Your Google Business Profile category selection directly determines whether customers find you or your competitors. The right primary category can increase your visibility in local search results by positioning your business for the exact queries your ideal customers type into Google Maps and Search.
Most business owners treat category selection as a one-time setup task, missing significant ranking opportunities. This guide breaks down the complete GMB category system, provides industry-specific recommendations, and delivers a proven selection strategy.
You will learn how Google uses categories for local rankings, access comprehensive category lists by industry, and follow a step-by-step process to optimize your selections for maximum local visibility.
What Are GMB Categories?
Google Business Profile categories are predefined classifications that tell Google what your business does and which searches should trigger your listing. Google maintains a database of approximately 4,000 categories that cover virtually every business type, from urgent care centers to artisan bakeries.
Categories function as the primary signal Google uses to understand your business relevance. When someone searches “urgent care near me,” Google filters results to show businesses with the Urgent Care Center category. Without the correct category, your business becomes invisible for your most valuable searches.
Your category selections also influence which features appear on your profile. Restaurants see menu options. Hotels display booking widgets. Service businesses get appointment scheduling. The category you choose unlocks specific functionality designed for your business type.
Primary Category vs Secondary Categories Explained
Your primary category carries the most weight in Google’s ranking algorithm. This single selection tells Google your main business function and determines your eligibility for the most relevant local searches. Choose the category that best describes your core revenue-generating service.
Secondary categories expand your visibility for related searches without diluting your primary focus. A dental office might use “Dentist” as the primary category while adding “Cosmetic Dentist,” “Emergency Dental Service,” and “Teeth Whitening Service” as secondary options.
The key distinction lies in ranking power. Your primary category directly influences your position in the Local Pack for your main keywords. Secondary categories help you appear for adjacent searches but rarely drive top-three placements on their own.
How Google Uses Categories to Rank Local Businesses
Google’s local algorithm weighs three primary factors: relevance, distance, and prominence. Categories directly impact relevance by matching your business to user queries. A search for “walk-in clinic” triggers listings with that specific category before considering broader medical categories.
Category matching happens at the query level. Google analyzes search intent, identifies the most relevant category, and filters businesses accordingly. This filtering occurs before distance and prominence calculations, making category selection a prerequisite for ranking consideration.
Google also uses categories to understand entity relationships. When you select “Urgent Care Center,” Google associates your business with related entities like emergency medicine, extended hours healthcare, and no-appointment medical services. These associations influence which searches surface your listing.
Complete List of Google Business Profile Categories
Google organizes categories into broad industry groups, each containing dozens of specific options. Understanding the full landscape helps you identify the most precise category for your business rather than settling for generic alternatives.
Healthcare & Medical Categories
Healthcare represents one of the most detailed category groups, reflecting the specialized nature of medical services. Precision matters significantly here because patients search for specific care types.
Urgent Care Center
The Urgent Care Center category targets businesses providing immediate medical attention for non-life-threatening conditions. This category triggers for searches like “urgent care near me,” “walk-in medical care,” and “after hours doctor.”
Businesses using this category typically offer extended hours, accept walk-in patients, and treat conditions requiring same-day attention. Google expects urgent care centers to provide services between emergency rooms and primary care offices.
Medical Clinic
Medical Clinic serves as a broader category for general healthcare facilities. This option works for practices offering multiple services without a single specialty focus. Primary care offices, community health centers, and multi-specialty practices often use this category.
The trade-off involves search specificity. Medical Clinic captures general healthcare searches but faces more competition than specialized categories. Consider whether your patient acquisition strategy targets general or specific medical searches.
Walk-In Clinic
Walk-In Clinic emphasizes the no-appointment-necessary aspect of healthcare delivery. This category performs well for searches emphasizing convenience and immediate access rather than specific medical conditions.
Retail clinics inside pharmacies, minute clinics, and express care facilities benefit from this category. The distinction from Urgent Care Center lies in the severity of conditions treated and the clinical setting.
Emergency Care Service
Emergency Care Service targets facilities handling life-threatening conditions requiring immediate intervention. Hospital emergency departments and freestanding emergency rooms use this category.
Google applies stricter verification for emergency-related categories due to the critical nature of these services. Misusing this category can result in listing suspension and violates Google’s guidelines.
Retail & Shopping Categories
Retail categories span from broad classifications like “Department Store” to highly specific options like “Vintage Clothing Store” or “Board Game Store.” Google provides approximately 400 retail-specific categories.
General merchandise retailers typically choose categories matching their primary product focus. A store selling primarily electronics would select “Electronics Store” rather than “Department Store,” even if they carry other product lines.
Specialty retailers benefit from niche categories that match specific customer searches. “Running Shoe Store” outperforms “Shoe Store” for businesses targeting runners because it matches the exact search intent of that customer segment.
Food & Restaurant Categories
Restaurant categories number over 150 options, covering cuisine types, service styles, and specialty food businesses. Google distinguishes between full-service restaurants, quick-service establishments, and food retailers.
Cuisine-specific categories like “Italian Restaurant,” “Thai Restaurant,” or “Mexican Restaurant” typically outperform generic “Restaurant” selections. Customers searching for specific cuisines see listings matching their exact preference.
Service-style categories matter for businesses with unique models. “Food Truck,” “Buffet Restaurant,” “Cafeteria,” and “Ghost Kitchen” each target different customer expectations and search behaviors.
Professional Services Categories
Professional services span legal, financial, consulting, and business support categories. Google maintains distinct categories for most licensed professions and specialized service providers.
Legal categories include options for general practice and specializations like “Personal Injury Attorney,” “Immigration Attorney,” and “Criminal Justice Attorney.” Specialization categories typically drive higher-intent traffic.
Financial services categories distinguish between “Accountant,” “Tax Preparation Service,” “Financial Planner,” and “Investment Service.” Each targets different customer needs and search patterns.
Home Services Categories
Home services represent a competitive local search vertical with highly specific categories. Google provides distinct options for most trade specialties and home improvement services.
Trade-specific categories like “Electrician,” “Plumber,” and “HVAC Contractor” target customers searching for specific expertise. These categories outperform broader options like “Home Improvement Store” for service businesses.
Specialty services have dedicated categories including “Garage Door Supplier,” “Fence Contractor,” “Pool Cleaning Service,” and “Lawn Care Service.” Using the most specific available category improves relevance matching.
Automotive Categories
Automotive categories cover vehicle sales, service, parts, and specialty businesses. Google distinguishes between new car dealers, used car dealers, and specific brand dealerships.
Service categories include “Auto Repair Shop,” “Oil Change Service,” “Tire Shop,” and “Auto Body Shop.” Each targets different maintenance and repair searches with distinct customer intent.
Specialty automotive businesses find categories like “Car Detailing Service,” “Auto Glass Shop,” “Transmission Shop,” and “Brake Shop.” Specificity improves ranking potential for targeted searches.
Beauty & Personal Care Categories
Beauty categories span salons, spas, and personal care services with options for most specializations. Google provides distinct categories for hair, nail, skin, and body services.
Hair service categories include “Hair Salon,” “Barber Shop,” “Hair Extensions Supplier,” and “Hair Removal Service.” Each targets different customer segments and service expectations.
Spa and wellness categories distinguish between “Day Spa,” “Medical Spa,” “Massage Therapist,” and “Acupuncturist.” Service scope and licensing requirements differ significantly across these categories.
Entertainment & Recreation Categories
Entertainment categories cover venues, activities, and recreational businesses. Google maintains options for most leisure activities and entertainment formats.
Venue categories include “Movie Theater,” “Concert Hall,” “Bowling Alley,” and “Amusement Park.” Each triggers for different entertainment searches and customer expectations.
Activity-based categories like “Escape Room Center,” “Laser Tag Center,” “Mini Golf Course,” and “Go Kart Track” target customers searching for specific experiences.
Travel & Hospitality Categories
Hospitality categories distinguish between accommodation types, travel services, and tourism businesses. Google provides specific options for most lodging formats.
Accommodation categories include “Hotel,” “Motel,” “Bed and Breakfast,” “Hostel,” and “Vacation Rental Agency.” Each targets different traveler segments and booking behaviors.
Travel service categories cover “Travel Agency,” “Tour Operator,” “Tourist Attraction,” and “Visitor Center.” These target customers at different stages of travel planning.
Education & Training Categories
Education categories span formal institutions, training providers, and specialty schools. Google distinguishes between academic levels and subject specializations.
Academic categories include “Elementary School,” “High School,” “University,” and “Community College.” Each serves different student populations and search contexts.
Training categories like “Driving School,” “Cooking School,” “Dance School,” and “Music School” target students seeking specific skill development.
How to Choose the Right GMB Primary Category
Category selection requires strategic analysis rather than intuitive guessing. The right primary category positions your business for your most valuable searches while accurately representing your services.
Step 1: Identify Your Core Service
Start by defining the single service that generates the majority of your revenue or represents your primary business function. This core service should align with how customers describe what you do.
Ask yourself what customers would search to find a business like yours. An urgent care facility might consider whether patients search “urgent care,” “walk-in clinic,” or “medical clinic.” The answer depends on your specific service model and target patient.
Document your top three to five services ranked by revenue contribution. Your primary category should match your highest-value service unless strategic reasons suggest otherwise.
Step 2: Research Competitor Categories
Analyze the Google Business Profiles of businesses ranking in the Local Pack for your target searches. Their category selections reveal what Google considers relevant for those queries.
Search your primary keywords and examine the top three Local Pack results. Note their primary categories using browser extensions or by viewing their full profiles. Patterns emerge showing which categories Google associates with specific searches.
Identify gaps where competitors use broad categories while more specific options exist. These gaps represent opportunities to differentiate through more precise category selection.
Step 3: Match Category to Search Intent
Align your category selection with the actual searches your ideal customers perform. Category-to-query matching determines whether Google considers your business relevant for specific searches.
Use keyword research tools to identify search volume for terms related to different category options. Compare search volume for “urgent care near me” versus “walk-in clinic near me” to understand which category captures more potential patients.
Consider the customer journey stage each category targets. Some categories attract customers ready to purchase while others capture earlier research phases. Match your category to your desired customer acquisition point.
Step 4: Test and Validate Your Selection
Category changes take effect within days, allowing you to test different selections and measure impact. Monitor your Google Business Profile insights to track impression and action changes.
Establish baseline metrics before making changes. Record your current impressions, search queries, and customer actions. After changing categories, compare performance over a 30-day period.
Test secondary category additions individually to isolate their impact. Adding multiple categories simultaneously makes it impossible to determine which changes drove results.
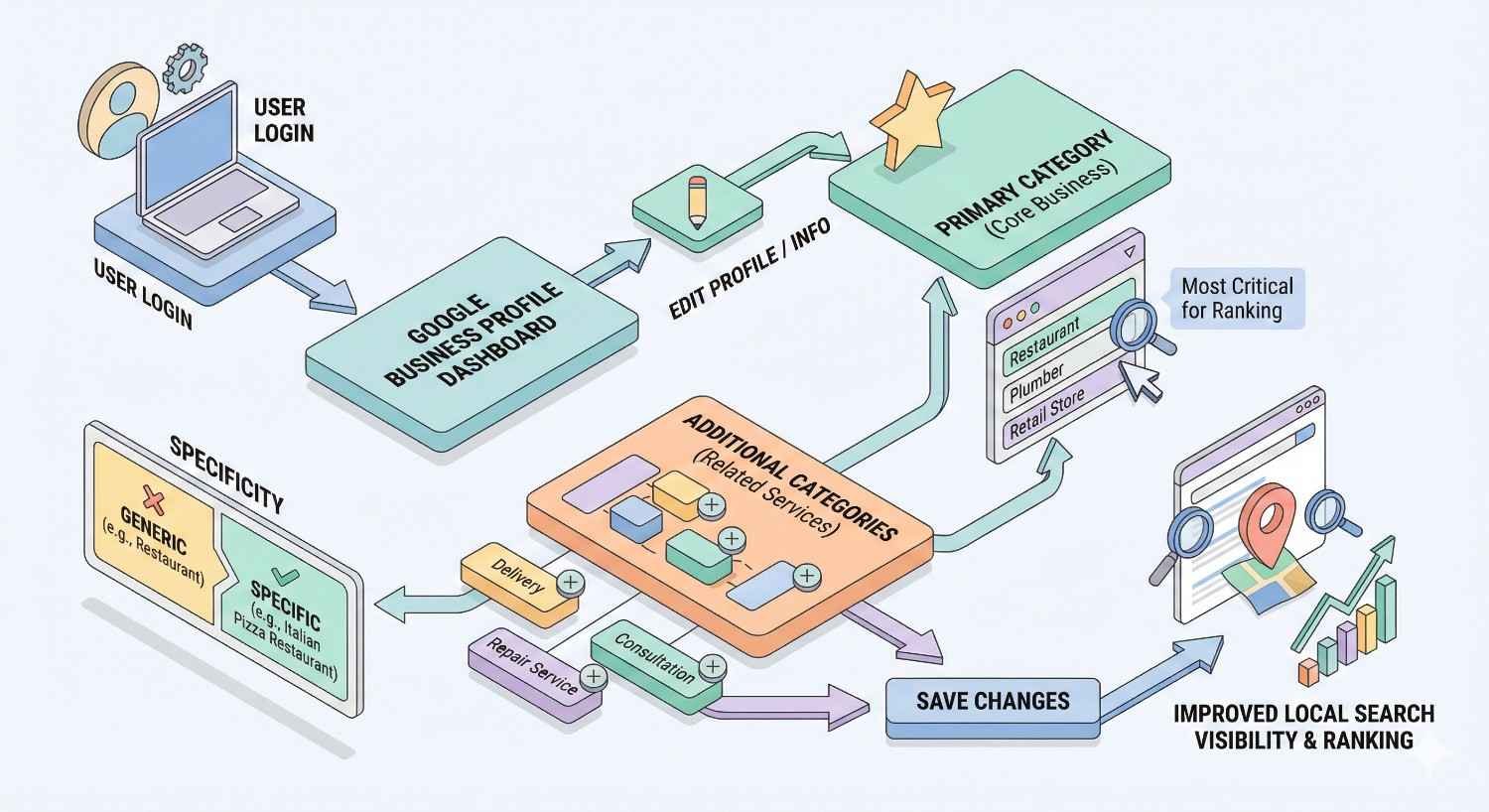
How to Add and Change GMB Categories
Google Business Profile provides straightforward category management through the dashboard. Understanding the process and limitations helps you optimize effectively.
Adding Categories in Google Business Profile
Access your Google Business Profile dashboard and navigate to the “Edit profile” section. Select “Business category” to view and modify your current selections.
Your primary category appears first with secondary categories listed below. Click “Add another category” to expand your selections. Google’s autocomplete suggests options as you type, helping you discover available categories.
Save changes and allow 24-72 hours for updates to reflect in search results. Google may review category changes for accuracy, particularly for sensitive business types.
Changing Your Primary Category
Primary category changes require careful consideration due to their ranking impact. Switching categories can temporarily affect your visibility while Google reassesses your relevance.
To change your primary category, click the existing selection and search for your new preferred option. Google will prompt you to confirm the change before saving.
Monitor your performance closely after primary category changes. Temporary ranking fluctuations are normal as Google recalculates your relevance for different search queries.
How Many Secondary Categories Should You Use?
Google allows up to nine secondary categories in addition to your primary selection. However, more categories do not automatically mean better performance.
Add secondary categories only when they accurately describe services you actively provide. Each category should represent a legitimate business function that customers might search for independently.
Quality trumps quantity in category selection. Three highly relevant secondary categories outperform nine loosely related options. Irrelevant categories can dilute your relevance signals and trigger Google reviews.
GMB Category Best Practices for Local SEO
Strategic category management extends beyond initial selection. Ongoing optimization ensures your categories continue supporting your local search visibility.
Category Specificity vs Broad Categories
Specific categories typically outperform broad alternatives for targeted searches. “Personal Injury Attorney” captures more relevant traffic than “Lawyer” for firms specializing in injury cases.
Broad categories make sense when your business genuinely serves diverse needs. A general practice law firm handling multiple case types might appropriately use “Lawyer” as the primary category.
Test specificity levels by monitoring which searches trigger your listing. Google Business Profile insights show the queries generating impressions, revealing whether your category matches customer search behavior.
Avoiding Category Spam and Violations
Google prohibits adding categories that do not accurately represent your business services. Category spam can result in listing suspension or removal from search results entirely.
Common violations include adding aspirational categories for services you plan to offer, selecting categories based solely on search volume, and using categories that describe products rather than services.
Google’s guidelines specify that categories should reflect your business “as it exists today.” Future services, occasional offerings, and minor business functions do not justify category additions.
Seasonal Category Adjustments
Some businesses legitimately offer seasonal services warranting temporary category additions. A landscaping company might add “Snow Removal Service” during winter months.
Document your seasonal category strategy to ensure consistent annual implementation. Set calendar reminders to add and remove seasonal categories at appropriate times.
Avoid frequent category changes that might signal manipulation to Google. Seasonal adjustments should follow predictable patterns aligned with genuine service availability changes.
GMB Categories for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare category selection requires particular attention due to the specialized nature of medical searches and Google’s heightened scrutiny of health-related businesses.
Best Categories for Urgent Care Centers
Urgent care facilities should typically use “Urgent Care Center” as their primary category. This selection directly matches the highest-volume searches from patients seeking immediate care.
Recommended secondary categories for urgent care centers include:
- Medical Clinic
- Walk-In Clinic
- Occupational Health Service (if applicable)
- X-Ray Lab (if on-site imaging available)
- Laboratory (if on-site testing available)
Avoid adding emergency-related categories unless your facility genuinely provides emergency-level care. Misrepresentation in healthcare categories carries significant compliance and liability implications.
Medical Clinic vs Urgent Care Center Category
The distinction between these categories reflects different service models and patient expectations. Understanding the difference helps you select the option matching your actual operations.
Medical Clinic suggests scheduled appointments, ongoing patient relationships, and comprehensive primary care. Patients searching for medical clinics often seek a regular healthcare provider rather than immediate treatment.
Urgent Care Center signals walk-in availability, extended hours, and treatment for acute conditions. Patients using this search term typically need same-day care without prior appointments.
Choose based on your primary patient acquisition model. Facilities emphasizing convenience and immediate access benefit from Urgent Care Center. Practices building long-term patient relationships might prefer Medical Clinic.
Multi-Location Healthcare Category Strategy
Healthcare organizations with multiple locations face category decisions at both the organizational and location levels. Each location should have categories reflecting its specific services.
Avoid using identical categories across all locations if services differ. A healthcare system might have urgent care centers, primary care offices, and specialty clinics requiring different category selections.
Maintain consistency for locations offering identical services. Patients expect similar experiences from same-branded locations, and consistent categories support that expectation.
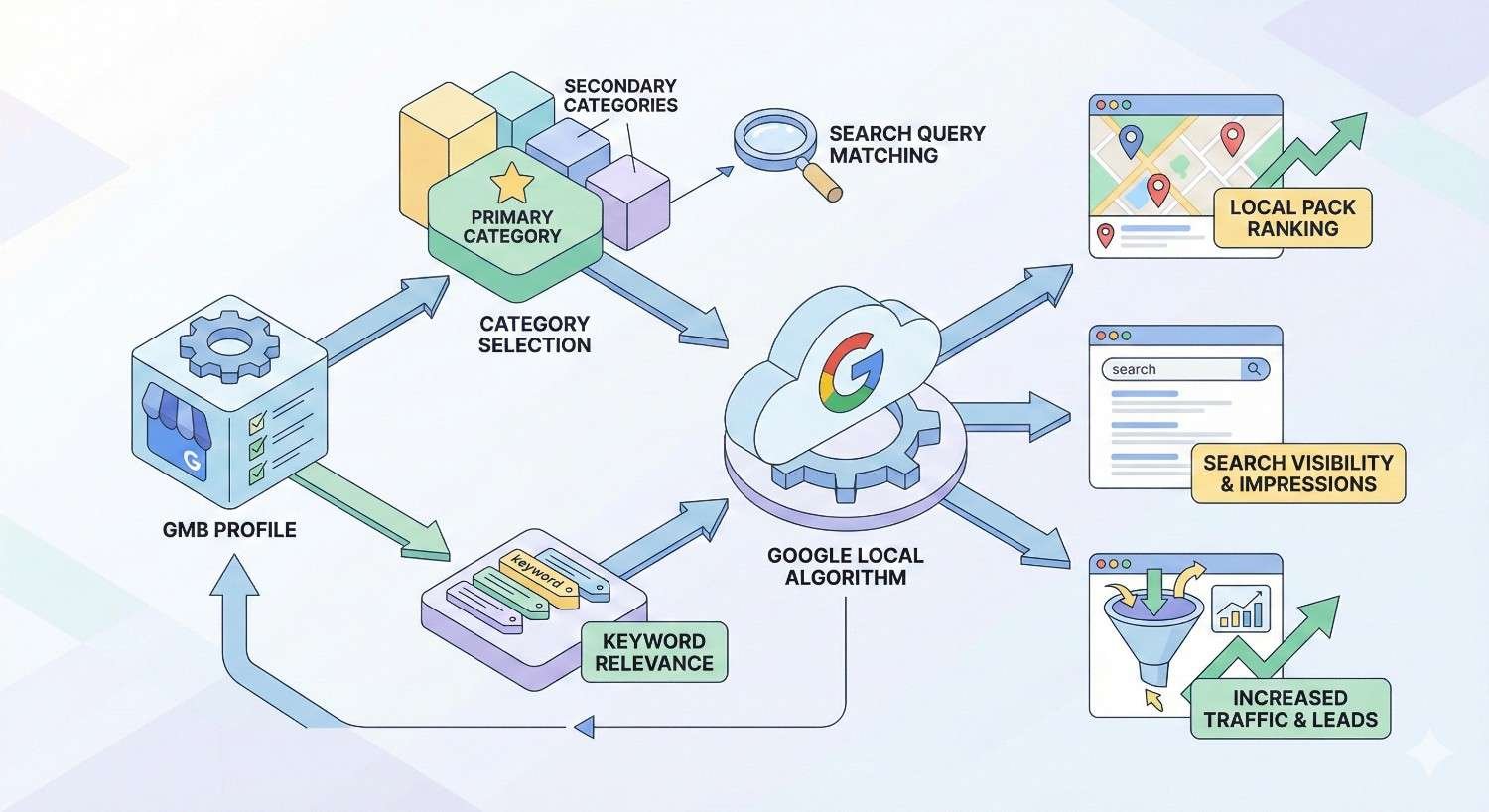
How GMB Categories Affect Your Local Search Visibility
Category selection influences multiple aspects of local search performance beyond simple query matching. Understanding these effects helps you maximize category optimization value.
Category Impact on Google Maps Rankings
Google Maps rankings depend heavily on category relevance for location-based searches. Your category determines which searches include your business in the initial candidate set.
The Local Pack filtering process starts with category matching. Google identifies businesses with relevant categories before applying distance and prominence factors. Without the right category, your business never enters consideration.
Category specificity affects competitive density. Broad categories like “Restaurant” face more competition than specific options like “Ethiopian Restaurant.” Less competition can mean easier ranking for businesses in niche categories.
Category Relevance and Customer Reviews
Reviews mentioning services aligned with your categories strengthen relevance signals. Google’s natural language processing identifies service mentions in reviews and associates them with your category selections.
Encourage customers to describe the specific services they received in reviews. A review mentioning “urgent care visit” reinforces the Urgent Care Center category more than generic positive feedback.
Review content also influences which searches trigger your listing. Service-specific reviews can help you appear for related searches even without exact category matches.
Categories and Google Local Pack Placement
Local Pack placement requires category relevance as a baseline qualification. The three businesses appearing in the Local Pack for any search all have categories Google considers relevant.
Category optimization alone does not guarantee Local Pack placement. Prominence factors including review quantity, review quality, and overall online presence also influence rankings.
However, category misalignment guarantees Local Pack exclusion. No amount of prominence can overcome fundamental relevance mismatches caused by incorrect category selection.
Common GMB Category Mistakes to Avoid
Category errors can significantly harm local search performance. Recognizing common mistakes helps you avoid pitfalls that limit your visibility.
Choosing Overly Broad Categories
Broad categories seem safe but often underperform compared to specific alternatives. “Store” captures fewer relevant searches than “Hardware Store” for a business selling tools and building materials.
Broad categories also increase competition. You compete against every business in that category rather than a focused subset matching your specialization.
Review your current categories and identify more specific alternatives. Google’s category database includes options for most business specializations that outperform generic selections.
Adding Irrelevant Secondary Categories
Secondary category spam dilutes your relevance signals and risks Google penalties. Each category should represent a genuine, active business function.
Common mistakes include adding categories for services you rarely provide, selecting categories based on search volume rather than accuracy, and including categories describing products you sell rather than services you offer.
Audit your secondary categories quarterly. Remove any that no longer accurately represent your current service offerings.
Ignoring Category Updates from Google
Google regularly adds, removes, and modifies available categories. New categories might better match your business than options available when you created your profile.
Monitor industry news and Google Business Profile announcements for category changes. New categories often appear for emerging business types and service models.
Review your category options annually even without announced changes. Google’s autocomplete suggestions reveal available options that might improve your current selections.
GMB Category FAQs
Can I Create a Custom GMB Category?
Google does not allow custom category creation. You must select from Google’s predefined list of approximately 4,000 options. If your exact business type is not listed, choose the closest available match and use your business description to clarify your specific services.
How Often Should I Review My Categories?
Review your categories quarterly and whenever you add or remove significant services. Annual reviews should include checking for new category options that might better match your business. Immediate reviews are necessary after any major business model changes.
Do Categories Affect Google Ads Performance?
GMB categories do not directly influence Google Ads performance. However, your Google Business Profile information can appear in local ad extensions, making accurate categories important for ad relevance. Consistent category and ad targeting alignment improves overall local marketing effectiveness.
What If My Business Type Isn’t Listed?
Select the most accurate available category even if it is not a perfect match. Use your business description, services section, and posts to clarify your specific offerings. Submit feedback to Google requesting new categories for underserved business types through the Google Business Profile help center.
How Long Do Category Changes Take to Affect Rankings?
Category changes typically reflect in search results within 24-72 hours. However, ranking impact may take 2-4 weeks to stabilize as Google reassesses your relevance for different queries. Monitor your Google Business Profile insights to track impression changes following category modifications.
Can Competitors See My Category Selections?
Yes, your categories are visible to anyone viewing your Google Business Profile. Competitors can analyze your category strategy, and you can research theirs. This transparency makes category optimization a competitive intelligence opportunity for understanding market positioning.
Should Multi-Service Businesses Use Multiple Profiles?
Google’s guidelines prohibit multiple profiles for the same business at the same location. Multi-service businesses should use one profile with a primary category matching their main service and secondary categories covering additional offerings. Separate locations can have separate profiles with location-appropriate categories.
Conclusion: Optimizing Your GMB Categories for Maximum Visibility
GMB category selection directly influences your local search visibility, determining which customer searches include your business in results. Strategic category choices based on your core services, competitor analysis, and search intent matching position your business for sustainable local ranking improvements.
Category optimization represents one component of comprehensive local SEO strategy. Combining accurate categories with complete profile information, consistent citations, quality reviews, and ongoing engagement maximizes your Google Business Profile performance.
We help businesses worldwide develop and execute local SEO strategies that drive measurable results. Contact White Label SEO Service to discuss how our team can optimize your Google Business Profile categories and overall local search presence for maximum visibility and customer acquisition.



