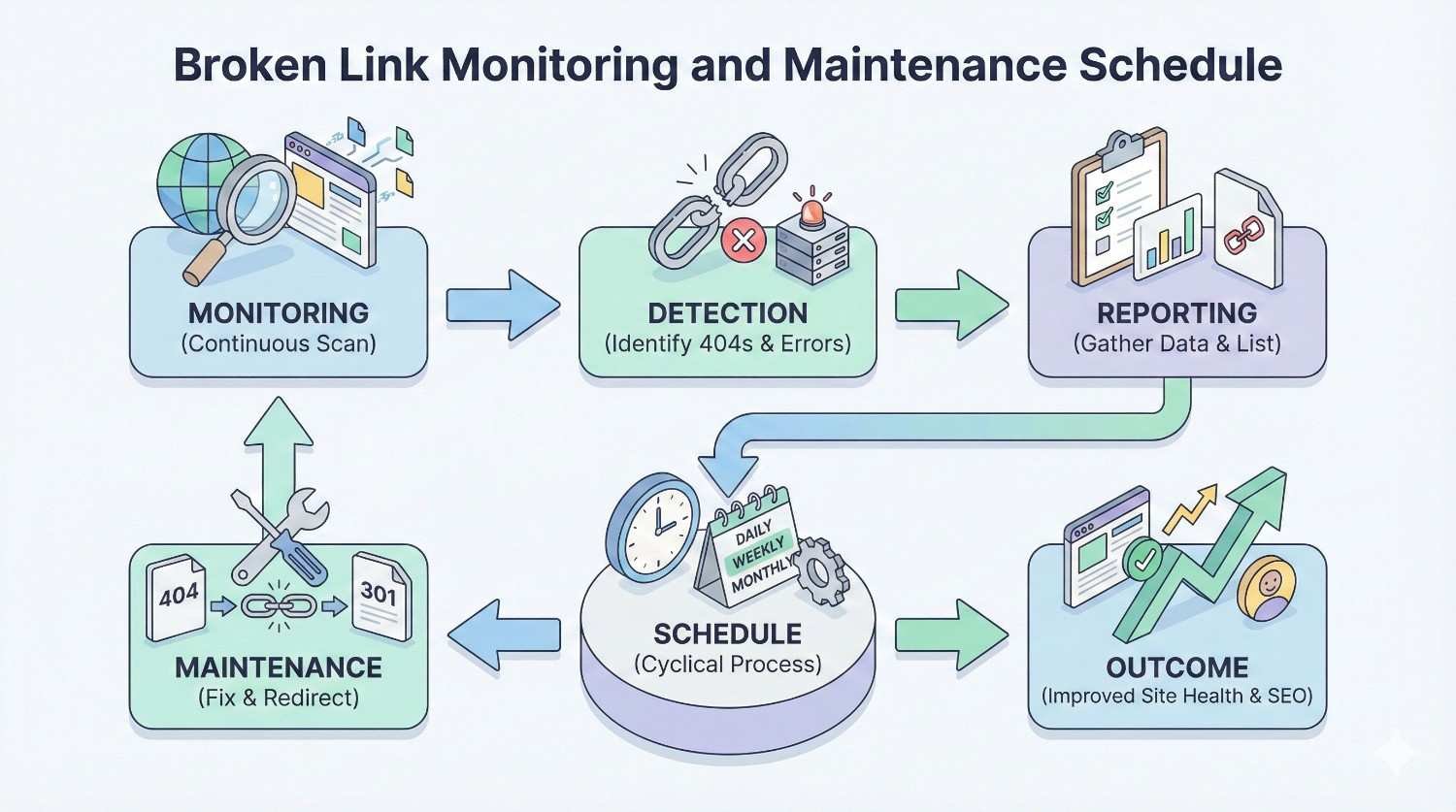
Broken Link Monitoring and Maintenance Schedule
Consistent monitoring catches problems early. Your schedule should match your site’s size and change frequency.
How Often to Audit for Broken Links
Small sites (under 500 pages) need monthly comprehensive audits. With fewer pages, crawls complete quickly and the total number of potential broken links remains manageable. Monthly checks catch issues before they compound.
Medium sites (500-5,000 pages) benefit from bi-weekly monitoring. More pages mean more opportunities for broken links. Automated weekly crawls with bi-weekly manual review balances thoroughness with efficiency.
Large sites (5,000+ pages) require weekly automated monitoring with daily checks on critical sections. Enterprise sites generate broken links continuously through content updates, product changes, and external link decay. Continuous monitoring is essential.
Setting Up Ongoing Monitoring
Automated crawl scheduling removes the need to remember manual checks. Configure your SEO tool to crawl on a set schedule. Most tools allow daily, weekly, or monthly options. Choose based on your site’s change velocity.
Email alerts and notifications ensure broken links get attention. Set up alerts for new 404 errors exceeding a threshold. A sudden spike in broken links often indicates a larger problem like a failed deployment or accidental deletion.
Dashboard tracking provides visibility into trends. Track broken link counts over time. Increasing trends indicate process problems. Stable or decreasing trends confirm your prevention efforts work.
Creating a Broken Link Maintenance Workflow
Assign ownership so someone is accountable. Designate a team member or role responsible for broken link monitoring and resolution. Without clear ownership, broken links accumulate.
Define response times based on severity. Critical broken links in navigation or checkout flows need same-day fixes. Lower-priority broken links in archived content can wait for batch processing.
Document fix procedures so anyone can execute. Create standard operating procedures for implementing redirects, updating links, and verifying fixes. This enables consistent handling regardless of who addresses the issue.
Broken Link Building: Turning Errors Into Opportunities
Broken links on other websites create link building opportunities. This strategy involves finding broken links on relevant sites and offering your content as a replacement.
What Is Broken Link Building?
Broken link building identifies pages on other websites that link to now-dead resources. You then create or identify content on your site that could replace the dead resource. Finally, you reach out to the linking site suggesting they update their link to point to your content.
This approach works because you’re helping webmasters fix a problem on their site while earning a link. It’s a value exchange rather than a cold request.
How to Find Broken Link Building Opportunities
Finding broken pages with backlinks starts with identifying dead pages in your niche that earned links. Use Ahrefs Content Explorer to find pages with backlinks that return 404 errors. Filter by your industry or topic to find relevant opportunities.
Identifying competitor broken links reveals opportunities specific to your market. Run competitor domains through Ahrefs Site Explorer and check for broken pages with backlinks. These are topics your competitors covered but no longer support.
Using tools to scale discovery makes this strategy efficient. Ahrefs, Semrush, and Majestic all offer broken backlink reports. Browser extensions like Check My Links help verify broken links on specific pages during manual prospecting.
Outreach Strategy for Broken Link Building
Crafting effective outreach emails requires personalization and value focus. Mention the specific broken link you found. Explain why it matters to their readers. Suggest your content as a replacement without being pushy. Keep emails concise and professional.
Offering genuine value means your replacement content must actually be good. Don’t suggest marginally relevant pages. Your content should genuinely serve the same purpose as the dead resource, ideally better.
Follow-up best practices include waiting 5-7 days before a single follow-up. Don’t send multiple follow-ups. Accept that many outreach emails won’t receive responses. Focus on volume and quality rather than persistence with individual prospects.
Measuring Broken Link Building Success
Track outreach volume, response rates, and links earned. Calculate the ratio of links earned to emails sent. Monitor the domain authority of sites that link to you. Compare the cost per link to other link building methods.
Successful broken link building campaigns typically see 5-15% success rates on well-targeted outreach. The links earned tend to be contextually relevant and from established pages, making them valuable despite the effort required.
Measuring the Impact of Fixing Broken Links
Quantifying results justifies the effort and guides future prioritization. Track specific metrics before and after your broken link fixes.
Key Metrics to Track
Crawl error reduction shows immediate technical improvement. Monitor the 404 count in Google Search Console. A decreasing trend confirms your fixes are working and Google is recognizing the changes.
Organic traffic recovery measures business impact. Compare traffic to pages that received redirects versus their historical performance. Successful redirects should recover a significant portion of the original page’s traffic.
Ranking improvements may follow broken link fixes, especially for pages that lost internal link support. Track keyword rankings for pages affected by broken link repairs. Improvements typically appear within 2-8 weeks.
User engagement metrics reflect experience improvements. Monitor bounce rates and time on site for pages where you fixed broken outbound links. Users who find working links engage more deeply.
Link equity preservation is harder to measure directly but shows in overall site authority. Track your domain’s total referring domains and overall organic visibility. Fixing broken backlinks should stabilize or improve these metrics.
Before and After Analysis
Document your baseline metrics before beginning broken link fixes. Record total 404 errors, affected page traffic, and relevant rankings. After implementing fixes, measure the same metrics at 30, 60, and 90 days.
Create comparison reports showing the change. Visualize the reduction in errors and recovery in traffic. This data supports future investment in technical SEO maintenance.
Reporting Broken Link Fixes to Stakeholders
Translate technical fixes into business language. Instead of “reduced 404 errors by 200,” report “recovered access to pages that previously received 5,000 monthly visits.” Connect crawl budget savings to faster indexing of new content.
Include before/after screenshots from Google Search Console. Show traffic graphs for recovered pages. Quantify the link equity preserved through redirect implementation. Make the value tangible for non-technical stakeholders.
Common Broken Link Mistakes to Avoid
Even well-intentioned fixes can create new problems. Avoid these common errors.
Redirecting All 404s to Homepage
Mass redirecting every 404 to your homepage seems efficient but harms SEO and user experience. Google treats irrelevant redirects as soft 404s, providing no ranking benefit. Users landing on your homepage when they expected specific content get frustrated.
Redirect each broken URL to the most relevant existing page. If no relevant page exists, consider recreating the content or allowing the 404 to remain.
Creating Redirect Chains
Adding redirects without checking existing ones creates chains. URL A redirects to B, which redirects to C, which redirects to D. Each hop loses link equity and adds latency. Chains of three or more hops significantly impact performance.
Before adding any redirect, verify the destination doesn’t already redirect elsewhere. Update existing redirects to point directly to final destinations.
Ignoring Broken Backlinks
Focusing only on internal broken links misses significant opportunity. External sites linking to your 404 pages represent authority you’re not capturing. These broken backlinks often have more SEO value than internal links.
Include broken backlink analysis in every audit. Prioritize fixing broken URLs that have external links pointing to them.
Using 302 Instead of 301 Redirects
302 redirects signal temporary moves and don’t pass full link equity. Using 302 for permanent URL changes wastes the authority those pages accumulated. Search engines may continue trying to index the old URL.
Use 301 redirects for any permanent URL change. Reserve 302 only for genuinely temporary situations like maintenance pages or A/B tests.
Not Testing Redirects After Implementation
Implementing redirects without verification leads to silent failures. Typos in redirect rules, incorrect syntax, or server configuration issues can prevent redirects from working. You think the problem is solved while users still hit 404s.
Test every redirect after implementation. Use tools like Redirect Checker or simply visit the old URL and verify it reaches the correct destination.
When to Get Professional Help with Broken Links
Some broken link situations exceed typical in-house capabilities. Recognizing when to seek expert support saves time and prevents costly mistakes.
Signs You Need Expert SEO Support
Large-scale site migrations involve thousands of URL changes simultaneously. Mapping redirects, implementing them correctly, and verifying results requires specialized experience. Migration mistakes can devastate organic traffic for months.
Persistent crawl errors that don’t resolve despite your efforts indicate deeper technical issues. Server configuration problems, CMS limitations, or complex redirect logic may require expert diagnosis.
Complex redirect mapping for sites with multiple URL pattern changes needs systematic approaches. When simple one-to-one redirects won’t work, regex-based rules and careful testing become necessary.
Significant traffic loss following URL changes demands rapid expert response. Every day of lost traffic costs revenue. Experienced professionals diagnose and fix issues faster than teams learning on the job.
What a Professional SEO Audit Includes
Comprehensive technical analysis examines your entire site architecture. This goes beyond broken links to identify all technical SEO issues affecting performance. You get a complete picture of your site’s health.
Redirect strategy and implementation provides a documented plan for fixing current issues and preventing future ones. Professionals create redirect maps, implement rules correctly, and verify results systematically.
Link equity recovery identifies and addresses broken backlinks. This includes redirect implementation, content recreation recommendations, and outreach strategies for high-value link recovery.
Ongoing monitoring setup establishes systems to catch future issues early. Professionals configure tools, set appropriate alerts, and create maintenance workflows your team can follow.
How We Help Businesses Fix and Prevent Broken Links
Technical SEO foundation starts with comprehensive audits identifying every broken link across your site. We categorize issues by impact and create prioritized fix plans that address the most damaging problems first.
Proactive monitoring systems prevent broken links from accumulating. We configure automated crawling, set up alert thresholds, and establish review processes that catch issues before they impact rankings or user experience.
Strategic redirect planning ensures URL changes don’t sacrifice existing authority. Before any migration or restructure, we map every redirect, test implementations, and verify results. Your link equity stays intact.
Performance tracking and reporting demonstrates the value of broken link management. We document baseline metrics, track improvements, and provide clear reports showing traffic recovery, error reduction, and authority preservation.
Conclusion
Broken links represent preventable damage to your SEO performance, user experience, and site authority. Regular audits, systematic fixes, and proactive prevention keep your site healthy and your link equity intact.
The investment in broken link management pays returns through recovered traffic, preserved rankings, and improved crawl efficiency. Every redirect you implement captures value that would otherwise disappear.
We help businesses build and maintain technically sound websites that support long-term organic growth. Contact White Label SEO Service to audit your site’s broken links and implement a sustainable maintenance strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I check for broken links on my website?
Check monthly for sites under 500 pages, bi-weekly for medium sites, and weekly for large sites. Automated monitoring with alerts catches issues between scheduled audits. More frequent checks suit sites with regular content updates.
Do broken links directly hurt my Google rankings?
Broken links don’t directly trigger ranking penalties, but they cause indirect damage. Lost link equity, wasted crawl budget, poor user signals, and diminished site quality all affect rankings negatively over time.
What’s the difference between a 404 and 410 error?
A 404 indicates a page wasn’t found but might return. A 410 explicitly states the content is permanently gone. Use 410 for intentionally deleted content to tell search engines to stop checking that URL.
Should I redirect all broken links to my homepage?
No. Redirect each broken URL to the most relevant existing page. Mass homepage redirects provide poor user experience and Google treats them as soft 404s, passing no ranking benefit.
How do I find broken links pointing to my site from other websites?
Use Ahrefs Site Explorer or Semrush Backlink Analytics to identify external links pointing to your 404 pages. These tools show which of your broken URLs have backlinks you could recover through redirects.
Can I prevent broken links entirely?
You can minimize them significantly through proper processes. Implement redirects before deleting pages, use relative URLs, maintain link inventories, and run pre-launch checks before site changes. Some external link decay is unavoidable.
How long does it take for Google to recognize my redirect fixes?
Google typically processes redirects within days to weeks depending on crawl frequency. High-traffic pages get recrawled faster. Use Google Search Console’s URL Inspection tool to request recrawling of important fixed URLs.



