Breadcrumb navigation is one of the most underutilized technical SEO elements that directly improves crawlability, internal linking, and SERP visibility. These small navigational aids help search engines understand your site hierarchy while giving users a clear path back through your content structure.
For business owners and marketing teams focused on organic growth, breadcrumbs represent a low-effort, high-impact optimization. They strengthen site architecture signals, qualify for rich snippets in search results, and reduce bounce rates by simplifying navigation.
This guide covers everything from breadcrumb types and implementation methods to schema markup, platform-specific setup, and performance measurement. You’ll learn exactly how to leverage breadcrumbs for measurable SEO gains.
What Is Breadcrumb Navigation?
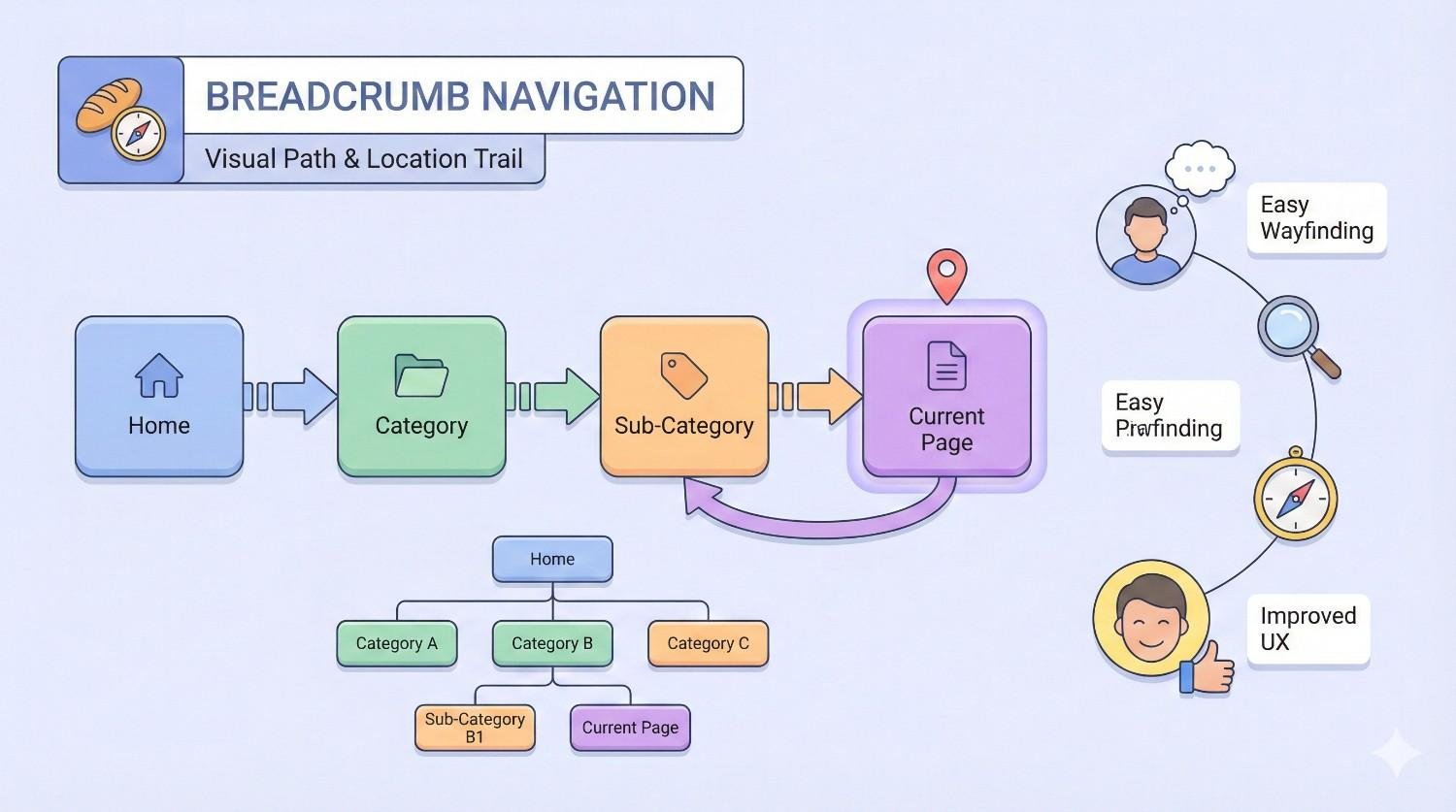
Breadcrumb navigation serves as a secondary navigation system that reveals a user’s location within a website’s hierarchical structure. Named after the trail of breadcrumbs in the Hansel and Gretel fairy tale, these navigational elements create a clickable path from the homepage to the current page.
Definition and Core Function
Breadcrumbs are a row of internal links that display the page hierarchy, typically appearing near the top of a webpage below the main navigation. Their core function is twofold: they help users understand where they are within a site’s structure and provide quick access to higher-level pages.
From an SEO perspective, breadcrumbs establish clear parent-child relationships between pages. This hierarchical mapping helps search engine crawlers understand content organization and topical relationships across your site.
The standard breadcrumb format follows this pattern: Home > Category > Subcategory > Current Page. Each element except the current page is clickable, allowing users to navigate backward through the site structure.
How Breadcrumbs Appear on Websites
On websites, breadcrumbs typically display as a horizontal text trail positioned below the header or main navigation menu. They appear above the main content area, making them immediately visible when a page loads.
The visual presentation usually includes separator characters between each level. Common separators include greater-than symbols (>), forward slashes (/), or arrows (→). Each breadcrumb element uses anchor text that describes the destination page.
In search engine results pages, breadcrumbs can replace the standard URL display when proper schema markup is implemented. Google’s search documentation confirms that breadcrumb structured data enables rich results that show the page hierarchy directly in SERPs.
Breadcrumb Navigation vs. Other Navigation Types
Breadcrumbs differ fundamentally from primary navigation menus. Main navigation provides access to top-level site sections and remains consistent across all pages. Breadcrumbs, conversely, are contextual and change based on the current page’s position in the hierarchy.
Unlike footer navigation that offers comprehensive site links, breadcrumbs focus exclusively on the vertical path from homepage to current location. They don’t provide horizontal navigation between sibling pages or unrelated sections.
Sidebar navigation often displays category listings or related content. Breadcrumbs complement this by showing the exact hierarchical path rather than browsing options. Together, these navigation types create a complete wayfinding system.
Types of Breadcrumb Navigation
Different breadcrumb types serve distinct purposes depending on your site structure and user needs. Choosing the right type impacts both usability and SEO effectiveness.
Hierarchy-Based Breadcrumbs (Location Breadcrumbs)
Hierarchy-based breadcrumbs are the most common type and the most valuable for SEO. They display the page’s position within the site’s structural hierarchy, regardless of how the user arrived at that page.
Example: Home > Electronics > Laptops > Gaming Laptops > Product Name
These breadcrumbs reflect your site’s information architecture. They remain consistent for each page, meaning every user sees the same breadcrumb trail for a given URL. This consistency helps search engines map your content taxonomy accurately.
Location breadcrumbs work best for sites with clear categorical structures. E-commerce stores, content publishers, and service businesses with defined service categories benefit most from this approach.
Attribute-Based Breadcrumbs
Attribute-based breadcrumbs display the characteristics or attributes of the current page rather than its location in a hierarchy. They’re particularly useful for e-commerce sites where products have multiple defining features.
Example: Home > Laptops > 15-inch > Intel Core i7 > 16GB RAM
This type helps users understand what filters or attributes define the current view. When a user applies multiple filters on a category page, attribute breadcrumbs show exactly which parameters are active.
For SEO, attribute breadcrumbs can create keyword-rich navigation paths. However, they require careful implementation to avoid creating confusing or overly long trails. They work best when combined with hierarchy-based breadcrumbs.
History-Based Breadcrumbs (Path Breadcrumbs)
History-based breadcrumbs show the actual path a user took to reach the current page. They function like a browser’s back button history, displaying the sequence of pages visited during the current session.
Example: Home > Search Results > Category Page > Product Page
This type provides less SEO value because the trail varies based on user behavior rather than site structure. Search engines cannot rely on history-based breadcrumbs to understand page relationships since the path changes with each visitor.
History breadcrumbs can improve user experience in specific scenarios, such as complex research journeys. However, most SEO professionals recommend hierarchy-based breadcrumbs as the primary implementation due to their consistent structural signals.
Why Breadcrumb Navigation Matters for SEO
Breadcrumbs deliver multiple SEO benefits that compound over time. They influence how search engines crawl, understand, and display your content in search results.
Improved Site Architecture and Crawlability
Breadcrumbs reinforce your site’s hierarchical structure for search engine crawlers. Each breadcrumb trail creates explicit parent-child relationships that help Googlebot understand how pages connect within your content taxonomy.
When crawlers encounter breadcrumb links, they receive clear signals about page importance and topical groupings. A product page with breadcrumbs pointing to its category and subcategory helps search engines understand that page’s context within your broader catalog.
This improved understanding can lead to more efficient crawl budget allocation. Search engines can prioritize crawling based on the hierarchical importance signals breadcrumbs provide, ensuring your most valuable pages receive adequate crawl attention.
Enhanced Internal Linking Structure
Every breadcrumb element is an internal link pointing to a higher-level page. This creates a systematic internal linking structure that distributes link equity throughout your site hierarchy.
Category pages receive links from every product or article within that category. Subcategory pages link back to parent categories. This pyramid of internal links strengthens the authority of your most important hub pages.
The anchor text in breadcrumbs typically contains relevant keywords describing each destination page. These keyword-rich internal links provide contextual signals that help search engines understand what each linked page covers.
Rich Snippets and SERP Visibility
Properly implemented breadcrumb schema markup enables rich results in Google Search. Instead of displaying a plain URL, Google can show your breadcrumb hierarchy directly in the search snippet.
Google’s rich results documentation shows that breadcrumb rich snippets display the site hierarchy with clickable links. This enhanced display increases visual prominence and can improve click-through rates.
Rich breadcrumb snippets also provide users with immediate context about where the page sits within your site. This transparency can attract more qualified clicks from users who understand exactly what content category they’re entering.
Reduced Bounce Rate and Improved User Signals
Breadcrumbs give users an immediate escape route when they land on a page that doesn’t match their intent. Rather than bouncing back to search results, users can click a breadcrumb to explore related content within your site.
This navigation option keeps users engaged with your site even when the initial landing page isn’t perfect. A user searching for “gaming laptops” who lands on a specific product page can easily click the “Gaming Laptops” breadcrumb to browse alternatives.
Lower bounce rates and longer session durations send positive engagement signals to search engines. While Google hasn’t confirmed these as direct ranking factors, improved user engagement correlates with better search performance across numerous studies.
Keyword Relevance and Contextual Signals
Breadcrumb anchor text naturally incorporates relevant keywords for each page level. A breadcrumb trail like “Home > Digital Marketing > SEO Services > Technical SEO Audits” includes multiple keyword variations that reinforce topical relevance.
These contextual keyword signals help search engines understand the semantic relationships between pages. The breadcrumb structure shows that “Technical SEO Audits” is a subset of “SEO Services,” which falls under “Digital Marketing.”
This hierarchical keyword mapping supports topical authority building. Search engines can see that your site covers a topic comprehensively, from broad category pages down to specific service or product pages.
How Breadcrumbs Impact User Experience
Beyond SEO benefits, breadcrumbs significantly improve how users interact with your website. Better user experience leads to improved engagement metrics that indirectly support search performance.
Simplified Navigation and Orientation
Breadcrumbs answer the fundamental user question: “Where am I?” This orientation is especially valuable for users who arrive via search engines or external links and land deep within your site structure.
Without breadcrumbs, users must rely on the URL or page content to understand their location. Breadcrumbs provide instant clarity with descriptive labels that explain the page’s context within your site.
This orientation reduces cognitive load. Users don’t need to analyze the URL structure or hunt for navigation cues. The breadcrumb trail immediately communicates their position and available navigation paths.
Faster Content Discovery
Breadcrumbs enable efficient vertical navigation through your site hierarchy. Users can jump directly to any parent level without returning to the homepage or using the main navigation menu.
A user reading a blog post about “Python list comprehensions” can click the “Python Tutorials” breadcrumb to discover related content. This one-click access to category pages accelerates content discovery and exploration.
For e-commerce sites, breadcrumbs help shoppers browse related products quickly. After viewing a specific item, users can click category breadcrumbs to see alternatives without starting a new search.
Mobile Usability Considerations
On mobile devices, screen space is limited and navigation can be challenging. Breadcrumbs provide a compact navigation solution that doesn’t require opening menus or scrolling to find navigation options.
Mobile breadcrumbs often use truncation or horizontal scrolling to fit smaller screens. The key is maintaining functionality while adapting to space constraints. Users should still be able to access all breadcrumb levels.
Google’s mobile-first indexing means your mobile breadcrumb implementation matters for SEO. Ensure breadcrumbs are visible, functional, and properly marked up on mobile versions of your pages.
How to Implement Breadcrumb Navigation
Implementing breadcrumbs requires attention to placement, HTML structure, and schema markup. The technical details matter for both user experience and SEO effectiveness.
Breadcrumb Placement Best Practices
Position breadcrumbs near the top of the page, below the main navigation but above the primary content. This placement ensures visibility without interfering with the main content area.
Consistent placement across all pages helps users develop expectations about where to find breadcrumbs. Avoid moving breadcrumb position between different page templates or sections.
Breadcrumbs should appear on all pages except the homepage. The homepage is the root of your hierarchy and doesn’t need breadcrumbs pointing to itself. Some sites also omit breadcrumbs from top-level category pages, though including them maintains consistency.
HTML Structure for Breadcrumbs
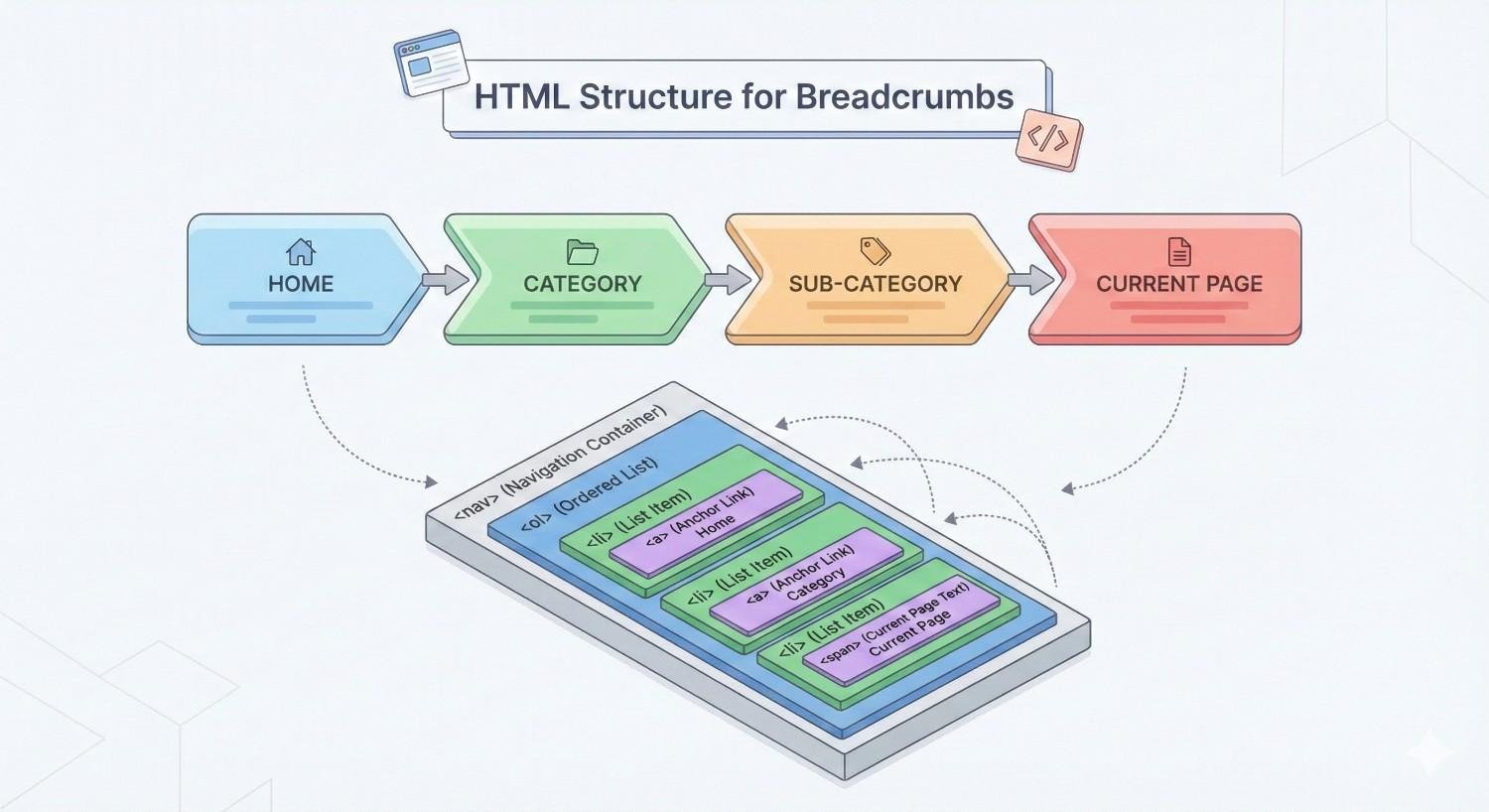
Semantic HTML provides the foundation for accessible, SEO-friendly breadcrumbs. Use a <nav> element with an appropriate aria-label to identify the breadcrumb navigation region.
html
Copy
<nav aria-label=”Breadcrumb“>
<ol>
<li><a href=”/“>Home</a></li>
<li><a href=”/category/“>Category</a></li>
<li><a href=”/category/subcategory/“>Subcategory</a></li>
<li aria-current=”page“>Current Page</li>
</ol>
</nav>
The ordered list (<ol>) element is semantically appropriate because breadcrumbs represent a sequential hierarchy. Each list item contains either a link to that level or plain text for the current page.
The aria-current=”page” attribute on the final item indicates the current page for screen reader users. This accessibility consideration improves usability for all visitors.
Adding Breadcrumb Schema Markup (JSON-LD)
JSON-LD is Google’s preferred format for structured data, including breadcrumb markup. This script-based approach separates structured data from HTML, making implementation and maintenance easier.
json
Copy
<script type=“application/ld+json”>
{
“@context”: “https://schema.org”,
“@type”: “BreadcrumbList”,
“itemListElement”: [
{
“@type”: “ListItem”,
“position”: 1,
“name”: “Home”,
“item”: “https://example.com/”
},
{
“@type”: “ListItem”,
“position”: 2,
“name”: “Category”,
“item”: “https://example.com/category/”
},
{
“@type”: “ListItem”,
“position”: 3,
“name”: “Current Page”,
“item”: “https://example.com/category/current-page/”
}
]
}
</script>
Place the JSON-LD script in the <head> section or at the end of the <body>. Each breadcrumb level needs a position number, display name, and full URL.
The final item (current page) should include the full URL. Some implementations omit the URL for the current page, but including it provides complete information to search engines.
Breadcrumb Implementation in WordPress
WordPress offers multiple breadcrumb implementation options. The most popular approach uses SEO plugins that include breadcrumb functionality.
Yoast SEO provides built-in breadcrumbs with schema markup. Enable breadcrumbs in Yoast settings, then add the breadcrumb shortcode or PHP function to your theme templates:
php
Copy
<?php
if ( function_exists(‘yoast_breadcrumb’) ) {
yoast_breadcrumb( ‘<p id=”breadcrumbs”>’,‘</p>’ );
}
?>
Rank Math similarly includes breadcrumb functionality with automatic schema markup. Both plugins handle the technical implementation, including proper structured data formatting.
For theme-based solutions, many WordPress themes include native breadcrumb support. Check your theme’s documentation for built-in breadcrumb options before adding plugin-based solutions.
Breadcrumb Implementation in Shopify
Shopify themes typically include breadcrumb functionality, though implementation quality varies. Check your theme’s settings for breadcrumb options before custom coding.
For themes without built-in breadcrumbs, you’ll need to edit theme files. Add breadcrumb code to your theme’s product.liquid, collection.liquid, and other relevant templates.
liquid
Copy
<nav aria-label=”Breadcrumb“>
<ol>
<li><a href=”/“>Home</a></li>
{% if collection %}
<li><a href=”{{ collection.url }}“>{{ collection.title }}</a></li>
{% endif %}
{% if product %}
<li aria-current=”page“>{{ product.title }}</li>
{% endif %}
</ol>
</nav>
Shopify apps like “SEO Manager” or “JSON-LD for SEO” can add breadcrumb schema markup without theme editing. These apps automatically generate structured data based on your store’s category structure.
Breadcrumb Implementation in Custom CMS
Custom CMS implementations require manual breadcrumb development. The approach depends on your site’s architecture and how page hierarchy is stored in your database.
Start by establishing how your CMS tracks parent-child page relationships. Most systems use a parent ID field or nested set model to define hierarchy. Your breadcrumb function will traverse this hierarchy to build the trail.
php
Copy
function get_breadcrumbs($page_id) {
$breadcrumbs = array();
$current = get_page($page_id);
while ($current) {
array_unshift($breadcrumbs, array(
‘title’ => $current->title,
‘url’ => $current->url
));
$current = $current->parent_id ? get_page($current->parent_id) : null;
}
return $breadcrumbs;
}
Generate both the HTML output and JSON-LD schema from the same data source. This ensures consistency between visible breadcrumbs and structured data markup.
Breadcrumb Schema Markup and Structured Data
Schema markup transforms breadcrumbs from a visual element into machine-readable data that search engines can process and display in rich results.
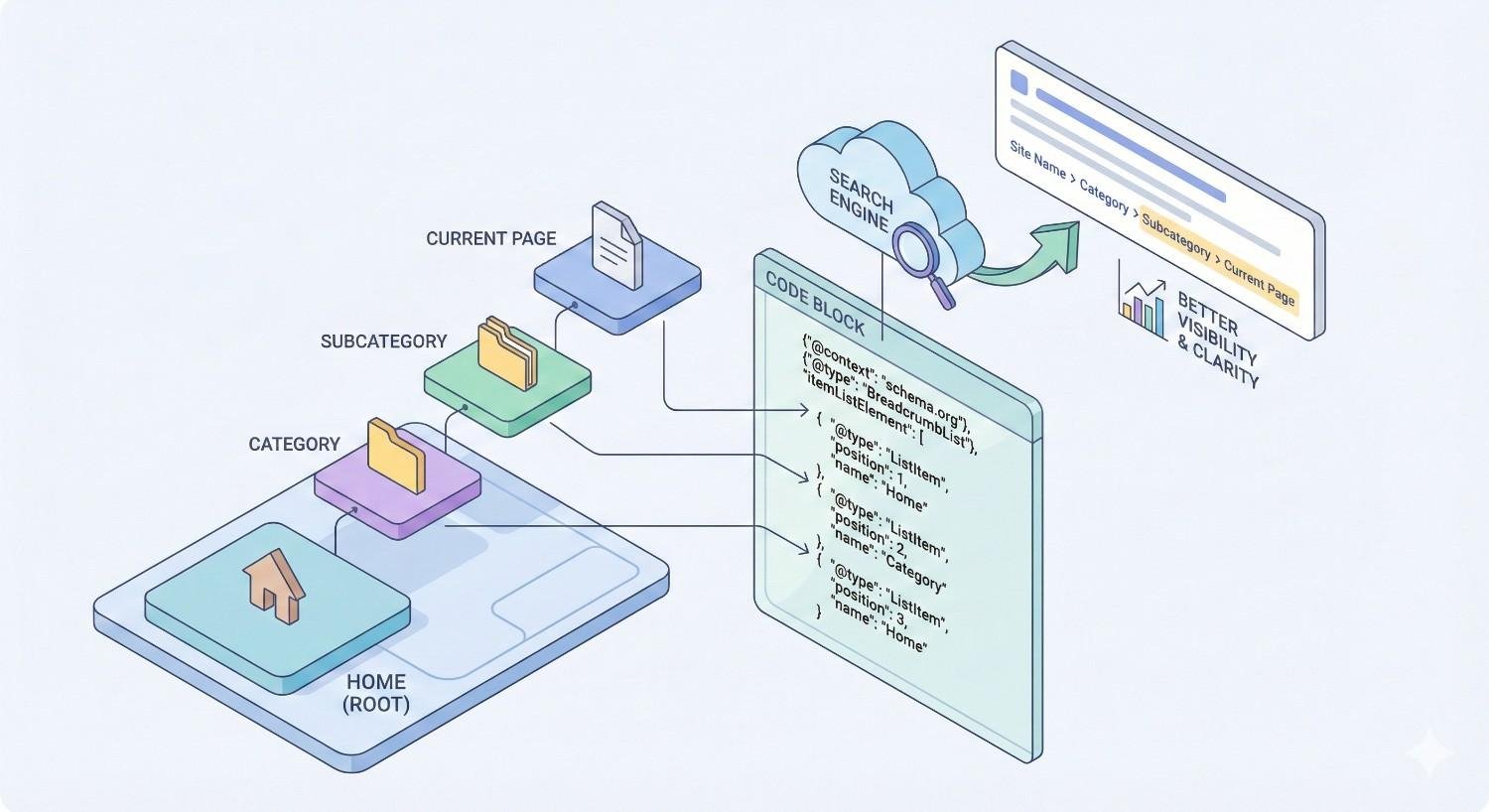
What Is BreadcrumbList Schema?
BreadcrumbList is a Schema.org type specifically designed for breadcrumb navigation markup. It defines a list of items representing a breadcrumb trail, with each item containing position, name, and URL information.
The schema tells search engines exactly how your pages relate hierarchically. This explicit declaration removes ambiguity that might exist if search engines had to infer relationships from link patterns alone.
Schema.org’s BreadcrumbList documentation defines the required and optional properties. At minimum, each ListItem needs a position and name. Including the item URL is strongly recommended for complete implementation.
JSON-LD vs. Microdata vs. RDFa
Three formats exist for implementing structured data: JSON-LD, Microdata, and RDFa. Each has distinct characteristics affecting implementation complexity and maintenance.
JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data) is Google’s recommended format. It uses a script block separate from HTML content, making it easier to implement and modify without touching page markup. JSON-LD is the cleanest option for most implementations.
Microdata embeds structured data directly in HTML elements using special attributes. While functional, it mixes content and metadata, making templates more complex and harder to maintain.
RDFa (Resource Description Framework in Attributes) also embeds data in HTML but uses a different attribute syntax. It’s less common for breadcrumbs and offers no advantages over JSON-LD for most use cases.
For new implementations, use JSON-LD. It’s easier to implement, debug, and maintain while providing full functionality for breadcrumb rich results.
Testing Breadcrumb Markup with Google Tools
Google provides free tools to validate your breadcrumb structured data before and after deployment.
Rich Results Test checks whether your page is eligible for rich results, including breadcrumb display. Enter a URL or paste code to see how Google interprets your markup.
Schema Markup Validator validates structured data against Schema.org specifications. It catches syntax errors and missing required properties that might prevent rich results.
Google Search Console shows breadcrumb performance data under the Enhancements section. Monitor for errors, warnings, and valid items across your site. Search Console also reports which pages have breadcrumb markup detected.
Test breadcrumbs on multiple page types: homepage, category pages, product pages, and blog posts. Each template may have different implementation details that need validation.
Common Schema Markup Errors to Avoid
Several common mistakes prevent breadcrumb schema from generating rich results or cause validation errors.
Missing position property: Every ListItem must include a position number starting from 1. Omitting positions or using non-sequential numbers causes validation failures.
Incorrect URL format: Use absolute URLs (https://example.com/page/) rather than relative URLs (/page/). Relative URLs may not resolve correctly when search engines process the markup.
Mismatched visible and schema breadcrumbs: The breadcrumb trail in your schema should match what users see on the page. Discrepancies between visible breadcrumbs and structured data can be seen as deceptive.
Duplicate breadcrumb markup: Having multiple BreadcrumbList schemas on one page confuses search engines. Ensure only one breadcrumb schema exists per page.
Empty or placeholder values: Don’t include ListItems with empty names or placeholder URLs. Every item should contain real, accurate information.
Breadcrumb Navigation Best Practices for SEO
Following established best practices ensures your breadcrumbs deliver maximum SEO value while maintaining excellent user experience.
Use Descriptive Anchor Text with Keywords
Breadcrumb anchor text should describe the destination page using relevant keywords. Avoid generic labels like “Category 1” or “Level 2” that provide no semantic value.
Good example: Home > Digital Marketing > SEO Services > Technical Audits
Poor example: Home > Services > Sub-services > Page
Descriptive anchor text helps users understand where each link leads while providing keyword context to search engines. Balance keyword inclusion with natural, readable labels.
Don’t force exact-match keywords into breadcrumbs unnaturally. “SEO Services” is better than “Best SEO Services Company” as a breadcrumb label. Keep labels concise and user-friendly.
Maintain Consistent Hierarchy
Every page should have a logical, consistent position in your site hierarchy. Breadcrumbs should reflect this structure accurately across all pages.
Inconsistent hierarchies confuse both users and search engines. If a product appears under “Electronics > Computers” on one page but “Office Equipment > Computers” on another, the conflicting signals weaken your site architecture.
Audit your site structure before implementing breadcrumbs. Resolve any hierarchy inconsistencies first, then implement breadcrumbs that accurately reflect the cleaned-up structure.
Ensure Clickable Links (Except Current Page)
Every breadcrumb element except the current page should be a clickable link. Users expect to navigate by clicking breadcrumb items.
The current page should appear in the breadcrumb trail but not as a link. Linking to the current page creates a self-referential link that serves no purpose and can confuse users.
Display the current page differently from linked items. Common approaches include removing the link, using different text styling, or adding an indicator like “You are here.”
Keep Breadcrumb Trails Concise
Breadcrumb trails should be long enough to show meaningful hierarchy but short enough to remain usable. Extremely long trails become difficult to read and may truncate on smaller screens.
Aim for 3-5 levels in most breadcrumb trails. If your hierarchy requires more levels, consider whether your site structure is too deep. Flatter hierarchies generally perform better for both SEO and usability.
For very deep hierarchies, consider showing only key levels rather than every intermediate page. Home > Category > … > Current Page can indicate depth while maintaining readability.
Align Breadcrumbs with URL Structure
Breadcrumb hierarchy should mirror your URL structure when possible. This alignment reinforces site architecture signals and creates predictable navigation patterns.
If your URL is example.com/services/seo/technical-audits/, your breadcrumbs should follow: Home > Services > SEO > Technical Audits.
Misalignment between URLs and breadcrumbs creates confusion. Users and search engines expect these navigation elements to tell the same story about page relationships.
Common Breadcrumb Navigation Mistakes
Avoiding common implementation errors ensures your breadcrumbs support rather than hinder your SEO efforts.
Inconsistent or Missing Breadcrumb Trails
Some sites implement breadcrumbs on certain page types but not others. This inconsistency weakens the structural signals breadcrumbs provide.
Missing breadcrumbs on deep pages leave gaps in your internal linking structure. Those pages lose the link equity and contextual signals that breadcrumbs provide.
Audit all page templates to ensure breadcrumb implementation is complete. Category pages, product pages, blog posts, and service pages should all include appropriate breadcrumbs.
Using Non-Descriptive Labels
Generic breadcrumb labels waste an opportunity to provide keyword context and user guidance. Labels like “Products,” “Page,” or “Item” tell users nothing useful.
Replace generic labels with specific, descriptive text. “Running Shoes” is more valuable than “Products” as a breadcrumb label for both users and search engines.
Review your breadcrumb labels across all page types. Identify any generic terms and replace them with descriptive alternatives that accurately represent each page’s content.
Incorrect Schema Implementation
Schema markup errors prevent breadcrumbs from appearing in rich results. Common issues include syntax errors, missing required properties, and incorrect data types.
Validate schema markup using Google’s testing tools before deployment. Fix any errors or warnings before pushing changes to production.
Monitor Search Console’s Enhancement reports for ongoing schema issues. New errors can appear as content changes or templates are updated.
Breadcrumbs That Don’t Match Site Hierarchy
Breadcrumbs should accurately reflect your actual site structure. Creating breadcrumb trails that don’t match the real page relationships misleads users and search engines.
If breadcrumbs show a page under “Category A” but the page actually lives under “Category B” in your navigation and URL structure, you’re sending conflicting signals.
Ensure breadcrumb generation logic pulls from the same source of truth as your navigation and URL structure. Automated breadcrumb generation based on actual page relationships prevents mismatches.
Breadcrumb Navigation for E-commerce Websites
E-commerce sites have unique breadcrumb considerations due to complex product catalogs and multiple category structures.
Category and Subcategory Breadcrumbs
E-commerce breadcrumbs typically follow the category hierarchy: Home > Department > Category > Subcategory > Product.
Category pages should show their position within the broader catalog structure. A “Running Shoes” category page might display: Home > Footwear > Athletic Shoes > Running Shoes.
Subcategory breadcrumbs help users understand product groupings and navigate to related items. Clear category breadcrumbs support both browsing behavior and search engine understanding of your product taxonomy.
Product Page Breadcrumb Strategies
Product pages benefit significantly from breadcrumbs that show category context. Users arriving from search results immediately understand where the product fits in your catalog.
Include the full category path leading to the product. This creates internal links to category pages and provides keyword-rich context about the product’s classification.
For products with long names, consider whether to include the full product name in the breadcrumb trail or truncate it. The current page indicator doesn’t need to repeat the entire product title if it’s already displayed prominently on the page.
Handling Products in Multiple Categories
Many products logically belong in multiple categories. A laptop might fit under “Computers,” “Electronics,” and “Back to School” categories. This creates a breadcrumb challenge.
The most common solution is choosing a primary category for each product. Breadcrumbs always show the primary category path, even if users arrived via a secondary category.
Alternative approaches include dynamic breadcrumbs that reflect the user’s navigation path. However, this creates inconsistent breadcrumb trails that provide weaker SEO signals than fixed primary category breadcrumbs.
For schema markup, you can include multiple breadcrumb trails representing different valid paths to the product. Google can choose which to display based on the user’s search context.
Measuring Breadcrumb Navigation Performance
Tracking breadcrumb performance helps you understand their impact and identify optimization opportunities.
Tracking Breadcrumb Clicks in Google Analytics
Google Analytics can track breadcrumb interactions as events. This data reveals how users engage with breadcrumb navigation and which levels receive the most clicks.
In GA4, set up event tracking for breadcrumb link clicks. Use the link URL or breadcrumb level as event parameters to segment the data.
javascript
Copy
document.querySelectorAll(‘.breadcrumb a’).forEach(link => {
link.addEventListener(‘click’, function() {
gtag(‘event’, ‘breadcrumb_click’, {
‘breadcrumb_level’: this.dataset.level,
‘breadcrumb_destination’: this.href
});
});
});
Analyze which breadcrumb levels users click most frequently. High click rates on category breadcrumbs suggest users value the ability to browse related content.
Monitoring Rich Snippet Appearance in Search Console
Google Search Console reports breadcrumb rich result performance under the Enhancements section. Monitor this report for implementation issues and coverage data.
The Breadcrumbs report shows:
- Valid items: Pages with correctly implemented breadcrumb markup
- Items with errors: Pages where markup issues prevent rich results
- Items with warnings: Pages with non-critical issues
Click into specific issues to see affected URLs and error details. Prioritize fixing errors that affect high-traffic or high-value pages.
Track the trend of valid breadcrumb items over time. Increasing coverage indicates successful implementation across your site.
Analyzing User Behavior and Navigation Patterns
Beyond click tracking, analyze how breadcrumbs affect overall user behavior. Compare engagement metrics for pages with and without breadcrumbs.
Key metrics to monitor:
- Bounce rate differences
- Pages per session
- Average session duration
- Navigation paths through your site
Use behavior flow reports to see how users move through your site. Breadcrumbs should facilitate movement from deep pages back to category levels.
A/B testing can isolate breadcrumb impact. Test pages with and without breadcrumbs to measure differences in user engagement and conversion rates.
Breadcrumb Navigation FAQs
Do Breadcrumbs Directly Improve Rankings?
Breadcrumbs don’t directly boost rankings as a standalone factor. However, they improve crawlability, internal linking, and user experience signals that collectively support better search performance. The rich snippet visibility they enable can also increase click-through rates from search results.
Should Every Page Have Breadcrumbs?
Most pages benefit from breadcrumbs, with the homepage being the main exception. Category pages, product pages, blog posts, and service pages should all include breadcrumbs. Landing pages designed for specific campaigns may omit breadcrumbs if they intentionally limit navigation options.
How Do Breadcrumbs Affect Mobile SEO?
Breadcrumbs support mobile SEO by providing compact navigation that works well on small screens. With mobile-first indexing, your mobile breadcrumb implementation directly affects how Google evaluates your site. Ensure breadcrumbs are visible and functional on mobile devices.
Can Breadcrumbs Replace Main Navigation?
Breadcrumbs should complement, not replace, main navigation. They serve different purposes: main navigation provides access to all major site sections, while breadcrumbs show the current page’s hierarchical position. Users need both navigation types for complete site wayfinding.
How to Get Started with Breadcrumb Navigation
Implementing breadcrumbs effectively requires a systematic approach. Follow these steps to add breadcrumbs that support your SEO goals.
Audit Your Current Site Structure
Before implementing breadcrumbs, understand your existing site hierarchy. Map out how pages relate to each other and identify any structural inconsistencies.
Review your URL structure, navigation menus, and internal linking patterns. These elements should align with the breadcrumb hierarchy you plan to create.
Identify pages that lack clear parent categories. These orphan pages need to be integrated into your hierarchy before breadcrumbs can accurately represent their position.
Choose the Right Breadcrumb Type
Select the breadcrumb type that best fits your site structure and user needs. Hierarchy-based breadcrumbs work for most sites and provide the strongest SEO signals.
E-commerce sites may benefit from combining hierarchy and attribute breadcrumbs. Content sites typically need only hierarchy-based breadcrumbs.
Avoid history-based breadcrumbs as your primary implementation. Their inconsistent nature provides limited SEO value compared to hierarchy-based alternatives.
Implement and Validate Schema Markup
Add BreadcrumbList schema markup using JSON-LD format. Test your implementation with Google’s Rich Results Test before deploying to production.
Monitor Search Console after deployment for any markup errors. Address issues promptly to ensure your breadcrumbs qualify for rich results.
Validate schema on multiple page types. Each template may require different implementation details to generate accurate breadcrumb markup.
Partner with an SEO Expert for Technical Implementation
Complex sites or custom CMS platforms may require specialized expertise for proper breadcrumb implementation. Technical SEO professionals can ensure breadcrumbs integrate correctly with your existing site architecture.
Expert implementation addresses edge cases like products in multiple categories, dynamic content, and international site structures. Professional guidance prevents common mistakes that undermine breadcrumb effectiveness.
Ongoing monitoring and optimization ensure breadcrumbs continue supporting your SEO goals as your site evolves.
Conclusion
Breadcrumb navigation delivers measurable SEO benefits through improved crawlability, enhanced internal linking, and rich snippet eligibility. When implemented correctly with proper schema markup, breadcrumbs strengthen your site architecture while improving user experience.
At White Label SEO Service, we help businesses implement technical SEO elements like breadcrumbs as part of comprehensive organic growth strategies. Our team handles everything from site structure audits to schema markup implementation.
Ready to optimize your site’s navigation and technical SEO foundation? Contact us to discuss how breadcrumb implementation fits into your broader search visibility goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best breadcrumb type for SEO purposes?
Hierarchy-based breadcrumbs provide the strongest SEO value because they create consistent structural signals that search engines can reliably interpret. They establish clear parent-child relationships between pages and generate predictable internal linking patterns.
How long should a breadcrumb trail be?
Aim for 3-5 levels in most breadcrumb trails. Longer trails become difficult to read and may indicate an overly deep site structure. If your hierarchy requires more levels, consider flattening your site architecture.
Do breadcrumbs help with voice search optimization?
Breadcrumbs indirectly support voice search by clarifying content context and hierarchy. When search engines better understand your page relationships, they can more accurately match your content to voice queries seeking specific information.
Should I include the current page in the breadcrumb trail?
Yes, include the current page as the final breadcrumb element, but don’t make it a clickable link. This shows users their exact location while avoiding unnecessary self-referential links.
How do breadcrumbs affect page load speed?
Properly implemented breadcrumbs have minimal impact on page load speed. The HTML and JSON-LD markup add negligible file size. Avoid loading breadcrumbs via JavaScript if possible, as this can delay their rendering.
Can I have multiple breadcrumb trails on one page?
You can include multiple BreadcrumbList schemas to represent different valid paths to a page. This is useful for products in multiple categories. However, only display one visible breadcrumb trail to avoid confusing users.
How often should I audit my breadcrumb implementation?
Review breadcrumb implementation quarterly or whenever you make significant site structure changes. Monitor Search Console’s Breadcrumbs report continuously for errors that need immediate attention.



