A manual action for links can devastate your organic traffic overnight, but full recovery is achievable with the right process. Google issues these penalties when human reviewers identify link schemes or manipulative practices in your backlink profile, and the path back requires systematic cleanup, documentation, and a well-crafted reconsideration request.
Whether you discovered the notification in Google Search Console yesterday or have been struggling with declined requests, this situation demands immediate, strategic action. Your rankings, traffic, and revenue depend on executing the recovery process correctly the first time.
This guide walks you through every step of manual action recovery, from identifying the specific violation to submitting a successful reconsideration request and rebuilding your organic presence.
What Is a Manual Action for Links?
A manual action represents Google’s most direct form of penalty enforcement. Unlike algorithmic adjustments that happen automatically, manual actions result from human reviewers at Google examining your site and determining it violates their Webmaster Guidelines. When links are involved, the penalty specifically targets manipulative link building practices designed to artificially inflate search rankings.
Understanding the nature of your manual action is the first step toward recovery. The penalty type, scope, and specific violations all influence your cleanup strategy and reconsideration approach.
Google’s Definition of Manual Actions
According to Google’s Search Central documentation, a manual action is a penalty applied by a human reviewer who has determined that pages on your site do not comply with Google’s spam policies. For link-related manual actions, this means someone at Google examined your backlink profile and found evidence of link schemes.
Google’s spam team reviews sites flagged by algorithms or reported by users. When they find violations, they apply manual actions that can affect specific pages, sections, or your entire domain. The penalty remains active until you address the issues and successfully submit a reconsideration request.
Manual actions appear in Google Search Console with specific descriptions of the violation. This transparency is intentional. Google wants webmasters to understand what went wrong and provides enough information to guide cleanup efforts.
Manual Action vs Algorithmic Penalty
The distinction between manual actions and algorithmic penalties fundamentally changes your recovery approach. Manual actions require explicit reconsideration requests. Algorithmic penalties lift automatically once you fix the underlying issues and Google recrawls your site.
Manual actions come with notifications in Search Console. You know exactly when they were applied and what Google found problematic. Algorithmic impacts from updates like Penguin happen without notification. Your traffic drops, but Google never confirms the cause.
Recovery timelines differ significantly. Manual action recovery depends on Google’s review queue, typically taking days to weeks after submission. Algorithmic recovery can take months as Google gradually reassesses your site through normal crawling and indexing cycles.
The documentation requirements also vary. Manual action recovery demands detailed evidence of your cleanup efforts. Algorithmic recovery requires fixing issues but no formal submission process.
Types of Link-Related Manual Actions
Google categorizes link manual actions into two primary types, each requiring different cleanup approaches.
Unnatural Links to Your Site
This manual action targets inbound links pointing to your domain. Google has determined that other sites are linking to you in ways that violate their guidelines. Common triggers include purchased links, private blog networks, link farms, and excessive reciprocal linking.
The notification typically reads: “Google has detected a pattern of unnatural, artificial, deceptive, or manipulative links pointing to pages on this site.”
Recovery requires identifying and removing or disavowing the problematic inbound links. You cannot directly control links on other websites, which makes this penalty particularly challenging. Your options are outreach for removal or using Google’s Disavow Tool.
Unnatural Links from Your Site
This manual action targets outbound links from your domain to other sites. Google has determined you are selling links, participating in link schemes, or linking out in manipulative ways without proper disclosure.
The notification typically reads: “Google has detected a pattern of unnatural, artificial, deceptive, or manipulative outbound links on this site.”
Recovery requires auditing your outbound links and removing or adding nofollow/sponsored attributes to problematic ones. Since these links exist on your own site, you have direct control over the fix.
Why Google Issues Manual Actions for Links
Google’s search algorithm relies heavily on links as trust signals. When sites manipulate these signals, search results quality degrades. Manual actions exist to enforce link guidelines when algorithmic detection alone proves insufficient.
Understanding why Google penalizes specific practices helps you identify violations in your own backlink profile and avoid future issues.
Link Schemes and Manipulative Practices
Google’s link spam policies explicitly define link schemes as any behavior intended to manipulate rankings through links. This includes buying or selling links that pass PageRank, excessive link exchanges, large-scale article marketing with keyword-rich anchor text, and automated link building programs.
Private blog networks represent one of the most common triggers for manual actions. These networks of sites exist solely to create artificial link signals. Google has become increasingly sophisticated at identifying PBN footprints, including shared hosting, similar site structures, and unnatural linking patterns.
Guest posting at scale with optimized anchor text also triggers manual actions. While legitimate guest contributions remain acceptable, patterns of low-quality guest posts with exact-match anchor text signal manipulation.
Comment spam, forum signature links, and widget links with embedded backlinks all fall under link schemes. Any tactic designed primarily to generate links rather than provide value to users risks manual action.
Paid Links Without Proper Disclosure
Purchasing links that pass PageRank violates Google’s guidelines regardless of how natural the placement appears. The issue is not advertising itself but rather undisclosed paid links designed to influence rankings.
Sponsored content, affiliate links, and paid placements are acceptable when properly disclosed using rel=”sponsored” or rel=”nofollow” attributes. The violation occurs when paid links appear as organic editorial endorsements.
Google’s reviewers look for patterns suggesting paid link activity. Sudden influxes of links from unrelated sites, links from known link sellers, and anchor text patterns inconsistent with natural linking all raise flags.
The penalty applies whether you purchased links directly or through an agency. Claiming ignorance of your link building vendor’s practices does not exempt you from the manual action.
Excessive Link Exchanges
Reciprocal linking at scale signals manipulation to Google. While occasional natural link exchanges between related sites remain acceptable, systematic “link to me and I’ll link to you” arrangements violate guidelines.
Three-way link exchanges designed to obscure the reciprocal nature also trigger manual actions. Google’s algorithms can detect these patterns across large datasets.
The key factor is intent. Links should exist because they provide value to users, not because of an agreement to exchange ranking signals. When link exchanges become a primary link building strategy, manual action risk increases substantially.
Low-Quality Directory and Bookmark Site Links
Mass directory submissions were once a standard SEO tactic. Today, links from low-quality directories with no editorial standards frequently contribute to manual actions.
The distinction matters. Legitimate industry directories, local business listings, and curated resource pages provide value. Generic directories that accept any submission for a fee or automatically exist solely for link building purposes.
Social bookmarking sites designed for link building rather than genuine content sharing fall into the same category. Profiles created solely to post links, automated bookmarking, and patterns of self-promotional submissions all signal manipulation.
How to Identify a Manual Action in Google Search Console
Google Search Console serves as your primary notification system for manual actions. Regular monitoring ensures you catch penalties quickly and begin recovery before traffic losses compound.
Accessing the Manual Actions Report
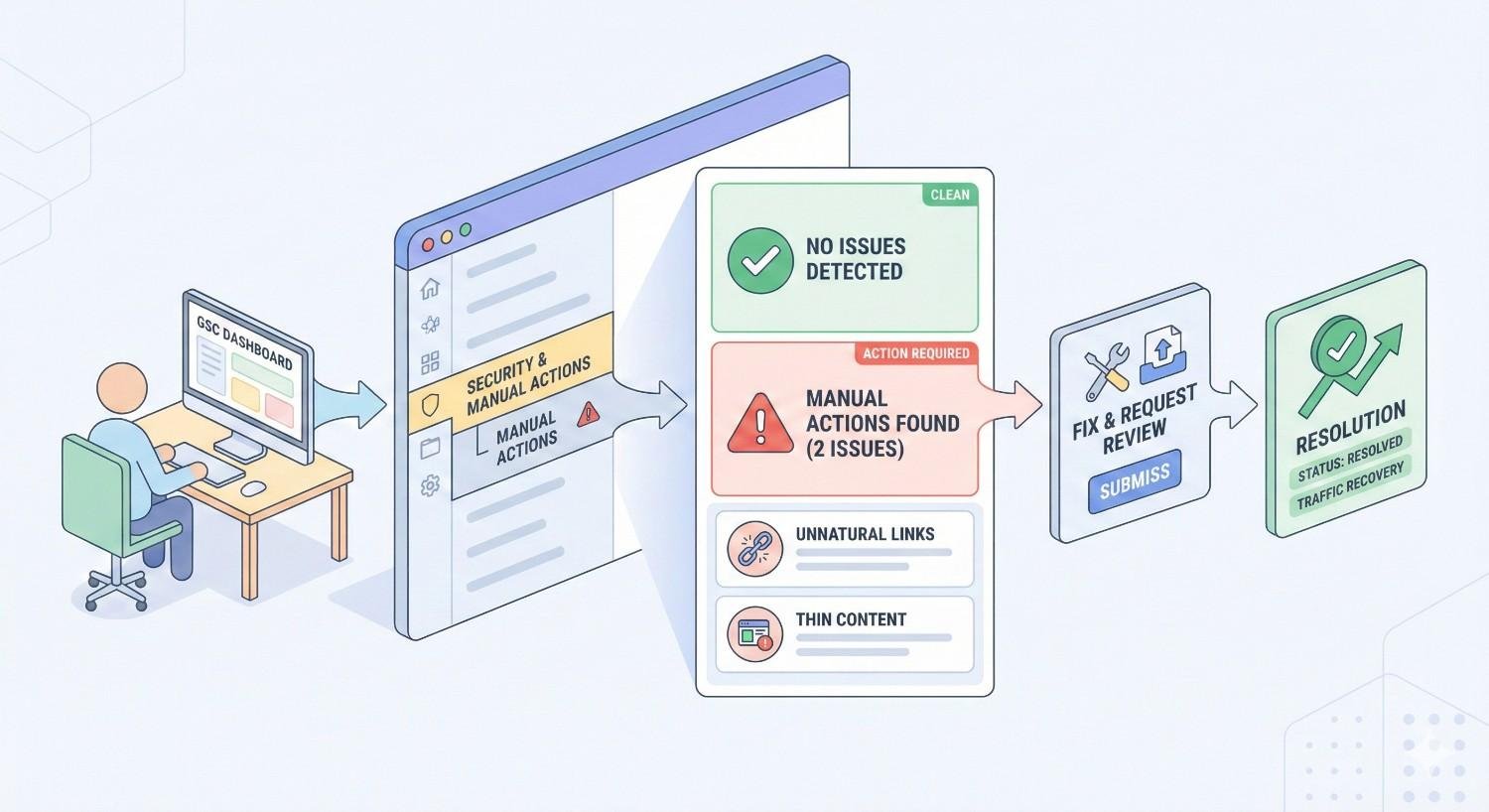
Log into Google Search Console and select your property. In the left navigation menu, expand the “Security & Manual Actions” section. Click “Manual Actions” to view your current status.
If no manual actions exist, you will see a green checkmark with the message “No issues detected.” This confirmation means Google’s human reviewers have not applied any penalties to your site.
If a manual action exists, the report displays the specific violation type, affected pages or sections, and the date the action was applied. This information guides your entire recovery strategy.
Check this report regularly, ideally weekly. Manual actions can be applied at any time, and early detection minimizes ranking and traffic damage.
Understanding the Notification Message
Google’s manual action notifications follow a standard format. The message identifies the violation type, describes what Google found, and indicates the scope of the penalty.
For link-related manual actions, the notification specifies whether the issue involves inbound links, outbound links, or both. The description provides context about the patterns Google identified.
Pay close attention to the exact wording. “Unnatural links to your site” requires different remediation than “Unnatural links from your site.” Misunderstanding the violation type leads to ineffective cleanup efforts and rejected reconsideration requests.
Google sometimes provides example URLs affected by the manual action. These examples help you understand the specific issues but do not represent a complete list. Your audit must be comprehensive, not limited to the examples provided.
Determining Scope: Site-Wide vs Partial Match
Manual actions can affect your entire domain or specific sections. The scope significantly impacts both the severity of traffic loss and the complexity of recovery.
Site-wide manual actions apply to your entire domain. Every page loses ranking ability until the penalty is lifted. These typically result from pervasive link scheme participation affecting the domain as a whole.
Partial match manual actions affect specific pages, directories, or sections. The rest of your site continues ranking normally. These often result from localized link building campaigns targeting specific pages.
The Search Console report indicates the scope. Site-wide actions state they affect “the entire site.” Partial actions specify affected URLs or patterns.
Recovery requirements differ by scope. Site-wide actions demand comprehensive backlink audits covering your entire link profile. Partial actions allow more focused cleanup on the affected sections, though thorough documentation remains essential.
Step-by-Step Manual Action Recovery Process
Recovery from a link-related manual action follows a structured process. Skipping steps or rushing through the process typically results in rejected reconsideration requests and prolonged penalties.
The timeline from discovery to recovery typically spans four to twelve weeks, depending on the severity of the violation and the thoroughness of your cleanup efforts.
Step 1 – Audit Your Backlink Profile
A comprehensive backlink audit forms the foundation of your recovery effort. You cannot fix what you have not identified. This step requires gathering data from multiple sources and systematically evaluating every link pointing to your site.
Using Google Search Console Link Data
Start with Google’s own data. In Search Console, navigate to “Links” in the left menu. The “Top linking sites” report shows domains linking to you, while “Top linked pages” shows which of your pages receive the most links.
Export this data using the export button. You will receive a list of linking domains and the pages they link to. This data comes directly from Google’s index, making it the most relevant source for understanding what Google sees.
Search Console data has limitations. It does not show every link, and it lacks detailed metrics about link quality. Use it as your baseline, then supplement with third-party tools.
Third-Party Backlink Analysis Tools
Tools like Ahrefs, Semrush, Moz, and Majestic provide more comprehensive backlink data. Each tool crawls the web independently, so combining multiple sources gives you the most complete picture.
Export backlink reports from at least two tools. Compare the data to identify links that appear across sources. Links found by multiple crawlers are more likely to be indexed and influential.
These tools provide quality metrics like Domain Rating, Trust Flow, and spam scores. While not perfect, these metrics help prioritize which links to investigate first.
Identifying Toxic and Unnatural Links
Not every low-quality link requires action. Focus on links that match the patterns Google penalizes.
Red flags include:
- Links from sites in unrelated languages or industries
- Links from known link networks or PBN footprints
- Links with exact-match anchor text at unnatural rates
- Links from sites with no real content or traffic
- Links from pages that exist solely to link out
- Paid links you know were purchased
- Links from hacked sites or malware-infected domains
Evaluate each suspicious link in context. A single low-quality link rarely triggers manual actions. Patterns of manipulative links across dozens or hundreds of domains cause penalties.
Step 2 – Document Problematic Links
Documentation serves two purposes. It organizes your cleanup efforts and provides evidence for your reconsideration request. Google wants to see that you understand what went wrong and took systematic action to fix it.
Creating a Link Audit Spreadsheet
Build a spreadsheet with columns for:
- Linking URL (the page containing the link)
- Linking domain (root domain)
- Target URL (your page being linked to)
- Anchor text
- Link type (text, image, redirect)
- Risk assessment (high, medium, low)
- Action taken (removal requested, disavowed, kept)
- Date of action
- Response received
This spreadsheet becomes your primary documentation for the reconsideration request. Maintain it meticulously throughout the process.
Include every link you evaluate, not just the ones you remove. Showing Google that you reviewed your entire profile and made informed decisions demonstrates thoroughness.
Categorizing Links by Risk Level
Assign risk levels based on how likely each link contributed to the manual action.
High risk links require immediate action. These include obvious paid links, PBN links, links from link farms, and any links you know violate guidelines.
Medium risk links warrant removal attempts but may not be critical. These include links from low-quality directories, excessive reciprocal links, and links from sites with thin content.
Low risk links can typically remain. These include legitimate editorial links, links from real businesses, and links that appear natural even if from lower-authority sites.
When uncertain, err toward removal or disavowal. The goal is demonstrating to Google that you have cleaned up your link profile, not preserving every possible link.
Step 3 – Request Link Removal
Before using the Disavow Tool, attempt to remove links directly. Google expects good-faith efforts to actually remove problematic links, not just disavow everything.
Outreach Email Templates
Contact webmasters of sites linking to you with problematic links. Keep emails professional, concise, and specific.
Example template:
Subject: Link Removal Request – [Your Domain]
Hello,
I am contacting you regarding a link from your website [linking URL] to my site [your domain].
We are currently cleaning up our backlink profile to comply with Google’s Webmaster Guidelines. We would appreciate if you could remove this link or add a nofollow attribute.
The specific link is located at: [exact URL] Linking to: [your page URL]
Thank you for your assistance.
[Your name] [Contact information]
Avoid threatening language or excessive follow-ups. Many webmasters will not respond, and that is expected.
Tracking Removal Requests
Log every outreach attempt in your spreadsheet. Record:
- Date email sent
- Contact method used
- Response received (if any)
- Date link was removed (if applicable)
This documentation proves to Google that you attempted removal before resorting to disavow. Send at least two outreach attempts before moving to disavow, spaced one to two weeks apart.
When to Move to Disavow
Move to disavow when:
- Webmaster does not respond after two attempts
- Webmaster refuses to remove the link
- No contact information exists for the site
- The site appears abandoned or hacked
- Removal would take too long given the urgency
Do not wait indefinitely for responses. After two to three weeks of outreach attempts, proceed with disavowing unresponsive sites.
Step 4 – Create and Submit a Disavow File
The Disavow Tool tells Google to ignore specific links when assessing your site. It is a powerful tool that should be used carefully and only for links you genuinely want Google to discount.
Disavow File Format Requirements
The disavow file is a plain text file (.txt) with specific formatting requirements.
Each line contains either a URL or a domain to disavow. Domain-level disavows use the format: domain:example.com
Comments begin with # and help document your reasoning.
Example file structure:
Copy
# Links from known PBN network
domain:spammysite1.com
domain:spammysite2.com
# Paid links – removal requested, no response
domain:linkfarm.net
# Specific URLs from otherwise legitimate sites
http://example.com/spammy-page-with-link
Save the file as plain text with UTF-8 encoding. Name it clearly, such as “disavow-file-2025.txt.”
Domain-Level vs URL-Level Disavow
Domain-level disavow (domain:example.com) tells Google to ignore all links from that entire domain. Use this when the entire site is problematic or when multiple pages from the same domain link to you.
URL-level disavow (http://example.com/page) tells Google to ignore only that specific URL. Use this when a legitimate site has one problematic page linking to you but other links from that domain are valuable.
When in doubt, use domain-level disavow. It is more thorough and prevents future problematic links from the same source.
Uploading to Google Disavow Tool
Access the Disavow Tool at Google Search Console’s Disavow Links page. Select your property and upload your file.
Google confirms the upload and displays any formatting errors. Fix errors and re-upload if necessary.
The disavow file replaces any previous version. If you need to update your disavow list, download the existing file, add new entries, and upload the complete updated file.
Processing takes time. Google does not immediately ignore disavowed links. The effect occurs as Google recrawls the disavowed pages, which can take weeks or months.
Step 5 – Submit a Reconsideration Request
The reconsideration request is your formal appeal to Google asking them to review your site and lift the manual action. This step only applies to manual actions, not algorithmic penalties.
What to Include in Your Request
Your reconsideration request should contain:
- Acknowledgment of the violation and acceptance of responsibility
- Explanation of how the problematic links were acquired
- Detailed description of your cleanup efforts
- Documentation of removal attempts and outcomes
- Confirmation that you have submitted a disavow file
- Commitment to following Google’s guidelines going forward
Be specific and factual. Vague statements like “we cleaned up our links” are insufficient. Provide numbers, dates, and evidence.
Documenting Your Cleanup Efforts
Attach or reference your documentation spreadsheet. Summarize key metrics:
- Total links audited
- Number of links identified as problematic
- Number of removal requests sent
- Number of links successfully removed
- Number of links disavowed
If you used an agency or contractor for link building, explain what happened and confirm you have terminated that relationship.
Tone and Transparency Best Practices
Write professionally and honestly. Google reviewers read thousands of these requests. They can identify genuine efforts versus attempts to game the system.
Admit mistakes without excessive self-flagellation. A straightforward acknowledgment that you violated guidelines, intentionally or not, demonstrates maturity.
Do not blame others exclusively. Even if an agency built bad links, you are responsible for your site. Accept that responsibility while explaining the circumstances.
Avoid technical jargon or SEO industry terms. Write as if explaining to someone unfamiliar with link building tactics.
Express genuine commitment to compliance. Explain what processes you have implemented to prevent future violations.
How Long Does Manual Action Recovery Take?
Recovery timelines vary based on multiple factors. Setting realistic expectations helps you plan resources and communicate with stakeholders.
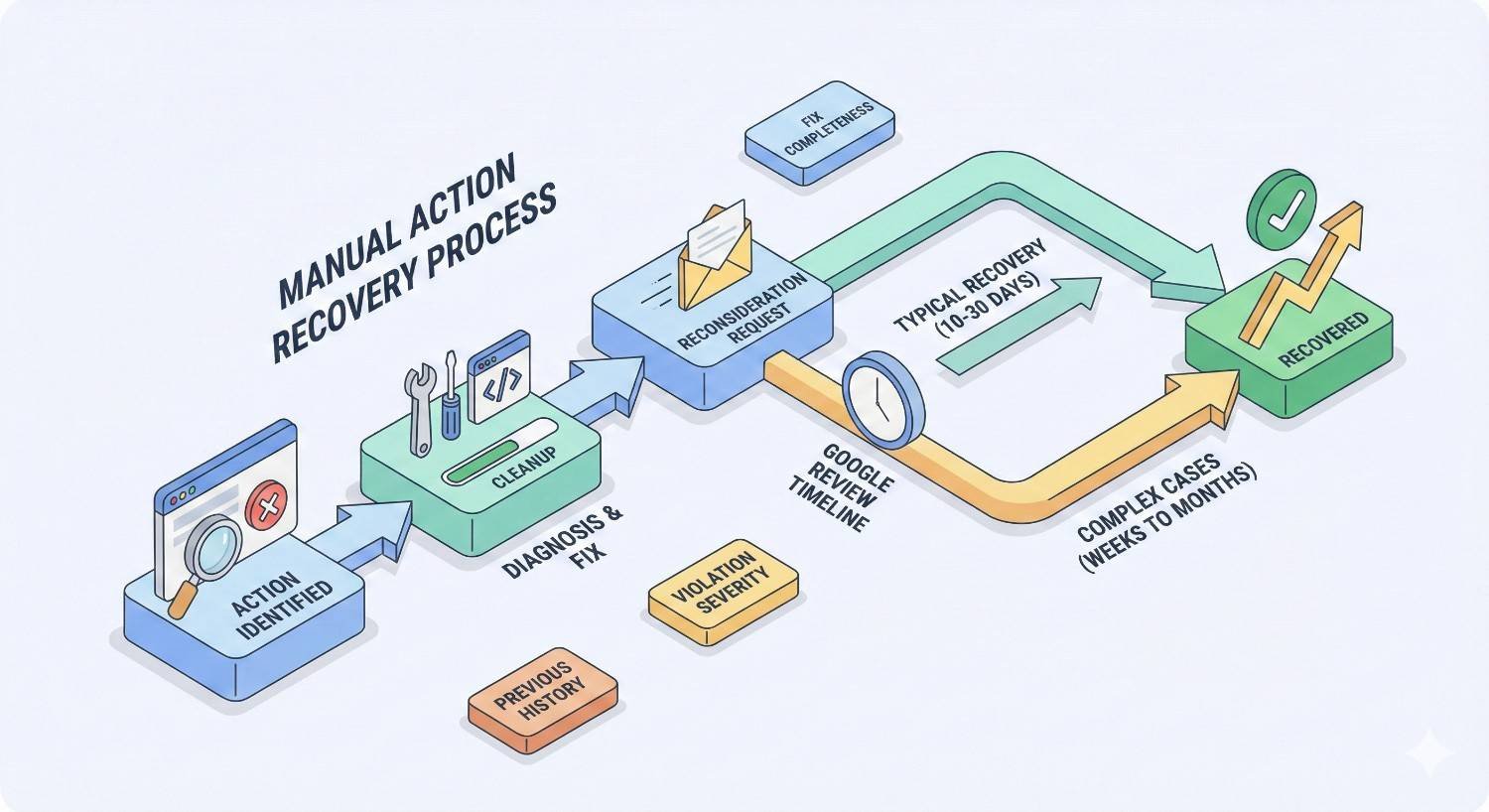
Google Review Timeframes
After submitting a reconsideration request, Google typically responds within a few days to several weeks. Google’s documentation indicates most reviews complete within days, but complex cases take longer.
You receive notification in Search Console when the review completes. The response indicates whether the manual action was lifted, partially lifted, or remains in place.
During high-volume periods or for complex cases, reviews can extend to several weeks. There is no way to expedite the process.
Factors Affecting Recovery Speed
Several factors influence how quickly you recover:
Cleanup thoroughness: Comprehensive cleanup with strong documentation typically results in faster approval. Incomplete efforts lead to rejection and restart.
Violation severity: Sites with extensive link scheme participation face more scrutiny than those with limited violations.
Site history: First-time offenders often receive faster reviews than sites with previous manual actions.
Documentation quality: Clear, organized evidence of your efforts helps reviewers process your request efficiently.
Request clarity: Well-written requests that directly address the violation and demonstrate understanding speed the review process.
What to Do If Your Request Is Denied
Rejected reconsideration requests include feedback explaining why. Read this feedback carefully. It identifies gaps in your cleanup or documentation.
Common rejection reasons include:
- Incomplete link cleanup (problematic links remain)
- Insufficient removal attempts before disavowing
- Poor documentation of efforts
- New problematic links acquired during cleanup
- Failure to address all aspects of the violation
After rejection, return to your audit. Identify what you missed. Expand your cleanup efforts. Update your documentation. Submit a new request only after addressing the feedback.
There is no limit to reconsideration request submissions, but repeated rejections without meaningful improvement waste time. Each rejection extends your penalty duration.
Reconsideration Request Examples and Templates
Learning from successful requests helps you craft your own. The following examples illustrate effective approaches.
Successful Reconsideration Request Sample
Example request:
“We acknowledge that our site received a manual action for unnatural links pointing to our domain. After thorough investigation, we identified that links were acquired through a third-party SEO agency we hired in 2023. We have terminated this relationship.
Our cleanup process included:
- Complete backlink audit using Google Search Console, Ahrefs, and Semrush data
- Identification of 847 problematic links across 312 domains
- Outreach to all 312 domains requesting link removal (documentation attached)
- Successful removal of 89 links from 34 domains
- Disavowal of remaining 758 links across 278 domains (disavow file submitted)
We have implemented new link building guidelines requiring editorial approval for all link acquisition activities. Our team has completed training on Google’s Webmaster Guidelines.
We respectfully request review of our site and removal of the manual action. We are committed to maintaining compliance with Google’s guidelines.”
This example works because it accepts responsibility, provides specific numbers, documents efforts, and demonstrates forward-looking compliance.
Common Mistakes That Lead to Rejection
Blaming others without accepting responsibility: “Our agency built bad links without our knowledge” without acknowledging your oversight fails.
Vague cleanup descriptions: “We removed the bad links” without specifics suggests incomplete work.
Disavowing everything: Disavowing your entire backlink profile signals you do not understand which links were problematic.
No removal attempts: Jumping straight to disavow without outreach suggests laziness or lack of genuine effort.
Defensive tone: Arguing that your links were not actually bad or that Google made a mistake never works.
Incomplete cleanup: Leaving obvious problematic links in place while claiming thorough cleanup results in immediate rejection.
Rushing the process: Submitting requests within days of discovering the manual action rarely succeeds. Thorough cleanup takes time.
How to Prevent Future Link-Related Manual Actions
Recovery is only half the battle. Preventing recurrence protects your long-term organic visibility and avoids the traffic and revenue losses that accompany manual actions.
Building a Sustainable Link Acquisition Strategy
Focus on earning links through valuable content and genuine relationships. Links that come naturally because your content deserves citation never trigger manual actions.
Create linkable assets: original research, comprehensive guides, useful tools, and unique data. These attract editorial links without outreach.
When conducting outreach, focus on relevance and value. Pitch content that genuinely benefits the target site’s audience, not just your link profile.
Diversify link sources naturally. A healthy link profile includes various referring domains, anchor text variations, and link types. Patterns suggesting manipulation stand out.
Avoid shortcuts. If a link building tactic seems too easy or too good to be true, it probably violates guidelines.
Regular Backlink Monitoring and Audits
Monitor your backlink profile continuously, not just after problems arise. Set up alerts for new backlinks using tools like Ahrefs or Google Alerts.
Conduct quarterly backlink audits. Review new links acquired, identify any suspicious patterns, and address issues before they accumulate.
Watch for negative SEO attacks. Competitors occasionally build spammy links to trigger manual actions. Regular monitoring helps you catch and disavow these quickly.
Track your anchor text distribution. Sudden spikes in exact-match anchor text signal potential problems, whether from your own efforts or external attacks.
Vetting Link Opportunities Before Acquisition
Evaluate every link opportunity before pursuing it. Ask whether the link would exist if search engines did not.
Check the linking site’s quality. Real traffic, genuine content, and editorial standards indicate legitimate opportunities. Sites that exist solely for link building are dangerous.
Review the site’s outbound link patterns. Pages with dozens of unrelated outbound links signal link selling or low editorial standards.
Consider the relevance. Links from topically related sites carry more value and less risk than random placements.
Avoid any arrangement that feels transactional. If you are paying for placement without clear sponsored disclosure, you are violating guidelines.
Training Teams on Google’s Link Guidelines
Ensure everyone involved in your marketing understands link guidelines. This includes in-house teams, agencies, and contractors.
Review Google’s link spam policies with your team. Make compliance a documented requirement in all contracts and agreements.
Establish approval processes for link building activities. No links should be acquired without review against your compliance standards.
Create clear documentation of acceptable and unacceptable practices. When team members understand the boundaries, violations become less likely.
What Happens After Manual Action Recovery?
Lifting the manual action is a milestone, not the finish line. Understanding what comes next helps you set realistic expectations and plan your recovery strategy.
Ranking Recovery Timeline Expectations
Manual action removal does not instantly restore rankings. Your site must be recrawled and reassessed by Google’s algorithms.
Initial ranking improvements often appear within days to weeks of manual action removal. However, full recovery to pre-penalty positions can take months.
The recovery trajectory depends on how long the manual action was in place, how much your competitors advanced during your penalty, and the overall quality of your site.
Some rankings may never fully recover if competitors have strengthened their positions significantly. Focus on continued improvement rather than exact restoration of previous rankings.
Rebuilding Domain Authority Post-Penalty
Your link cleanup likely removed or disavowed links that, while problematic, contributed to your domain authority metrics. Rebuilding requires earning new, legitimate links.
Prioritize quality over quantity. A few high-authority editorial links provide more value than dozens of low-quality placements.
Leverage your recovery story. Case studies about overcoming manual actions can attract links from SEO and marketing publications.
Invest in content that naturally attracts links. Original research, comprehensive resources, and genuinely useful tools earn editorial citations without outreach.
Measuring Organic Traffic Recovery
Track organic traffic trends in Google Analytics. Compare current performance to pre-penalty baselines, accounting for seasonality and market changes.
Monitor Search Console performance data. Impressions, clicks, and average position provide granular insight into recovery progress.
Track rankings for your most important keywords. Recovery often happens unevenly, with some terms recovering faster than others.
Set realistic benchmarks. Full traffic recovery to pre-penalty levels may take six to twelve months, depending on penalty duration and competitive dynamics.
When to Hire an SEO Professional for Manual Action Recovery
Manual action recovery is complex and high-stakes. Professional assistance often accelerates recovery and improves success rates.
Signs You Need Expert Help
Consider professional help if:
- Your first reconsideration request was rejected
- Your backlink profile contains thousands of links requiring evaluation
- You lack experience with backlink analysis tools
- The manual action has persisted for months
- Your business depends heavily on organic traffic
- You do not have internal resources to dedicate to recovery
The cost of professional assistance is typically far less than the ongoing revenue loss from a prolonged manual action.
What to Look for in a Recovery Specialist
Seek specialists with documented manual action recovery experience. Ask for case studies and references from previous recovery projects.
Verify they understand the complete process, from audit through reconsideration. Partial expertise leads to incomplete recovery efforts.
Ensure they use legitimate methods. Any specialist suggesting shortcuts or guaranteed timelines should raise concerns.
Look for transparent communication. You should understand exactly what they are doing and why at every stage.
Questions to Ask Before Hiring
Before engaging a recovery specialist, ask:
- How many manual action recoveries have you completed?
- What is your success rate for reconsideration requests?
- Can you provide references from previous recovery clients?
- What is your process for backlink auditing?
- How do you document cleanup efforts for reconsideration requests?
- What is your timeline estimate for my specific situation?
- What happens if the first reconsideration request is rejected?
Evaluate answers for specificity and realism. Vague promises or guaranteed outcomes indicate inexperience or dishonesty.
Conclusion
Manual action recovery for links demands systematic effort, thorough documentation, and patience. The process from discovery through successful reconsideration typically spans weeks to months, but full recovery is achievable when you follow the correct steps.
At White Label SEO Service, we specialize in helping businesses navigate manual action recovery. Our team has guided dozens of sites through successful reconsideration requests, restoring organic visibility and protecting long-term search performance.
If you are facing a link-related manual action, contact our recovery specialists for a confidential assessment. We will evaluate your situation, outline a recovery plan, and help you regain your rankings as quickly as possible.
Frequently Asked Questions About Manual Action Recovery
Can I recover from a manual action without disavowing?
Recovery without disavowing is possible but rare. It requires successfully removing all problematic links through direct outreach. Most sites find that some linking webmasters do not respond, making disavow necessary for complete cleanup.
Will removing links hurt my rankings?
Removing manipulative links may cause short-term ranking fluctuations, but these links were not providing sustainable value. Long-term, a clean link profile supports healthier rankings than one inflated by scheme links.
How many times can I submit a reconsideration request?
There is no formal limit on reconsideration request submissions. However, repeated submissions without addressing Google’s feedback waste time and extend your penalty. Each submission should reflect meaningful additional cleanup.
Does a manual action affect all my pages?
Manual actions can be site-wide or partial. Site-wide actions affect your entire domain. Partial actions affect only specific pages or sections. The Search Console report specifies the scope of your particular penalty.
How long does Google take to review a reconsideration request?
Most reconsideration requests receive responses within a few days to several weeks. Complex cases or high-volume periods can extend timelines. There is no way to expedite the review process.
Can I prevent negative SEO from causing manual actions?
Regular backlink monitoring helps you identify and disavow suspicious links before they accumulate. While you cannot prevent others from building spammy links to your site, proactive monitoring and disavowal minimize risk.
Should I disavow links I am unsure about?
When genuinely uncertain, err toward disavowal for links that appear low-quality or unnatural. The risk of keeping a problematic link typically outweighs the value of a questionable one. However, do not disavow legitimate editorial links out of excessive caution.



