Outreach automation transforms how businesses connect with prospects, partners, and customers at scale. When implemented correctly, automated outreach systems deliver consistent touchpoints, improve response rates, and free your team to focus on high-value conversations. The difference between campaigns that convert and those that land in spam folders comes down to strategic planning, proper execution, and continuous optimization.
This guide covers everything you need to build effective outreach automation systems. You’ll learn the foundational strategies, technical requirements, and advanced techniques that separate successful campaigns from wasted effort. Whether you’re launching your first automated sequence or scaling existing operations, these best practices will help you achieve measurable results.
What Is Outreach Automation?
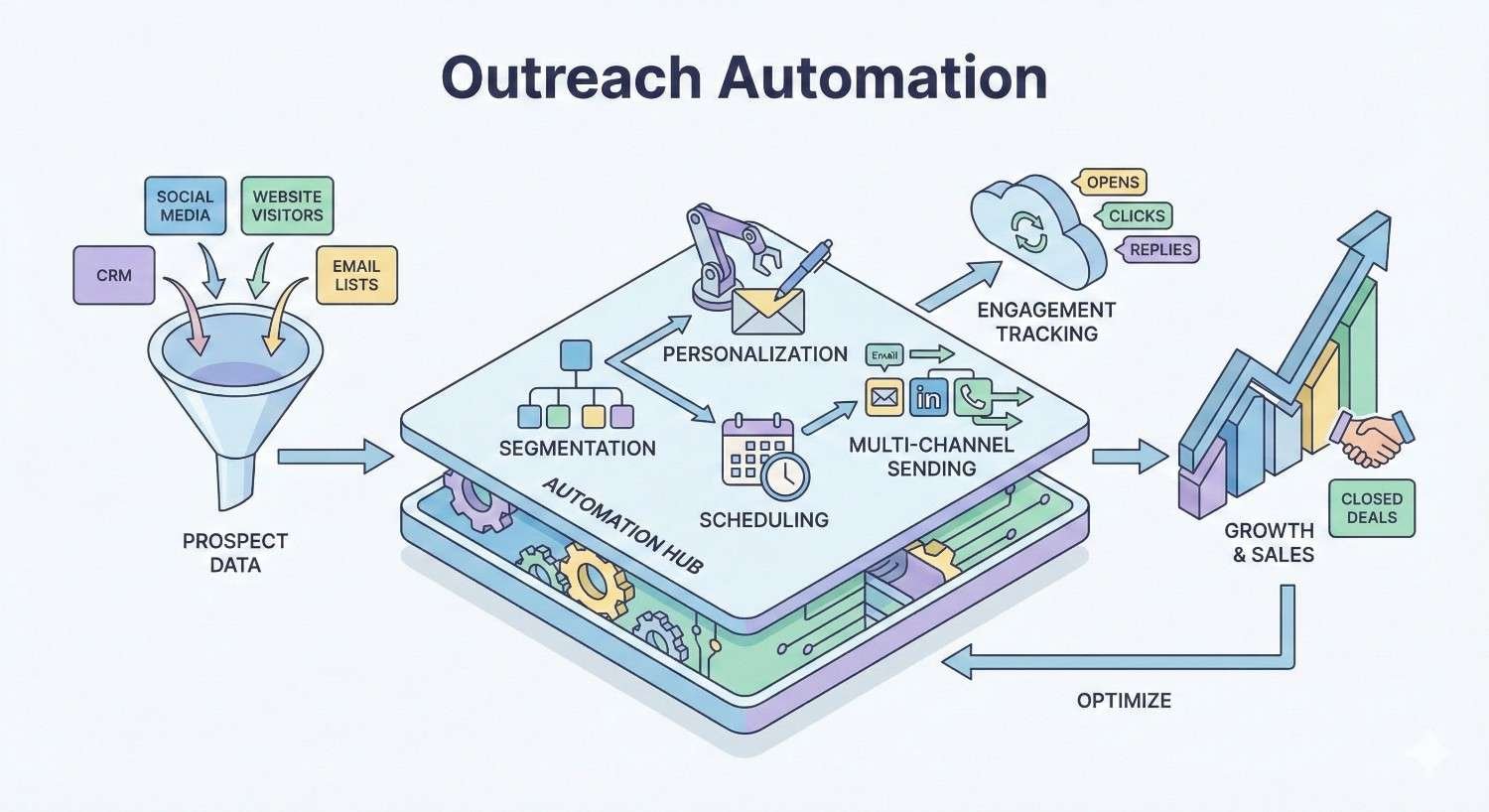
Outreach automation uses software tools and predefined workflows to send personalized messages to prospects across multiple channels without manual intervention for each contact. These systems handle email sequences, LinkedIn messages, follow-ups, and cross-channel coordination while maintaining the appearance of one-to-one communication.
The technology has evolved significantly from basic mail merge functionality. Modern outreach automation platforms incorporate behavioral triggers, AI-powered personalization, and sophisticated timing algorithms that adapt to recipient engagement patterns.
Core Components of Outreach Automation Systems
Effective outreach automation relies on several interconnected components working together. Contact databases store prospect information and engagement history. Sequence builders create multi-step campaigns with conditional logic. Sending infrastructure manages deliverability and compliance. Analytics dashboards track performance metrics across all touchpoints.
Integration capabilities connect these components to your existing tech stack. CRM synchronization ensures sales teams have visibility into automated touchpoints. Calendar integrations enable seamless meeting booking. Data enrichment tools keep contact information current and complete.
The orchestration layer coordinates timing across channels and sequences. This prevents overwhelming prospects with simultaneous messages while ensuring consistent follow-up cadences.
Manual vs. Automated Outreach: Key Differences
Manual outreach offers complete control over every message but limits scale dramatically. A sales representative might send 50-100 personalized emails daily. Automated systems can manage thousands of contacts simultaneously while maintaining personalization through dynamic content insertion.
Response time represents another critical difference. Manual processes depend on individual availability and attention. Automated systems respond to triggers instantly, whether that’s a website visit, email open, or form submission.
Consistency improves with automation. Every prospect receives the planned sequence of touchpoints at optimal intervals. Manual outreach suffers from human inconsistency, forgotten follow-ups, and varying message quality.
However, automation requires upfront investment in strategy, content creation, and system configuration. Manual outreach can start immediately with minimal setup.
When Automation Makes Sense for Your Business
Automation delivers the strongest ROI when you have repeatable outreach processes and sufficient volume to justify the investment. If your team sends similar messages to similar prospects regularly, automation eliminates redundant work.
Consider automation when manual processes create bottlenecks. Sales teams spending hours on initial outreach have less time for qualified conversations. Marketing teams manually nurturing leads cannot scale with business growth.
Automation also makes sense when timing matters. Responding to inbound inquiries within minutes rather than hours significantly impacts conversion rates. Automated sequences ensure immediate engagement regardless of team availability.
Evaluate your current outreach volume, team capacity, and growth projections. Most businesses benefit from automation once they’re sending more than 200 outreach messages monthly.
Strategic Foundation: Planning Before Automating
Rushing into automation without strategic planning creates expensive problems. Poorly targeted campaigns damage sender reputation. Misaligned messaging wastes prospect attention. Incomplete tracking prevents optimization.
Successful outreach automation starts with clear objectives, defined audiences, and mapped customer journeys. This foundation determines every subsequent decision about tools, content, and execution.
Defining Clear Outreach Objectives and KPIs
Start by identifying what success looks like for your outreach program. Lead generation campaigns measure different outcomes than partnership outreach or customer reactivation efforts.
Common outreach objectives include generating qualified meetings, building backlink relationships, recruiting affiliates, or nurturing prospects through long sales cycles. Each objective requires different messaging, timing, and success metrics.
Establish specific KPIs aligned with your objectives. Meeting-focused campaigns track booked calls and show rates. Link building outreach measures placement rates and domain authority of acquired links. Define baseline metrics before launching automation to enable meaningful comparison.
Set realistic targets based on industry benchmarks and your historical performance. Cold email campaigns typically see 1-5% response rates for well-targeted lists. Warm outreach to engaged contacts performs significantly better.
Audience Segmentation and Targeting Strategies
Effective segmentation dramatically improves outreach performance. Sending identical messages to all contacts ignores the different needs, pain points, and buying stages within your audience.
Segment by firmographic data including company size, industry, location, and technology stack. A message resonating with enterprise software companies may fall flat with small retail businesses.
Behavioral segmentation groups contacts by their actions. Website visitors who viewed pricing pages have different intent than those who read blog posts. Email subscribers who opened recent messages differ from those who haven’t engaged in months.
Create segment-specific messaging that addresses unique challenges and opportunities. The additional effort in crafting targeted content delivers substantially higher response rates than generic outreach.
Building Your Ideal Customer Profile (ICP)
Your ICP defines the characteristics of companies and contacts most likely to become valuable customers. This profile guides list building, messaging, and qualification criteria.
Analyze your best existing customers to identify common attributes. Look for patterns in company size, industry, growth stage, technology usage, and organizational structure. Interview sales teams about which prospects convert most easily and deliver highest lifetime value.
Document specific criteria that indicate good fit. Include both required attributes and preferred characteristics. A B2B software company might require prospects with 50+ employees, specific technology integrations, and dedicated marketing teams.
Use your ICP to score and prioritize contacts within your automation system. Higher-fit prospects might receive more touchpoints or faster follow-up sequences.
Mapping the Outreach Funnel and Touchpoints
Visualize the complete journey from initial contact to desired outcome. Identify every touchpoint where automation can add value without replacing necessary human interaction.
Map typical paths prospects take through your funnel. Some respond immediately to initial outreach. Others require multiple touches across different channels before engaging. Understanding these patterns informs sequence design.
Identify decision points where prospects need different content or approaches. Someone who clicked a case study link has different information needs than someone who ignored all previous messages.
Plan handoff points between automated and human engagement. Define clear triggers for when sales representatives should take over conversations. Automation should warm prospects and qualify interest, not replace relationship building.
Best Practices for Email Outreach Automation
Email remains the primary channel for B2B outreach automation. It offers direct access to decision-makers, measurable engagement, and scalable personalization capabilities.
However, email automation requires careful attention to deliverability, compliance, and recipient experience. Poor practices quickly damage sender reputation and campaign performance.
Personalization at Scale: Balancing Automation and Authenticity
Generic mass emails perform poorly. Recipients recognize templated messages and respond accordingly. Effective automation creates the experience of personal communication despite reaching hundreds or thousands of contacts.
Use merge fields for basic personalization including name, company, and role. But go beyond these basics with research-driven customization. Reference recent company news, specific challenges in their industry, or mutual connections.
Create message variants for different segments rather than one-size-fits-all templates. A CFO cares about different outcomes than a marketing director. Tailor value propositions to each audience.
Include specific, verifiable details that demonstrate genuine research. Mentioning a prospect’s recent podcast appearance or conference presentation shows effort that templates cannot replicate.
Email Sequence Design and Timing Optimization
Multi-step sequences outperform single emails significantly. Most responses come from follow-up messages rather than initial outreach. Plan sequences of 4-7 emails spaced appropriately for your audience and offer.
Vary your approach across the sequence. If the first email focuses on a specific pain point, the second might share relevant content. The third could offer social proof. Each message should provide new value rather than simply asking again.
Timing between messages matters. B2B outreach typically performs best with 3-5 day gaps between emails. Shorter intervals feel aggressive. Longer gaps lose momentum.
Test send times for your specific audience. HubSpot research suggests Tuesday through Thursday mornings often perform well, but your audience may differ. Let data guide optimization.
Subject Line and Copy Best Practices
Subject lines determine whether emails get opened. Keep them short, specific, and curiosity-inducing. Avoid spam trigger words and excessive punctuation.
Personalized subject lines including the recipient’s name or company typically outperform generic alternatives. Questions often generate higher open rates than statements.
Email body copy should be concise and scannable. Busy professionals won’t read lengthy pitches. Lead with value, not your company description. Focus on recipient benefits rather than product features.
Include one clear call-to-action per email. Multiple asks create confusion and reduce response rates. Make the desired action obvious and easy to complete.
A/B Testing and Performance Optimization
Systematic testing improves results over time. Test one variable at a time to identify what drives performance changes.
Start with high-impact elements. Subject lines affect open rates dramatically. Call-to-action phrasing influences response rates. Test these before optimizing minor copy variations.
Ensure statistical significance before declaring winners. Small sample sizes produce unreliable results. Most tests need several hundred sends per variant for meaningful conclusions.
Document test results and apply learnings across campaigns. Build an organizational knowledge base of what works for your audience and offers.
Deliverability and Sender Reputation Management
Deliverability determines whether emails reach inboxes or spam folders. Technical setup, sending practices, and engagement metrics all influence deliverability.
Domain Warming and Authentication
New sending domains require gradual volume increases. Start with small batches of emails to engaged contacts. Increase volume slowly over 4-8 weeks as positive engagement signals build.
Implement authentication protocols including SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. These verify your identity to receiving mail servers and prevent spoofing. Most email service providers offer setup guidance.
Consider dedicated sending domains separate from your primary business domain. This protects your main domain reputation if outreach campaigns encounter deliverability issues.
Avoiding Spam Filters and Compliance
Spam filters evaluate content, sending patterns, and engagement metrics. Avoid trigger words like “free,” “guarantee,” and “act now.” Limit images and links in cold outreach.
Maintain clean sending practices. Never purchase email lists. Always include unsubscribe options. Honor opt-out requests immediately.
Comply with regulations including CAN-SPAM, GDPR, and CASL depending on your audience locations. Include physical addresses in emails. Identify messages as advertisements when required.
Monitoring Bounce Rates and Engagement Metrics
Track bounce rates closely. Hard bounces indicate invalid addresses and should trigger immediate removal. Soft bounces may resolve but warrant monitoring.
Keep bounce rates below 2% to maintain sender reputation. Higher rates signal list quality problems requiring attention.
Monitor engagement metrics including open rates, click rates, and reply rates. Low engagement tells email providers your messages aren’t wanted. Segment or remove unengaged contacts to protect deliverability.
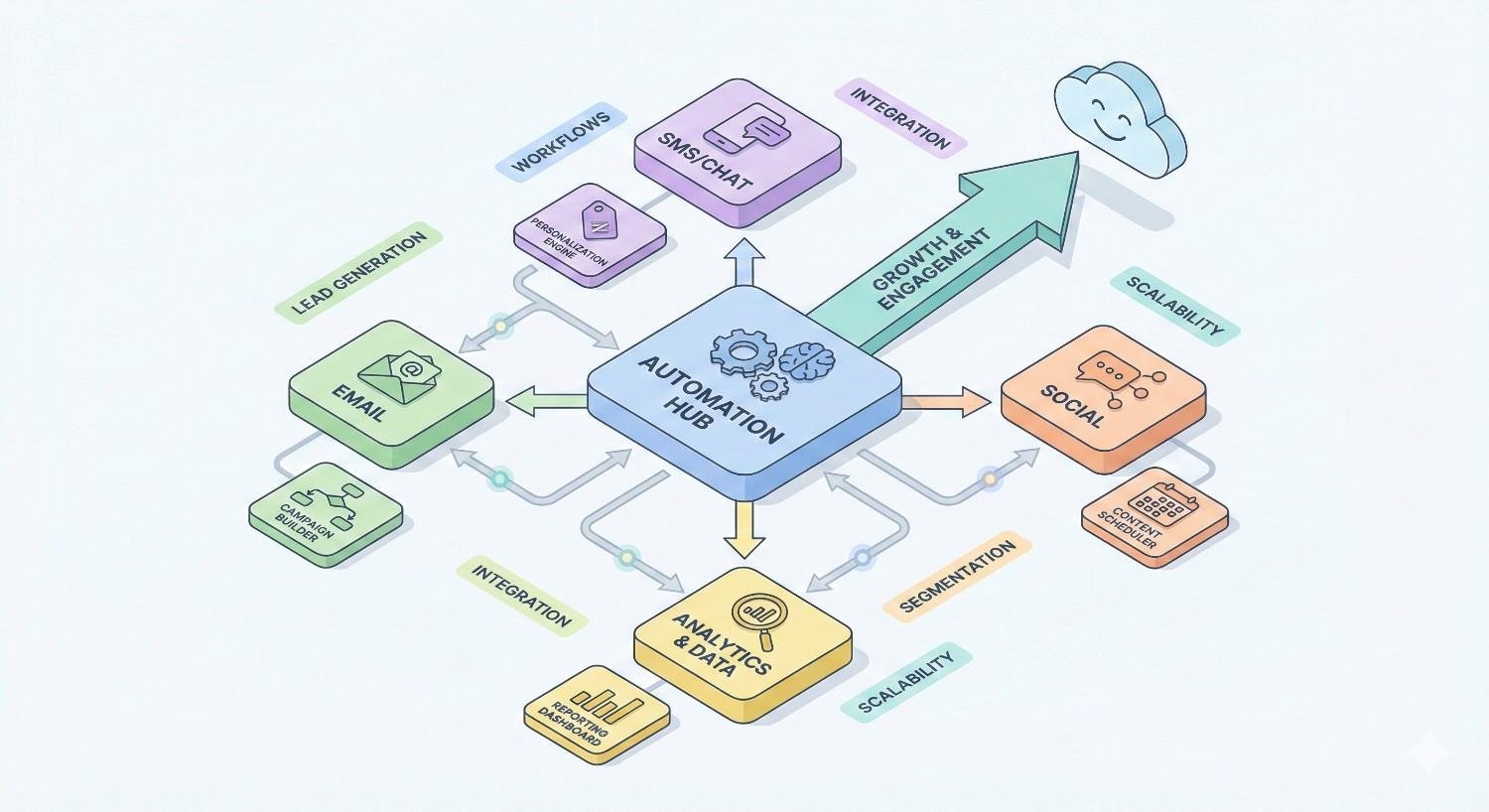
Multi-Channel Outreach Automation Strategies
Email alone rarely maximizes outreach effectiveness. Prospects engage across multiple platforms. Coordinated multi-channel sequences increase touchpoint frequency without overwhelming any single channel.
LinkedIn Automation Best Practices
LinkedIn offers direct access to professional decision-makers. Automation tools can manage connection requests, messages, and profile engagement at scale.
Respect platform limits to avoid account restrictions. LinkedIn monitors automated activity and penalizes aggressive behavior. Keep daily connection requests under 100 and message volumes reasonable.
Personalize connection requests with specific reasons for connecting. Generic requests get ignored. Reference shared connections, groups, or relevant content.
Combine LinkedIn touches with email sequences. A connection request followed by an email creates multiple impressions. Profile views before outreach can warm prospects to your name.
Social Media Outreach Integration
Twitter, Instagram, and other platforms offer additional touchpoints for certain audiences. Engage authentically before pitching. Like posts, leave thoughtful comments, and share relevant content.
Social engagement works best as a complement to direct outreach rather than a primary channel. Use social touches to build familiarity before email or LinkedIn messages.
Monitor social mentions and conversations relevant to your offering. Timely engagement with prospects discussing relevant challenges creates natural outreach opportunities.
SMS and Messaging App Automation
SMS delivers extremely high open rates but requires careful use. Reserve text messages for time-sensitive communications or audiences who have explicitly opted in.
Messaging apps like WhatsApp and Slack offer additional channels for certain markets. International audiences may prefer WhatsApp over email. Tech-savvy prospects might engage through Slack communities.
Always obtain explicit consent before SMS outreach. Regulations around text messaging are stricter than email in most jurisdictions.
Coordinating Cross-Channel Sequences
Effective multi-channel automation coordinates timing across platforms. Avoid sending email and LinkedIn messages on the same day. Space touchpoints to maintain presence without annoyance.
Use channel-appropriate messaging. LinkedIn messages should feel conversational. Emails can be slightly more formal. SMS requires extreme brevity.
Track engagement across all channels in a unified view. A prospect who responded on LinkedIn shouldn’t receive the next automated email asking for a response.
Data Management and List Hygiene
Outreach automation is only as good as the data powering it. Poor data quality wastes resources, damages reputation, and produces misleading metrics.
Building and Maintaining Quality Contact Lists
Build lists from reliable sources. First-party data from website signups and event registrations offers highest quality. Third-party data providers vary significantly in accuracy.
Verify contact information before adding to automation sequences. Invalid emails hurt deliverability. Wrong names in personalization fields damage credibility.
Regularly audit and clean your database. Remove bounced addresses, unsubscribes, and long-term non-engagers. Smaller, cleaner lists outperform large, dirty ones.
Data Enrichment and Verification Processes
Enrichment tools add missing information to contact records. Append job titles, company details, social profiles, and technographic data to enable better segmentation and personalization.
Verify email addresses before sending. Verification services check whether addresses are valid and deliverable without actually sending messages. This protects sender reputation.
Schedule regular enrichment and verification cycles. Contact information decays as people change jobs and companies evolve. Data decay rates suggest 30% of B2B data becomes outdated annually.
CRM Integration and Data Synchronization
Connect outreach automation tools to your CRM for unified contact management. Synchronize engagement data so sales teams see automated touchpoints alongside manual activities.
Establish clear data ownership and update rules. Define which system serves as the source of truth for different data types. Prevent duplicate records and conflicting information.
Automate status updates based on outreach outcomes. Responses should update contact stages. Bounces should flag data quality issues. Meeting bookings should create opportunities.
GDPR, CAN-SPAM, and Compliance Requirements
Understand regulations governing your outreach. GDPR applies to EU residents regardless of your location. CAN-SPAM covers commercial emails to US recipients. CASL governs Canadian contacts.
Maintain records of consent and opt-out requests. Document the legal basis for contacting each person. Implement processes to honor data subject requests within required timeframes.
Include required elements in all outreach. Physical addresses, unsubscribe mechanisms, and accurate sender identification are mandatory in most jurisdictions.
Personalization Techniques That Scale
Advanced personalization creates individual experiences without individual effort. The right techniques make automated messages feel handcrafted.
Dynamic Content and Merge Tags
Merge tags insert contact-specific information into templates. Beyond basic name and company fields, use custom fields for industry-specific language, relevant case studies, or personalized offers.
Dynamic content blocks show different message sections based on contact attributes. A single template can display different value propositions for different industries or company sizes.
Create content libraries with variations for common personalization needs. Pre-written snippets for different industries, use cases, or objections enable rapid customization.
Behavioral Triggers and Conditional Logic
Trigger messages based on prospect actions rather than fixed schedules. Website visits, email opens, link clicks, and content downloads all indicate interest worth addressing.
Build conditional sequences that adapt to engagement. Prospects who open emails might receive different follow-ups than those who don’t. Link clickers could skip educational content and move to conversion-focused messages.
Set up real-time alerts for high-intent behaviors. Pricing page visits or demo video completions warrant immediate human follow-up rather than waiting for automated sequences.
AI-Powered Personalization Strategies
AI tools can generate personalized content elements at scale. Feed prospect information into AI systems to create custom opening lines, relevant pain point references, or tailored value propositions.
Use AI for research synthesis. Tools can analyze prospect websites, recent news, and social profiles to identify personalization opportunities humans might miss.
Maintain human oversight of AI-generated content. Review outputs for accuracy, tone, and brand alignment before deployment. AI assists personalization but shouldn’t replace human judgment entirely.
Balancing Volume with Relevance
Higher volume doesn’t always mean better results. Sending more messages to poorly targeted contacts wastes resources and damages reputation.
Prioritize relevance over reach. Smaller, highly targeted campaigns typically outperform broad, generic outreach. Focus resources on prospects most likely to convert.
Monitor response quality alongside quantity. High response rates mean little if responses are negative or from unqualified contacts. Optimize for meaningful engagement, not just any engagement.
Response Management and Follow-Up Automation
Generating responses is only half the challenge. Managing those responses efficiently determines whether outreach converts to outcomes.
Automated Response Detection and Categorization
Configure systems to detect and categorize incoming responses. Positive replies indicating interest need different handling than objections, out-of-office messages, or unsubscribe requests.
Use keyword detection and AI classification to route responses appropriately. Interested prospects should reach sales teams immediately. Negative responses should stop sequences and update contact status.
Create response templates for common scenarios. Quick, consistent replies to frequently asked questions improve response times without requiring individual composition.
Follow-Up Sequence Optimization
Design follow-up sequences for different response types. Interested but not ready prospects might enter nurture sequences. Objection responses could trigger specific counter-messaging.
Time follow-ups appropriately. Immediate responses to positive replies demonstrate attentiveness. Delayed follow-ups to soft objections give prospects space while maintaining contact.
Track which follow-up approaches convert best. Some prospects respond to persistence. Others need new angles or additional value. Let data guide sequence refinement.
When to Stop Automated Sequences
Define clear exit criteria for sequences. Continued outreach to uninterested prospects wastes resources and risks spam complaints.
Stop sequences after explicit negative responses. “Not interested” means stop, not try harder. Respect prospect preferences to maintain professional reputation.
Set maximum touchpoint limits. If prospects haven’t engaged after 6-8 touches, additional automation rarely helps. Move to long-term nurture or remove from active outreach.
Transitioning from Automation to Human Engagement
Plan smooth handoffs between automated and human touchpoints. Prospects shouldn’t feel jarring transitions or receive conflicting messages.
Brief sales teams on automated touchpoints before handoff. Representatives should know what messages prospects received and how they engaged.
Maintain automation support even after human engagement begins. Automated reminders, meeting confirmations, and follow-up sequences can support sales conversations without replacing them.
Choosing the Right Outreach Automation Tools
Tool selection significantly impacts outreach effectiveness. The right platform matches your needs, integrates with existing systems, and scales with growth.
Essential Features to Look For
Prioritize features aligned with your outreach strategy. Email-focused campaigns need strong deliverability tools. Multi-channel approaches require cross-platform coordination capabilities.
Core features to evaluate include sequence builders, personalization options, A/B testing, analytics dashboards, and integration capabilities. Advanced features like AI assistance, intent data, and predictive analytics add value for sophisticated programs.
Assess usability alongside functionality. Powerful features matter little if teams struggle to use them. Request demos and trials to evaluate actual user experience.
Popular Outreach Automation Platforms Compared
The market offers numerous options across different price points and capability levels. Entry-level tools like Mailshake and Lemlist serve smaller teams with straightforward needs. Mid-market platforms like Outreach.io and Salesloft offer comprehensive features for growing organizations. Enterprise solutions like Salesforce and HubSpot provide extensive customization and integration.
Evaluate platforms against your specific requirements rather than general rankings. The best tool for a 5-person startup differs from the best choice for a 500-person sales organization.
Consider total cost of ownership including implementation, training, and ongoing management. Lower subscription costs sometimes mean higher operational overhead.
Integration Capabilities and Tech Stack Fit
Assess how platforms connect with your existing tools. CRM integration is typically essential. Marketing automation, calendar, and communication tool connections add significant value.
Evaluate integration depth, not just existence. Some integrations offer basic data sync. Others enable sophisticated workflow automation across platforms.
Consider API capabilities for custom integrations. Growing organizations often need connections beyond standard offerings. Robust APIs enable future flexibility.
Pricing Models and ROI Considerations
Understand pricing structures before committing. Some platforms charge per user. Others price by contact volume or feature tier. Calculate costs at your expected scale, not just starting volume.
Factor in implementation and training costs. Complex platforms may require professional services for setup. Simpler tools might need more internal time investment.
Build ROI models based on realistic performance expectations. Calculate the value of meetings generated, deals closed, or relationships built against total platform costs.
Measuring Success: Key Metrics and Analytics
Data-driven optimization separates high-performing outreach programs from mediocre ones. Track the right metrics, establish benchmarks, and iterate continuously.
Core Outreach Automation KPIs
Focus on metrics that connect to business outcomes, not just activity levels. Sending more emails matters little if they don’t generate results.
Open Rates and Click-Through Rates
Open rates indicate subject line effectiveness and sender reputation. Healthy cold email open rates range from 15-25%. Significantly lower rates suggest deliverability or targeting problems.
Click-through rates measure content engagement. Recipients who click links demonstrate interest worth pursuing. Track which content generates clicks to inform future messaging.
Note that open rate tracking has become less reliable due to privacy features in email clients. Use opens as directional indicators rather than precise measurements.
Response Rates and Conversion Rates
Response rates directly measure outreach effectiveness. Cold email campaigns typically see 1-5% response rates. Warm outreach to engaged contacts should perform significantly better.
Track response quality alongside quantity. Positive responses indicating genuine interest matter more than total reply volume. Categorize responses to understand true engagement.
Conversion rates measure progression through your funnel. Track what percentage of responses become meetings, and what percentage of meetings become opportunities or customers.
Pipeline Contribution and Revenue Attribution
Connect outreach activities to revenue outcomes. Track which campaigns generate pipeline and closed deals. Calculate cost per opportunity and customer acquisition cost.
Implement attribution models appropriate for your sales cycle. First-touch attribution credits initial outreach. Multi-touch models distribute credit across all touchpoints. Choose models that reflect your actual buyer journey.
Report outreach ROI to stakeholders in business terms. Pipeline generated and revenue influenced resonate more than open rates and click-through percentages.
Setting Up Tracking and Reporting Dashboards
Build dashboards that surface actionable insights. Include leading indicators like engagement metrics alongside lagging indicators like revenue contribution.
Segment reporting by campaign, audience, and channel. Aggregate metrics hide important variations. Understanding what works for which audiences enables optimization.
Automate reporting where possible. Manual report generation consumes time better spent on optimization. Schedule regular report delivery to stakeholders.
Benchmarking Performance Against Industry Standards
Compare your metrics against industry benchmarks to contextualize performance. Understand whether results reflect your execution or broader market conditions.
Seek benchmarks specific to your industry, audience, and outreach type. B2B software outreach benchmarks differ from professional services or e-commerce.
Use benchmarks as reference points, not absolute standards. Your specific situation may warrant different expectations. Focus on improving your own metrics over time.
Continuous Improvement and Iteration Cycles
Establish regular optimization cadences. Weekly reviews of active campaigns catch problems quickly. Monthly analysis identifies longer-term trends and opportunities.
Prioritize improvements by potential impact. Fixing deliverability problems affects all campaigns. Optimizing a single subject line affects one sequence. Address high-impact issues first.
Document learnings and share across teams. Insights from one campaign should inform others. Build organizational knowledge about what works for your audiences.
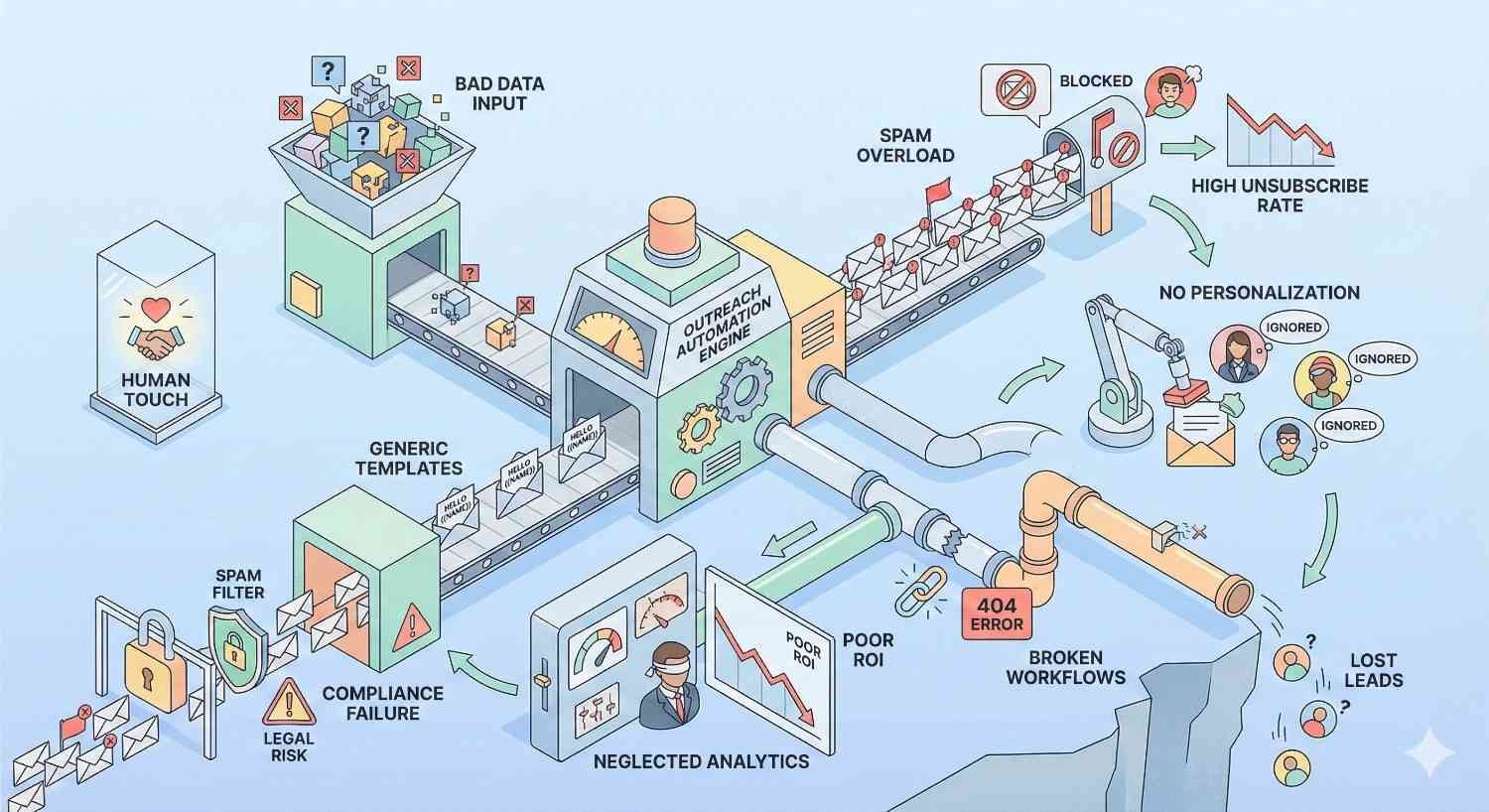
Common Outreach Automation Mistakes to Avoid
Learning from others’ mistakes accelerates success. These common pitfalls derail outreach programs across industries and company sizes.
Over-Automation and Loss of Authenticity
Automation should enhance human connection, not replace it. Prospects recognize and resent obviously automated messages. Maintain authentic voice and genuine personalization.
Avoid automating touchpoints that require human judgment. Complex objections, sensitive situations, and high-value opportunities deserve personal attention.
Review automated messages regularly. Templates that felt fresh initially become stale over time. Update content to maintain relevance and authenticity.
Poor List Quality and Targeting Errors
Bad data produces bad results regardless of message quality. Verify contact information before automation. Target prospects who actually match your ICP.
Avoid the temptation to maximize list size at the expense of quality. Smaller, accurate lists outperform larger, questionable ones. Quality over quantity applies to data as much as messaging.
Implement ongoing list hygiene processes. Remove bounces, unsubscribes, and non-engagers regularly. Refresh data to account for job changes and company evolution.
Ignoring Compliance and Legal Requirements
Compliance violations carry significant consequences. Fines, blacklisting, and reputation damage far exceed any short-term gains from aggressive practices.
Stay current on regulations affecting your outreach. Laws evolve, and enforcement increases. What was acceptable previously may now violate requirements.
When uncertain, err on the side of caution. Obtain explicit consent when possible. Honor opt-out requests immediately. Maintain documentation of compliance efforts.
Neglecting Testing and Optimization
Set-and-forget approaches waste automation potential. Continuous testing and optimization compound improvements over time.
Allocate time specifically for optimization activities. Without dedicated focus, urgent tasks crowd out important improvement work.
Test systematically rather than randomly. Develop hypotheses based on data. Design tests to validate or invalidate those hypotheses. Apply learnings consistently.
Failing to Monitor and Adjust Campaigns
Active campaigns require ongoing attention. Deliverability can shift suddenly. Response patterns change over time. Market conditions evolve.
Set up alerts for significant metric changes. Sudden drops in open rates or spikes in bounces warrant immediate investigation.
Review campaign performance against objectives regularly. Campaigns meeting goals might still have optimization opportunities. Underperforming campaigns need diagnosis and adjustment.
Advanced Strategies for Scaling Outreach
Once fundamentals are solid, advanced strategies unlock additional performance and efficiency gains.
Account-Based Marketing (ABM) Automation
ABM focuses resources on high-value target accounts rather than broad outreach. Automation supports ABM through coordinated multi-stakeholder engagement and personalized account journeys.
Identify target accounts based on fit and intent signals. Prioritize accounts showing buying behavior or matching ideal customer characteristics.
Orchestrate touchpoints across multiple contacts within target accounts. Coordinate messaging to different stakeholders while maintaining consistent account narratives.
Intent Data and Predictive Analytics Integration
Intent data reveals which companies are actively researching relevant topics. Prioritize outreach to accounts showing buying signals.
Integrate intent data into automation workflows. Trigger sequences when target accounts show relevant intent. Adjust messaging based on specific topics researched.
Predictive analytics identify accounts likely to convert based on historical patterns. Focus resources on highest-probability opportunities.
Multi-Touch Attribution Modeling
Understand how different touchpoints contribute to conversions. Attribution models inform resource allocation and optimization priorities.
Implement tracking across all channels and touchpoints. Gaps in tracking create blind spots in attribution analysis.
Choose attribution models appropriate for your sales cycle complexity. Simple models work for short cycles. Complex B2B sales often require sophisticated multi-touch approaches.
Building Sustainable Outreach Systems
Design systems for long-term performance, not just immediate results. Sustainable approaches maintain effectiveness as you scale.
Protect sender reputation through consistent best practices. Short-term aggressive tactics often damage long-term deliverability.
Build processes that don’t depend on individual knowledge. Document workflows, templates, and optimization learnings. Enable team members to maintain and improve systems.
Team Structure and Workflow Optimization
People and processes matter as much as technology. Effective team structures and workflows maximize automation ROI.
Roles and Responsibilities in Automated Outreach
Define clear ownership for different aspects of outreach automation. Strategy, content creation, technical management, and optimization may require different skills.
Common roles include outreach strategists who design campaigns, copywriters who create messaging, operations specialists who manage technical systems, and analysts who track performance.
Smaller teams may combine roles. Larger organizations benefit from specialization. Match structure to your scale and complexity.
Training and Onboarding Best Practices
Invest in training for everyone touching outreach systems. Tool proficiency, best practices knowledge, and strategic understanding all contribute to success.
Create documentation for common tasks and processes. Reduce dependence on tribal knowledge. Enable new team members to contribute quickly.
Establish ongoing learning practices. The outreach landscape evolves continuously. Regular training keeps teams current on new capabilities and best practices.
Collaboration Between Sales and Marketing
Outreach automation often spans traditional sales and marketing boundaries. Effective collaboration prevents gaps and conflicts.
Align on definitions and handoff criteria. When does a marketing-nurtured lead become sales-ready? What information should transfer at handoff?
Share insights bidirectionally. Sales conversations reveal messaging effectiveness. Marketing data informs sales prioritization. Regular communication improves both functions.
Documentation and Process Standardization
Document everything that matters for consistency and continuity. Templates, sequences, targeting criteria, and optimization learnings all warrant documentation.
Standardize processes where consistency adds value. Sequence structures, approval workflows, and reporting cadences benefit from standardization.
Balance standardization with flexibility. Overly rigid processes prevent adaptation. Find the right level of structure for your organization.
Building a Long-Term Outreach Automation Strategy
Sustainable success requires strategic thinking beyond individual campaigns. Align automation with business objectives and plan for evolution.
Aligning Automation with Business Growth Goals
Connect outreach automation to broader business strategy. Understand how outreach supports revenue targets, market expansion, or customer acquisition goals.
Set automation objectives that ladder up to business objectives. If the business needs 100 new customers, calculate the outreach volume and conversion rates required to contribute.
Adjust automation strategy as business priorities shift. New markets, products, or customer segments may require different approaches.
Scaling Without Sacrificing Quality
Growth creates pressure to increase volume. Resist the temptation to sacrifice quality for quantity.
Scale through efficiency improvements rather than just volume increases. Better targeting, stronger messaging, and optimized sequences can grow results without proportional volume growth.
Maintain quality standards as you scale. Review samples of automated messages regularly. Monitor response quality alongside quantity. Address degradation quickly.
Future Trends in Outreach Automation
Stay informed about emerging capabilities and changing landscapes. AI advancement continues to expand personalization possibilities. Privacy regulations evolve and tighten. Channel preferences shift across audiences.
Evaluate new tools and techniques regularly. Early adoption of effective innovations creates competitive advantage. But avoid chasing every new trend without strategic fit.
Build flexibility into your systems. Platforms and practices that adapt to change outlast rigid approaches.
Working with SEO and Outreach Experts for Sustainable Growth
Complex outreach programs often benefit from specialized expertise. Agencies and consultants bring experience across many campaigns and industries.
Consider external support for strategy development, technical implementation, or ongoing optimization. Match external resources to your internal capability gaps.
Evaluate partners based on relevant experience and demonstrated results. Request case studies and references specific to your industry and objectives.
Conclusion
Outreach automation best practices combine strategic planning, technical excellence, and continuous optimization. Success requires clear objectives, quality data, authentic personalization, and rigorous measurement. The organizations that master these elements build sustainable competitive advantages in prospect engagement.
Building effective outreach automation systems demands expertise across multiple disciplines. From deliverability management to multi-channel coordination, each component requires specialized knowledge and ongoing attention.
We help businesses implement outreach automation strategies that drive measurable results. White Label SEO Service provides the technical expertise and strategic guidance needed to build sustainable organic growth through effective outreach systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the ideal number of emails in an outreach sequence?
Most effective sequences contain 4-7 emails spaced 3-5 days apart. This provides enough touchpoints to reach busy prospects without becoming annoying. Test different sequence lengths for your specific audience and adjust based on response patterns.
How do I improve my cold email open rates?
Focus on subject lines, sender reputation, and targeting accuracy. Keep subject lines short and specific. Maintain clean sending practices to protect deliverability. Ensure you’re reaching the right people with relevant messages. Test different approaches systematically.
What’s the difference between outreach automation and marketing automation?
Outreach automation focuses on one-to-one communication at scale, typically for sales prospecting or relationship building. Marketing automation handles broader campaigns including newsletters, nurture sequences, and lead scoring. Many organizations use both for different purposes.
How do I avoid spam filters with automated outreach?
Implement proper email authentication including SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. Warm new sending domains gradually. Avoid spam trigger words and excessive links. Maintain list hygiene and remove bounces promptly. Monitor engagement metrics and adjust targeting if rates drop.
What metrics matter most for outreach automation success?
Focus on metrics connected to business outcomes. Response rates and conversion rates indicate messaging effectiveness. Pipeline contribution and revenue attribution show business impact. Open rates and click rates provide useful diagnostic information but shouldn’t be primary success measures.
How much personalization is enough for automated outreach?
Effective personalization goes beyond name and company merge fields. Include specific references demonstrating research such as recent company news, relevant challenges, or mutual connections. The goal is making recipients feel the message was written specifically for them.
When should I stop an automated outreach sequence?
Stop sequences after explicit negative responses, unsubscribe requests, or hard bounces. Set maximum touchpoint limits, typically 6-8 emails, for non-responsive contacts. Move non-engagers to long-term nurture or remove from active outreach to protect sender reputation.



