A structured content workflow management system transforms chaotic content production into a predictable engine for organic growth, reducing production time by up to 40% while improving content quality and SEO consistency. Without clear workflows, marketing teams waste hours on miscommunication, missed deadlines, and inconsistent output that undermines search visibility.
This matters because search engines reward consistent, high-quality content published at sustainable velocity. Disorganized teams struggle to maintain the publishing frequency needed to build topical authority and compete for rankings.
This guide covers everything from workflow fundamentals and key stages to tools, templates, and measurement frameworks. You’ll learn how to build, optimize, and scale content workflows that directly support your SEO strategy and business growth.
What Is Content Workflow Management?
Content workflow management is the systematic approach to planning, creating, reviewing, publishing, and optimizing content across your organization. It defines who does what, when they do it, and how each piece moves from concept to published asset.
Understanding this foundation helps you identify gaps in your current process and build systems that scale with your content ambitions.
Definition and Core Components
Content workflow management encompasses the processes, tools, and governance structures that guide content from ideation through publication and performance analysis. The core components include task assignment, status tracking, approval gates, deadline management, and feedback loops.
A complete workflow system addresses five essential elements. First, process documentation outlines each step in content creation. Second, role definitions clarify responsibilities. Third, approval hierarchies establish quality checkpoints. Fourth, timeline structures set realistic deadlines. Fifth, feedback mechanisms enable continuous improvement.
These components work together to eliminate ambiguity. When every team member knows their responsibilities and handoff points, content moves efficiently through the pipeline without bottlenecks or confusion.
How Content Workflows Differ from Project Management
Project management focuses on delivering specific outcomes within defined constraints of scope, time, and budget. Content workflows are specialized systems designed for the unique, repetitive nature of content production.
The key difference lies in repeatability. A project has a defined end point. Content workflows are ongoing cycles that repeat with each new piece. This requires different thinking about templates, automation, and process optimization.
Content workflows also involve creative processes that don’t fit neatly into traditional project management frameworks. Review cycles, stakeholder feedback, and SEO optimization require specialized checkpoints that generic project tools often lack.
The Role of Content Workflows in Marketing Operations
Within marketing operations, content workflows serve as the production backbone that enables consistent execution of content strategy. They connect strategic planning to tactical delivery.
Marketing operations depend on predictable content output to support campaigns, nurture sequences, and organic growth initiatives. Without reliable workflows, marketing teams cannot accurately forecast content availability or plan integrated campaigns.
Effective content workflows also provide visibility into production capacity. This helps marketing leaders make informed decisions about resource allocation, agency partnerships, and content investment priorities.
Why Content Workflow Management Matters for Business Growth
Content workflow management directly impacts your ability to scale content production, maintain quality standards, and achieve measurable business outcomes. The connection between operational efficiency and growth is often underestimated.
Organizations with mature content workflows consistently outperform competitors in content velocity, quality consistency, and organic search performance.
Impact on Team Productivity and Collaboration
Structured workflows eliminate the productivity drain caused by unclear responsibilities, redundant communication, and context switching. Teams spend less time figuring out what to do next and more time creating valuable content.
Collaboration improves when everyone understands the process. Writers know when to expect briefs. Editors know when drafts arrive. Stakeholders know when to provide feedback. This clarity reduces friction and accelerates production.
The productivity gains compound over time. As teams internalize workflows, they identify optimization opportunities and develop shortcuts that further increase efficiency without sacrificing quality.
Connection to Content Quality and Consistency
Quality control becomes systematic rather than accidental when embedded in workflows. Defined review stages, style guide checkpoints, and approval gates ensure every piece meets established standards before publication.
Consistency across content builds brand authority and reader trust. When workflows enforce consistent formatting, tone, voice, and accuracy standards, your content library presents a unified, professional presence.
This consistency also supports SEO performance. Search engines recognize topical expertise partly through consistent content quality and presentation. Erratic quality signals undermine the authority you’re trying to build.
How Workflows Affect SEO Performance and Organic Visibility
SEO success requires sustained effort over time. Content workflows enable the consistent publishing velocity that builds topical authority and signals relevance to search engines.
Workflows that incorporate SEO checkpoints ensure optimization isn’t an afterthought. Keyword targeting, internal linking, meta data, and technical requirements become standard steps rather than occasional additions.
The connection between workflow maturity and organic growth is measurable. Teams with documented workflows publish more consistently, maintain higher quality standards, and achieve better rankings than teams operating without structured processes.
Key Stages of a Content Workflow
Every content workflow includes distinct stages that move content from initial concept to published asset and beyond. Understanding these stages helps you identify where your current process succeeds and where it breaks down.
The specific implementation varies by team size and content type, but the fundamental stages remain consistent across organizations.
Ideation and Content Planning
Ideation transforms business objectives and audience needs into specific content concepts. This stage includes keyword research, competitive analysis, topic clustering, and content calendar planning.
Effective ideation workflows capture ideas from multiple sources. Sales teams share customer questions. Support teams identify knowledge gaps. SEO analysis reveals ranking opportunities. Strategic planning defines priority topics.
The output of this stage is a prioritized content backlog with clear briefs that guide creation. Each brief should include target keywords, search intent, audience segment, content format, and success metrics.
Content Creation and Drafting
Creation is where concepts become drafts. This stage includes research, outlining, writing, and initial self-editing by the content creator.
Workflows should define expected deliverables at this stage. What format should drafts use? What metadata should accompany submissions? What quality standards must drafts meet before advancing to review?
Clear creation guidelines reduce revision cycles. When writers understand expectations upfront, they produce drafts that require less editing and move through subsequent stages faster.
Review, Editing, and Approval Processes
Review stages ensure content meets quality, accuracy, and brand standards before publication. This typically includes editorial review, subject matter expert validation, legal or compliance checks, and final approval.
The number and type of review stages depends on content type and organizational requirements. Blog posts might need only editorial review. Product content might require legal approval. Technical content might need SME validation.
Workflows should specify who reviews what, in what order, and with what authority. Parallel reviews accelerate timelines. Sequential reviews ensure each stage builds on previous feedback.
Publishing and Distribution
Publishing involves more than clicking a button. This stage includes final formatting, metadata completion, image optimization, internal linking, and scheduling.
Distribution extends content reach beyond organic search. Workflows should define how content gets shared across email, social media, paid channels, and partner networks.
Effective publishing workflows include checklists that ensure nothing gets missed. Technical SEO requirements, tracking parameters, and promotional assets should all be verified before content goes live.
Performance Tracking and Optimization
The workflow doesn’t end at publication. Performance tracking identifies what’s working and what needs improvement. This stage includes analytics review, ranking monitoring, and optimization planning.
Workflows should define when and how content gets reviewed post-publication. Weekly ranking checks, monthly traffic analysis, and quarterly content audits each serve different purposes.
Optimization workflows determine how underperforming content gets updated. Clear criteria for refresh priority, update processes, and republishing protocols keep your content library performing over time.
How to Build an Effective Content Workflow
Building an effective workflow requires understanding your current state, defining your desired future state, and creating the bridge between them. This isn’t a one-time project but an ongoing process of refinement.
Start with what you have. Document existing processes before designing new ones. This reveals what’s working, what’s broken, and what’s missing entirely.
Auditing Your Current Content Process
Begin by mapping how content actually moves through your organization today. Interview team members. Review recent projects. Identify where delays occur and why.
Document the informal processes that have developed organically. These often contain valuable insights about what works in your specific context. They also reveal workarounds that indicate process gaps.
Quantify current performance where possible. How long does content take from concept to publication? How many revision cycles occur? What percentage of content meets deadlines? These baselines help you measure improvement.
Defining Roles, Responsibilities, and Ownership
Clear role definitions eliminate the confusion that causes delays and dropped tasks. Every workflow stage needs an owner responsible for completion and quality.
Common content workflow roles include content strategist, writer, editor, SEO specialist, designer, and approver. Smaller teams combine roles. Larger teams may have multiple people in each role.
Document not just who does what, but who decides what. Decision rights matter as much as task assignments. When disagreements arise, clear authority prevents stalemates.
Setting Up Approval Hierarchies and Checkpoints
Approval hierarchies balance quality control with production speed. Too few checkpoints risk publishing substandard content. Too many create bottlenecks that slow everything down.
Design approval stages based on risk. High-stakes content like product pages or legal statements needs more review. Routine blog posts might need less. Match oversight to consequence.
Define what happens when approvers are unavailable. Backup approvers, time-limited auto-approvals, or escalation paths prevent single points of failure from stopping production.
Establishing Timelines and Deadlines
Realistic timelines account for actual production capacity, not wishful thinking. Base estimates on historical performance, adjusted for complexity and priority.
Build buffer time into workflows. Unexpected delays happen. Stakeholder feedback takes longer than expected. Technical issues arise. Buffers prevent cascading deadline failures.
Communicate deadlines clearly and track them visibly. When everyone sees the timeline, accountability increases and coordination improves.
Documenting Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
SOPs transform tribal knowledge into organizational assets. Document each workflow stage with enough detail that someone new could follow the process successfully.
Effective SOPs include step-by-step instructions, decision criteria, quality standards, tool instructions, and troubleshooting guidance. They answer both “what to do” and “how to do it.”
Keep SOPs updated as processes evolve. Outdated documentation is worse than no documentation because it creates confusion and erodes trust in the system.
Content Workflow Management Tools and Software
The right tools amplify workflow effectiveness. The wrong tools create friction and frustration. Tool selection should follow process design, not precede it.
Understand your workflow requirements before evaluating tools. Features that don’t match your process add complexity without value.
Types of Content Workflow Platforms
Content workflow tools fall into several categories. Project management platforms like Asana, Monday, and Trello provide general task and workflow management. Content-specific platforms like CoSchedule, Contently, and GatherContent offer specialized features for content teams.
Enterprise content management systems include workflow capabilities alongside content storage and governance. Marketing automation platforms often include content workflow features integrated with campaign management.
Spreadsheets and documents remain viable for small teams with simple workflows. The best tool is the one your team will actually use consistently.
Key Features to Look for in Workflow Tools
Essential features include task assignment, status tracking, deadline management, and notification systems. These basics enable workflow execution regardless of platform.
Advanced features add value for complex workflows. Approval routing automates review sequences. Template libraries standardize recurring content types. Analytics dashboards provide visibility into workflow performance.
Integration capabilities matter increasingly as tech stacks grow. Tools that connect with your CMS, analytics, and communication platforms reduce manual data transfer and context switching.
Comparing Popular Content Workflow Solutions
Asana and Monday excel at flexible workflow configuration with strong collaboration features. They work well for teams that need customization and already use these tools for other projects.
CoSchedule and ContentCal focus specifically on content and social media workflows. They offer content calendar views and publishing integrations that general project tools lack.
Notion and Airtable provide database-driven flexibility that appeals to teams wanting to build custom workflow systems. They require more setup but offer maximum customization.
Enterprise solutions like Workfront and Wrike serve large organizations with complex approval requirements, resource management needs, and compliance obligations.
Integrating Workflow Tools with Your Tech Stack
Integration reduces friction between workflow management and content execution. Direct connections to your CMS eliminate manual content transfer. Analytics integrations bring performance data into workflow context.
Evaluate integration depth, not just availability. Native integrations typically work better than third-party connectors. API access enables custom integrations when needed.
Plan for integration maintenance. Connections break when platforms update. Someone needs responsibility for monitoring and fixing integrations when problems occur.
Content Workflow Best Practices
Best practices emerge from experience across many organizations and content types. They represent proven approaches that consistently improve workflow performance.
Apply these practices thoughtfully. What works for one team may need adaptation for another. Context matters.
Creating Repeatable and Scalable Processes
Repeatability comes from standardization. Templates, checklists, and documented procedures ensure consistent execution regardless of who performs the work.
Scalability requires processes that don’t break under increased volume. Identify bottlenecks before they become critical. Build capacity before you need it.
Automation supports both repeatability and scalability. Automate routine tasks like status updates, notifications, and handoffs. Reserve human attention for work that requires judgment.
Balancing Speed with Quality Control
Speed and quality exist in tension. Faster production risks quality problems. Excessive review slows everything down. Finding the right balance requires ongoing calibration.
Match review intensity to content risk. Not every piece needs the same scrutiny. Tiered review processes apply appropriate oversight without creating unnecessary delays.
Measure both speed and quality. Track production time and quality metrics together. Optimize for the combination, not either metric in isolation.
Managing Stakeholder Feedback Efficiently
Stakeholder feedback often creates workflow chaos. Multiple reviewers provide conflicting input. Feedback arrives late. Revision cycles multiply.
Consolidate feedback into single rounds where possible. Designate someone to reconcile conflicting input before returning to creators. Set clear deadlines for feedback with consequences for missing them.
Educate stakeholders on effective feedback. Specific, actionable comments improve content. Vague preferences create confusion. Training stakeholders improves feedback quality over time.
Continuous Workflow Improvement and Iteration
Workflows should evolve as your team, content strategy, and tools change. Build review cycles into your workflow management practice.
Gather feedback from workflow participants regularly. They see problems and opportunities that management misses. Create channels for suggestions and act on good ideas.
Measure workflow performance and set improvement targets. Production time, quality scores, deadline adherence, and team satisfaction all indicate workflow health.
Common Content Workflow Challenges and How to Solve Them
Every content team faces workflow challenges. Recognizing common problems helps you address them before they become critical.
Solutions exist for most workflow problems. The key is diagnosing accurately and implementing systematically.
Bottlenecks in the Approval Process
Approval bottlenecks occur when too much content requires too few approvers. Work queues up, deadlines slip, and frustration builds.
Solutions include adding backup approvers, implementing tiered approval based on content type, setting time limits on approval stages, and empowering more team members with approval authority for routine content.
Analyze where bottlenecks occur. Sometimes the problem isn’t approver capacity but unclear approval criteria that cause excessive back-and-forth.
Lack of Visibility Across Teams
When teams can’t see workflow status, coordination suffers. Writers don’t know if briefs are ready. Editors don’t know what’s coming. Leaders can’t forecast output.
Centralized workflow tools with shared dashboards solve visibility problems. Everyone sees the same information. Status updates happen in one place.
Regular workflow meetings supplement tool-based visibility. Brief daily or weekly check-ins surface issues that dashboards miss and maintain team alignment.
Inconsistent Content Quality
Quality inconsistency indicates process gaps. Some content meets standards while other content falls short. The difference usually traces to unclear standards, inadequate review, or skill gaps.
Document quality standards explicitly. Style guides, brand guidelines, and quality checklists give creators clear targets. Review processes should verify compliance with documented standards.
Address skill gaps through training, feedback, and coaching. When creators understand what quality looks like and how to achieve it, consistency improves.
Scaling Workflows for Growing Teams
Workflows that work for small teams often break as teams grow. Communication becomes harder. Coordination complexity increases. Informal processes that worked with five people fail with fifteen.
Anticipate scaling challenges before they arrive. Document processes while they’re still simple. Build systems that can accommodate growth.
Add structure incrementally as needed. Over-engineering workflows for a small team creates unnecessary overhead. Under-engineering for a large team creates chaos. Match structure to scale.
Content Workflow Management for Different Team Sizes
Team size significantly influences optimal workflow design. What works for a solopreneur differs dramatically from enterprise requirements.
Match your workflow complexity to your team reality. Aspiring to enterprise processes with a three-person team creates frustration, not efficiency.
Workflows for Solopreneurs and Small Teams
Solopreneurs and small teams need simple, lightweight workflows. Complex systems consume more time to maintain than they save.
Focus on the essentials. A content calendar, basic checklists, and simple templates provide structure without overhead. Tools like Notion, Trello, or even spreadsheets work well at this scale.
Document enough to maintain consistency but don’t over-engineer. As a small team, you can hold process knowledge in your head. Documentation becomes critical only as you grow.
Workflows for Mid-Size Marketing Teams
Mid-size teams of five to twenty people need more formal workflows. Informal coordination breaks down. Role clarity becomes essential.
Invest in proper workflow tools at this stage. The productivity gains justify the cost. Choose tools that can grow with you to avoid painful migrations later.
Designate workflow ownership. Someone needs responsibility for maintaining and improving processes. Without ownership, workflows drift and degrade.
Enterprise-Level Content Workflow Structures
Enterprise content workflows involve multiple teams, complex approval chains, compliance requirements, and integration with broader organizational systems.
Governance becomes critical at enterprise scale. Content standards, brand guidelines, and approval authorities need formal documentation and enforcement.
Enterprise workflows often require dedicated workflow management roles or teams. The complexity justifies specialized attention that smaller organizations can’t afford.
Measuring Content Workflow Effectiveness
Measurement enables improvement. Without metrics, you’re guessing about workflow performance. With metrics, you can identify problems, track progress, and demonstrate value.
Choose metrics that matter for your goals. Not everything measurable is worth measuring.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Workflows
Core workflow KPIs include production time, on-time delivery rate, revision cycles, and throughput. These metrics indicate operational efficiency.
Quality KPIs complement efficiency metrics. Error rates, compliance scores, and stakeholder satisfaction indicate whether speed comes at quality’s expense.
Team metrics matter too. Workload balance, overtime hours, and satisfaction scores indicate workflow sustainability. Efficient workflows that burn out teams aren’t truly effective.
Tracking Content Production Velocity
Content velocity measures how much content your team produces over time. Track pieces published, words produced, or content value delivered depending on what matters for your strategy.
Velocity trends matter more than absolute numbers. Increasing velocity indicates improving efficiency. Decreasing velocity signals problems requiring investigation.
Segment velocity by content type, team, or channel to identify specific improvement opportunities. Aggregate metrics hide important variations.
Connecting Workflow Metrics to Business Outcomes
Workflow metrics gain meaning when connected to business results. Production efficiency matters because it enables the content volume that drives organic growth.
Track the relationship between workflow performance and SEO outcomes. Does increased velocity correlate with traffic growth? Does quality improvement correlate with better rankings?
Build the business case for workflow investment by demonstrating ROI. Time saved, quality improved, and growth achieved all translate to business value.
Content Workflow Templates and Examples
Templates accelerate workflow implementation. Rather than designing from scratch, adapt proven structures to your specific needs.
These templates provide starting points. Customize them based on your team, content types, and organizational requirements.
Blog Content Workflow Template
A standard blog workflow includes seven stages. Ideation captures and prioritizes topics. Briefing creates detailed content specifications. Drafting produces initial content. Editing refines quality and accuracy. SEO optimization ensures search readiness. Approval confirms publication readiness. Publishing and promotion complete the cycle.
Each stage needs an owner, timeline, and completion criteria. For a typical blog post, allow two to three days for drafting, one to two days for editing, and one day for final optimization and approval.
Build in feedback loops. Post-publication performance review informs future ideation. Lessons learned improve subsequent content.
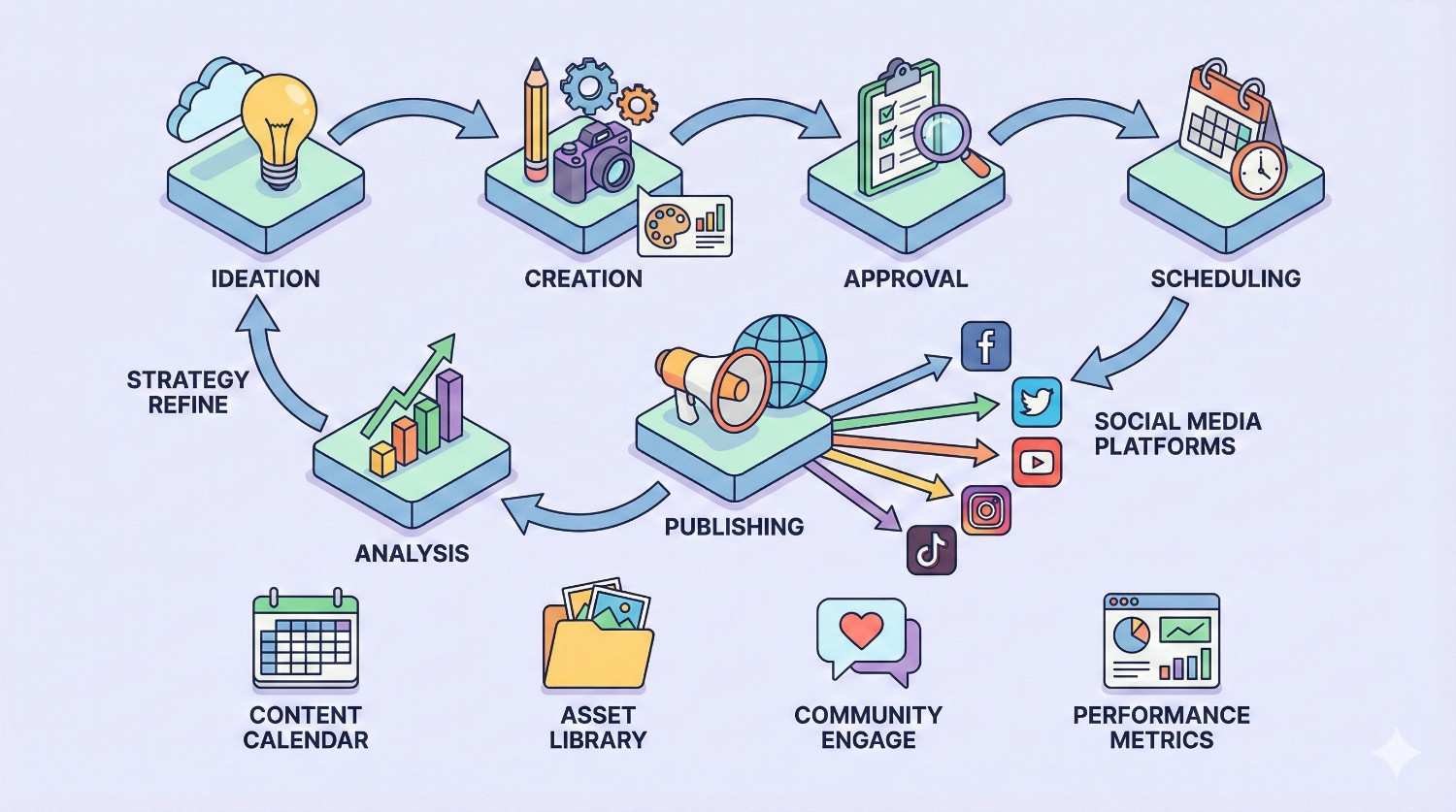
Social Media Content Workflow Template
Social media workflows operate on compressed timelines with higher volume. Batch creation improves efficiency. Approval processes must be fast.
A typical social workflow includes content planning, creation, review, scheduling, publishing, and engagement monitoring. The entire cycle might happen in hours rather than days.
Calendar-based planning enables batch creation. Create a week or month of content in focused sessions rather than scrambling daily.
Multi-Channel Content Campaign Workflow
Campaign workflows coordinate content across multiple channels and formats. A single campaign might include blog posts, social content, email sequences, landing pages, and paid media assets.
Start with campaign planning that defines objectives, audiences, messages, and channel mix. Then create channel-specific workflows that feed into the master campaign timeline.
Coordination checkpoints ensure channel consistency. Review meetings, shared calendars, and integrated tools keep everyone aligned on messaging and timing.
How Content Workflow Management Supports SEO Strategy
Content workflows and SEO strategy are deeply connected. Workflows enable the consistent, quality content production that SEO success requires.
Integrating SEO requirements into workflows ensures optimization happens systematically rather than sporadically.
Aligning Content Production with Keyword Targeting
Keyword strategy should drive content planning. Workflows that start with keyword research ensure every piece targets specific search opportunities.
Build keyword assignment into content briefs. Writers should know primary and secondary keywords, search intent, and competitive context before they start drafting.
Track keyword coverage across your content library. Workflow reporting should show which target keywords have content, which need content, and which need content updates.
Ensuring Technical SEO Requirements in Workflows
Technical SEO requirements belong in publishing checklists. Meta titles, descriptions, header structure, image optimization, schema markup, and internal linking should all be verified before publication.
Create SEO review stages for content that targets competitive keywords. SEO specialists should validate optimization before high-priority content publishes.
Automate technical checks where possible. Tools can verify meta data length, image alt text presence, and other technical requirements automatically.
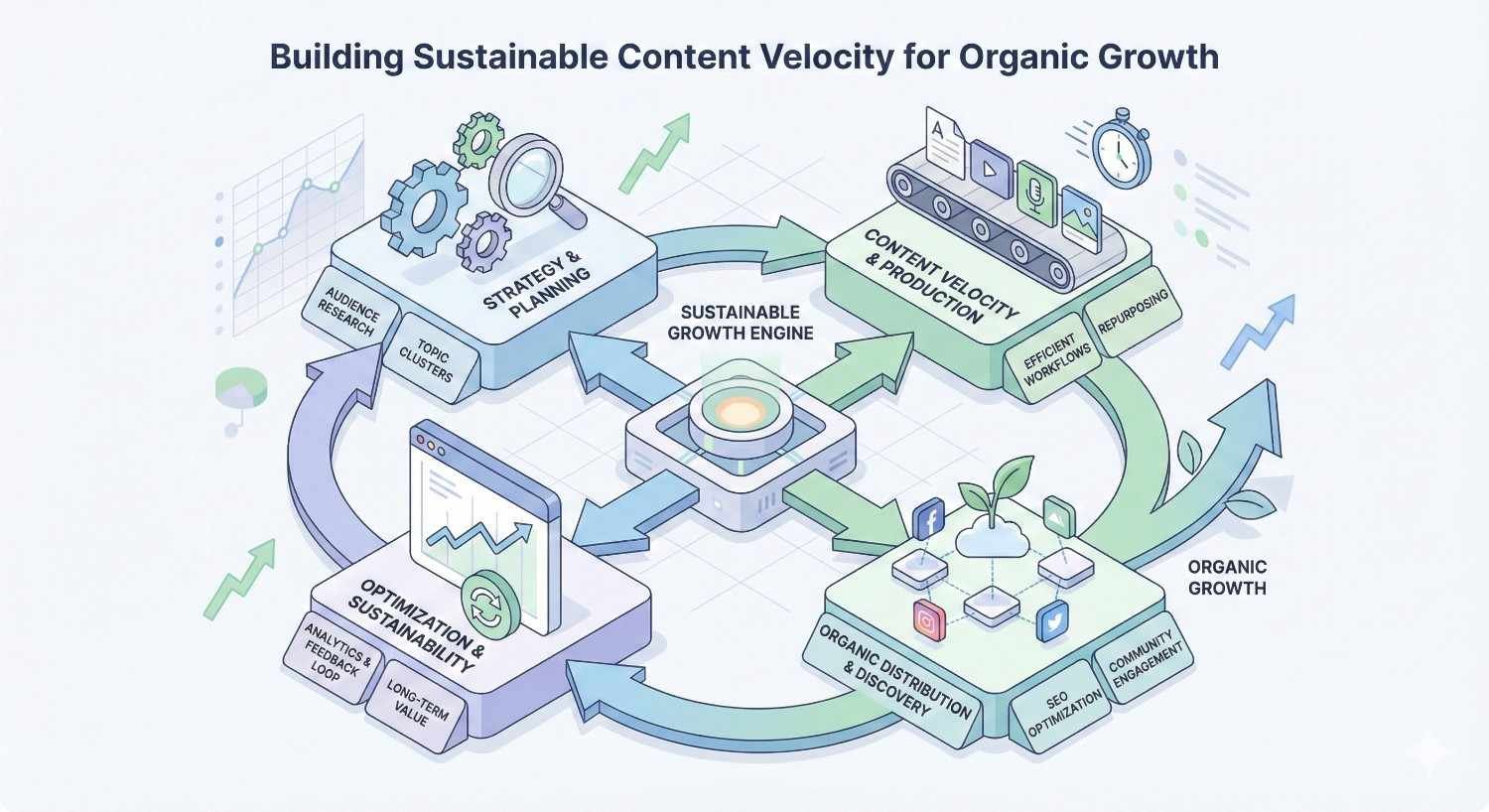
Building Sustainable Content Velocity for Organic Growth
Organic growth requires sustained content production over months and years. Workflows enable the consistency that builds topical authority and compounds ranking gains.
Plan content velocity based on realistic capacity. Ambitious targets that teams can’t sustain lead to burnout and quality problems. Sustainable velocity beats unsustainable sprints.
Use workflow metrics to optimize velocity over time. As processes improve and teams develop, capacity increases. Gradually increase targets as efficiency gains allow.
Conclusion
Content workflow management transforms content production from chaotic improvisation into a strategic capability that drives measurable business growth. The investment in process design, tool selection, and continuous improvement pays dividends through increased productivity, consistent quality, and sustainable SEO performance.
Your content workflow directly impacts your ability to build topical authority, maintain publishing consistency, and achieve the organic visibility that generates leads and revenue. Organizations that master workflow management gain competitive advantages that compound over time.
We help businesses build content workflows that support long-term organic growth. White Label SEO Service provides the strategic guidance and execution support you need to transform your content operations. Contact us to discuss how we can help you build workflows that drive results.
Frequently Asked Questions About Content Workflow Management
What is the difference between content workflow and content calendar?
A content calendar shows what content publishes when. A content workflow defines how content moves from idea to publication. The calendar is a scheduling tool. The workflow is the production system that delivers content to meet calendar commitments.
How do I get team buy-in for a new content workflow?
Involve team members in workflow design from the start. Show how the new workflow solves problems they experience. Start with a pilot project to demonstrate value before full rollout. Address concerns directly and adjust based on feedback.
Can content workflows be automated?
Many workflow elements can be automated. Status updates, notifications, task assignments, and handoffs work well with automation. Creative work like writing and strategic decisions require human judgment. The best workflows combine automation for routine tasks with human attention for high-value work.
How often should content workflows be reviewed and updated?
Review workflows quarterly at minimum. Conduct deeper reviews when team size changes significantly, when you adopt new tools, or when performance metrics indicate problems. Continuous small improvements work better than infrequent major overhauls.
How long does it take to implement a content workflow?
Basic workflow implementation takes two to four weeks for small teams. Mid-size teams typically need one to two months. Enterprise implementations can take three to six months or longer. The timeline depends on current process maturity, team size, tool complexity, and change management requirements.
What are the most common content workflow mistakes?
Common mistakes include over-engineering workflows for team size, failing to document processes, creating too many approval stages, not assigning clear ownership, and neglecting to measure performance. The biggest mistake is implementing workflows without team input, which leads to resistance and workarounds.
How do content workflows improve SEO results?
Workflows improve SEO by enabling consistent publishing velocity, ensuring optimization requirements are met systematically, maintaining quality standards that build authority, and creating feedback loops that connect performance data to content planning. Teams with mature workflows consistently outperform those without structured processes.



