Cheap link building typically costs under $100 per link and almost always damages your site’s rankings, reputation, and revenue. The appeal is obvious: faster results at lower prices. But Google’s algorithms have become remarkably sophisticated at detecting manipulative links, and the consequences range from ranking drops to complete deindexing.
This matters because your competitors who invest in quality links are building sustainable authority while cheap tactics create compounding technical debt. The short-term savings become long-term losses.
This guide covers exactly what makes link building “cheap,” the specific risks involved, how Google detects low-quality links, and proven strategies for building authority on any budget.
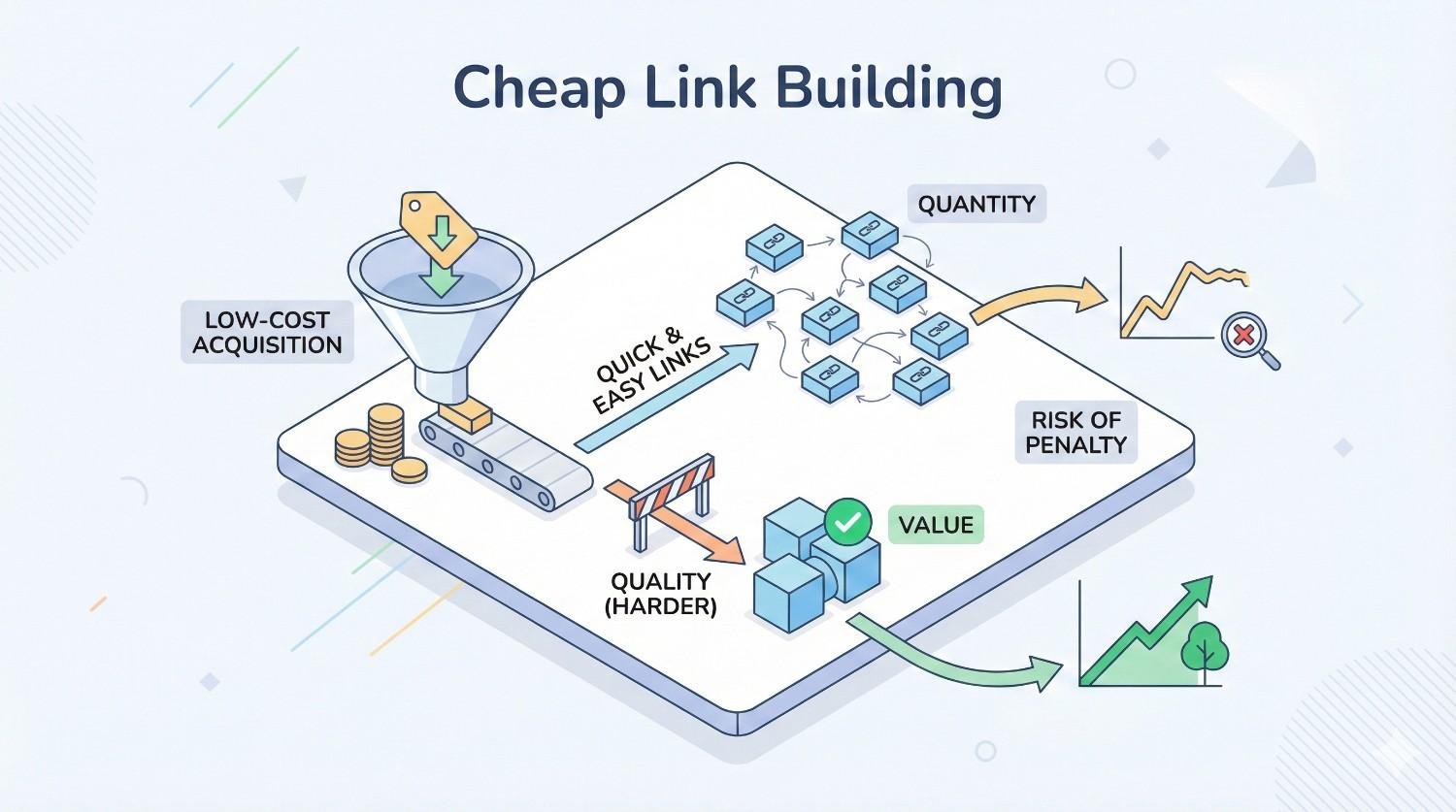
What Is Cheap Link Building?
Understanding what qualifies as “cheap” link building requires looking beyond price tags. The distinction involves methodology, source quality, and long-term value rather than simple cost comparisons.
Defining “Cheap” in Link Building Context
Cheap link building refers to acquiring backlinks through low-cost, high-volume methods that prioritize quantity over relevance and authority. These links typically come from sites with minimal editorial standards, low domain authority, or networks specifically created to sell links.
The price threshold varies by industry, but links priced under $50-100 generally indicate compromised quality. According to Ahrefs’ link building survey, quality editorial links from legitimate publications average $300-500 per placement, with premium placements exceeding $1,000.
Cheap doesn’t always mean inexpensive in absolute terms. A $200 link from a private blog network is “cheap” because it provides no lasting value and carries significant risk. Meanwhile, a $150 link earned through genuine outreach to a relevant industry blog represents legitimate value.
The defining characteristics of cheap links include:
- Placement on sites with no real audience or traffic
- Lack of editorial review or content standards
- Obvious patterns (same anchor text, similar site templates)
- No topical relevance to your business
- Purchased in bulk packages
Common Cheap Link Building Methods
Several tactics dominate the cheap link building market. Each carries specific risks and detection signatures that Google’s algorithms recognize.
Fiverr and marketplace gig services offer packages promising hundreds of links for under $50. These typically involve automated submissions to web directories, article sites, and comment sections. The links come from sites with no traffic, no authority, and often exist solely to sell links.
Link packages from overseas providers frequently advertise “500 backlinks for $99” or similar bulk offerings. These operations use automated tools to create profiles, submit articles, and post comments across thousands of low-quality sites.
Guest post farms operate networks of sites that accept any content in exchange for payment. The sites have no genuine readership, publish content on random topics, and exist primarily as link placement vehicles.
Expired domain networks purchase domains with existing backlink profiles, then repurpose them as link sources. While the domains may show historical authority metrics, Google recognizes when sites change purpose dramatically.
Social bookmarking and Web 2.0 submissions involve creating profiles and posts on platforms like Tumblr, Medium, or social bookmarking sites purely for link placement. When done at scale without genuine engagement, these provide minimal value.
Why Cheap Link Building Remains Popular
Despite well-documented risks, cheap link building persists because it occasionally produces short-term results and appeals to businesses facing budget constraints.
Immediate visibility of results creates a compelling illusion. New links appear in backlink reports within days, and some sites experience temporary ranking improvements. This creates false confidence that the strategy works.
Budget pressure drives many decisions. Small businesses and startups often lack the $2,000-5,000 monthly budgets that quality link building campaigns require. Cheap options appear to offer a path forward when resources are limited.
Lack of SEO knowledge means many business owners cannot distinguish between legitimate and manipulative tactics. Providers use technical language and impressive-sounding metrics to obscure the true nature of their services.
Competitor activity creates pressure. When businesses see competitors apparently succeeding with aggressive link building, they feel compelled to match those efforts without understanding the risks involved.
Delayed consequences allow cheap tactics to seem successful initially. Google penalties and algorithmic devaluations often take months to materialize, creating a window where the strategy appears effective.
The Real Risks of Cheap Link Building
The consequences of cheap link building extend far beyond wasted money. Understanding these risks helps contextualize why quality matters more than quantity in link acquisition.
Google Penalties and Manual Actions
Google issues manual actions when human reviewers identify link schemes violating their guidelines. These penalties can devastate organic traffic overnight.
Manual action notifications appear in Google Search Console when reviewers determine a site has participated in link schemes. The notification specifies whether the penalty affects the entire site or specific pages.
Unnatural links to your site represents the most common manual action related to link building. This penalty indicates Google found evidence of purchased, exchanged, or artificially created links pointing to your domain.
Recovery requires identifying and removing problematic links, then submitting a reconsideration request. According to Google’s documentation, this process typically takes 2-6 months when executed properly, though some sites never fully recover their previous rankings.
Site-wide penalties remove entire domains from search results. While rare, these occur when Google determines a site’s primary purpose involves link manipulation or when violations are severe and widespread.
The manual review process has become more sophisticated. Google’s webspam team uses pattern recognition, link graph analysis, and machine learning to identify sites participating in link schemes even when individual links appear natural.
Algorithmic Devaluation and Ranking Loss
Beyond manual penalties, Google’s algorithms automatically devalue suspicious links without notification. This creates gradual ranking declines that are difficult to diagnose.
Penguin algorithm integration means link quality assessment happens continuously as part of Google’s core ranking system. Unlike earlier versions that caused dramatic ranking drops during periodic updates, modern Penguin works in real-time.
Link devaluation differs from penalties. Rather than punishing your site, Google simply ignores low-quality links when calculating rankings. This means the money spent on cheap links produces zero benefit while potentially triggering additional scrutiny.
Ranking volatility often indicates algorithmic issues. Sites with unnatural link profiles experience more dramatic fluctuations during core updates as Google reassesses link quality signals.
The challenge with algorithmic devaluation is invisibility. You receive no notification, and the effects blend with normal ranking fluctuations. Many sites experience gradual traffic declines without understanding the cause.
Brand Reputation and Trust Damage
Cheap link building often places your brand on sites that damage credibility with potential customers who encounter them.
Association with low-quality content occurs when your links appear alongside spam, adult content, or misleading information. Potential customers who discover these placements may question your legitimacy.
Competitor awareness means your rivals can identify cheap link building tactics and use that information in sales conversations. “Have you seen where their links come from?” becomes a competitive weapon.
Industry reputation suffers when peers recognize manipulative tactics. In B2B contexts especially, being known for black-hat SEO damages relationships and partnership opportunities.
Customer trust erosion happens when sophisticated buyers research vendors thoroughly. Finding your brand promoted through spam sites raises questions about your business practices generally.
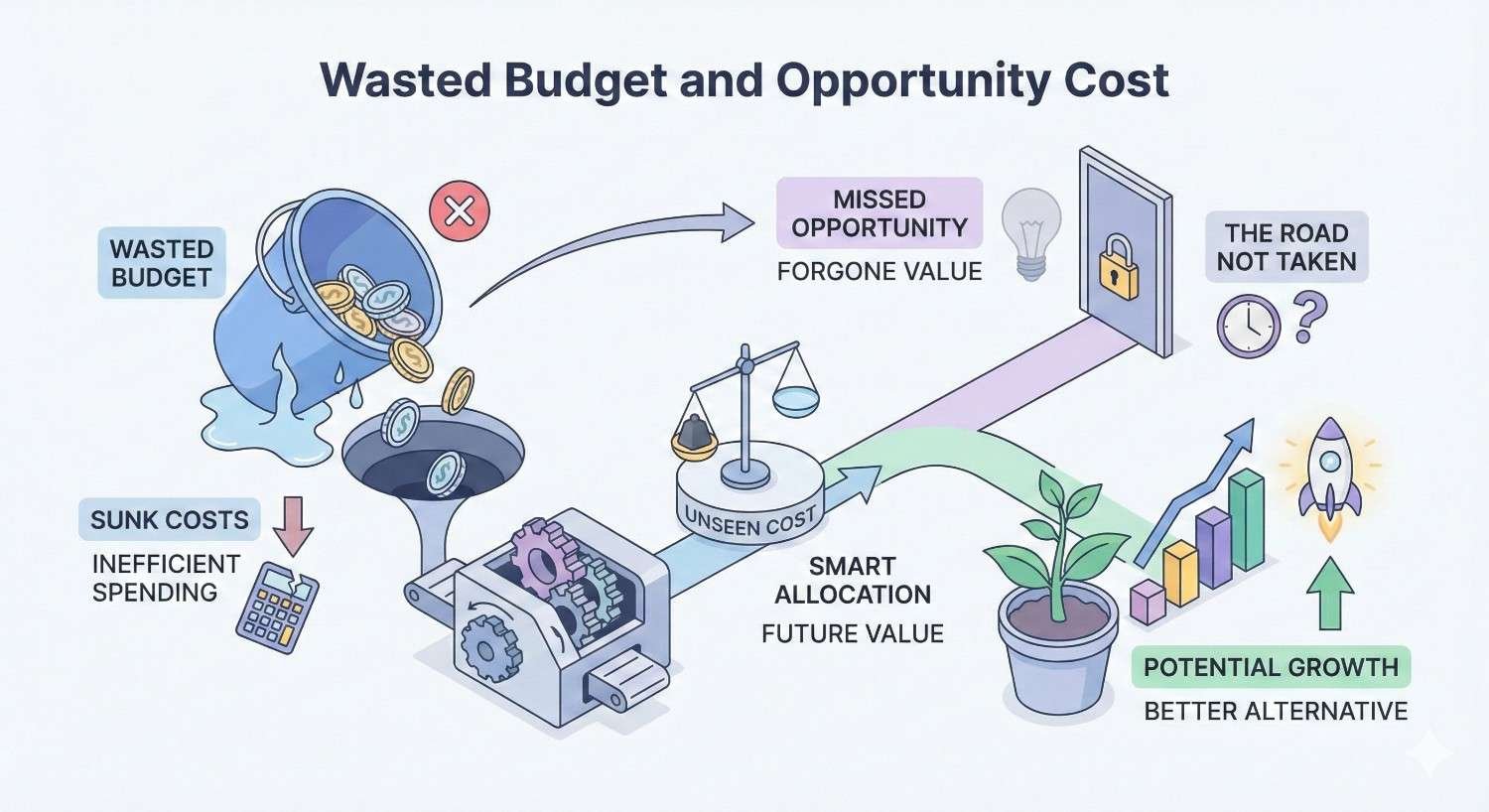
Wasted Budget and Opportunity Cost
Money spent on cheap links cannot be recovered and represents resources that could have built genuine authority.
Direct financial loss includes the cost of purchasing links that provide no value or actively harm your site. Even “affordable” packages of $200-500 monthly compound into significant waste over time.
Opportunity cost represents the greater loss. Those same resources invested in quality content, legitimate outreach, or digital PR would have produced lasting results. A year of cheap link building might cost $3,000-6,000 while building nothing of value.
Recovery investment adds to the total cost. Cleaning up a toxic link profile requires professional tools, expertise, and time. Many businesses spend more on recovery than they originally “saved” on cheap links.
Delayed progress means competitors who invested in quality links continue building authority while you address problems. The gap widens during recovery periods.
Long-Term Recovery Challenges
Recovering from cheap link building damage requires sustained effort and produces uncertain outcomes.
Link removal difficulty stems from the nature of cheap link sources. Many sites that sold links have no contact information, ignore removal requests, or demand payment to remove links they were paid to place.
Disavow file management becomes an ongoing responsibility. Google’s disavow tool helps, but requires careful analysis to avoid disavowing legitimate links while ensuring all toxic links are addressed.
Trust rebuilding takes longer than the original damage. Even after removing problematic links and receiving penalty reconsideration, rankings often recover slowly as Google reassesses your site’s legitimacy.
Ongoing monitoring becomes necessary. Sites that previously engaged in cheap link building often continue receiving spam links from automated systems, requiring continuous vigilance.
How Google Identifies Low-Quality Links
Understanding Google’s detection methods reveals why cheap link building fails consistently. The sophistication of these systems makes manipulation increasingly difficult.
Link Spam Detection Algorithms
Google employs multiple algorithmic systems specifically designed to identify and devalue manipulative links.
SpamBrain represents Google’s AI-based spam detection system. Announced in Google’s 2022 spam report, SpamBrain identifies both spam sites and sites purchasing links from spam networks.
Link graph analysis examines relationships between sites at massive scale. Patterns invisible to humans become obvious when analyzing billions of links. Sites that only link out for payment, sites that receive links only from known spam sources, and unnatural clustering all trigger algorithmic flags.
Anchor text analysis identifies manipulation through statistical anomalies. Natural link profiles show diverse anchor text with branded terms dominating. Profiles heavy with exact-match commercial keywords indicate manipulation.
Velocity detection flags unnatural link acquisition patterns. Legitimate sites gain links gradually as content spreads. Sudden spikes of dozens or hundreds of links suggest purchased campaigns.
Pattern Recognition and Link Schemes
Google’s systems excel at identifying patterns that indicate coordinated link manipulation.
Network detection identifies groups of sites operating together. Private blog networks, link farms, and guest post networks share technical footprints including hosting providers, registration patterns, content management systems, and linking behaviors.
Template recognition flags sites using common designs associated with link selling. Many cheap link sources use identical or similar templates, making network identification straightforward.
Content quality signals help identify sites existing primarily for link placement. Thin content, random topic coverage, excessive outbound links, and lack of genuine engagement all indicate link farms.
Temporal patterns reveal coordinated campaigns. When multiple sites link to the same target within short timeframes using similar anchor text, the coordination becomes obvious.
Quality Signals Google Evaluates
Beyond detecting manipulation, Google assesses positive quality signals that legitimate links possess.
Topical relevance measures whether linking sites cover related subjects. A link from a marketing blog to an SEO service makes sense. A link from a pet care site to the same SEO service suggests manipulation.
Traffic and engagement indicate whether linking sites have genuine audiences. Sites with no traffic provide no referral value and likely exist only for link selling.
Editorial standards reflect whether sites review content before publication. Legitimate publications have submission guidelines, editorial processes, and quality thresholds. Link farms accept anything.
Link placement context matters significantly. Links embedded naturally within relevant content carry more weight than links in author bios, footers, or sidebar widgets.
Domain authority and trust accumulate over time through legitimate activity. New domains or domains with suspicious histories provide less value and may indicate manipulation.
The Role of Manual Review Teams
Human reviewers complement algorithmic detection, focusing on cases requiring judgment.
Webspam team investigations target sites flagged by algorithms or user reports. Reviewers examine link profiles, content quality, and business practices to determine whether violations occurred.
Reconsideration request review involves human assessment of penalty appeals. Reviewers evaluate whether sites have genuinely addressed violations or merely attempted to hide them.
Quality rater guidelines inform both human reviewers and algorithm development. These publicly available guidelines explain how Google defines quality, helping site owners understand expectations.
Feedback loops between manual reviews and algorithms improve detection over time. Patterns identified by human reviewers inform machine learning systems, making future detection more accurate.
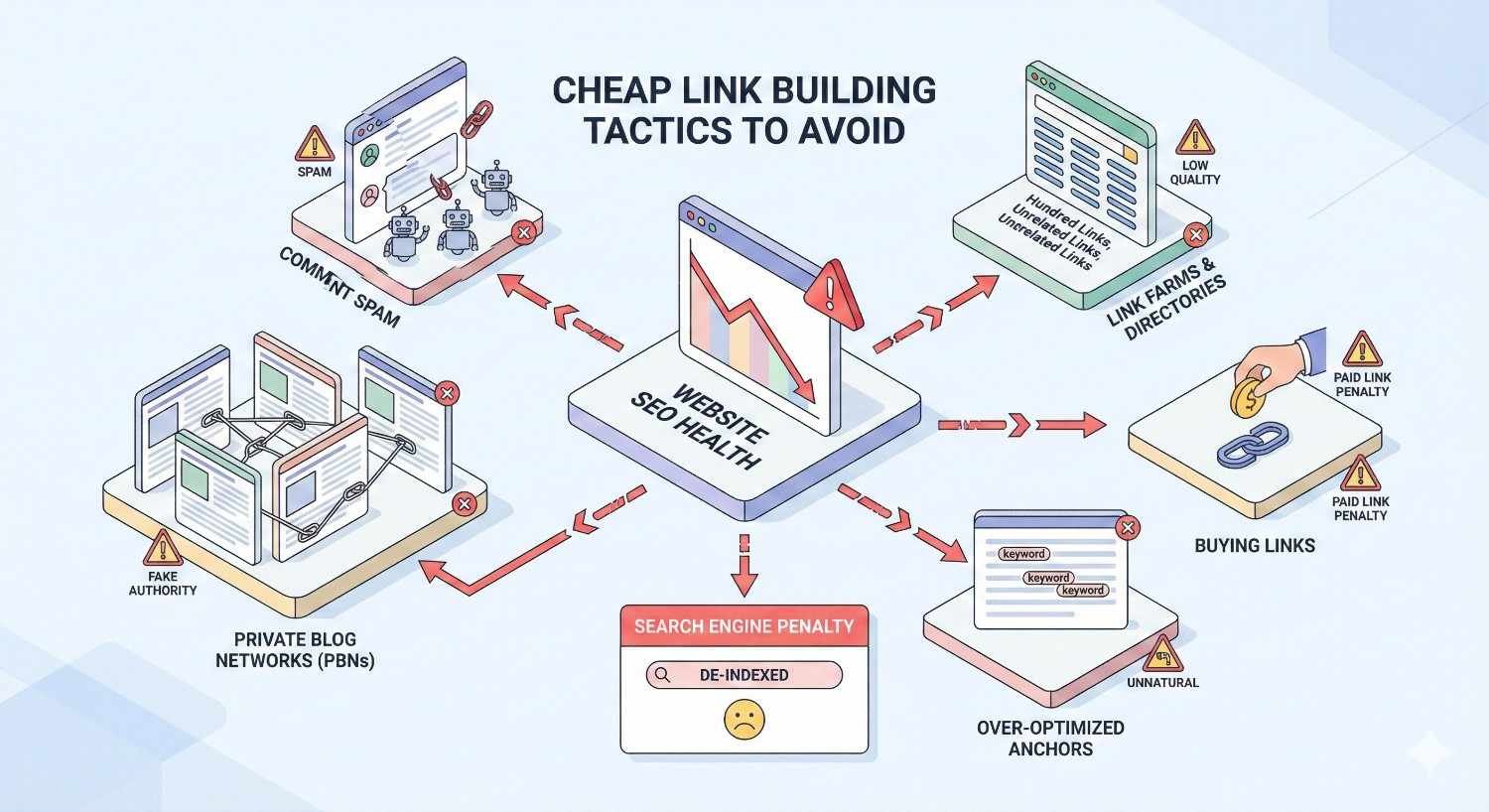
Common Cheap Link Building Tactics to Avoid
Specific tactics carry particular risks. Understanding these methods helps identify and avoid problematic services.
Private Blog Networks (PBNs)
Private blog networks consist of multiple websites controlled by a single entity, used to create artificial link authority.
How PBNs work: Operators purchase expired domains with existing backlink profiles, then create minimal content and sell links to clients. The domains’ historical authority passes through these links, temporarily boosting rankings.
Why PBNs fail: Google has become exceptionally skilled at identifying PBN footprints. Shared hosting, similar site structures, registration patterns, and linking behaviors reveal network connections. When Google identifies a PBN, all sites in the network and all sites receiving links face penalties.
Detection indicators include sites with minimal content, random topic coverage, no social presence, and links only to commercial sites. The domains often have gaps in their archive history where the original site existed before expiration.
Risk level: Extremely high. PBN penalties affect both the network sites and client sites receiving links. Recovery requires removing all PBN links and often results in permanent ranking damage.
Link Farms and Link Exchanges
Link farms aggregate sites specifically for mutual linking, while exchanges facilitate direct link trades between sites.
Link farm characteristics include sites with hundreds of outbound links, minimal original content, and no genuine purpose beyond link placement. These sites often organize links by category, creating pages of nothing but external links.
Link exchange schemes involve agreements to trade links between sites. “You link to me, I’ll link to you” arrangements violate Google’s guidelines when done for ranking manipulation rather than genuine recommendation.
Three-way exchanges attempt to obscure direct trades by involving intermediary sites. Site A links to Site B, Site B links to Site C, Site C links to Site A. Google’s link graph analysis easily identifies these patterns.
Risk level: High. Link farms provide no value and create obvious manipulation signals. Exchanges are detectable through pattern analysis and provide minimal benefit even when undetected.
Low-Quality Directory Submissions
While legitimate directories exist, most directory submission services target low-quality sites that provide no value.
Legitimate directories serve genuine purposes: industry associations, local business listings, professional organizations. These directories have editorial standards, limited listings, and actual users.
Spam directories accept any submission, often automatically. They exist solely to collect submission fees or sell links. Characteristics include thousands of listings, no editorial review, and categories covering every possible topic.
Submission services promising hundreds of directory listings for low fees target exclusively spam directories. The links provide no authority, no traffic, and create spam signals.
Risk level: Moderate to high depending on volume. A few low-quality directory links rarely cause penalties, but bulk submissions create obvious patterns.
Article Spinning and Syndication Networks
Article spinning involves using software to create multiple versions of content by replacing words with synonyms, then distributing these versions across networks.
How spinning works: Original content is processed through spinning software that substitutes words and phrases. “The quick brown fox” becomes “The fast tan canine.” The resulting content is grammatically correct but often nonsensical.
Syndication networks distribute spun content across hundreds of sites, each version containing links back to the client site. The goal is creating the appearance of widespread content distribution.
Why this fails: Google’s natural language processing easily identifies spun content. The awkward phrasing, unusual word choices, and semantic inconsistencies create clear signals. Sites hosting spun content get devalued, and links from them provide no benefit.
Risk level: High. Beyond link devaluation, association with spun content damages brand reputation and may trigger manual review.
Comment Spam and Forum Profile Links
Automated comment posting and forum profile creation represent among the oldest and least effective link building tactics.
Comment spam involves posting comments on blogs with links back to target sites. Automated tools can post thousands of comments daily across blogs with open comment sections.
Forum profile links come from creating accounts on forums solely to include website links in profile signatures or bio sections. No genuine participation occurs.
Why these fail: Most comment and profile links are nofollow, providing no ranking benefit. Even dofollow links from these sources carry minimal weight. The volume and patterns of automated posting create obvious spam signals.
Risk level: Low to moderate for rankings, but high for brand reputation. Having your brand associated with spam comments damages credibility.
Paid Links Without Proper Attribution
Purchasing links for ranking purposes violates Google’s guidelines. Proper disclosure through nofollow or sponsored attributes is required.
Undisclosed paid links involve purchasing placement without appropriate rel attributes. This includes sponsored content, paid reviews, and advertorial placements that pass PageRank.
Google’s requirements specify that paid links must use rel=”sponsored” or rel=”nofollow” attributes. These attributes tell Google not to count the link for ranking purposes.
Detection methods include analyzing link patterns, identifying sites known for selling links, and examining content for promotional language without disclosure.
Risk level: High when detected. Google specifically targets paid link schemes, and penalties affect both buyers and sellers.
The True Cost of Cheap Links
Calculating the actual cost of cheap link building requires looking beyond initial expenditure to include all consequences.
Short-Term Gains vs. Long-Term Consequences
Cheap links sometimes produce temporary ranking improvements, creating dangerous false confidence.
Initial results may appear positive. New links show in backlink reports, and some sites experience ranking increases within weeks. This creates the impression that the strategy works.
The delay factor obscures consequences. Google’s algorithms don’t always act immediately. Penalties and devaluations may take 3-12 months to materialize, long after the initial “success” seemed to validate the approach.
Compounding damage occurs when initial results encourage continued investment. Sites that see early gains often double down on cheap tactics, creating larger problems that become harder to resolve.
The reversal eventually comes. Rankings drop, traffic declines, and the site faces either algorithmic devaluation or manual penalty. The gains disappear, often leaving the site worse off than before.
Recovery Costs After Penalties
Recovering from link-related penalties requires significant investment in expertise, tools, and time.
Professional audit costs range from $1,000-5,000 depending on link profile size and complexity. Identifying toxic links requires specialized tools and expertise to distinguish harmful links from legitimate ones.
Link removal outreach involves contacting webmasters to request link removal. This labor-intensive process often requires multiple attempts and may involve hundreds of sites. Costs range from $500-3,000 for outreach campaigns.
Disavow file creation requires careful analysis to avoid disavowing legitimate links while ensuring all toxic links are addressed. Professional disavow services cost $500-2,000.
Reconsideration request preparation for manual penalties requires documenting all remediation efforts and demonstrating genuine commitment to compliance. Professional assistance costs $500-1,500.
Ongoing monitoring becomes necessary to prevent recurrence. Tools and services for continuous link profile monitoring add $100-500 monthly.
Total recovery costs typically range from $3,000-15,000, often exceeding the original “savings” from cheap link building by significant margins.
Lost Revenue and Traffic Impact
The business impact of ranking losses extends far beyond SEO metrics.
Traffic decline during penalty periods can reach 50-90% for organic search. Sites heavily dependent on search traffic face existential threats.
Revenue impact correlates directly with traffic loss. E-commerce sites may see sales drop proportionally. Lead generation sites lose pipeline. Content sites lose advertising revenue.
Recovery timeline extends the damage. Even after addressing link issues, rankings typically take 6-18 months to recover fully. Some sites never regain their previous positions.
Customer acquisition cost increases when organic traffic declines. Businesses must compensate through paid advertising, increasing marketing costs substantially.
Lifetime value calculation reveals the true cost. A site generating $10,000 monthly from organic traffic that loses 60% of that traffic for 12 months loses $72,000 in revenue, far exceeding any savings from cheap links.
Competitive Disadvantage Over Time
While you address link problems, competitors continue building legitimate authority.
Authority gap widening occurs during recovery periods. Competitors investing in quality links gain ground that becomes increasingly difficult to recover.
Market position erosion happens as competitors capture customers you would have reached. These relationships may never transfer back even after recovery.
Reputation damage in competitive contexts can be permanent. Competitors aware of your penalty may use that information in sales situations.
Resource diversion means recovery efforts consume budget and attention that could have gone toward growth. The opportunity cost compounds the direct losses.
What Quality Link Building Actually Costs
Understanding legitimate link building costs helps set realistic expectations and identify suspicious pricing.
Industry Pricing Benchmarks
Quality link building requires significant investment, reflecting the expertise and effort involved.
Editorial links from legitimate publications typically cost $300-1,500 per placement depending on publication authority and relevance. Premium placements in major publications can exceed $5,000.
Guest posting on quality sites ranges from $150-500 per placement when working with legitimate publications that have editorial standards and genuine audiences.
Digital PR campaigns producing multiple high-authority links typically cost $3,000-10,000 monthly for ongoing campaigns, or $5,000-20,000 for project-based work.
Link building agency retainers generally start at $2,000-5,000 monthly for quality services, with enterprise-level campaigns reaching $10,000-25,000 monthly.
Per-link pricing from reputable providers typically falls between $200-800 for quality placements, with premium opportunities exceeding $1,000.
According to Authority Hacker’s link building survey, the average cost per link among successful SEO professionals is approximately $361, with significant variation based on link quality and acquisition method.
Factors That Influence Link Building Costs
Several variables affect legitimate link building pricing.
Domain authority of target sites directly impacts cost. Links from DA 70+ sites cost significantly more than links from DA 30-40 sites. The authority transfer justifies the premium.
Relevance and niche affect availability and pricing. Competitive industries like finance, legal, and health have fewer quality link opportunities, driving prices higher.
Content requirements add to costs. Quality placements require quality content. Creating articles worthy of publication on authoritative sites requires skilled writers and subject matter expertise.
Outreach effort varies by niche and target. Some industries have abundant link opportunities; others require extensive research and relationship building.
Geographic targeting influences costs for local and regional campaigns. Links from location-specific publications may be scarcer and more expensive.
Exclusivity and competition affect pricing. Popular link targets receive many requests, allowing them to charge premium rates.
ROI of Quality vs. Cheap Link Building
Comparing returns reveals why quality investment outperforms cheap alternatives.
Quality link ROI calculation:
- Investment: $5,000 for 10 quality links
- Result: Sustainable ranking improvement, referral traffic, brand exposure
- Timeline: Results compound over 12-24 months
- Risk: Minimal when following guidelines
Cheap link ROI calculation:
- Investment: $500 for 100 cheap links
- Result: Temporary or no ranking improvement, potential penalty
- Timeline: Any gains reverse within 6-12 months
- Risk: High probability of negative outcome
Long-term value comparison: Quality links continue providing value for years. A single link from an authoritative publication may drive rankings and referral traffic indefinitely. Cheap links provide temporary benefit at best and lasting damage at worst.
Risk-adjusted returns favor quality dramatically. Even if cheap links occasionally work short-term, the probability-weighted outcome including penalty risk makes quality investment superior.
Realistic Budget Expectations by Business Size
Different business scales require different link building investments.
Small businesses and startups should budget $1,000-3,000 monthly for link building, focusing on local citations, industry directories, and targeted outreach. At this level, prioritize fewer quality links over volume.
Growing SMEs typically need $3,000-7,000 monthly to compete effectively. This budget supports ongoing content creation, digital PR efforts, and consistent quality link acquisition.
Established mid-market companies often invest $7,000-15,000 monthly in link building as part of comprehensive SEO programs. This level supports dedicated resources and sophisticated campaigns.
Enterprise organizations may allocate $15,000-50,000+ monthly for link building, supporting multiple campaigns, premium placements, and dedicated teams.
Budget allocation guidance: Link building should represent approximately 30-50% of total SEO investment, with the remainder supporting technical SEO, content creation, and analytics.
Sustainable Link Building Strategies for Limited Budgets
Quality link building doesn’t require unlimited resources. Strategic approaches can build authority effectively within budget constraints.
Digital PR and Newsworthy Content
Creating content that naturally attracts links and media coverage provides excellent ROI.
Data-driven content including original research, surveys, and industry analysis attracts links from journalists and bloggers seeking sources. Investment in research can yield dozens of high-quality links.
Newsjacking involves creating timely content responding to current events relevant to your industry. Quick, insightful commentary on breaking news can attract significant coverage.
Expert commentary positions your team as sources for journalists. Building relationships with reporters covering your industry creates ongoing link opportunities.
Visual assets including infographics, charts, and interactive tools get shared and linked more frequently than text content. Investment in design pays dividends through natural link acquisition.
Cost efficiency: A single piece of research content costing $2,000-5,000 to produce can generate 10-50+ links from authoritative sources, dramatically reducing per-link costs.
Strategic Guest Posting
Guest posting remains effective when approached strategically rather than as a volume play.
Target selection criteria should prioritize sites with genuine audiences, editorial standards, and topical relevance. Avoid sites that accept any submission or primarily exist for link placement.
Content quality requirements mean guest posts should match or exceed the quality of your own site’s content. Thin, promotional content damages both your reputation and link value.
Relationship building transforms one-time placements into ongoing opportunities. Becoming a regular contributor to respected publications provides sustained link acquisition.
Pitch personalization dramatically improves acceptance rates. Generic pitches get ignored; customized proposals demonstrating understanding of the publication succeed.
Realistic expectations: Quality guest posting yields 2-5 placements monthly for most businesses, not dozens. Focus on impact rather than volume.
Resource Page Link Building
Many websites maintain resource pages linking to helpful content in their field. Getting included provides relevant, editorial links.
Resource page identification involves searching for pages that compile links to useful resources in your industry. Search operators like “keyword + resources” or “keyword + useful links” help locate opportunities.
Content requirements mean you need genuinely useful resources worth linking to. Comprehensive guides, tools, templates, and reference materials qualify.
Outreach approach should be helpful rather than promotional. Explain how your resource benefits their audience rather than focusing on your link needs.
Success rates for resource page outreach typically range from 5-15%, making it a numbers game requiring consistent effort.
Broken Link Replacement
Finding broken links on relevant sites and offering your content as a replacement provides value while earning links.
Broken link identification uses tools like Ahrefs, Screaming Frog, or Check My Links to find pages with dead outbound links in your niche.
Content matching requires having or creating content that serves as a suitable replacement for the broken link’s original destination.
Outreach framing positions you as helping the webmaster fix a problem rather than asking for a favor. You’re improving their site while earning a link.
Efficiency considerations: Broken link building requires significant research time. Focus on high-value targets where the effort justifies the potential return.
Unlinked Brand Mentions
When sites mention your brand without linking, outreach can convert mentions into links.
Mention monitoring using tools like Google Alerts, Mention, or Ahrefs’ Content Explorer identifies when your brand appears online without links.
Outreach simplicity makes this approach efficient. The site already knows and referenced your brand; you’re simply asking them to make the mention clickable.
Success rates for unlinked mention outreach typically exceed 20-30%, making it among the most efficient link building tactics.
Proactive brand building increases mention frequency. PR efforts, thought leadership, and industry participation create more opportunities to convert.
Industry Partnerships and Collaborations
Business relationships naturally create link opportunities when approached strategically.
Partner cross-promotion involves featuring partners on your site and requesting reciprocal features. When relationships are genuine, these links are natural and valuable.
Industry association membership often includes directory listings and member spotlights that provide quality links from authoritative industry sources.
Event participation as speakers, sponsors, or exhibitors typically includes links from event websites, often high-authority domains.
Collaborative content including joint research, co-authored articles, and shared resources creates natural linking relationships between participating organizations.
Supplier and vendor relationships can include links through case studies, testimonials, and partner directories.
How to Audit Your Existing Link Profile
Regular link profile audits identify problems before they cause damage and inform ongoing strategy.
Tools for Link Analysis
Several tools provide the data needed for comprehensive link audits.
Ahrefs offers the largest backlink index and detailed metrics including Domain Rating, referring domains, anchor text distribution, and link velocity. Pricing starts at $99 monthly.
Semrush provides backlink analytics alongside broader SEO tools, including toxic score assessments and competitor comparison. Plans start at $129.95 monthly.
Moz Link Explorer offers Domain Authority metrics and spam score assessments. Limited free access available; full access requires Moz Pro subscription starting at $99 monthly.
Google Search Console provides free access to Google’s view of your backlinks, though with limited detail compared to third-party tools. Essential for identifying links Google actually sees.
Majestic specializes in link analysis with unique metrics including Trust Flow and Citation Flow. Plans start at $49.99 monthly.
Tool combination often provides the most complete picture. Using Google Search Console alongside one premium tool covers most needs.
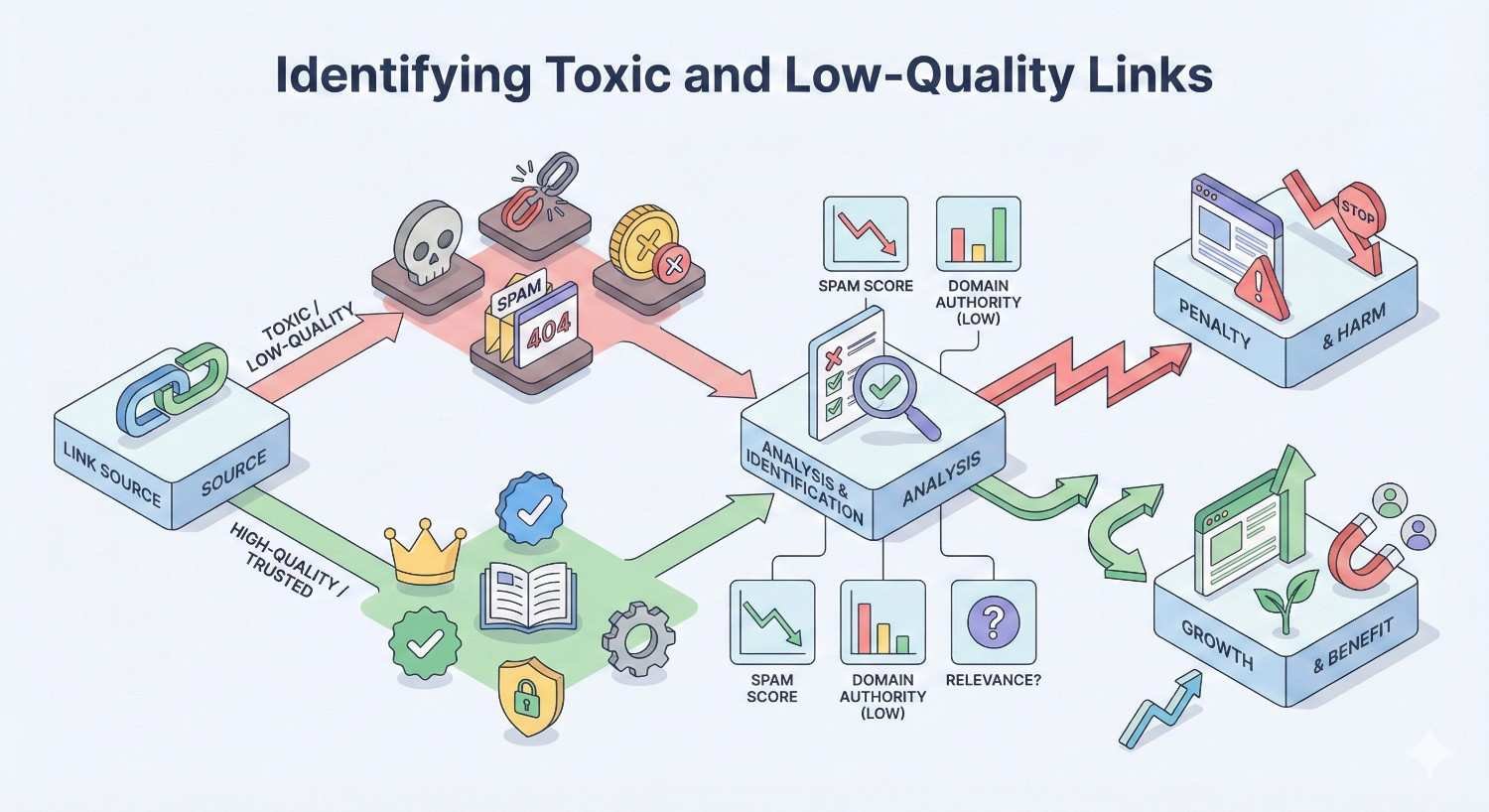
Identifying Toxic and Low-Quality Links
Systematic evaluation helps distinguish harmful links from legitimate ones.
Spam indicators include links from sites with no traffic, excessive outbound links, thin content, unrelated topics, and known link selling patterns.
Anchor text analysis reveals manipulation. Natural profiles show diverse anchors dominated by branded terms. Profiles heavy with exact-match commercial keywords indicate problems.
Link velocity anomalies suggest purchased campaigns. Sudden spikes of many links followed by periods of no acquisition indicate unnatural patterns.
Source site evaluation should assess whether linking sites have genuine audiences, editorial standards, and topical relevance. Sites existing only to sell links provide no value.
Geographic patterns may indicate manipulation. Links predominantly from countries unrelated to your business or audience suggest purchased campaigns.
Toxic score tools from Semrush and other providers automate initial assessment, though manual review remains necessary for accurate evaluation.
Prioritizing Links for Disavowal
Not all low-quality links require disavowal. Strategic prioritization focuses effort where it matters.
High-priority disavowal candidates:
- Links from known spam networks or PBNs
- Links from sites penalized by Google
- Links with manipulative anchor text
- Links from completely irrelevant sites
- Links you know were purchased
Lower priority or skip:
- Random low-quality links that appear naturally
- Links from legitimate sites with low authority
- Old links from defunct sites
- Links you’re uncertain about
Volume considerations: A few low-quality links rarely cause problems. Focus on patterns and significant toxic link clusters rather than individual questionable links.
Documentation of your analysis supports reconsideration requests if needed and helps track decisions over time.
When to Use Google’s Disavow Tool
The disavow tool should be used carefully and only when necessary.
Appropriate use cases:
- Recovering from manual penalties
- Addressing significant toxic link patterns
- Cleaning up after known bad link building
- Preemptive action when you’ve identified clear manipulation
When to avoid disavowing:
- For links you’re merely uncertain about
- As a precautionary measure without evidence of problems
- For legitimate links from low-authority sites
- When you haven’t attempted removal first
Process requirements: Google recommends attempting link removal before disavowing. Document outreach attempts for reconsideration requests.
File format: Disavow files use specific formatting. Errors can cause the file to be ignored or misinterpreted. Verify format before submission.
Monitoring after disavowal: Track ranking changes and continue monitoring for new toxic links. Disavowal isn’t a one-time fix but an ongoing maintenance task.
Building a Quality Link Strategy on Any Budget
Effective link building requires strategic planning regardless of budget size.
Setting Realistic Link Acquisition Goals
Appropriate goals depend on your competitive landscape, resources, and timeline.
Competitive analysis establishes benchmarks. Examine how many referring domains top competitors have and their acquisition velocity. Your goals should reflect what’s needed to compete.
Quality over quantity should guide goal-setting. Five high-quality links monthly outperforms fifty low-quality links. Set goals around link quality metrics, not just volume.
Timeline expectations should be realistic. Quality link building produces results over 6-12 months, not weeks. Set quarterly goals rather than expecting immediate impact.
Resource alignment ensures goals match capacity. Ambitious goals without adequate resources lead to shortcuts and quality compromises.
Measurable targets might include:
- Number of referring domains from DA 40+ sites
- Links from industry-relevant publications
- Referral traffic from link sources
- Ranking improvements for target keywords
Allocating Resources Effectively
Strategic resource allocation maximizes link building impact.
Content investment should precede outreach. Without link-worthy content, outreach efforts fail. Allocate 40-50% of link building budget to content creation.
Tool subscriptions enable efficient work. Budget $100-300 monthly for essential tools including backlink analysis and outreach management.
Outreach capacity determines campaign scale. Whether using internal resources or agencies, ensure adequate capacity for consistent outreach.
Relationship building requires time investment. Allocate resources for industry participation, networking, and maintaining media relationships.
Testing and optimization should receive ongoing investment. Try different approaches, measure results, and shift resources toward what works.
In-House vs. Agency Link Building
Both approaches have advantages depending on your situation.
In-house advantages:
- Direct control over quality and methods
- Deeper understanding of your business and industry
- Lower ongoing costs once systems are established
- Faster communication and iteration
In-house challenges:
- Requires hiring or training specialized talent
- Limited scalability without additional hires
- May lack established media relationships
- Learning curve delays initial results
Agency advantages:
- Established processes and relationships
- Scalable capacity without hiring
- Diverse experience across industries
- Faster ramp-up to productive campaigns
Agency challenges:
- Less control over specific methods
- Higher ongoing costs
- Potential quality variation
- Requires careful vetting to avoid bad actors
Hybrid approaches often work well. Handle relationship-based link building internally while using agencies for specific campaigns or overflow capacity.
Measuring Link Building Performance
Effective measurement connects link building to business outcomes.
Link metrics to track:
- New referring domains monthly
- Domain authority of linking sites
- Topical relevance of link sources
- Anchor text distribution
- Link velocity trends
SEO impact metrics:
- Ranking changes for target keywords
- Organic traffic growth
- Domain authority progression
- Indexed page growth
Business outcome metrics:
- Organic conversions and revenue
- Cost per acquisition from organic
- Referral traffic from links
- Brand mention growth
Attribution challenges make direct link-to-revenue measurement difficult. Focus on correlation between link building activity and organic performance trends.
Reporting cadence: Monthly reporting tracks tactical progress; quarterly reviews assess strategic impact and inform adjustments.
Scaling Link Building Over Time
Successful programs grow systematically as results justify increased investment.
Foundation phase (months 1-6): Establish processes, build initial content assets, develop outreach systems. Expect modest link acquisition while building infrastructure.
Growth phase (months 7-18): Increase outreach volume, expand content production, develop media relationships. Link acquisition should accelerate as systems mature.
Optimization phase (ongoing): Refine targeting, improve conversion rates, expand into new link opportunities. Focus shifts from building systems to maximizing efficiency.
Budget scaling should follow results. Increase investment when current spending produces positive ROI. Avoid scaling before proving effectiveness.
Team expansion may become necessary. As programs grow, dedicated link building roles or expanded agency relationships support increased activity.
Red Flags When Evaluating Link Building Services
Identifying problematic providers prevents costly mistakes.
Guaranteed Rankings and Quick Results
Legitimate providers cannot guarantee specific ranking outcomes.
Why guarantees are impossible: Google’s algorithm considers hundreds of factors. No provider controls enough variables to guarantee specific positions.
What guarantees indicate: Providers offering ranking guarantees either don’t understand SEO or are willing to make promises they can’t keep. Neither reflects well on their services.
Realistic promises focus on activities and quality: number of links, authority levels of targets, content quality standards. Outcomes depend on many factors beyond link building.
Timeline red flags: Quality link building takes months to show results. Promises of quick rankings suggest manipulative tactics.
Extremely Low Pricing
Prices significantly below market rates indicate quality compromises.
Cost floor reality: Quality link building requires skilled labor, tool subscriptions, and content creation. Providers charging $50-100 per link cannot cover these costs while maintaining quality.
What low prices mean: Either links come from low-quality sources, content is automated or spun, or the provider operates at unsustainable margins that will eventually affect service.
Price comparison: If a provider charges 80% less than competitors, ask what they’re not doing that others are. The answer usually involves quality shortcuts.
Value vs. price: The cheapest option rarely provides the best value. Consider cost per quality link rather than absolute pricing.
Lack of Transparency in Methods
Legitimate providers explain their processes clearly.
Transparency expectations: Providers should explain where links will come from, how they identify targets, what content they create, and how they conduct outreach.
Evasion indicators: Vague answers about methods, reluctance to share example placements, or claims that methods are “proprietary secrets” suggest problematic tactics.
Reporting requirements: Quality providers offer detailed reporting showing exactly which links were acquired, from which sites, with what anchor text.
Site list review: Before engagement, request examples of sites where they’ve placed links. Review these sites for quality, relevance, and legitimacy.
No Vetting or Quality Standards
Quality providers have clear criteria for link targets.
Vetting process questions:
- How do you evaluate potential link sources?
- What metrics must sites meet for inclusion?
- How do you assess topical relevance?
- What disqualifies a site from your targets?
Quality standards documentation: Reputable providers can articulate specific standards: minimum domain authority, traffic thresholds, content quality requirements, relevance criteria.
Rejection rates: Quality providers reject many potential link opportunities. If a provider accepts every site, they’re not maintaining standards.
Ongoing quality monitoring: Ask how providers ensure continued quality of sites they’ve used previously. Sites can decline in quality over time.
Questions to Ask Before Hiring
Thorough vetting prevents problems.
Essential questions:
- Can you share examples of links you’ve built for similar clients?
- What is your process for identifying and vetting link targets?
- How do you create content for placements?
- What metrics do you use to measure success?
- How do you handle links that get removed?
- What happens if a link source is later penalized?
- Can you provide references from current clients?
- How do you ensure compliance with Google’s guidelines?
Red flag responses:
- Inability to provide specific examples
- Vague or evasive answers about methods
- Guarantees of specific rankings
- Unwillingness to provide references
- Defensive reactions to quality questions
Contract review: Examine contracts for deliverable specifics, quality guarantees, and remediation processes. Vague contracts enable quality shortcuts.
Case Studies: Cheap Link Building Gone Wrong
Real-world examples illustrate the consequences of cheap link building decisions.
E-commerce Site Penalty Recovery
A mid-sized e-commerce retailer learned expensive lessons about link building shortcuts.
Background: The company sold specialty outdoor equipment, generating approximately $150,000 monthly in organic revenue. Seeking faster growth, they engaged a provider offering 100 links monthly for $500.
The approach: The provider used a combination of PBN links, article directory submissions, and comment spam. Initial results seemed positive, with rankings improving for several target keywords.
The penalty: Eight months later, the site received a manual action for unnatural links. Organic traffic dropped 75% within weeks, reducing monthly organic revenue to approximately $37,500.
Recovery process: The company hired an SEO consultant for $8,000 to audit their link profile and develop a recovery plan. They spent an additional $3,500 on outreach for link removal and disavow file preparation.
Timeline: The reconsideration request was approved after 4 months. Full traffic recovery took an additional 14 months. Total recovery time: 18 months.
Financial impact:
- Lost revenue during recovery: approximately $180,000
- Recovery costs: $11,500
- Original “savings” from cheap links: $4,000 (compared to quality alternatives)
- Net loss: approximately $187,500
Local Business Algorithmic Devaluation
A regional service business experienced gradual decline from algorithmic issues.
Background: A plumbing company serving a metropolitan area ranked well for local search terms, generating 30-40 leads monthly from organic search.
The approach: The owner purchased a $299 “local SEO package” that included directory submissions, citation building, and “authority links.” The package delivered 200+ links over three months.
The decline: Unlike a sudden penalty, rankings declined gradually over 6 months. The business didn’t connect the decline to link building initially, attributing it to increased competition.
Discovery: When organic leads dropped to 8-10 monthly, the owner hired an SEO auditor who identified the link profile issues. Most links came from irrelevant directories, link farms, and low-quality guest posts.
Recovery approach: Without a manual penalty, recovery focused on building quality links to dilute the toxic profile rather than extensive disavowal. This required $2,000 monthly investment over 12 months.
Outcome: Rankings recovered to approximately 80% of previous levels after 18 months. Some positions were never regained due to competitors who had built legitimate authority during the decline period.
Lessons learned: Algorithmic devaluation is harder to diagnose than manual penalties. The gradual nature delays recognition and response, extending damage.
SaaS Startup Link Profile Cleanup
A software startup inherited link problems from previous marketing efforts.
Background: A B2B SaaS company raised Series A funding and hired a new marketing team. The audit revealed the previous team had engaged in aggressive link building using multiple questionable providers.
The discovery: The link profile contained approximately 2,400 links, of which analysis identified 1,800+ as low-quality or toxic. Sources included PBNs, link farms, foreign language spam sites, and hacked websites.
The challenge: The company hadn’t received a manual penalty but rankings were stagnant despite quality content. The toxic link profile was suppressing potential growth.
Cleanup process:
- Comprehensive audit: $5,000
- Link removal outreach (3 months): $4,500
- Disavow file creation and submission: $1,500
- Ongoing monitoring (12 months): $2,400
- Quality link building to rebuild profile: $36,000 (12 months at $3,000/month)
Total investment: $49,400
Results: After 18 months, organic traffic increased 340% from the post-cleanup baseline. The company estimated the toxic links had been suppressing 60-70% of their organic potential.
Key insight: Even without penalties, toxic links create drag on organic performance. The opportunity cost of suppressed rankings often exceeds direct penalty damage.
Making Informed Link Building Investment Decisions
Strategic decision-making ensures link building investments produce positive returns.
Evaluating Link Building Proposals
Systematic evaluation helps identify quality providers.
Proposal components to examine:
- Specific deliverables with quality criteria
- Target site examples and vetting process
- Content creation approach and samples
- Reporting format and frequency
- Pricing structure and what’s included
- Timeline and milestone expectations
Comparison framework: Create a scoring matrix evaluating proposals on:
- Transparency of methods
- Quality of example work
- Relevance of experience
- Reasonableness of pricing
- Clarity of deliverables
- Reference quality
Trial period consideration: When possible, start with a limited engagement to evaluate quality before committing to long-term contracts.
Contract negotiation: Ensure contracts specify quality standards, reporting requirements, and remediation processes for underperformance.
Building Internal Link Building Capabilities
Developing in-house expertise provides long-term advantages.
Skill requirements:
- Content creation and editing
- Outreach and relationship building
- Data analysis and reporting
- Industry knowledge and networking
Training investments:
- SEO courses and certifications
- Tool training and proficiency
- Industry conference attendance
- Mentorship from experienced practitioners
Process development:
- Target identification workflows
- Outreach templates and sequences
- Quality assessment criteria
- Reporting and tracking systems
Timeline expectations: Building effective internal capabilities typically requires 6-12 months of development before reaching full productivity.
Hybrid transition: Many organizations start with agency support while building internal capabilities, gradually shifting work in-house as skills develop.
Long-Term Link Strategy Planning
Sustainable link building requires strategic planning beyond tactical execution.
Annual planning elements:
- Competitive gap analysis
- Content calendar aligned with link opportunities
- Resource allocation across tactics
- Milestone and measurement framework
- Budget allocation and contingencies
Quarterly review process:
- Performance against goals
- Tactic effectiveness assessment
- Resource reallocation decisions
- Strategy adjustments based on results
Integration with broader SEO: Link building should align with technical SEO improvements, content strategy, and overall marketing objectives. Isolated link building produces suboptimal results.
Risk management:
- Diversify link sources and tactics
- Maintain quality standards regardless of pressure
- Monitor for algorithm updates affecting link evaluation
- Build relationships rather than just links
When to Invest in Professional Link Building
Certain situations justify professional link building investment.
Strong investment indicators:
- Competitive keywords requiring authority to rank
- Sufficient budget for quality services
- Internal capacity limitations
- Need for faster results than organic growth provides
- Specific campaigns requiring concentrated effort
Caution indicators:
- Limited budget forcing quality compromises
- Unrealistic timeline expectations
- Lack of link-worthy content to promote
- Technical SEO issues that should be addressed first
- No clear measurement framework
Investment timing:
- After technical SEO foundations are solid
- When quality content exists to support outreach
- With realistic expectations about timelines
- As part of comprehensive SEO strategy
Budget thresholds: Quality link building typically requires minimum $2,000-3,000 monthly investment. Budgets below this level often produce better results through content investment and organic link attraction.
Conclusion
Cheap link building creates a false economy where apparent savings transform into substantial losses through penalties, recovery costs, and missed opportunities. The data consistently shows that quality link investment, while requiring larger upfront commitment, produces superior risk-adjusted returns over any meaningful timeframe.
Understanding these dynamics empowers better decision-making. Whether building links in-house or evaluating service providers, the principles remain consistent: prioritize relevance and authority over volume, maintain transparency in methods, and measure success through business outcomes rather than link counts.
At White Label SEO Service, we help businesses build sustainable organic authority through strategic link acquisition that aligns with Google’s guidelines and delivers measurable results. Contact our team to discuss how quality link building can support your growth objectives without the risks that cheap alternatives create.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much should I realistically budget for quality link building?
Quality link building typically requires $2,000-5,000 monthly for small to mid-sized businesses. This budget supports 5-15 quality links monthly from relevant, authoritative sources. Budgets below $1,500 monthly often force quality compromises that undermine results.
Can I recover from a Google penalty caused by bad links?
Yes, recovery is possible but requires systematic effort. The process involves auditing your link profile, removing or disavowing toxic links, and submitting a reconsideration request. Recovery typically takes 6-18 months and costs $5,000-15,000 in professional services.
How do I know if my current links are hurting my rankings?
Warning signs include stagnant rankings despite quality content, sudden traffic drops, or manual action notifications in Search Console. Use tools like Ahrefs or Semrush to analyze your link profile for spam indicators, irrelevant sources, and manipulative anchor text patterns.
What’s the difference between cheap links and affordable link building?
Cheap links come from low-quality sources using manipulative tactics regardless of price. Affordable link building uses legitimate methods efficiently, such as strategic guest posting, digital PR, and relationship-based outreach. The distinction is methodology, not just cost.
How long does quality link building take to show results?
Expect 3-6 months before seeing measurable ranking improvements from quality link building. Full impact typically materializes over 12-18 months as authority compounds. Promises of faster results usually indicate manipulative tactics.
Should I disavow all my low-quality links?
No. Disavow only links that are clearly toxic or manipulative. Google ignores most low-quality links automatically. Over-disavowing can remove legitimate links and signals. Focus on obvious spam, PBN links, and links from penalized sites.
Is guest posting still a valid link building strategy?
Yes, when done correctly. Quality guest posting targets relevant publications with genuine audiences and editorial standards. Avoid sites that accept any content or exist primarily for link placement. Focus on providing genuine value to the publication’s readers.



