Ecommerce SEO services combine technical optimization, content strategy, and authority building to help online stores rank higher in search results and convert organic traffic into revenue. For store owners competing against thousands of similar products, professional SEO represents the difference between page-one visibility and digital obscurity.
The stakes are significant. Organic search drives the majority of ecommerce traffic, yet most online stores struggle with duplicate content, poor site architecture, and weak product page optimization. These technical gaps cost businesses thousands in lost sales every month.
This guide covers everything you need to know about ecommerce SEO services, from core components and realistic timelines to pricing models and platform-specific strategies. You’ll learn how to evaluate providers, avoid common mistakes, and measure ROI effectively.

What Are Ecommerce SEO Services?
Ecommerce SEO services are specialized search engine optimization strategies designed specifically for online stores. Unlike general SEO, these services address the unique challenges of product catalogs, category hierarchies, and transactional search intent that define online retail.
Definition and Core Components
Ecommerce SEO encompasses all activities that improve an online store’s visibility in organic search results. The goal is straightforward: attract qualified shoppers who are actively searching for products you sell.
Core components include technical website optimization, product and category page optimization, keyword research targeting buyer intent, content development supporting the purchase journey, and link building that establishes domain authority. Each component works together to create a comprehensive organic growth strategy.
Professional ecommerce SEO services typically deliver these components through structured monthly engagements. Providers conduct initial audits, develop customized strategies, implement optimizations, and continuously refine approaches based on performance data.
How Ecommerce SEO Differs from Traditional SEO
Traditional SEO focuses on ranking informational content and service pages. Ecommerce SEO operates in a fundamentally different environment with distinct challenges.
Scale complexity sets ecommerce apart immediately. A typical service business might optimize 20-50 pages. An online store often manages thousands of product pages, each requiring unique optimization. This scale demands systematic approaches and automation where appropriate.
Transactional intent dominates ecommerce searches. Users searching “buy running shoes size 10” have different needs than someone searching “how to start running.” Ecommerce SEO prioritizes commercial and transactional keywords that indicate purchase readiness.
Duplicate content challenges plague online stores. Product variants, filtered navigation, and manufacturer descriptions create massive duplication issues that rarely affect traditional websites. Solving these problems requires specialized technical knowledge.
Structured data requirements are more complex for ecommerce. Product schema, review markup, price information, and availability status all influence how products appear in search results. Rich snippets can dramatically impact click-through rates.
Conversion tracking connects directly to revenue in ecommerce. Traditional SEO might measure leads or engagement. Ecommerce SEO tracks actual purchases, allowing precise ROI calculations that justify ongoing investment.
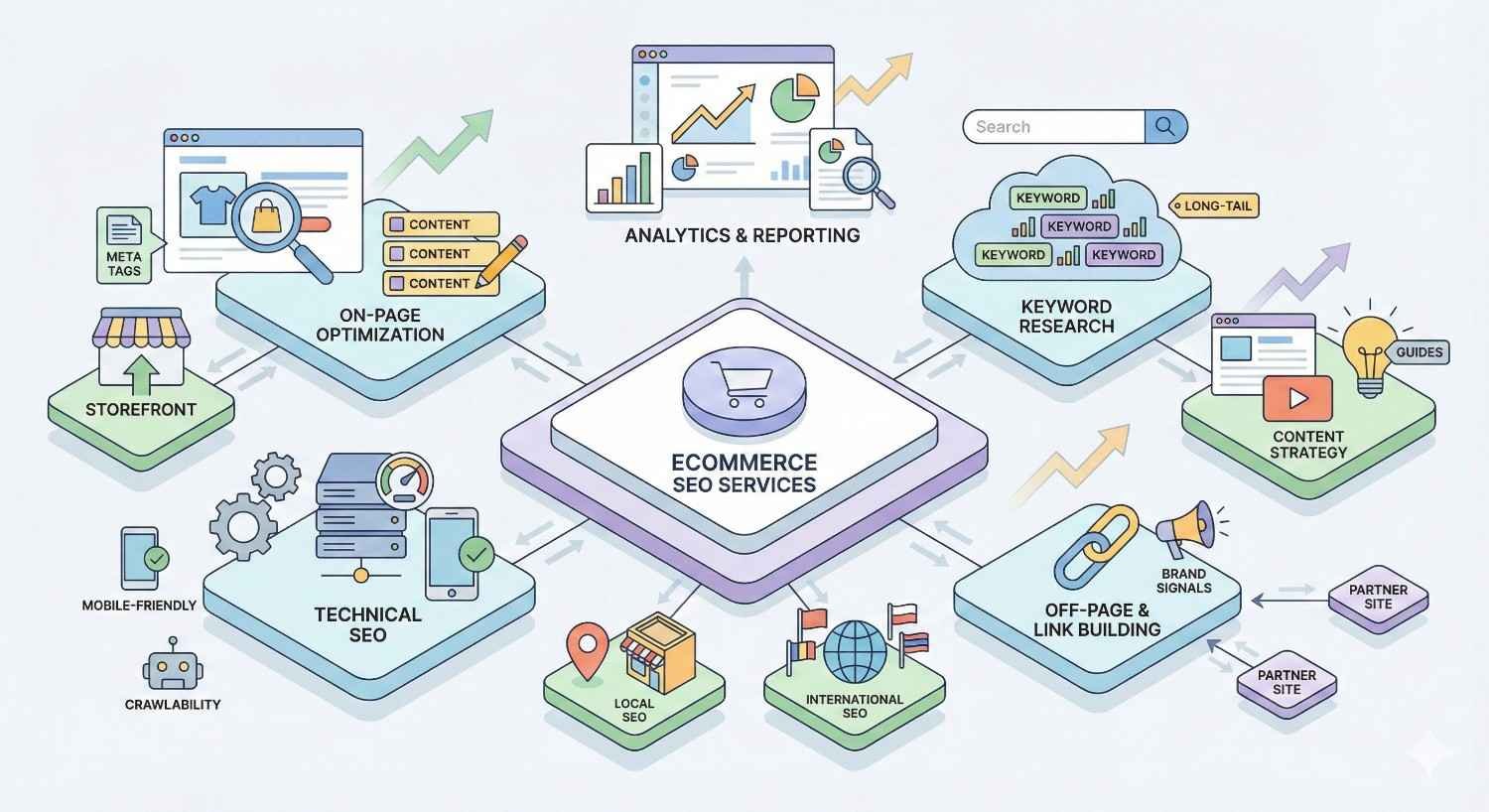
Types of Ecommerce SEO Services
Professional ecommerce SEO encompasses several specialized service categories. Most comprehensive programs include all these elements, though some providers specialize in specific areas.
Technical SEO for Online Stores
Technical SEO ensures search engines can efficiently crawl, index, and understand your entire product catalog. This includes site architecture optimization, page speed improvements, mobile responsiveness, URL structure, schema implementation, and crawl budget management.
For large catalogs, technical SEO often represents the highest-impact starting point. Fixing crawlability issues can unlock thousands of previously invisible product pages.
On-Page Optimization for Product Pages
On-page SEO transforms product pages into ranking assets. This involves optimizing titles, meta descriptions, product descriptions, images, and internal linking structures. The goal is making each product page the best possible answer for relevant search queries.
Effective product page optimization balances SEO requirements with conversion optimization. Pages must rank well and convert visitors into buyers.
Content Strategy for Ecommerce
Content strategy extends beyond product pages to capture shoppers at every journey stage. This includes buying guides, comparison content, how-to articles, and educational resources that attract top-of-funnel traffic.
Strong content programs build topical authority that lifts rankings across entire product categories. A comprehensive guide about running shoe selection can boost rankings for dozens of related product pages.
Link Building for Online Retailers
Link building establishes domain authority through quality backlinks from relevant websites. Ecommerce link building leverages products, expertise, and industry relationships to earn editorial links.
Effective strategies include digital PR, product reviews, influencer partnerships, and resource link building. The focus is always on quality over quantity.
Local SEO for Ecommerce Businesses
Local SEO helps online stores with physical locations or regional focus capture geographically targeted searches. This includes Google Business Profile optimization, local citation building, and location-specific content.
Even pure-play online retailers benefit from local signals when targeting specific markets or competing against local competitors.

Why Online Stores Need Professional SEO Services
The ecommerce landscape has grown increasingly competitive. Professional SEO services provide the expertise and systematic execution needed to compete effectively for organic visibility.
The Competitive Landscape of Ecommerce Search
Ecommerce search results are dominated by established players with significant SEO investments. Amazon, major retailers, and category leaders occupy top positions for most product searches.
Competing requires more than basic optimization. You need comprehensive strategies that address technical foundations, content depth, and authority signals simultaneously. Partial efforts rarely produce meaningful results.
The competition continues intensifying. More businesses recognize SEO’s value, increasing investment levels across the industry. Standing still means falling behind.
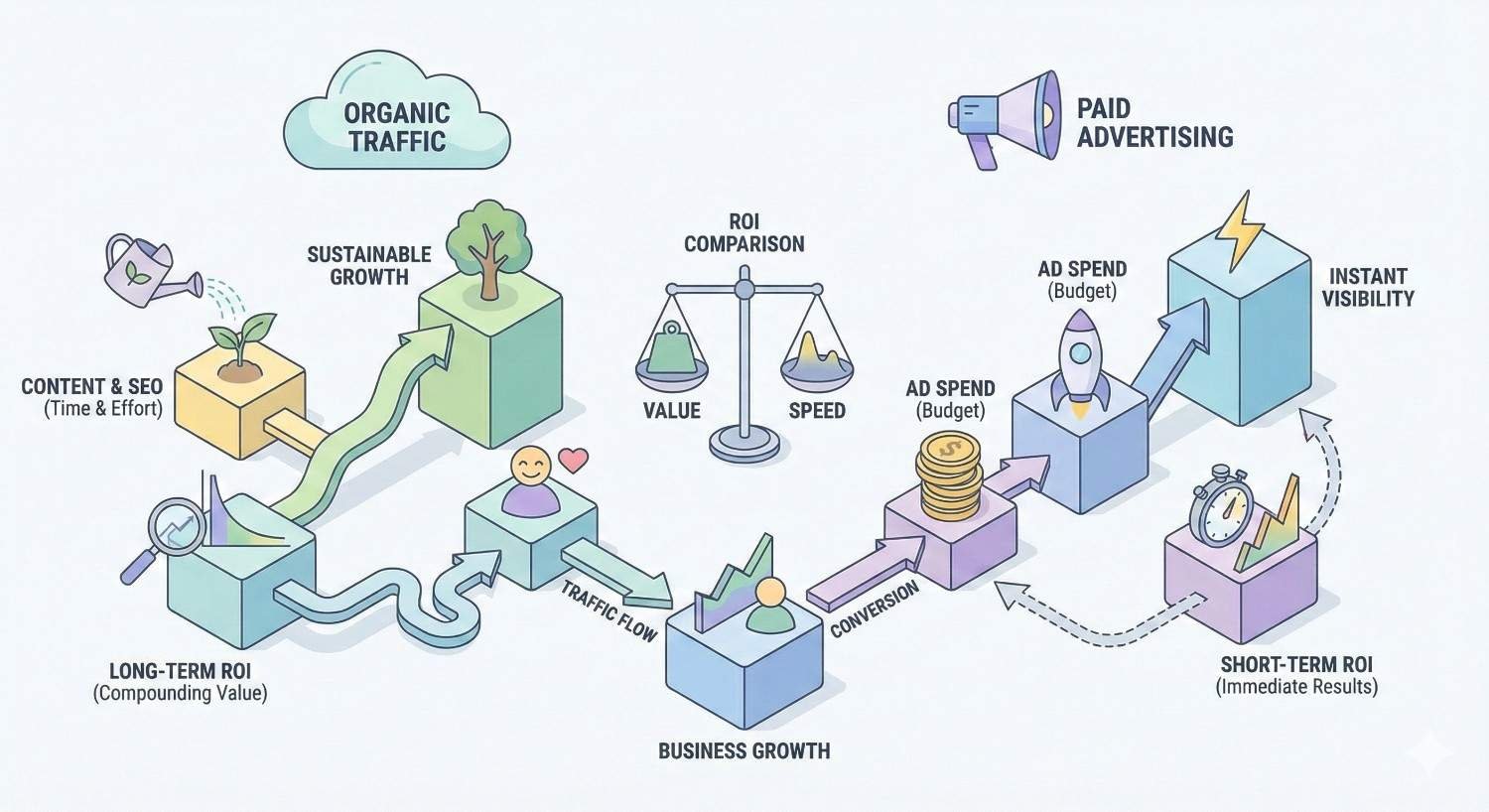
Organic Traffic vs. Paid Advertising ROI
Organic search traffic delivers fundamentally different economics than paid advertising. Understanding this difference clarifies why SEO investment makes strategic sense.
Paid advertising costs scale linearly with traffic. Double your visitors, double your ad spend. This creates a ceiling on profitability, especially in competitive categories where cost-per-click continues rising.
Organic traffic costs are front-loaded. Initial investment builds assets that generate traffic indefinitely. Once rankings are established, maintaining them costs far less than acquiring equivalent paid traffic.
The compounding effect matters significantly. SEO improvements build on each other. Technical fixes enable content to rank. Content attracts links. Links boost authority. Authority lifts all rankings. This virtuous cycle accelerates results over time.
For most ecommerce businesses, a balanced approach works best. Paid advertising drives immediate traffic while SEO builds long-term organic assets. Over time, organic traffic should represent an increasing share of total visitors.
Long-Term Revenue Impact of SEO Investment
SEO investment creates lasting business value that extends beyond monthly traffic reports. Understanding this long-term impact helps justify appropriate investment levels.
Asset creation distinguishes SEO from advertising. Optimized pages, quality content, and earned backlinks remain valuable indefinitely. These assets continue generating traffic long after initial investment.
Reduced customer acquisition costs improve unit economics over time. As organic traffic grows, blended acquisition costs decrease. This margin improvement flows directly to profitability.
Competitive moats develop through sustained SEO investment. Established rankings, domain authority, and content libraries create barriers that competitors cannot quickly overcome. First-mover advantages compound over years.
Business valuation increasingly considers organic traffic quality. Acquirers and investors recognize that sustainable organic traffic represents more valuable revenue than paid-dependent models.
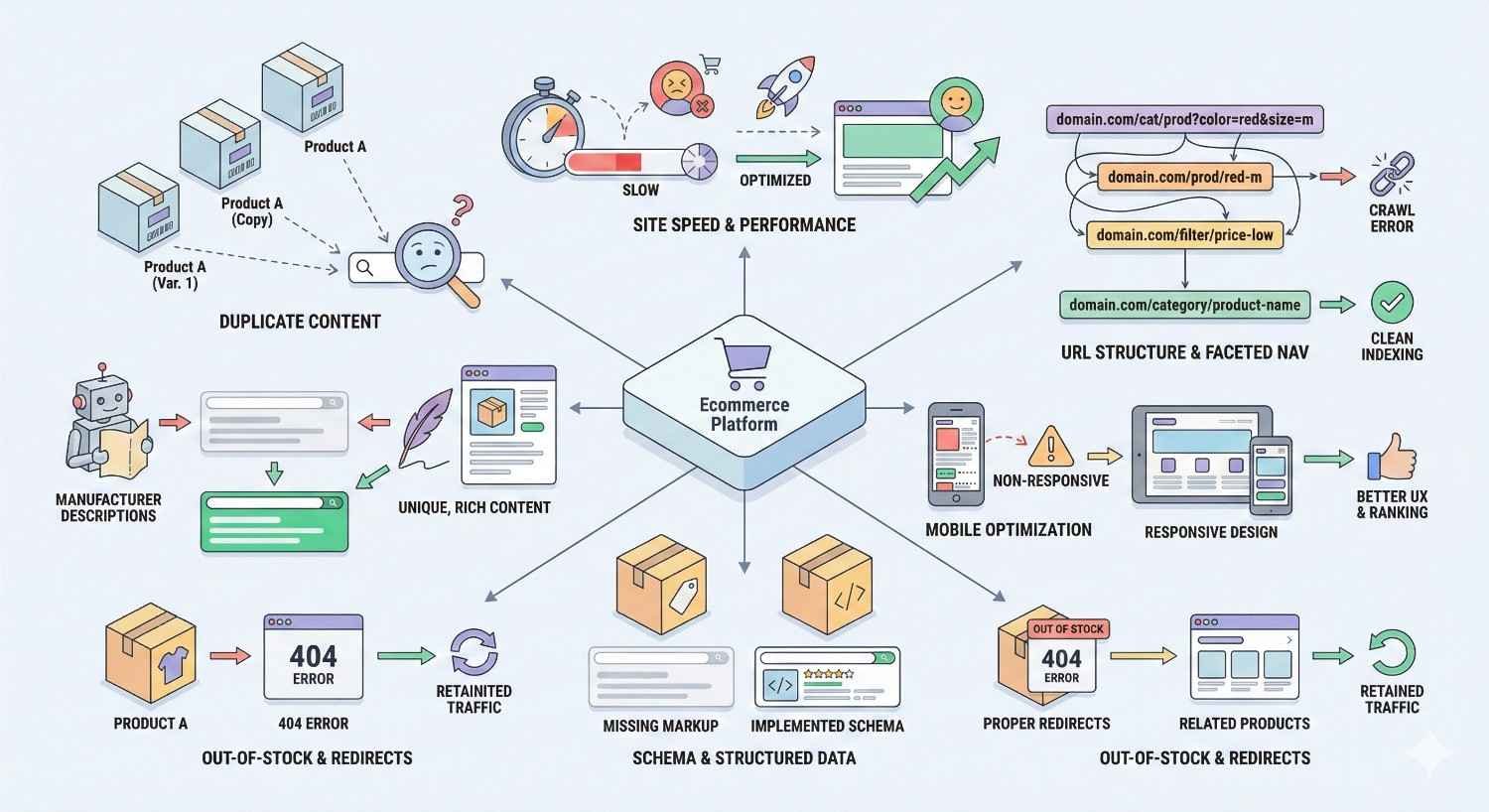
Common SEO Challenges Unique to Ecommerce
Ecommerce websites face specific challenges that require specialized solutions. Understanding these challenges helps set realistic expectations and prioritize efforts appropriately.
Massive scale creates management complexity. Optimizing thousands of product pages requires systematic approaches, automation tools, and prioritization frameworks. Manual optimization simply cannot scale.
Inventory changes constantly alter site content. Products go out of stock, new items launch, and seasonal inventory rotates. SEO strategies must accommodate this dynamism without losing ranking equity.
Faceted navigation creates crawl budget and duplicate content issues. Filters for size, color, price, and other attributes generate countless URL variations that can dilute ranking signals and waste crawl resources.
Thin content plagues product pages. Manufacturer descriptions, minimal specifications, and lack of unique value make many product pages indistinguishable from competitors. Standing out requires content investment.
Platform limitations constrain optimization options. Many ecommerce platforms restrict access to technical elements, URL structures, or page templates. Working within these constraints requires creative solutions.
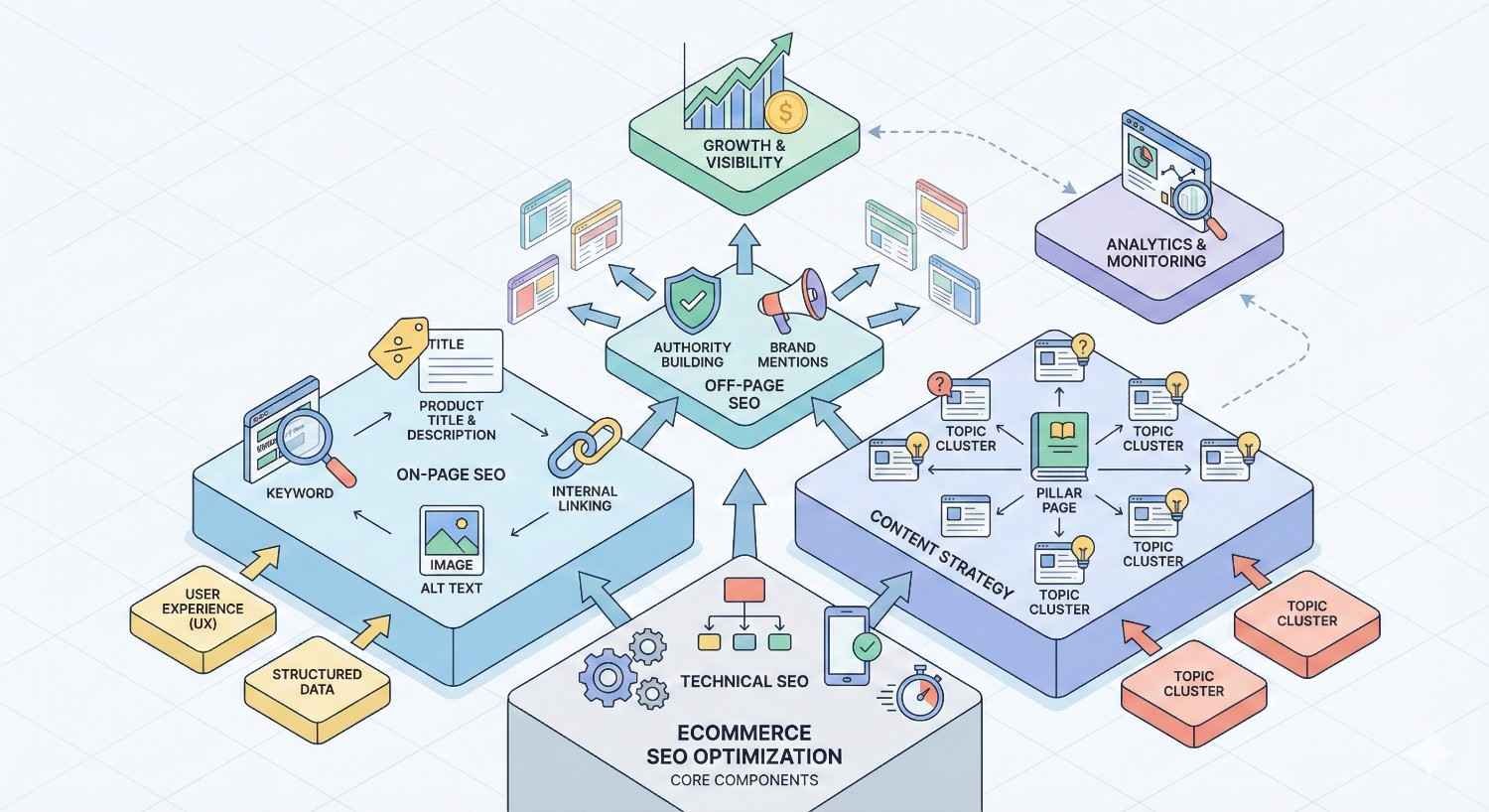
Core Components of Ecommerce SEO Optimization
Effective ecommerce SEO integrates multiple optimization disciplines into a cohesive strategy. Each component addresses specific ranking factors while supporting overall organic growth objectives.
Technical SEO for Ecommerce Websites
Technical SEO creates the foundation for all other optimization efforts. Without proper technical implementation, even excellent content and strong backlinks cannot achieve their ranking potential.
Site Architecture and Crawlability
Site architecture determines how search engines discover and understand your product catalog. Optimal architecture balances crawl efficiency with user experience.
Flat hierarchy keeps important pages within three clicks of the homepage. Deep pages receive less crawl attention and link equity. Structure your categories and subcategories to minimize depth while maintaining logical organization.
Internal linking distributes authority throughout your site. Category pages should link to products. Products should link to related items. Blog content should link to relevant product pages. This interconnection helps search engines understand relationships and importance.
XML sitemaps ensure all important pages are discoverable. For large catalogs, segment sitemaps by category or product type. Submit sitemaps through Google Search Console and monitor indexation status regularly.
Crawl budget optimization becomes critical for large sites. Block crawling of low-value pages like filtered navigation results, internal search pages, and duplicate content. Use robots.txt and meta robots tags strategically.
Pagination handling affects how search engines process category pages with multiple pages of products. Implement proper pagination markup and consider infinite scroll implications for crawlability.
Page Speed and Core Web Vitals
Page speed directly impacts both rankings and conversions. Google’s Core Web Vitals measure real-user experience across three key metrics.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) measures loading performance. Target under 2.5 seconds. For ecommerce, optimize hero images, implement lazy loading, and use content delivery networks to improve LCP scores.
First Input Delay (FID) measures interactivity. Target under 100 milliseconds. Minimize JavaScript execution time, break up long tasks, and optimize third-party script loading to improve FID.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) measures visual stability. Target under 0.1. Reserve space for images and ads, avoid inserting content above existing content, and use transform animations instead of layout-triggering properties.
Image optimization significantly impacts ecommerce page speed. Compress images appropriately, use modern formats like WebP, implement responsive images, and lazy load below-fold images.
Server response time affects all other metrics. Choose quality hosting, implement caching effectively, and consider server-side rendering for JavaScript-heavy sites.
Mobile Optimization for Shopping
Mobile commerce continues growing as a share of total ecommerce. Google’s mobile-first indexing means mobile experience directly determines rankings.
Responsive design adapts layouts to any screen size. Ensure product images, descriptions, and purchase buttons work seamlessly across devices. Test on actual devices, not just browser emulators.
Touch-friendly interfaces accommodate finger navigation. Buttons and links need adequate size and spacing. Form fields should be easy to complete on mobile keyboards.
Mobile page speed often differs significantly from desktop. Mobile networks and devices have different constraints. Test and optimize specifically for mobile performance.
Mobile checkout optimization reduces abandonment. Streamline forms, offer mobile payment options, and minimize steps required to complete purchases.
URL Structure for Product Catalogs
URL structure affects both crawlability and user experience. Clean, logical URLs help search engines understand page content and hierarchy.
Descriptive URLs include relevant keywords naturally. Use “/category/product-name” structures rather than “/product?id=12345”. Readable URLs improve click-through rates from search results.
Consistent patterns make site structure predictable. Establish URL conventions and apply them consistently across all product and category pages.
Avoid parameters when possible. Dynamic parameters create duplicate content issues and complicate tracking. Use static URLs with canonical tags when parameters are necessary.
Handle URL changes carefully. Implement 301 redirects for any changed URLs. Map old URLs to new equivalents to preserve ranking equity and avoid broken links.
Schema Markup for Products and Reviews
Schema markup helps search engines understand page content and enables rich results in search listings. Product schema is particularly valuable for ecommerce.
Product schema communicates essential product information including name, description, price, availability, and brand. This data can appear directly in search results, improving visibility and click-through rates.
Review schema displays star ratings in search results. Aggregate ratings from customer reviews create compelling visual differentiation that increases clicks.
Breadcrumb schema shows site hierarchy in search results. This helps users understand page context and can improve click-through rates for category and product pages.
FAQ schema enables expandable questions and answers in search results. Use this for product pages with common questions to capture additional SERP real estate.
Organization schema establishes brand identity and can enable knowledge panel features. Include logo, social profiles, and contact information.
Handling Duplicate Content and Canonicalization
Duplicate content is perhaps the most common technical issue affecting ecommerce sites. Multiple URLs displaying identical or similar content dilute ranking signals and waste crawl budget.
Canonical tags indicate preferred URLs when duplicate content exists. Point all variant URLs to a single canonical version. This consolidates ranking signals on your preferred page.
Product variants require careful handling. Color and size variations often share most content. Use canonical tags to consolidate variants or ensure each variant has sufficient unique content to justify separate indexation.
Faceted navigation creates exponential URL variations. Block crawling of filtered URLs through robots.txt or use noindex tags. Implement canonical tags pointing to unfiltered category pages.
Pagination can create duplicate content when page 2, 3, etc. contain similar content. Use rel=”next” and rel=”prev” markup and ensure paginated pages have unique title tags.
HTTP vs. HTTPS and www vs. non-www variations create duplicates. Implement redirects to consolidate all traffic on a single version and set preferred domain in Search Console.
On-Page SEO for Product and Category Pages
On-page optimization transforms individual pages into ranking assets. For ecommerce, this means optimizing both product pages and category pages for relevant search queries.
Product Title Optimization
Product titles serve multiple purposes: they’re the H1 heading, often the meta title, and the primary ranking signal for product-specific searches.
Include primary keywords naturally in product titles. Place the most important terms early. “Men’s Running Shoes – Nike Air Max 270” is better than “Nike Air Max 270 – Men’s Running Shoes” if “men’s running shoes” is your target keyword.
Add differentiating details that match search behavior. Size, color, model number, and key features help match long-tail searches. “Nike Air Max 270 Men’s Running Shoes – Black/White – Size 10” captures more specific queries.
Maintain readability despite keyword inclusion. Titles should make sense to human readers. Avoid keyword stuffing that creates awkward phrasing.
Keep titles concise for display purposes. Aim for 50-60 characters to avoid truncation in search results. Front-load important information.
Meta Descriptions That Drive Clicks
Meta descriptions don’t directly impact rankings but significantly influence click-through rates. Compelling descriptions differentiate your listing from competitors.
Include target keywords to trigger bold highlighting in search results. When users see their search terms bolded, they’re more likely to click.
Highlight unique value that differentiates your offering. Free shipping, price matching, exclusive features, or superior selection give users reasons to choose your listing.
Include calls to action that encourage clicks. “Shop now,” “Free shipping on orders over $50,” or “In stock and ready to ship” create urgency and clarity.
Stay within length limits of approximately 150-160 characters. Longer descriptions get truncated, potentially cutting off important information.
Write unique descriptions for each page. Duplicate meta descriptions across products waste opportunities to target different keywords and appeals.
Product Description Best Practices
Product descriptions directly impact both rankings and conversions. Effective descriptions balance SEO requirements with persuasive copywriting.
Write unique content for every product. Avoid using manufacturer descriptions that appear on countless other sites. Unique content differentiates your pages and provides ranking opportunities.
Address customer questions within descriptions. What materials is it made from? How does it fit? What problems does it solve? Anticipating and answering questions improves both SEO and conversions.
Include relevant keywords naturally throughout descriptions. Use variations and related terms rather than repeating exact phrases. Semantic richness signals topical relevance to search engines.
Structure content for scannability. Use bullet points for specifications, short paragraphs for benefits, and clear headings for different sections. Most users scan rather than read completely.
Highlight benefits alongside features. Features describe what a product is; benefits explain why it matters. “Breathable mesh upper” is a feature. “Keeps your feet cool during long runs” is a benefit.
Category Page Optimization Strategies
Category pages often have higher ranking potential than individual product pages. They target broader keywords with higher search volume and can rank for numerous related queries.
Add unique content to category pages beyond product listings. Introductory paragraphs, buying guides, and FAQ sections provide ranking signals and user value.
Optimize category titles for target keywords. “Women’s Running Shoes” is better than “Running” for a women’s running shoe category.
Implement proper heading hierarchy with H1 for the category name and H2s for subcategories or content sections.
Include internal links to related categories and featured products. This distributes link equity and helps users navigate.
Manage pagination effectively. Ensure paginated category pages have unique titles and descriptions. Consider “view all” options for smaller categories.
Image Optimization and Alt Text
Images are essential for ecommerce but can significantly impact page speed and accessibility. Proper optimization addresses both concerns while adding SEO value.
Compress images without visible quality loss. Use tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim to reduce file sizes. Smaller files load faster without sacrificing visual quality.
Use descriptive file names that include relevant keywords. “nike-air-max-270-mens-running-shoe-black.jpg” is better than “IMG_12345.jpg”.
Write descriptive alt text for every product image. Alt text serves accessibility purposes and provides additional keyword signals. Describe what the image shows naturally.
Implement multiple images showing products from different angles. More images improve user experience and provide additional optimization opportunities.
Use appropriate formats for different image types. JPEG for photographs, PNG for graphics with transparency, WebP for modern browsers that support it.
Internal Linking for Ecommerce Sites
Internal linking distributes authority throughout your site and helps search engines understand page relationships and importance.
Link from category pages to top products and subcategories. These links pass authority to important pages and improve crawlability.
Implement related products sections on product pages. Links to similar items keep users engaged and distribute link equity across your catalog.
Link from blog content to relevant product and category pages. Informational content often attracts backlinks; internal links pass that authority to commercial pages.
Use descriptive anchor text that includes relevant keywords. “Men’s running shoes” is better anchor text than “click here” or “learn more.”
Audit internal links regularly to identify orphaned pages and broken links. Every important page should be reachable through internal navigation.
Keyword Research for Online Stores
Keyword research identifies the search terms your target customers use when looking for products you sell. Effective research balances search volume, competition, and commercial intent.
Transactional vs. Informational Keywords
Understanding keyword intent helps prioritize efforts and match content to user needs.
Transactional keywords indicate purchase readiness. Terms like “buy,” “price,” “discount,” “free shipping,” and specific product names signal users ready to purchase. These keywords should target product and category pages.
Informational keywords indicate research mode. Terms like “how to,” “best,” “vs,” “review,” and “guide” signal users gathering information before purchasing. These keywords should target blog content and buying guides.
Commercial investigation keywords fall between informational and transactional. Users are comparing options and narrowing choices. Target these with comparison content and detailed product information.
Navigational keywords target specific brands or websites. Users searching your brand name or specific product names have high intent and should find exactly what they’re looking for.
Long-Tail Keywords for Product Pages
Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific phrases with lower search volume but higher conversion potential.
Product-specific long-tails include detailed attributes. “Nike Air Max 270 men’s running shoes size 10 black” is highly specific and indicates strong purchase intent.
Problem-solution long-tails describe what users want to accomplish. “Running shoes for flat feet” or “waterproof hiking boots for wide feet” target specific needs.
Comparison long-tails indicate users evaluating options. “Nike vs Adidas running shoes” or “best running shoes under $100” signal commercial investigation.
Question-based long-tails often appear in voice searches. “What are the best running shoes for beginners” or “where to buy Nike Air Max 270” capture conversational queries.
Competitor Keyword Analysis
Analyzing competitor keywords reveals opportunities and gaps in your current strategy.
Identify ranking competitors for your target keywords. These may differ from your business competitors. Focus on sites that rank for terms you want to target.
Analyze competitor content to understand what’s ranking. What topics do they cover? How comprehensive is their content? What can you do better?
Find keyword gaps where competitors rank but you don’t. These represent opportunities to expand your keyword targeting.
Identify your advantages where you rank but competitors don’t. Protect and strengthen these positions.
Seasonal and Trending Keyword Opportunities
Ecommerce search behavior varies significantly by season and trends. Capturing these opportunities requires proactive planning.
Map seasonal patterns for your product categories. When do searches peak? Plan content and optimization efforts to coincide with demand increases.
Prepare content early for seasonal keywords. Pages need time to rank. Create and optimize seasonal content months before peak demand.
Monitor trending topics relevant to your products. Google Trends, social media, and industry news reveal emerging opportunities.
Update existing content to reflect current trends. Refresh product descriptions, blog posts, and category content to remain relevant.
Keyword Mapping to Site Structure
Keyword mapping assigns target keywords to specific pages, ensuring comprehensive coverage without internal competition.
One primary keyword per page prevents cannibalization. Each page should target a distinct primary keyword, though secondary keywords can overlap.
Map keywords to page types appropriately. Broad category keywords go to category pages. Specific product keywords go to product pages. Informational keywords go to blog content.
Identify gaps where valuable keywords lack corresponding pages. Create new content to capture these opportunities.
Document your mapping for reference and coordination. A keyword map helps teams avoid conflicts and track coverage.
Content Strategy for Ecommerce SEO
Content strategy extends beyond product pages to capture traffic throughout the buyer journey. Strategic content builds topical authority and attracts links that benefit your entire site.
Blog Content for Buyer Journey Stages
Blog content targets informational queries that product pages cannot effectively address. Mapping content to journey stages ensures comprehensive coverage.
Awareness stage content introduces problems and solutions. Users don’t know what they need yet. Content like “Signs you need new running shoes” or “How to choose the right running shoe” captures early-stage researchers.
Consideration stage content helps users evaluate options. Comparison guides, feature explanations, and detailed reviews help users narrow choices.
Decision stage content supports final purchase decisions. Size guides, care instructions, and warranty information address last-minute concerns.
Post-purchase content supports customers after buying. How-to guides, maintenance tips, and troubleshooting content build loyalty and reduce returns.
Buying Guides and Comparison Content
Buying guides and comparisons target high-value commercial investigation keywords while providing genuine user value.
Comprehensive buying guides cover everything users need to know before purchasing. Include selection criteria, feature explanations, price ranges, and specific recommendations.
Product comparisons help users choose between options. Compare your products to competitors or compare different products within your catalog.
Best-of lists capture “best [product category]” searches. These high-volume keywords drive significant traffic when you rank well.
Price-focused content targets budget-conscious shoppers. “Best running shoes under $100” or “affordable alternatives to [premium brand]” capture price-sensitive searches.
User-Generated Content and Reviews
User-generated content provides unique, constantly refreshing content that search engines value.
Customer reviews add unique content to product pages. Each review contains keywords and phrases that help pages rank for long-tail queries.
Q&A sections capture question-based searches. Customer questions and answers create content that matches how users search.
Photo and video submissions from customers add authentic content. User photos showing products in real use build trust and provide additional optimization opportunities.
Incentivize submissions through follow-up emails, loyalty programs, or contests. More user content means more ranking opportunities.
FAQ Pages and Knowledge Bases
FAQ content captures question-based searches and can earn featured snippet positions.
Product-specific FAQs address common questions about individual items. Sizing, compatibility, care instructions, and shipping questions are common topics.
Category-level FAQs address broader questions about product types. “How to choose running shoes” or “What’s the difference between trail and road running shoes” target category-level queries.
Site-wide FAQs cover policies and procedures. Shipping, returns, payment options, and customer service questions belong here.
Structure for featured snippets by using question headings with concise, direct answers. FAQ schema markup enables rich results.
Video Content for Product SEO
Video content engages users and can rank in both standard and video search results.
Product demonstration videos show items in use. These help users understand products better and can rank for “[product] review” searches.
How-to videos support informational content. Tutorial content attracts links and establishes expertise.
Optimize video metadata including titles, descriptions, and tags. Include target keywords naturally.
Host strategically based on your goals. YouTube provides discovery but sends traffic away. Self-hosting keeps users on your site but limits discovery.
Link Building for Ecommerce Websites
Link building establishes domain authority through backlinks from other websites. For ecommerce, this requires strategies that leverage products, expertise, and industry relationships.
Product-Based Link Acquisition
Products themselves can attract links when positioned effectively.
Product reviews from bloggers and publications generate authoritative links. Reach out to relevant reviewers with samples and information.
Gift guides and roundups frequently link to featured products. Pitch your products for inclusion in seasonal and topical guides.
Resource pages in your industry may link to useful products. Identify relevant resource pages and suggest your products for inclusion.
Unique or innovative products naturally attract attention. If you sell something genuinely novel, promote it to relevant publications.
Digital PR for Online Retailers
Digital PR earns links through newsworthy content and brand stories.
Data-driven content attracts journalist attention. Original research, surveys, and industry analysis provide citation-worthy material.
Expert commentary positions your brand as an authority. Offer insights on industry trends and news to relevant publications.
Brand stories humanize your business. Founding stories, mission-driven initiatives, and company culture can earn feature coverage.
Newsjacking connects your brand to trending topics. Quick, relevant commentary on breaking news can earn timely coverage.
Influencer and Affiliate Partnerships
Partnerships extend your reach and can generate valuable links.
Influencer collaborations create content that links back to your store. Product features, reviews, and sponsored content from relevant influencers build awareness and links.
Affiliate programs incentivize link creation. Affiliates create content promoting your products, generating links alongside sales.
Brand partnerships with complementary businesses create mutual linking opportunities. Co-created content, joint promotions, and cross-promotions benefit both parties.
Sponsored content on relevant publications can include followed links when done appropriately. Ensure compliance with disclosure requirements.
Broken Link Building Strategies
Broken link building finds dead links on other sites and offers your content as a replacement.
Find relevant broken links using tools like Ahrefs or Check My Links. Look for broken links to products or content similar to yours.
Create replacement content if needed. Sometimes you’ll need to create content that matches what the broken link originally referenced.
Reach out helpfully to site owners. Alert them to the broken link and suggest your content as a replacement. Focus on being helpful rather than promotional.
Scale systematically by building processes for finding and pursuing broken link opportunities. This strategy works best with consistent effort.
Avoiding Toxic Backlinks
Not all links help rankings. Some can actively harm your site.
Identify toxic links through regular backlink audits. Look for links from spammy sites, irrelevant directories, and known link schemes.
Disavow harmful links through Google Search Console. The disavow tool tells Google to ignore specific links when assessing your site.
Avoid link schemes that violate Google’s guidelines. Paid links, excessive link exchanges, and automated link building create risk.
Focus on quality over quantity. A few links from authoritative, relevant sites provide more value than hundreds of low-quality links.
Ecommerce SEO Ranking Factors Explained
Understanding ranking factors helps prioritize optimization efforts. While Google uses hundreds of signals, certain factors carry particular weight for ecommerce sites.
Google’s Algorithm and Ecommerce Signals
Google’s algorithm evaluates pages based on relevance, quality, and user experience. For ecommerce, specific signals indicate whether product pages deserve top rankings.
Relevance signals determine whether your page matches search intent. Keyword usage, content comprehensiveness, and semantic relationships all contribute.
Quality signals assess whether your content provides value. Unique descriptions, helpful information, and expert knowledge demonstrate quality.
Authority signals evaluate your site’s credibility. Backlinks, brand mentions, and domain history establish authority.
User experience signals measure how visitors interact with your site. Page speed, mobile usability, and engagement metrics influence rankings.
E-E-A-T for Online Stores (Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trust)
E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) represents Google’s quality guidelines. For ecommerce, demonstrating E-E-A-T builds ranking potential.
Experience shows first-hand knowledge of products. Customer reviews, staff picks with explanations, and detailed product knowledge demonstrate experience.
Expertise establishes your knowledge in your product category. Detailed buying guides, technical specifications, and educational content show expertise.
Authoritativeness comes from recognition by others. Backlinks, brand mentions, press coverage, and industry awards build authority.
Trustworthiness assures users your site is safe and reliable. Secure checkout, clear policies, contact information, and customer reviews build trust.
User Experience Signals That Impact Rankings
User experience directly influences rankings through measurable engagement signals.
Click-through rate from search results indicates relevance. Compelling titles and descriptions improve CTR, which can boost rankings.
Bounce rate and dwell time suggest content quality. Users who quickly return to search results signal dissatisfaction.
Page engagement metrics like scroll depth and interaction indicate content value. Engaged users suggest quality content.
Mobile usability affects rankings directly through mobile-first indexing. Poor mobile experience hurts rankings regardless of desktop quality.
Site Security and HTTPS Requirements
Security is a confirmed ranking factor and essential for ecommerce trust.
HTTPS encryption is mandatory for ecommerce sites. Google flags non-HTTPS sites as insecure, damaging trust and rankings.
SSL certificate quality matters for user trust. Extended validation certificates display company information, building confidence.
Security badges and trust seals reassure users. Display payment security, privacy certifications, and industry credentials prominently.
Regular security audits prevent vulnerabilities. Compromised sites face ranking penalties and devastating trust damage.
Reviews, Ratings, and Social Proof Signals
Reviews and ratings influence both rankings and conversions.
Review quantity signals product popularity and provides fresh content. More reviews generally correlate with better rankings.
Review quality and sentiment affect user decisions. Positive reviews build trust; negative reviews handled well demonstrate customer service.
Star ratings in search results improve click-through rates. Implement review schema to display ratings in SERPs.
Social proof beyond reviews includes social media engagement, user-generated content, and community activity.
Ecommerce SEO Timeline: What to Expect
SEO results develop over months, not days. Understanding realistic timelines helps set appropriate expectations and maintain commitment through the growth period.
Month 1-3: Foundation and Technical Fixes
The first three months focus on establishing foundations and fixing critical issues.
Technical audit identifies all issues affecting crawlability, indexation, and performance. Prioritize fixes based on impact and effort.
Quick wins address obvious problems with immediate impact. Fixing broken links, adding missing meta tags, and resolving duplicate content issues often show early results.
Architecture improvements may require significant development work. Plan and begin implementing structural changes.
Baseline measurement establishes starting metrics. Document current rankings, traffic, and conversions for comparison.
Strategy development creates the roadmap for ongoing optimization. Keyword research, content planning, and link building strategies take shape.
Month 4-6: Content Development and On-Page Optimization
Months four through six focus on content creation and page-level optimization.
Product page optimization improves titles, descriptions, and content across priority pages. Start with highest-potential products and categories.
Content creation begins producing blog posts, guides, and supporting content. Focus on high-value keywords identified during research.
Internal linking improvements distribute authority to priority pages. Implement related products, category links, and content cross-links.
Initial ranking movements may appear for less competitive keywords. Long-tail terms often show improvement first.
Continued technical work addresses remaining issues and implements ongoing improvements.
Month 7-12: Authority Building and Ranking Growth
The second half of year one focuses on building authority and achieving meaningful ranking improvements.
Link building efforts begin producing results. Outreach campaigns, content promotion, and partnership development generate backlinks.
Content expansion continues building topical coverage. Fill gaps identified during initial research and respond to emerging opportunities.
Ranking improvements become more visible for competitive keywords. Pages optimized in earlier months begin climbing.
Traffic growth accelerates as rankings improve. Organic traffic should show clear upward trends.
Conversion optimization refines pages based on traffic data. Improve pages that rank well but don’t convert effectively.
Year 2+: Scaling and Maintaining Organic Visibility
Beyond year one, focus shifts to scaling success and maintaining positions.
Expand keyword targeting to capture additional opportunities. Build on successful categories and explore adjacent topics.
Defend rankings against competitors. Monitor positions and respond to competitive threats.
Content refreshes keep existing content current and competitive. Update statistics, add new information, and improve underperforming content.
Technical maintenance prevents regression. Regular audits catch new issues before they impact rankings.
Scale successful strategies that proved effective in year one. Double down on what works.
Factors That Accelerate or Delay Results
Several factors influence how quickly SEO produces results.
Accelerating factors:
- Strong existing domain authority
- Technical foundation already solid
- Less competitive niche
- Aggressive content investment
- Quality link building
- Dedicated internal resources
Delaying factors:
- New domain with no history
- Significant technical debt
- Highly competitive market
- Limited content resources
- Weak backlink profile
- Platform limitations
Measuring Ecommerce SEO Success
Effective measurement connects SEO activities to business outcomes. Proper tracking enables data-driven decisions and demonstrates ROI.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Online Stores
Select KPIs that align with business objectives and provide actionable insights.
Organic traffic measures total visitors from search engines. Track overall trends and segment by landing page type.
Organic revenue connects traffic to business results. This is the ultimate measure of SEO success for ecommerce.
Keyword rankings track positions for target keywords. Monitor priority keywords and track movement over time.
Organic conversion rate measures how effectively organic traffic converts. Compare to other channels and identify improvement opportunities.
Pages indexed indicates how much of your catalog search engines can access. Monitor for indexation issues.
Backlink growth tracks authority building progress. Measure both quantity and quality of new links.
Setting Up Google Analytics 4 for Ecommerce
Google Analytics 4 provides essential ecommerce tracking when configured properly.
Enable enhanced ecommerce to track product views, add-to-cart actions, and purchases. This data reveals how organic visitors interact with products.
Configure conversion tracking for purchases and other valuable actions. Assign values to conversions for ROI calculation.
Create organic traffic segments to isolate SEO performance from other channels. Compare organic metrics to paid and direct traffic.
Set up custom reports for regular monitoring. Build dashboards that surface key metrics without manual analysis.
Connect to Search Console for integrated search data. Linking accounts enables query-level analysis within Analytics.
Google Search Console for Product Visibility
Google Search Console provides direct insight into how Google sees your site.
Monitor indexation status to ensure products are discoverable. Identify and resolve indexation issues promptly.
Analyze search queries driving impressions and clicks. Discover new keyword opportunities and optimize for high-impression, low-click queries.
Track click-through rates by query and page. Identify opportunities to improve titles and descriptions.
Review Core Web Vitals reports for performance issues. Address pages failing vital thresholds.
Submit sitemaps and monitor crawl statistics. Ensure Google can efficiently access your entire catalog.
Revenue Attribution and ROI Calculation
Connecting SEO investment to revenue demonstrates value and justifies continued investment.
Track organic revenue directly in analytics. This is your primary ROI metric.
Calculate customer lifetime value from organic acquisition. First-purchase revenue understates true value for repeat-purchase businesses.
Compare acquisition costs across channels. Organic traffic should show lower cost-per-acquisition than paid channels over time.
Account for assisted conversions where organic touchpoints contribute to conversions attributed to other channels.
Calculate ROI by comparing organic revenue to SEO investment. Include agency fees, tools, content costs, and internal time.
Reporting Frameworks and Dashboards
Regular reporting maintains visibility and enables timely optimization.
Weekly monitoring catches issues quickly. Track rankings, traffic, and indexation for early warning signs.
Monthly reporting provides comprehensive performance review. Analyze trends, compare to goals, and adjust strategies.
Quarterly business reviews connect SEO to broader business objectives. Present ROI, competitive position, and strategic recommendations.
Automated dashboards reduce reporting burden. Tools like Google Data Studio or Looker create real-time visualizations.
How to Choose an Ecommerce SEO Service Provider
Selecting the right SEO partner significantly impacts results. Thorough evaluation prevents costly mistakes and ensures alignment with your goals.
Questions to Ask Before Hiring an SEO Agency
Ask these questions to evaluate potential providers effectively.
What is your experience with ecommerce SEO specifically? General SEO experience doesn’t guarantee ecommerce expertise. Look for providers with relevant case studies.
How do you approach technical SEO for large product catalogs? The answer reveals whether they understand ecommerce-specific challenges.
What does your reporting include and how often? Transparency and communication frequency indicate partnership quality.
Who will actually work on my account? Understand whether you’ll work with senior strategists or junior staff.
How do you measure success? Alignment on KPIs prevents future disagreements.
What’s your link building approach? Ensure their methods align with Google’s guidelines.
Can you provide references from similar clients? Speaking with current clients reveals real experience.
Red Flags and Warning Signs to Avoid
Certain warning signs indicate providers to avoid.
Guaranteed rankings are impossible to promise. No one controls Google’s algorithm. Guarantees indicate either dishonesty or ignorance.
Secret methods they won’t explain suggest questionable tactics. Legitimate SEO is transparent.
Extremely low prices often mean low-quality work. Effective SEO requires significant expertise and effort.
No case studies or references may indicate lack of experience or poor results.
Focus on vanity metrics like keyword rankings without connecting to business outcomes suggests misaligned priorities.
Long-term contracts with no exit clause trap you if results disappoint. Reasonable contracts include performance-based exit options.
In-House vs. Agency vs. Freelance SEO
Different engagement models suit different situations.
In-house SEO provides dedicated focus and deep business knowledge. Best for large operations with sufficient budget for full-time specialists.
Agency SEO offers diverse expertise and scalable resources. Best for businesses wanting comprehensive services without building internal teams.
Freelance SEO provides flexibility and often lower costs. Best for specific projects or businesses with some internal capability.
Hybrid approaches combine models. Many businesses use agencies for strategy and specialized work while handling routine tasks internally.
Evaluating Case Studies and Past Results
Case studies reveal what providers can actually deliver.
Look for relevant examples in your industry or with similar challenges. Results in unrelated contexts may not transfer.
Verify claims when possible. Ask for references you can contact directly.
Understand the context behind results. What was the starting point? What resources were invested? What timeframe?
Look for sustainable results rather than short-term spikes. Long-term growth indicates sound strategies.
Ask about failures too. How providers handle setbacks reveals character and learning ability.
Understanding SEO Contracts and Deliverables
Clear contracts prevent misunderstandings and protect both parties.
Scope of work should detail exactly what’s included. Ambiguity leads to disputes.
Deliverables should be specific and measurable. “SEO services” is vague; “monthly technical audit, 4 blog posts, and 10 outreach emails” is specific.
Timeline expectations should be realistic. Promises of quick results indicate either dishonesty or misunderstanding.
Reporting requirements should specify frequency, format, and metrics included.
Termination clauses should allow exit if results disappoint. Reasonable notice periods protect both parties.
Ownership of work should be clear. You should own content and retain access to all accounts.
Ecommerce SEO Pricing and Investment
Understanding pricing helps budget appropriately and evaluate proposals. Costs vary significantly based on scope, competition, and provider quality.
Typical Pricing Models (Retainer, Project, Hourly)
Different pricing models suit different needs.
Monthly retainers provide ongoing services for a fixed fee. Most common for comprehensive SEO programs. Typical range: $2,000-$10,000+ monthly depending on scope and provider.
Project-based pricing covers specific initiatives with defined scope. Best for audits, migrations, or specific optimization projects. Typical range: $5,000-$50,000+ depending on complexity.
Hourly consulting provides flexible access to expertise. Best for businesses with internal capability needing strategic guidance. Typical range: $150-$500+ per hour.
Performance-based pricing ties fees to results. Less common due to attribution challenges but can align incentives effectively.
What Influences Ecommerce SEO Costs
Several factors affect pricing for ecommerce SEO services.
Site size directly impacts workload. Optimizing 100 products differs vastly from optimizing 10,000.
Competition level determines effort required. Highly competitive niches require more aggressive strategies.
Current state affects initial investment. Sites with significant technical debt require more foundational work.
Goals and timeline influence resource allocation. Aggressive growth targets require larger investments.
Provider quality correlates with pricing. Experienced specialists command premium rates.
Geographic location affects agency rates. Providers in high-cost markets typically charge more.
Budget Allocation Recommendations by Store Size
General guidelines help frame appropriate investment levels.
Small stores (under $500K revenue): $1,500-$3,000 monthly covers essential optimization. Focus on technical foundations and priority pages.
Mid-size stores ($500K-$5M revenue): $3,000-$7,000 monthly enables comprehensive programs. Include content development and link building.
Large stores ($5M+ revenue): $7,000-$15,000+ monthly supports aggressive growth. Full-service programs with dedicated resources.
Enterprise stores ($50M+ revenue): $15,000-$50,000+ monthly for complex, large-scale operations. Often combined with in-house teams.
Calculating Expected ROI from SEO Investment
ROI calculation justifies investment and guides budget decisions.
Estimate traffic potential based on keyword research. What traffic could you capture with top rankings?
Apply conversion rates to estimate orders. Use your current organic conversion rate or industry benchmarks.
Calculate revenue from estimated orders. Multiply by average order value.
Compare to investment to determine ROI. Healthy SEO programs should deliver 3-5x ROI or better over time.
Account for timeline in calculations. SEO investment compounds over time, improving ROI in later periods.
Ecommerce SEO by Platform
Different ecommerce platforms present unique SEO opportunities and challenges. Understanding platform-specific considerations helps optimize effectively.
Shopify SEO Services and Considerations
Shopify powers millions of online stores with a user-friendly platform that includes basic SEO capabilities.
Strengths: Clean code, mobile-responsive themes, built-in SSL, automatic sitemap generation, and app ecosystem for extended functionality.
Limitations: Restricted URL structure (forced “/collections/” and “/products/” prefixes), limited access to robots.txt, and theme-dependent technical implementation.
Key optimizations: Custom meta fields for products, app-based schema enhancement, blog content for informational keywords, and strategic collection page optimization.
Common issues: Duplicate content from product tags, pagination handling, and variant URL management require careful attention.
WooCommerce SEO Optimization
WooCommerce offers maximum flexibility as a WordPress plugin, enabling extensive customization.
Strengths: Full control over technical elements, extensive plugin ecosystem (Yoast, Rank Math), flexible URL structures, and unlimited customization potential.
Limitations: Requires more technical management, plugin conflicts can cause issues, and performance depends heavily on hosting and configuration.
Key optimizations: Proper permalink structure, schema plugins for product markup, category page content, and image optimization plugins.
Common issues: Plugin bloat affecting speed, security vulnerabilities requiring vigilance, and complexity requiring technical expertise.
BigCommerce SEO Strategies
BigCommerce provides enterprise-grade features with strong built-in SEO capabilities.
Strengths: Automatic image optimization, built-in CDN, customizable URLs, native faceted search handling, and strong technical foundation.
Limitations: Less flexibility than open-source platforms, theme customization constraints, and smaller app ecosystem than Shopify.
Key optimizations: Leverage built-in SEO features fully, customize meta templates, implement blog content strategy, and optimize category page content.
Common issues: Default settings may need adjustment, and some advanced customizations require developer support.
Magento/Adobe Commerce SEO
Magento (now Adobe Commerce) serves enterprise retailers with powerful but complex capabilities.
Strengths: Unlimited customization, powerful category and attribute management, multi-store capabilities, and enterprise-grade scalability.
Limitations: Significant technical complexity, expensive development and hosting, and steep learning curve.
Key optimizations: Proper layered navigation configuration, canonical tag implementation, category landing page content, and performance optimization.
Common issues: Duplicate content from layered navigation, slow page speed without optimization, and complex technical requirements.
Custom Ecommerce Platform SEO
Custom-built platforms offer complete control but require comprehensive SEO implementation.
Strengths: No platform limitations, optimized for specific needs, and complete technical control.
Limitations: All SEO features must be built, no community resources or plugins, and ongoing development requirements.
Key optimizations: Build SEO requirements into development specifications, implement comprehensive schema markup, and create flexible content management capabilities.
Common issues: SEO often overlooked during development, requiring retrofit. Ensure SEO expertise is involved from project inception.
Ecommerce SEO for Different Business Models
Different business models require adapted SEO strategies. Understanding model-specific considerations improves strategy effectiveness.
B2C Retail Store Optimization
B2C retail represents the most common ecommerce model with well-established SEO patterns.
Focus areas: Product page optimization, category page content, transactional keyword targeting, and conversion rate optimization.
Content strategy: Buying guides, product comparisons, trend content, and seasonal campaigns.
Link building: Product reviews, gift guides, influencer partnerships, and digital PR.
Key metrics: Organic revenue, conversion rate, and average order value from organic traffic.
B2B Ecommerce SEO Strategies
B2B ecommerce involves longer sales cycles and different buyer behavior.
Focus areas: Technical specifications, bulk ordering information, account-based features, and industry-specific content.
Content strategy: Technical documentation, case studies, ROI calculators, and industry guides.
Link building: Industry publications, trade associations, and professional partnerships.
Key metrics: Lead generation, quote requests, and account creation alongside direct sales.
Dropshipping SEO Considerations
Dropshipping faces unique challenges from using supplier content and competing with other dropshippers.
Focus areas: Unique product descriptions, niche specialization, brand building, and customer experience differentiation.
Content strategy: Extensive original content to differentiate from competitors using identical supplier descriptions.
Link building: Niche authority building, community engagement, and content-driven link acquisition.
Key metrics: Organic traffic quality, conversion rates, and customer acquisition cost.
Marketplace Seller SEO (Amazon, eBay Integration)
Sellers on marketplaces can benefit from SEO for their own stores while leveraging marketplace presence.
Focus areas: Own-site optimization for brand searches, content that marketplaces can’t provide, and customer relationship building.
Content strategy: Brand storytelling, detailed guides, and content that drives marketplace and direct sales.
Link building: Brand mentions, product reviews, and authority building that benefits both channels.
Key metrics: Direct site traffic, brand search volume, and marketplace ranking correlation.
Subscription-Based Ecommerce SEO
Subscription models require SEO strategies that support recurring revenue.
Focus areas: Subscription value proposition, comparison with alternatives, and retention-focused content.
Content strategy: Educational content supporting product use, community building, and subscriber success stories.
Link building: Lifestyle publications, subscription box reviews, and niche community partnerships.
Key metrics: Subscriber acquisition cost, lifetime value from organic acquisition, and churn rate by acquisition channel.
Common Ecommerce SEO Mistakes to Avoid
Learning from common mistakes helps avoid costly errors. These issues frequently undermine ecommerce SEO efforts.
Thin Product Descriptions
Minimal product descriptions fail to differentiate pages or provide ranking signals.
The problem: Using manufacturer descriptions that appear on countless sites, or writing minimal descriptions that don’t help users or search engines.
The solution: Write unique, comprehensive descriptions for every product. Include features, benefits, use cases, and specifications. Aim for at least 200-300 words for important products.
The impact: Unique descriptions improve rankings, reduce bounce rates, and increase conversions.
Ignoring Technical SEO Issues
Technical problems prevent even excellent content from ranking.
The problem: Crawl errors, slow page speed, mobile issues, and indexation problems silently undermine SEO efforts.
The solution: Conduct regular technical audits. Monitor Search Console for issues. Prioritize and fix problems systematically.
The impact: Technical fixes often produce quick ranking improvements by removing barriers to performance.
Duplicate Content Across Product Variants
Product variants create massive duplicate content issues when handled poorly.
The problem: Size, color, and other variants often share identical content across multiple URLs, diluting ranking signals.
The solution: Use canonical tags to consolidate variants, or ensure each variant has sufficient unique content. Consider whether variants need separate URLs at all.
The impact: Proper variant handling concentrates ranking signals and improves crawl efficiency.
Poor Site Architecture and Navigation
Confusing structure hurts both users and search engines.
The problem: Deep page hierarchies, illogical category structures, and poor internal linking make content hard to find and understand.
The solution: Design intuitive hierarchies with important pages within three clicks of the homepage. Use clear category names and logical groupings.
The impact: Good architecture improves crawlability, distributes link equity effectively, and enhances user experience.
Neglecting Mobile User Experience
Mobile commerce dominates, yet many sites still provide poor mobile experiences.
The problem: Difficult navigation, slow loading, and frustrating checkout on mobile devices drive users away.
The solution: Design mobile-first. Test on actual devices. Optimize for touch interaction and mobile page speed.
The impact: Mobile experience directly affects rankings through mobile-first indexing and impacts conversions significantly.
Expecting Immediate Results
Unrealistic timeline expectations lead to premature strategy abandonment.
The problem: Expecting significant results within weeks leads to frustration and potentially abandoning effective strategies before they produce results.
The solution: Set realistic expectations from the start. Plan for 6-12 months before expecting significant results. Celebrate incremental progress.
The impact: Patience allows strategies to mature and compound. Premature changes prevent learning what actually works.
Future of Ecommerce SEO
SEO continues evolving with technology and user behavior changes. Understanding emerging trends helps prepare for future success.
AI and Machine Learning in Search
Artificial intelligence increasingly influences search results and SEO practices.
Search algorithm evolution: Google’s AI systems better understand content quality, user intent, and semantic relationships. This rewards genuinely helpful content over keyword-optimized pages.
Content creation tools: AI writing assistants can help scale content production, but human expertise remains essential for quality and accuracy.
Personalization: Search results increasingly personalize based on user behavior, location, and preferences.
Preparation: Focus on creating genuinely valuable content that demonstrates expertise. AI rewards quality, not manipulation.
Voice Search Optimization for Shopping
Voice assistants change how some users search for products.
Conversational queries: Voice searches tend to be longer and more conversational than typed searches.
Local intent: Many voice searches have local intent, benefiting stores with physical presence.
Featured snippets: Voice assistants often read featured snippet content, making position zero valuable.
Preparation: Optimize for question-based queries, implement FAQ content, and ensure local SEO is strong if applicable.
Visual Search and Image SEO
Image-based search is growing, particularly for product discovery.
Platform adoption: Google Lens, Pinterest Lens, and similar tools enable searching by image.
Product discovery: Users can photograph items they like and find similar products to purchase.
Image optimization importance: Proper image optimization becomes more critical as visual search grows.
Preparation: Optimize all product images with descriptive file names, alt text, and surrounding context. Ensure images are high quality and show products clearly.
Zero-Click Searches and Featured Snippets
More searches are answered directly in search results without clicks to websites.
Information in SERPs: Featured snippets, knowledge panels, and rich results provide answers without requiring clicks.
Ecommerce impact: Product information, prices, and availability increasingly appear directly in search results.
Strategy adaptation: Optimize for featured snippets to capture visibility even when clicks decrease. Ensure structured data enables rich results.
Preparation: Implement comprehensive schema markup, structure content for featured snippets, and focus on queries where clicks remain valuable.
Our Ecommerce SEO Services Approach
White Label SEO Service delivers comprehensive ecommerce optimization through a proven methodology that balances technical excellence with strategic content development.
Discovery and Technical Audit Process
Every engagement begins with thorough discovery and analysis.
Business understanding: We learn your products, customers, competitive landscape, and business objectives before developing strategies.
Technical audit: Comprehensive analysis identifies all technical issues affecting crawlability, indexation, and performance.
Competitive analysis: We analyze what’s working for competitors and identify opportunities to outperform them.
Opportunity assessment: Keyword research and market analysis reveal the traffic and revenue potential from improved organic visibility.
Strategy Development and Roadmap
Discovery insights inform customized strategy development.
Prioritized recommendations: We rank opportunities by impact and effort, ensuring resources focus on highest-value activities.
Realistic timelines: Our roadmaps set appropriate expectations for when results will materialize.
Resource planning: We identify what’s needed from your team and what we’ll handle directly.
Goal alignment: Strategies connect directly to your business objectives, not vanity metrics.
Implementation and Optimization
Strategy becomes reality through systematic implementation.
Technical fixes: We address crawlability, speed, mobile, and structural issues that limit ranking potential.
On-page optimization: Product and category pages receive comprehensive optimization for target keywords.
Content development: We create content that captures informational traffic and builds topical authority.
Link building: Ethical outreach and content promotion build domain authority over time.
Ongoing Monitoring and Reporting
Continuous monitoring ensures strategies remain effective.
Performance tracking: We monitor rankings, traffic, and conversions to measure progress.
Regular reporting: Clear reports connect activities to results without overwhelming detail.
Issue identification: Proactive monitoring catches problems before they significantly impact performance.
Strategy refinement: Data insights inform ongoing optimization and strategy adjustments.
Continuous Improvement and Scaling
SEO success compounds through continuous improvement.
Expand successful strategies: We double down on what’s working and scale proven approaches.
Address new opportunities: Market changes and business growth create new optimization opportunities.
Maintain competitive position: Ongoing work protects rankings against competitive threats.
Evolve with algorithms: We adapt strategies as search engines evolve.
Getting Started with Ecommerce SEO
Taking the first step toward improved organic visibility is straightforward. Here’s how to begin.
Free SEO Audit for Your Online Store
We offer complimentary SEO audits to help you understand your current situation and opportunities.
What’s included: Technical health assessment, competitive positioning analysis, and priority opportunity identification.
What you’ll learn: Specific issues affecting your rankings, how you compare to competitors, and what improvements would have the greatest impact.
No obligation: The audit provides value regardless of whether you engage our services.
What to Prepare Before Your Consultation
Come prepared to make the most of your consultation.
Access credentials: Google Analytics, Search Console, and platform admin access enable thorough analysis.
Business context: Revenue goals, competitive landscape, and previous SEO efforts help us understand your situation.
Questions: Bring your questions about SEO, timelines, and what to expect.
Next Steps to Improve Your Organic Visibility
Ready to grow your organic traffic and revenue? Here’s how to proceed.
Request your audit: Contact us to schedule your complimentary SEO audit.
Review findings: We’ll walk through the audit results and discuss opportunities.
Develop your plan: If there’s a fit, we’ll create a customized strategy and roadmap.
Begin optimization: Implementation starts with highest-impact activities first.
Conclusion
Ecommerce SEO services provide the technical expertise, content strategy, and authority building that online stores need to compete effectively in organic search. From fixing crawlability issues to creating compelling product content and earning quality backlinks, comprehensive SEO addresses every factor influencing your rankings and revenue.
Success requires realistic expectations and sustained commitment. The first three months establish foundations, months four through six build content and optimize pages, and months seven through twelve see meaningful ranking improvements. Year two and beyond focus on scaling success and maintaining competitive positions.
We help online stores worldwide build sustainable organic growth through proven ecommerce SEO strategies. Contact White Label SEO Service today for your free audit and discover how professional optimization can transform your store’s organic visibility and revenue.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to see results from ecommerce SEO services?
Most ecommerce sites begin seeing measurable improvements within 4-6 months, with significant results typically appearing between months 7-12. Technical fixes may show quicker impact, while competitive keywords require longer timeframes. Factors like domain authority, competition level, and investment size influence specific timelines.
What’s the difference between ecommerce SEO and regular SEO?
Ecommerce SEO addresses challenges unique to online stores: managing thousands of product pages, handling duplicate content from variants, optimizing for transactional keywords, implementing product schema markup, and connecting optimization to revenue. Regular SEO typically focuses on fewer pages with informational intent.
How much should I budget for ecommerce SEO services?
Budget depends on store size and goals. Small stores typically invest $1,500-$3,000 monthly, mid-size stores $3,000-$7,000, and large stores $7,000-$15,000+. Quality SEO requires meaningful investment; extremely low prices usually indicate low-quality work that won’t produce results.
Can I do ecommerce SEO myself or do I need an agency?
Basic optimization is possible in-house with sufficient time and learning. However, comprehensive ecommerce SEO requires specialized expertise in technical SEO, content strategy, and link building that most businesses lack internally. Agencies provide expertise, tools, and bandwidth that accelerate results.
What ecommerce platforms are best for SEO?
All major platforms can achieve strong SEO results with proper optimization. Shopify offers ease of use with some limitations. WooCommerce provides maximum flexibility but requires more technical management. BigCommerce includes strong built-in SEO features. Platform choice should consider overall business needs, not just SEO.
How do I know if my ecommerce SEO is working?
Track organic traffic growth, keyword ranking improvements, and most importantly, organic revenue. Google Analytics 4 and Search Console provide essential data. Effective SEO shows steady improvement in these metrics over time, with organic revenue growth being the ultimate success measure.
What’s the most important ecommerce SEO factor to focus on first?
Technical SEO typically provides the highest initial impact. Fixing crawlability issues, improving page speed, and resolving duplicate content problems remove barriers that prevent other optimizations from working. Once technical foundations are solid, focus shifts to content and authority building.


