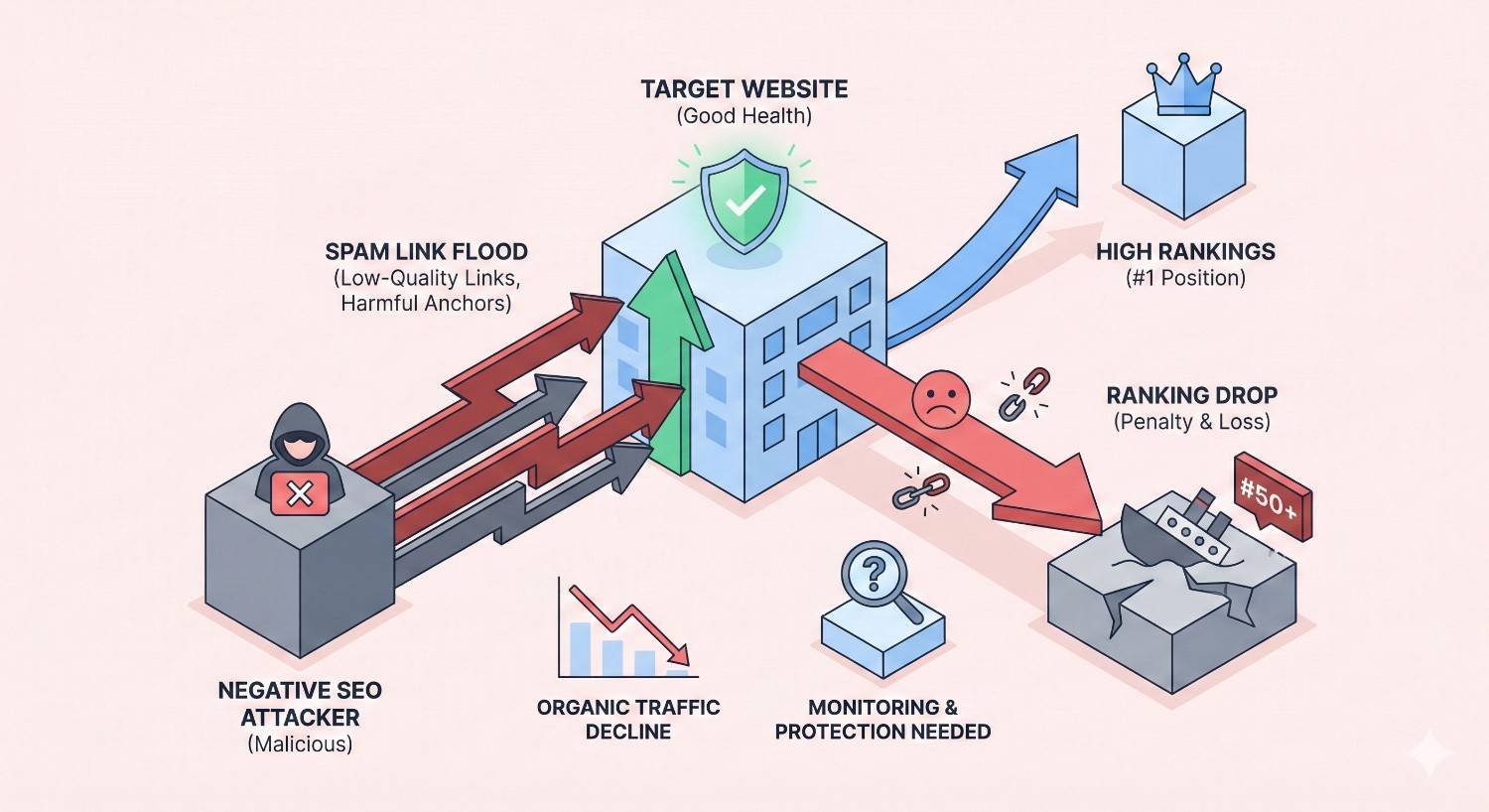
Negative SEO link attacks can devastate your rankings within days, but full recovery is achievable with the right strategy. When competitors or malicious actors flood your backlink profile with toxic links, Google may interpret these as manipulation attempts, triggering penalties that tank your organic traffic.
This threat is real and growing. Sites across every industry face link-based attacks designed to trigger algorithmic filters or manual actions. The damage compounds daily without intervention.
This guide covers detection methods, step-by-step removal processes, disavow file creation, penalty recovery, and long-term prevention. You’ll have a complete action plan by the end.
Understanding Negative SEO: Definition and Scope
Negative SEO refers to malicious tactics designed to harm a competitor’s search rankings rather than improve one’s own. Link attacks represent the most common and damaging form. Attackers deliberately build low-quality, spammy backlinks pointing to your domain, hoping Google will penalize you for apparent link scheme participation.
The scope extends beyond simple spam. Sophisticated attacks mimic patterns Google’s algorithms flag as manipulative. Attackers understand what triggers penalties and exploit this knowledge against targets.
Google has stated they try to ignore most spammy links rather than penalize sites for them. However, large-scale attacks with specific patterns still cause ranking damage. The algorithm cannot always distinguish between self-inflicted link schemes and external attacks.
Your vulnerability depends on several factors. Sites with thin content, weak existing backlink profiles, or previous penalty history face higher risk. Newer domains without established authority are particularly susceptible.
Types of Negative SEO Link Attacks
Toxic Backlink Injection
Toxic backlink injection involves creating thousands of links from low-quality sources pointing to your domain. These links typically come from hacked sites, spam blogs, forum profiles, and comment sections across the web.
Attackers use automated tools to generate these links rapidly. A single attack can create 10,000 to 100,000+ backlinks within weeks. The sheer volume signals manipulation to Google’s systems.
Common toxic link sources include:
- Hacked WordPress sites with injected links
- Auto-generated spam blogs
- Foreign language gambling and adult sites
- Scraped content farms
- Abandoned domains repurposed for link spam
Link Farm and PBN Attacks
Private Blog Networks (PBNs) and link farms present a more sophisticated threat. Attackers point links from known penalty-prone networks toward your site. When Google devalues these networks, your site gets caught in the crossfire.
Link farms operate as interconnected sites existing solely to manipulate rankings. Google maintains databases of identified link farms. Links from these sources carry immediate negative signals.
PBN attacks are particularly insidious because these networks often have decent metrics initially. The links appear legitimate until Google identifies and penalizes the network.
Anchor Text Manipulation Attacks
Anchor text attacks target your link profile’s anchor text distribution. Natural backlink profiles contain diverse anchor text, including branded terms, naked URLs, and generic phrases like “click here.”
Attackers create thousands of links using exact-match commercial anchors. If you sell “blue widgets,” they’ll build links with “buy blue widgets cheap” as anchor text repeatedly. This over-optimization pattern triggers algorithmic filters.
Google’s Penguin algorithm specifically targets unnatural anchor text patterns. A sudden spike in exact-match anchors signals manipulation, regardless of whether you created those links.
Competitor Sabotage Patterns
Competitor sabotage follows recognizable patterns. Attacks often coincide with your ranking improvements or their ranking losses. The timing reveals intent.
Common sabotage indicators include:
- Links appearing immediately after you outrank a competitor
- Attack intensity increasing during peak business seasons
- Multiple attack vectors deployed simultaneously
- Links from the same networks used against other sites in your industry
Some attackers combine link attacks with other negative SEO tactics. They might scrape and republish your content, creating duplicate content issues while building toxic links.
How Google Identifies and Penalizes Unnatural Links
Google uses both algorithmic systems and manual reviewers to identify unnatural link patterns. The Penguin algorithm, now part of Google’s core algorithm, evaluates link quality in real-time.
Algorithmic detection focuses on:
- Link velocity anomalies: Sudden spikes in new backlinks
- Source quality patterns: High concentration of links from low-quality domains
- Anchor text distribution: Unnatural keyword-rich anchor ratios
- Link neighborhood analysis: Links from sites associated with spam
- Temporal patterns: Links appearing in coordinated bursts
Manual actions occur when Google’s webspam team reviews your site directly. These result in explicit notifications in Google Search Console. Manual penalties require formal reconsideration requests for removal.
Algorithmic filters work differently. No notification appears. Rankings simply decline as the algorithm devalues your link profile. Recovery requires cleaning your backlink profile and waiting for algorithm updates to reassess your site.
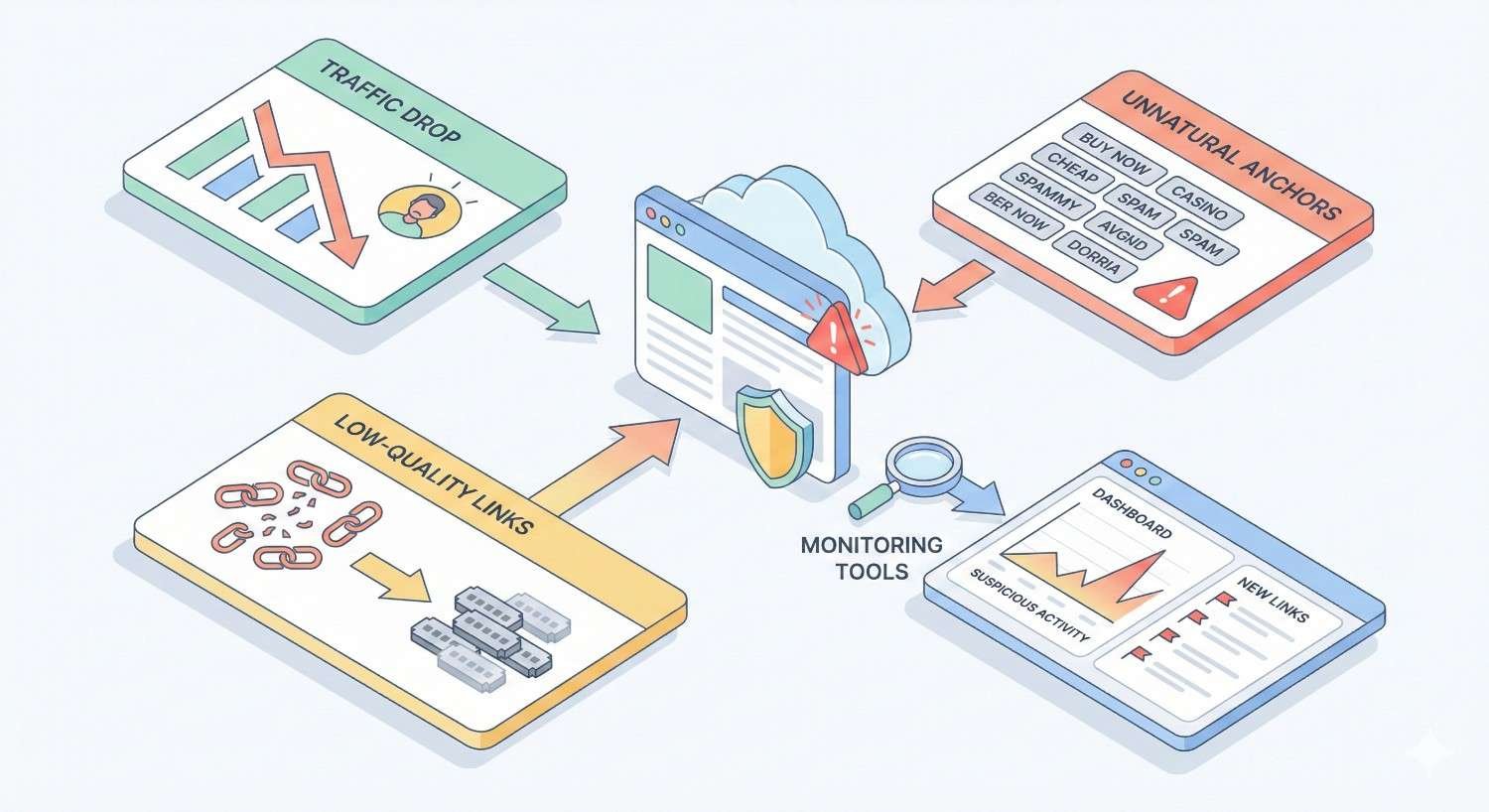
Detecting a Negative SEO Link Attack: Warning Signs and Symptoms
Sudden Ranking Drops and Traffic Decline Patterns
The first sign of a link attack is often a sudden ranking drop. Pages that ranked on page one disappear to page three or beyond. This happens without any changes to your site or content.
Traffic decline patterns reveal attack timing. Check Google Analytics for sharp drops rather than gradual declines. Algorithmic penalties from link attacks typically cause 30-70% traffic losses within days.
Compare organic traffic against other channels. If direct and referral traffic remain stable while organic plummets, a search penalty is likely. Seasonal fluctuations affect all channels proportionally.
Track specific keyword rankings, not just overall traffic. Link attacks often impact your most valuable commercial keywords first. Attackers target the terms driving your revenue.
Unnatural Backlink Profile Spikes
Backlink profile spikes are the clearest attack indicator. Normal link acquisition happens gradually. Attacks create dramatic spikes visible in any backlink monitoring tool.
Warning signs in your backlink data:
- Hundreds or thousands of new referring domains in days
- Links from irrelevant foreign-language sites
- Multiple links from the same IP ranges
- Links from domains with no real content
- Sudden appearance of links from known spam networks
Compare your link velocity against historical averages. If you typically gain 50 new referring domains monthly and suddenly see 500, investigate immediately.
Google Search Console Manual Action Notifications
Manual actions appear in Google Search Console under Security & Manual Actions. Google explicitly states the issue and affected pages or your entire site.
Link-related manual actions include:
- Unnatural links to your site: Google found patterns of artificial links pointing to your site
- Thin content with little or no added value: Sometimes accompanies link attacks
- Pure spam: Severe cases involving multiple violations
Check Search Console weekly at minimum. Manual action notifications don’t trigger email alerts by default. Enable email notifications in your Search Console settings.
Manual actions require formal reconsideration requests. You must demonstrate you’ve addressed the issue before Google will lift the penalty.
Algorithmic Penalty Indicators
Algorithmic penalties leave no notification. You must identify them through ranking and traffic analysis combined with timing correlation.
Key algorithmic penalty indicators:
- Rankings drop coinciding with known Google updates
- Gradual ranking decline over weeks without obvious cause
- Specific page types affected while others remain stable
- Recovery attempts through content changes show no improvement
Cross-reference your traffic drops with Google algorithm update trackers. Major updates like core updates and spam updates can trigger or intensify penalties from existing link issues.
Algorithmic penalties often compound. Initial link quality issues trigger minor ranking losses. Continued toxic link accumulation worsens the penalty over time.
Tools and Methods for Link Attack Detection
Google Search Console Link Reports
Google Search Console provides free access to your backlink data directly from Google. Navigate to Links in the left menu to access external link reports.
Key reports to review:
- Top linking sites: Identify unfamiliar domains linking heavily to you
- Top linking text: Spot unnatural anchor text patterns
- Top linked pages: See which pages attackers target
Export this data regularly. Compare current reports against historical baselines to identify anomalies. Google Search Console shows a sample of links, not the complete picture.
Third-Party Backlink Analysis Tools
Third-party tools provide more comprehensive backlink data than Search Console alone. Each tool crawls the web independently, capturing links Google’s sample might miss.
Essential tools for attack detection:
Ahrefs Site Explorer offers the largest backlink index. Use the “New” filter to see recently acquired links. The referring domains report shows link source quality at a glance.
Semrush Backlink Audit includes built-in toxicity scoring. The tool automatically flags potentially harmful links based on multiple quality signals.
Moz Link Explorer provides spam score metrics for linking domains. High spam scores indicate likely attack sources.
Majestic SEO offers Trust Flow and Citation Flow metrics. Large gaps between these metrics suggest manipulative link profiles.
Use multiple tools for comprehensive coverage. Each tool’s crawler captures different links. Combining data ensures you identify all attack vectors.
Toxic Link Identification Criteria
Not every low-quality link indicates an attack. Establish clear criteria for identifying genuinely toxic links versus normal web noise.
High-toxicity indicators:
- Domain spam score above 60%
- Links from hacked or compromised sites
- Exact-match anchor text on commercial keywords
- Links from link farms or known PBN networks
- Foreign language sites unrelated to your business
- Sites with no organic traffic themselves
- Domains created recently with immediate link building
Medium-toxicity indicators:
- Low domain authority combined with high external link counts
- Sites with thin, auto-generated content
- Excessive reciprocal linking patterns
- Links from unrelated industries
Document your criteria consistently. You’ll need this documentation for reconsideration requests and ongoing monitoring.
Immediate Response: First Steps When You Discover a Link Attack
Document the Attack: Data Collection and Evidence Gathering
Documentation begins immediately upon attack discovery. Thorough records support reconsideration requests and potential legal action.
Essential documentation includes:
- Screenshots of backlink reports showing the spike
- Exported backlink data with dates
- Ranking tracking data showing the decline timeline
- Traffic reports from Google Analytics
- Any manual action notifications
- Correspondence with hosting providers or webmasters
Create a dedicated folder for attack documentation. Organize by date and evidence type. Google’s webspam team reviews this documentation during reconsideration.
Export complete backlink profiles from multiple tools. Include timestamps showing when links first appeared. This timeline proves the links were externally created, not self-inflicted.
Assess the Damage: Impact Analysis on Rankings and Traffic
Quantify the attack’s impact before beginning recovery. This baseline helps measure recovery progress and demonstrates damage severity.
Damage assessment metrics:
- Ranking losses: Track position changes for top 50 keywords
- Traffic decline: Calculate percentage drop in organic sessions
- Revenue impact: Estimate lost conversions and sales
- Indexed pages: Check for deindexed content
- Crawl errors: Monitor for new crawl issues
Compare current performance against the 30-day period before the attack. This comparison provides clear before-and-after evidence.
Segment analysis by page type. Attacks often target specific sections. Understanding which pages suffered most guides prioritization.
Prioritize Toxic Links by Risk Level
Not all toxic links require equal urgency. Prioritize removal efforts based on risk level and potential impact.
Critical priority (address immediately):
- Links from domains with manual actions
- Links from known link farms in Google’s database
- Exact-match anchor text on money keywords
- Links from adult, gambling, or pharmaceutical spam sites
High priority (address within first week):
- Links from hacked sites
- Links from PBN networks
- High-volume links from single sources
- Links with manipulative anchor text patterns
Medium priority (address within first month):
- Links from low-quality directories
- Links from irrelevant foreign sites
- Links from thin content sites
Low priority (monitor but may not require action):
- Random low-quality links appearing naturally
- Old links from defunct sites
- Links Google likely already ignores
Focus resources on critical and high-priority links first. These cause the most damage and require the most effort to address.
Create a Recovery Timeline and Action Plan
Structured timelines keep recovery on track. Link attack recovery typically spans 4-12 weeks depending on attack severity and penalty type.
Week 1: Assessment and Documentation
- Complete backlink audit across all tools
- Document attack evidence
- Assess ranking and traffic damage
- Identify and categorize all toxic links
Weeks 2-3: Outreach and Removal Requests
- Send removal requests to webmasters
- Follow up on non-responses
- Document all outreach attempts
- Begin compiling disavow file
Week 4: Disavow Submission
- Finalize disavow file
- Submit through Google Search Console
- Submit reconsideration request if manual action exists
Weeks 5-12: Monitoring and Recovery
- Track ranking changes weekly
- Monitor for new attack links
- Adjust disavow file as needed
- Document recovery progress
Adjust timelines based on attack scale. Massive attacks with 50,000+ links require extended outreach periods.
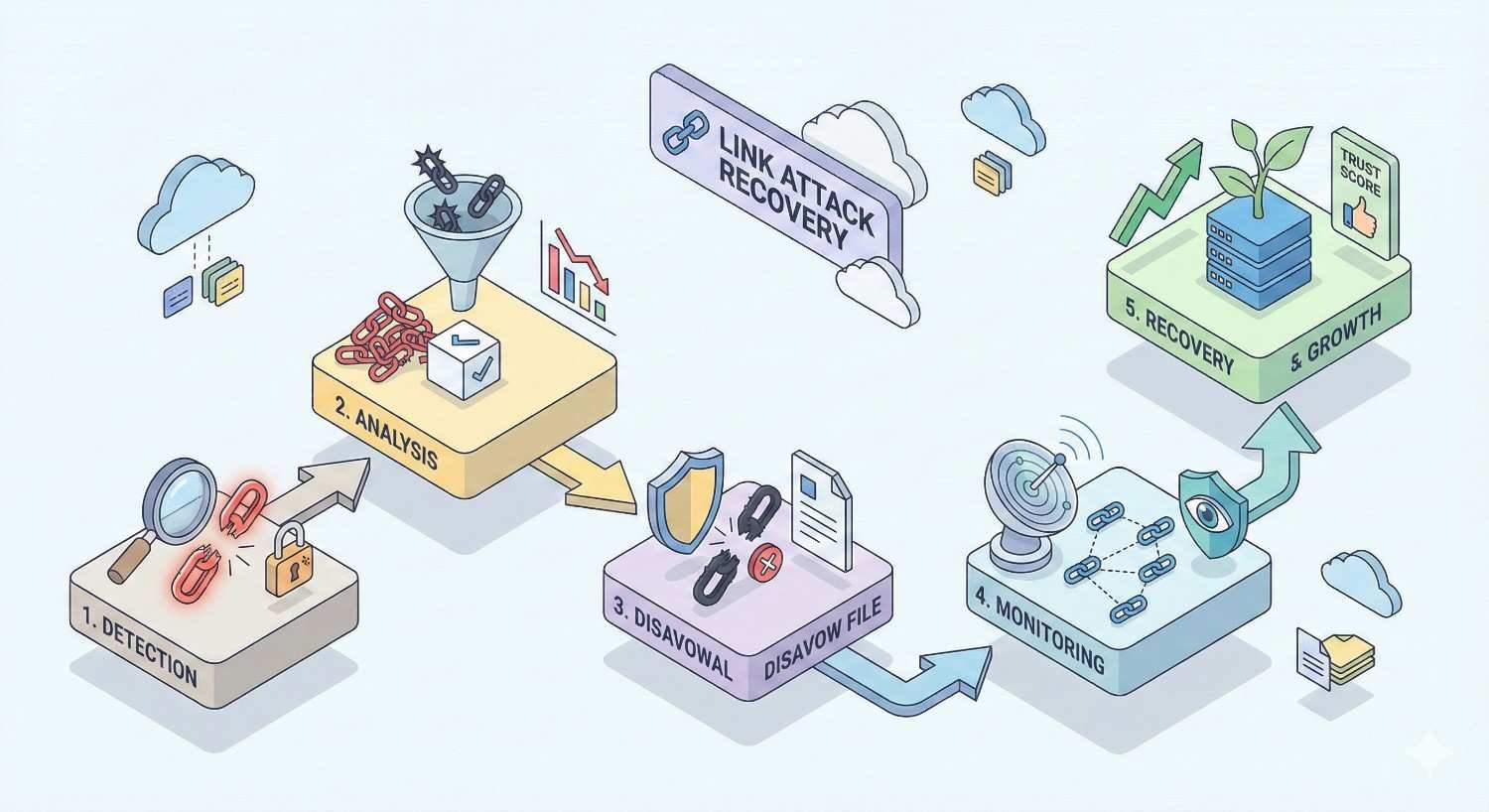
Link Attack Recovery Process: Step-by-Step Removal Strategy
Step 1: Export and Audit Your Complete Backlink Profile
Comprehensive backlink data forms the foundation of recovery. Export data from multiple sources to ensure complete coverage.
Export from Google Search Console:
- Navigate to Links > External links
- Click “Export external links” in the top right
- Download both “Top linking sites” and “Top linking text”
Export from third-party tools:
- Ahrefs: Backlink report > Export > Full export
- Semrush: Backlink Analytics > Export
- Moz: Link Explorer > Export CSV
- Majestic: Backlinks > Download
Combine exports into a master spreadsheet. Remove duplicates based on linking URL. Your master list should include:
- Linking URL
- Linking domain
- Target URL on your site
- Anchor text
- First seen date
- Domain metrics (DA, spam score, Trust Flow)
This master list becomes your working document throughout recovery.
Step 2: Identify and Categorize Toxic Links
Systematic categorization ensures no toxic links escape review. Apply consistent criteria across your entire backlink profile.
Spam Score Analysis
Spam score metrics predict link toxicity based on multiple signals. Moz’s spam score analyzes 27 factors including thin content, low traffic, and link patterns.
Spam score interpretation:
- 1-30%: Low risk, likely natural
- 31-60%: Medium risk, review manually
- 61-100%: High risk, likely toxic
Don’t rely solely on spam scores. Manual review catches issues automated scores miss. Use spam scores for initial sorting, then verify manually.
Domain Authority and Trust Metrics
Low domain authority alone doesn’t indicate toxicity. Many legitimate small sites have low DA. Combine DA analysis with other signals.
Concerning patterns:
- DA under 10 with hundreds of external links
- Large gap between Majestic Trust Flow and Citation Flow
- Domain authority that dropped significantly recently
- New domains with artificially inflated metrics
Compare linking domain metrics against their link profiles. Legitimate low-DA sites have proportional link counts. Spam sites have disproportionate outbound links.
Anchor Text Over-Optimization
Analyze anchor text distribution across your entire profile. Natural profiles show diversity. Attack profiles show concentration.
Healthy anchor text distribution:
- Branded anchors: 30-40%
- Naked URLs: 20-30%
- Generic anchors: 15-25%
- Partial match keywords: 10-15%
- Exact match keywords: 5-10%
Flag links contributing to over-optimization. If your exact-match anchor ratio exceeds 15-20%, those links likely need disavowing.
Link Velocity Anomalies
Chart your link acquisition over time. Natural growth shows gradual increases with occasional spikes from viral content or PR.
Attack patterns show:
- Sudden spikes without corresponding content or PR
- Sustained high velocity over weeks
- Velocity increases coinciding with ranking drops
- Links appearing in coordinated bursts from similar sources
Identify the attack start date through velocity analysis. All links appearing after this date from suspicious sources warrant scrutiny.
Step 3: Manual Outreach for Link Removal
Manual outreach demonstrates good faith effort to Google. While success rates are low, documented attempts strengthen reconsideration requests.
Crafting Effective Removal Requests
Keep removal requests brief and professional. Webmasters receive many such requests. Respect their time.
Effective removal request template:
Copy
Subject: Link Removal Request – [Your Domain]
Hello,
I’m contacting you regarding a link from your website [linking URL] to our site [your domain].
This link appears to violate Google’s Webmaster Guidelines, and we’re working to clean our backlink profile. We would appreciate if you could remove this link.
The specific link is:
From: [full linking URL]
To: [your target URL]
Thank you for your assistance.
[Your name]
[Contact information]
Avoid accusatory language. Many webmasters don’t know their sites contain spam links, especially if their sites were hacked.
Finding Contact Information
Locating webmaster contact information requires detective work. Many spam sites lack obvious contact details.
Contact finding methods:
- WHOIS lookup for domain registration email
- Contact pages on the website
- Social media profiles linked from the site
- LinkedIn searches for site owners
- Email patterns like admin@domain.com or webmaster@domain.com
Use tools like Hunter.io or Voila Norbert for email discovery. These tools find email patterns associated with domains.
For hacked sites, contact the legitimate owner. They may not know their site was compromised. Your notification helps them while potentially removing your toxic link.
Follow-Up Sequences and Timing
Initial outreach yields low response rates. Follow-up increases success but requires patience.
Recommended follow-up sequence:
- Day 1: Send initial removal request
- Day 7: First follow-up if no response
- Day 14: Second follow-up with slightly different subject line
- Day 21: Final follow-up noting you’ll proceed with disavow
Stop after three attempts. Further contact wastes resources and may appear harassing. Document each attempt for your records.
Documenting Removal Attempts
Thorough documentation proves your good faith efforts. Google’s webspam team reviews this documentation during reconsideration.
Document for each toxic link:
- Date of initial outreach
- Email address contacted
- Copy of email sent
- Any responses received
- Follow-up dates and content
- Outcome (removed, no response, refused)
Create a spreadsheet tracking all outreach. Include columns for each data point above. This becomes evidence for your reconsideration request.
Step 4: Prepare and Submit Google Disavow File
The disavow tool tells Google to ignore specific links when assessing your site. This is your primary weapon against link attacks.
Disavow File Format and Syntax
Disavow files use plain text format with specific syntax rules. Errors in formatting can invalidate entries.
Correct format:
Copy
# Disavow file for example.com
# Created: [date]
# Reason: Negative SEO link attack recovery
# Spam domains
domain:spamsite1.com
domain:spamsite2.com
# Specific URLs from partially legitimate sites
http://example.org/spam-page.html
https://anothersite.com/bad-link/
Syntax rules:
- One entry per line
- Comments start with # symbol
- Domain-level disavows use “domain:” prefix
- URL-level disavows use full URL including protocol
- File must be .txt format with UTF-8 encoding
Domain vs. URL-Level Disavows
Choose between domain-level and URL-level disavows based on the source site’s nature.
Use domain-level disavows when:
- The entire site is spam or a link farm
- Multiple pages from the same domain link to you
- The domain has no legitimate content
- You want to prevent future links from that domain
Use URL-level disavows when:
- Only specific pages contain toxic links
- The domain has some legitimate content
- You have legitimate links from other pages on that domain
- The site was hacked and only certain pages affected
Domain-level disavows are more efficient for large-scale attacks. They prevent future links from the same sources automatically.
Disavow File Best Practices
Effective disavow files balance thoroughness with precision. Over-disavowing harms your profile. Under-disavowing leaves toxic links active.
Best practices:
- Include comments explaining your reasoning
- Group entries by category (spam domains, hacked sites, PBNs)
- Date your file for version tracking
- Keep backup copies of previous versions
- Review and update quarterly
Avoid disavowing:
- Links from legitimate sites you don’t recognize
- Links from news sites or press coverage
- Links from industry directories with editorial standards
- Any link you’re uncertain about
When uncertain, err toward not disavowing. You can always add links later. Removing legitimate links from your disavow file doesn’t restore their value.
Submission Through Google Search Console
Submit your disavow file through Google Search Console’s disavow tool.
Submission process:
- Go to Google’s Disavow Links tool
- Select your property
- Click “Disavow Links”
- Upload your .txt file
- Confirm submission
Important notes:
- New files replace previous submissions entirely
- Include all links you want disavowed in each submission
- Processing takes weeks to months
- No confirmation of processing completion
Resubmit updated files as you identify new toxic links. Each submission replaces the previous file, so include all entries.
Step 5: Monitor Disavow Processing and Recovery Signals
Recovery monitoring requires patience and consistent tracking. Changes happen gradually over weeks and months.
Key monitoring activities:
- Weekly ranking checks: Track target keywords for position changes
- Monthly traffic analysis: Compare organic sessions month-over-month
- Backlink profile monitoring: Watch for new attack links
- Search Console review: Check for new manual actions or messages
Recovery signals to watch:
- Gradual ranking improvements for affected keywords
- Organic traffic stabilization then growth
- Crawl rate increases from Googlebot
- Indexed page count stabilization
Don’t expect immediate results. Disavow processing takes 2-4 weeks minimum. Algorithmic recovery can take 3-6 months after disavow processing.
Recovering from Google Penalties: Manual Actions vs. Algorithmic Filters
Manual Penalty Reconsideration Requests
Manual actions require formal reconsideration requests. Google won’t lift manual penalties automatically, regardless of cleanup efforts.
Writing Effective Reconsideration Requests
Reconsideration requests must demonstrate thorough cleanup and understanding of the issue. Vague requests get rejected.
Effective request structure:
Opening: Acknowledge the issue directly. Don’t make excuses or blame others initially.
Explanation: Describe what happened. If you were attacked, explain the evidence. If you made mistakes, own them.
Actions taken: Detail every cleanup step:
- Number of toxic links identified
- Outreach attempts made and response rates
- Disavow file submission date and contents
- Any other remediation steps
Prevention measures: Explain how you’ll prevent recurrence:
- Monitoring systems implemented
- Regular audit schedules
- Policy changes
Closing: Request review and express commitment to guidelines compliance.
Required Documentation and Evidence
Support your request with comprehensive documentation. Google’s team reviews this evidence when evaluating your request.
Essential documentation:
- Spreadsheet of toxic links identified
- Outreach log with dates and responses
- Copy of disavow file submitted
- Screenshots showing attack timeline
- Traffic and ranking data showing impact
- Evidence of attack origin if available
Organize documentation clearly. Label files descriptively. Make it easy for reviewers to verify your claims.
Response Times and Follow-Up Process
Google typically responds to reconsideration requests within 2-4 weeks. Complex cases may take longer.
Possible responses:
- Approved: Manual action lifted, rankings should recover
- Denied: Additional cleanup required, resubmit after addressing issues
- Partial: Some issues resolved, others remain
If denied, review Google’s feedback carefully. They often specify what issues remain. Address these specifically before resubmitting.
Wait at least two weeks between submissions. Rapid resubmissions without meaningful changes waste everyone’s time and may delay your case.
Algorithmic Recovery Timeline and Expectations
Algorithmic penalties have no reconsideration process. Recovery happens automatically when Google’s algorithms reassess your cleaned profile.
Timeline factors:
- Crawl frequency: How often Google recrawls linking pages
- Index updates: When Google processes disavow files
- Algorithm refreshes: Core updates can accelerate or reset recovery
- Profile severity: Worse profiles take longer to recover
Typical algorithmic recovery timeline:
- Weeks 1-4: Disavow processing, minimal visible change
- Weeks 5-8: Initial ranking stabilization
- Weeks 9-16: Gradual ranking improvements
- Months 4-6: Substantial recovery for most sites
Some sites recover faster. Others take longer. Severity of the original penalty and thoroughness of cleanup determine speed.
Tracking Recovery Metrics and KPIs
Establish clear metrics to measure recovery progress. Tracking prevents premature conclusions and guides ongoing efforts.
Primary recovery KPIs:
- Organic traffic: Weekly sessions compared to pre-attack baseline
- Keyword rankings: Position tracking for top 20-50 keywords
- Visibility score: Aggregate ranking metric from SEO tools
- Conversion rate: Ensure traffic quality recovers alongside volume
Secondary metrics:
- Crawl stats: Pages crawled per day in Search Console
- Index coverage: Total indexed pages
- Click-through rate: Search Console performance data
- Backlink profile health: Ongoing toxic link percentage
Create a recovery dashboard tracking these metrics weekly. Visual trends reveal progress that daily fluctuations obscure.
Advanced Link Attack Recovery Techniques
Dealing with Large-Scale Automated Attacks
Massive attacks involving 50,000+ links require modified approaches. Standard processes don’t scale efficiently.
Large-scale attack strategies:
Batch processing: Group toxic links by domain patterns. Many attacks use similar domain structures. Identify patterns and disavow at domain level.
Automated categorization: Use tools with bulk toxicity scoring. Manual review of 50,000 links is impractical. Focus manual review on borderline cases.
Prioritized cleanup: Address the most damaging links first. Links from known penalty networks and exact-match anchors cause the most harm.
Phased disavow submissions: Submit initial disavow covering critical links. Add additional links in subsequent submissions as you process more data.
For attacks exceeding 100,000 links, consider professional assistance. The complexity and time investment often justify expert help.
Recovering from Negative Anchor Text Attacks
Anchor text attacks require specific remediation beyond link removal. The damage persists even after toxic links are disavowed.
Anchor text recovery strategies:
Dilution through new links: Build legitimate links with natural anchor text. Branded anchors and naked URLs help normalize your profile.
Content optimization: Reduce on-page optimization for attacked keywords. This decreases the correlation between manipulative anchors and your content.
Anchor text monitoring: Track your anchor text distribution monthly. Watch for new attacks targeting the same keywords.
Recovery from anchor text attacks takes longer than standard link attacks. The algorithm needs time to recalculate your profile’s anchor distribution.
Handling Persistent or Recurring Attacks
Some attackers don’t stop after initial efforts. Persistent attacks require ongoing defense alongside recovery.
Persistent attack responses:
Real-time monitoring: Set up alerts for new backlinks. Catch new attack links within days rather than weeks.
Proactive disavow updates: Add new toxic links to your disavow file monthly. Don’t wait for damage to accumulate.
Pattern documentation: Track attack patterns for potential legal action. Consistent patterns from identifiable sources may support legal claims.
Competitor analysis: Monitor competitors’ backlink profiles. Attacks often target multiple sites in an industry simultaneously.
Consider whether the attacker is identifiable. Persistent attacks from traceable sources may warrant legal consultation.
When to Escalate to Google Support
Most link attack recovery happens through standard channels. Some situations warrant direct Google contact.
Escalation triggers:
- Reconsideration requests denied multiple times despite thorough cleanup
- Manual actions remain after documented complete remediation
- Attack involves Google properties or services
- Evidence of coordinated attacks across multiple sites
Escalation channels:
- Google Search Console help forums (monitored by Google staff)
- Google Webmaster Twitter account (@googlesearchc)
- Google Search Central documentation feedback
- Industry conferences where Google representatives attend
Escalation rarely provides faster resolution. Use standard processes first. Escalate only when standard processes have genuinely failed.
How Long Does Negative SEO Recovery Take?
Disavow Processing Timeframes
Disavow files don’t process instantly. Google must recrawl linking pages and reprocess your backlink profile.
Processing timeline:
- Submission confirmation: Immediate
- Initial processing: 2-4 weeks
- Full integration: 4-8 weeks
- Visible ranking impact: 6-12 weeks
Factors affecting processing speed:
- Size of disavow file
- Crawl frequency of linking domains
- Overall Google crawl budget for your site
- Timing relative to algorithm updates
Resubmitting updated disavow files restarts processing for new entries. Existing entries don’t reprocess unless the linking page changes.
Manual Action Removal Timeline
Manual action removal follows a more predictable timeline than algorithmic recovery.
Typical timeline:
- Reconsideration submission: Day 0
- Initial review: 1-2 weeks
- Decision communication: 2-4 weeks
- Penalty removal (if approved): Immediate upon approval
- Ranking recovery: 1-4 weeks after removal
Denied requests extend the timeline significantly. Each resubmission adds another 2-4 week review cycle.
First-time requests with thorough documentation have higher approval rates. Subsequent requests face increased scrutiny.
Algorithmic Recovery Expectations
Algorithmic recovery lacks the clear milestones of manual action removal. Progress happens gradually and sometimes inconsistently.
General expectations:
- Stabilization: 4-8 weeks after cleanup
- Initial improvements: 8-12 weeks
- Substantial recovery: 3-6 months
- Full recovery: 6-12 months for severe cases
Some rankings may never fully recover. Competitive landscapes change during recovery periods. Competitors may have strengthened while you were penalized.
Set realistic expectations. Recovery to pre-attack levels isn’t guaranteed. Recovery to competitive viability is the practical goal.
Factors That Affect Recovery Speed
Multiple factors influence how quickly your site recovers from link attacks.
Positive factors (faster recovery):
- Strong pre-attack domain authority
- Diverse, healthy existing backlink profile
- Quick attack detection and response
- Thorough cleanup and documentation
- Continued content publication during recovery
- New legitimate link acquisition
Negative factors (slower recovery):
- Weak pre-attack authority
- Previous penalty history
- Delayed response to attack
- Incomplete cleanup efforts
- Ongoing attack activity
- Competitive keyword targets
Sites with established authority before attacks typically recover faster. The algorithm has more positive signals to weigh against the negative.
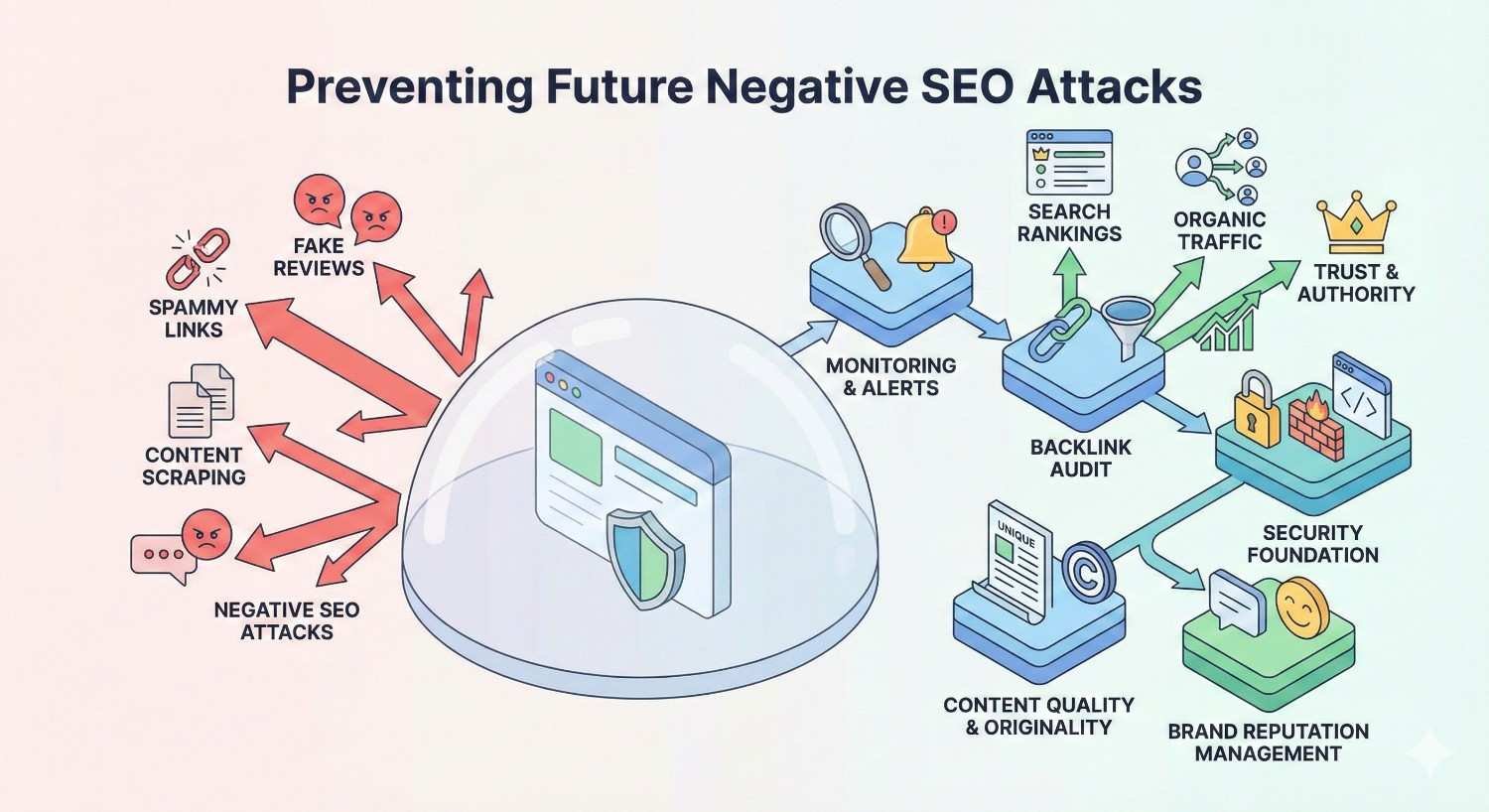
Preventing Future Negative SEO Attacks
Proactive Backlink Monitoring Systems
Prevention starts with visibility. You can’t respond to attacks you don’t detect.
Essential monitoring setup:
- Weekly backlink checks: Review new referring domains
- Anchor text tracking: Monitor distribution changes
- Link velocity alerts: Flag unusual acquisition spikes
- Competitor monitoring: Watch for industry-wide attacks
Establish baselines for normal activity. Your typical weekly new referring domains, anchor text distribution, and link sources. Deviations from baseline trigger investigation.
Setting Up Automated Alert Systems
Automated alerts enable rapid response. Manual checking alone misses fast-moving attacks.
Alert configuration:
Ahrefs alerts:
- New backlinks alert (daily)
- Lost backlinks alert (weekly)
- New referring domains alert (daily)
Semrush alerts:
- Backlink changes
- Toxic score increases
- Ranking drops
Google Search Console:
- Enable email notifications
- Check messages weekly minimum
Custom alerts:
- Google Alerts for brand mentions
- IFTTT recipes for social mentions
- Rank tracking alerts for position drops
Configure alert thresholds appropriately. Too sensitive creates noise. Too loose misses attacks.
Building a Strong Natural Link Profile as Defense
Strong backlink profiles resist attack damage better than weak ones. Legitimate links dilute toxic link impact.
Profile strengthening strategies:
- Content marketing: Create linkable assets that earn natural links
- Digital PR: Pursue press coverage and industry mentions
- Guest posting: Contribute to legitimate industry publications
- Resource link building: Create tools and resources others reference
- Relationship building: Develop connections that generate organic links
Diverse link sources provide resilience. Profiles dependent on few sources are vulnerable. Broad, natural profiles absorb attack links without proportional damage.
Regular Link Audits and Maintenance Schedule
Scheduled audits catch issues before they compound. Reactive-only approaches allow damage accumulation.
Recommended audit schedule:
- Monthly: Quick review of new links and anchor text changes
- Quarterly: Comprehensive backlink audit with toxicity analysis
- Annually: Full profile review with competitive benchmarking
Audit checklist:
- Export fresh backlink data from multiple tools
- Compare against previous audit baseline
- Identify new potentially toxic links
- Update disavow file if needed
- Document findings and actions
Treat audits as routine maintenance, not emergency response. Consistent attention prevents crises.
Legal Recourse and Reporting Malicious SEO
Legal options exist for documented, traceable attacks. Pursuing them requires clear evidence and realistic expectations.
Legal considerations:
- Documentation requirements: Prove attack origin and intent
- Jurisdiction challenges: Attackers often operate internationally
- Cost-benefit analysis: Legal action is expensive
- Practical outcomes: Injunctions may not stop determined attackers
Reporting options:
- Report to Google via spam report form
- Report to hosting providers of attack source sites
- Report to domain registrars for policy violations
- File complaints with relevant authorities for severe cases
Legal action makes sense for:
- Clearly identifiable attackers
- Documented financial damages
- Ongoing attacks despite other interventions
- Attacks involving additional illegal activity
Most link attacks don’t justify legal pursuit. Focus resources on recovery and prevention instead.
Negative SEO Recovery Tools and Resources
Essential Backlink Analysis Tools
Google Search Console
Google Search Console provides authoritative data directly from Google. It’s free and essential for any SEO work.
Key features for recovery:
- Links report showing external links to your site
- Manual actions section for penalty notifications
- Security issues alerts
- Disavow tool access
Limitations: Shows sampled data, not complete backlink profile. Use alongside third-party tools for comprehensive coverage.
Ahrefs Site Explorer
Ahrefs maintains one of the largest backlink indexes. Their crawler discovers links quickly, often before other tools.
Recovery-relevant features:
- New/lost backlinks tracking
- Referring domains analysis
- Anchor text reports
- Batch analysis for large link lists
- Disavow file export
Pricing starts at $99/month. The investment pays off for serious recovery efforts.
Semrush Backlink Audit
Semrush offers integrated toxicity scoring within their backlink audit tool. This streamlines toxic link identification.
Key features:
- Automatic toxicity scoring
- Toxic link categorization
- Outreach integration
- Disavow file generation
- Progress tracking
The audit tool specifically designed for cleanup work makes Semrush valuable for recovery projects.
Moz Link Explorer
Moz provides spam score metrics useful for toxicity assessment. Their domain authority metric remains an industry standard.
Useful features:
- Spam score for linking domains
- Domain authority tracking
- Link intersect analysis
- Discovered and lost links
Moz’s spam score algorithm analyzes 27 factors, providing nuanced toxicity assessment beyond simple metrics.
Majestic SEO
Majestic offers unique Trust Flow and Citation Flow metrics. The relationship between these metrics reveals link quality patterns.
Recovery applications:
- Trust Flow analysis for linking domains
- Topical Trust Flow for relevance assessment
- Historic index for finding old attack links
- Bulk backlink checker
Majestic’s historic index captures links other tools miss, valuable for identifying long-running attacks.
Toxic Link Detection Software
Specialized toxic link detection tools automate identification beyond general SEO platforms.
Notable options:
- Link Detox: Dedicated toxic link analysis with risk scoring
- Kerboo: Link auditing with removal workflow integration
- Linkody: Monitoring focused with toxicity alerts
- CognitiveSEO: Unnatural link detection algorithms
These tools complement rather than replace major platforms. Use them for second opinions on borderline links.
Disavow File Generators and Validators
Proper disavow file formatting prevents processing errors. Tools help ensure correct syntax.
Useful tools:
- Disavow File Generator (various): Convert spreadsheets to proper format
- Disavow File Validator: Check syntax before submission
- Merge tools: Combine multiple disavow files correctly
Most major SEO platforms include disavow export features. Semrush and Ahrefs both generate properly formatted files from their audit tools.
Monitoring and Alert Platforms
Continuous monitoring catches new attacks early. Dedicated monitoring platforms provide comprehensive coverage.
Monitoring solutions:
- Ahrefs Alerts: Backlink and mention monitoring
- Semrush Sensor: Algorithm volatility tracking
- Accuranker: Rank tracking with alerts
- Mention: Brand monitoring across web and social
Combine multiple monitoring approaches. No single tool catches everything. Layered monitoring provides comprehensive protection.
Case Studies: Successful Negative SEO Recovery Examples
E-commerce Site Recovery from 10,000+ Spam Links
An e-commerce site selling specialty kitchen equipment experienced a sudden 45% organic traffic drop over two weeks. Investigation revealed over 12,000 new backlinks from foreign gambling and pharmaceutical sites.
Attack characteristics:
- Links appeared over 10-day period
- Anchor text heavily used commercial keywords
- Links came from 3,400 unique referring domains
- Attack coincided with holiday shopping season
Recovery approach:
- Immediate documentation of all attack links
- Categorization by source type and toxicity level
- Outreach to 200 identifiable webmasters (8% response rate)
- Comprehensive disavow file covering 3,200 domains
- Reconsideration request with full documentation
Timeline and results:
- Week 1-2: Assessment and documentation
- Week 3-4: Outreach and disavow preparation
- Week 5: Disavow submission
- Week 8: Initial ranking stabilization
- Week 14: Traffic returned to 85% of pre-attack levels
- Week 20: Full recovery achieved
Key success factors: Quick detection, thorough documentation, comprehensive disavow file, patience during recovery period.
Local Business Manual Penalty Reversal
A local plumbing company received a manual action notification for “unnatural links to your site.” The business owner had no knowledge of link building activities.
Investigation findings:
- Previous SEO agency had built links from low-quality directories
- Competitor had added 500+ spam links targeting the business
- Combined issues triggered manual review
Recovery approach:
- Separated agency links from attack links
- Documented agency relationship and termination
- Outreach to directory sites for removal
- Disavow file for remaining toxic links
- Detailed reconsideration request explaining both issues
Reconsideration request strategy:
- Acknowledged agency link building was a mistake
- Provided evidence of attack links being external
- Documented all removal attempts
- Outlined new link monitoring procedures
Results:
- First reconsideration request denied (incomplete cleanup)
- Additional 200 links identified and addressed
- Second request approved after 3 weeks
- Rankings recovered within 6 weeks of penalty removal
Lesson learned: Thorough initial cleanup prevents denied requests. The second round of cleanup could have been included initially.
SaaS Company Algorithmic Recovery Timeline
A B2B SaaS company noticed gradual ranking decline over three months. No manual action appeared. Investigation revealed an algorithmic penalty from accumulated toxic links.
Situation analysis:
- Rankings declined 30% over 90 days
- No single attack event, but steady toxic link accumulation
- Competitor analysis suggested coordinated industry targeting
- Multiple SaaS companies in the space experienced similar issues
Recovery approach:
- Comprehensive backlink audit identifying 8,000 toxic links
- Pattern analysis revealing common attack sources
- Industry collaboration sharing attack source information
- Phased disavow submissions over 6 weeks
- Continued content marketing during recovery
Extended timeline:
- Month 1: Audit and initial disavow
- Month 2: Additional toxic links identified, disavow updated
- Month 3: Ranking stabilization observed
- Month 4: Gradual improvements begin
- Month 5-6: Significant recovery
- Month 8: Rankings exceeded pre-attack levels
Contributing factors to success:
- Continued publishing during recovery maintained freshness signals
- New legitimate links diluted toxic link percentage
- Industry collaboration identified attack sources faster
- Patient, systematic approach rather than panic responses
When to Hire Professional Help for Link Attack Recovery
Signs You Need Expert Assistance
Self-recovery works for many situations. Some circumstances warrant professional involvement.
Hire professionals when:
- Attack involves 25,000+ toxic links
- Multiple reconsideration requests denied
- Attack combines multiple negative SEO tactics
- Internal resources lack SEO expertise
- Revenue loss exceeds cost of professional help
- Attack is ongoing despite defensive measures
- Legal action may be necessary
Self-recovery is appropriate when:
- Attack is relatively small (under 5,000 links)
- You have SEO knowledge and available time
- Clear attack pattern is identifiable
- No manual action exists
- Budget constraints prevent professional engagement
Assess honestly. Underestimating attack severity delays recovery. Overestimating wastes resources on unnecessary services.
What Professional SEO Recovery Services Include
Professional recovery services provide expertise and resources beyond typical in-house capabilities.
Standard service components:
- Comprehensive backlink audit across all major tools
- Toxic link identification and categorization
- Outreach campaign management
- Disavow file creation and submission
- Reconsideration request writing
- Recovery monitoring and reporting
- Prevention strategy development
Advanced services may include:
- Legal consultation coordination
- Competitor attack analysis
- Industry-wide attack pattern research
- Ongoing monitoring and maintenance
- Staff training on prevention
Clarify deliverables before engagement. Understand exactly what’s included and what costs extra.
Evaluating Negative SEO Recovery Specialists
Not all SEO professionals have recovery expertise. Evaluate specialists specifically for this work.
Evaluation criteria:
- Documented recovery case studies
- Specific experience with your attack type
- Clear process explanation
- Realistic timeline expectations
- Transparent pricing structure
- References from recovery clients
- Knowledge of current Google guidelines
Red flags:
- Guaranteed recovery timelines
- Promises of specific ranking positions
- Unwillingness to explain methodology
- No case studies or references
- Pricing significantly below market rates
- Pressure tactics or urgency creation
Request detailed proposals from multiple providers. Compare approaches, not just prices.
Expected Costs and ROI of Professional Recovery
Professional recovery services vary widely in cost based on attack severity and service scope.
Typical cost ranges:
- Basic recovery (small attacks): $1,500-$5,000
- Standard recovery (medium attacks): $5,000-$15,000
- Complex recovery (large attacks, manual actions): $15,000-$50,000+
- Ongoing monitoring retainers: $500-$2,000/month
ROI calculation factors:
- Current organic traffic value
- Revenue per organic visitor
- Duration of ranking loss
- Cost of delayed recovery
- Internal resource opportunity cost
Calculate your daily revenue loss from the attack. Compare against professional service costs. If professional help accelerates recovery by even a few weeks, the ROI often justifies the investment.
Negative SEO Recovery Checklist and Action Plan
Immediate Actions (First 48 Hours)
Hour 1-4: Initial Assessment
- Check Google Search Console for manual actions
- Review recent ranking changes in tracking tools
- Export current backlink profile from primary tool
- Screenshot current traffic and ranking data
Hour 4-12: Attack Confirmation
- Identify new toxic backlinks
- Determine attack start date
- Assess attack scale (number of links/domains)
- Document attack characteristics
Hour 12-24: Stakeholder Communication
- Brief relevant team members
- Assess business impact
- Determine resource allocation for recovery
- Decide on professional help if needed
Hour 24-48: Initial Response
- Begin comprehensive backlink audit
- Start toxic link categorization
- Create documentation folder
- Establish monitoring for new attack links
Short-Term Recovery Tasks (Week 1-4)
Week 1: Complete Assessment
- Export backlinks from all major tools
- Create master toxic link spreadsheet
- Categorize links by toxicity level
- Prioritize links for removal/disavow
- Calculate total attack scope
Week 2: Outreach Campaign
- Identify contactable webmasters
- Send initial removal requests
- Document all outreach attempts
- Begin disavow file preparation
Week 3: Follow-Up and Disavow
- Send follow-up removal requests
- Finalize disavow file
- Review disavow file for errors
- Submit disavow through Search Console
Week 4: Reconsideration (if applicable)
- Compile all documentation
- Write reconsideration request
- Submit reconsideration request
- Continue monitoring for new attacks
Long-Term Monitoring and Prevention (Ongoing)
Monthly Tasks:
- Review new backlinks for toxicity
- Update disavow file if needed
- Check Search Console for issues
- Track ranking recovery progress
- Assess ongoing attack activity
Quarterly Tasks:
- Comprehensive backlink audit
- Anchor text distribution analysis
- Competitive backlink comparison
- Prevention system effectiveness review
- Update recovery documentation
Annual Tasks:
- Full backlink profile review
- Tool and process evaluation
- Team training on detection/response
- Prevention strategy update
- Budget review for tools/services
Downloadable Recovery Workflow Template
Create your recovery workflow document including:
Section 1: Attack Documentation
- Attack discovery date
- Attack characteristics
- Total toxic links identified
- Estimated business impact
Section 2: Recovery Timeline
- Key milestone dates
- Responsible parties
- Status tracking
- Completion verification
Section 3: Tool Access
- Google Search Console credentials
- Third-party tool logins
- Monitoring alert configurations
- Team access permissions
Section 4: Communication Log
- Outreach attempts record
- Response tracking
- Internal communications
- Google correspondence
Section 5: Recovery Metrics
- Baseline traffic/rankings
- Weekly progress tracking
- Recovery milestone achievements
- Final outcome documentation
Conclusion
Negative SEO link attacks threaten rankings, but systematic recovery restores organic visibility. Detection, documentation, disavow submission, and patient monitoring form the core recovery process. Most sites achieve substantial recovery within three to six months.
Prevention matters as much as recovery. Proactive monitoring, strong natural link profiles, and regular audits reduce vulnerability. The investment in prevention costs far less than recovery efforts.
We help businesses recover from link attacks and build resilient SEO foundations. White Label SEO Service provides comprehensive recovery support, from initial audit through full restoration. Contact us to assess your situation and develop your recovery plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if I’m experiencing a negative SEO attack?
Look for sudden ranking drops combined with backlink profile spikes. Check your backlink tools for hundreds of new links from low-quality, foreign, or spam sites appearing within days. Manual action notifications in Google Search Console confirm penalty situations.
Can Google automatically ignore negative SEO links?
Google claims to ignore most spammy links automatically. However, large-scale attacks with specific patterns still cause ranking damage. The disavow tool exists because automatic detection isn’t perfect. Proactive disavowing remains the safest approach for confirmed attacks.
How long does it take to recover from a link attack?
Recovery typically takes three to six months for algorithmic penalties. Manual action recovery can be faster once approved, usually two to four weeks after penalty removal. Severe attacks or denied reconsideration requests extend timelines significantly.
Should I disavow all low-quality links pointing to my site?
No. Disavow only confirmed toxic links from attacks or manipulative sources. Many low-quality links occur naturally and cause no harm. Over-disavowing can remove legitimate link equity. Focus on clearly toxic links with spam characteristics.
What’s the difference between a manual action and an algorithmic penalty?
Manual actions come from human reviewers and appear as notifications in Search Console. They require reconsideration requests for removal. Algorithmic penalties happen automatically with no notification. They resolve when algorithms reassess your cleaned profile during updates.
Can I sue someone for negative SEO attacks?
Legal action is possible but challenging. You need clear evidence of the attacker’s identity and intent, plus documented financial damages. International jurisdiction complicates most cases. Legal costs often exceed practical benefits. Focus on recovery first.
How often should I audit my backlink profile for attacks?
Monitor new backlinks weekly using automated alerts. Conduct comprehensive audits quarterly. Increase frequency if you’ve experienced previous attacks or operate in competitive industries where negative SEO is common.