Recovering from a Google Penguin penalty requires a systematic approach to identifying and removing toxic backlinks that violate Google’s webmaster guidelines. Most websites can expect recovery within 2-6 months when following proper link cleanup procedures, though severely affected sites may need longer.
The stakes are significant. A Penguin penalty can slash organic traffic by 50-90% overnight, directly impacting leads, revenue, and business growth. Understanding exactly what triggered the penalty and how to fix it separates successful recoveries from prolonged ranking struggles.
This guide walks you through the complete Penguin recovery process, from diagnosis and backlink auditing to disavow file creation and monitoring. You’ll learn the exact steps SEO professionals use to restore rankings and prevent future penalties.
What Is Google Penguin and How Does It Affect Your Website?
Google Penguin fundamentally changed how search engines evaluate backlink profiles. Understanding this algorithm helps you recognize why certain link building practices trigger penalties and what recovery actually requires.
Understanding the Google Penguin Algorithm
Google Penguin launched in April 2012 to combat webspam and manipulative link schemes. The algorithm specifically targets websites that artificially inflate rankings through unnatural backlinks, including paid links, link exchanges, and automated link building.
The original Penguin operated as periodic updates, meaning affected sites had to wait months for the next refresh to see recovery. In September 2016, Google integrated Penguin into its core algorithm, making it real-time. This change means the algorithm now continuously evaluates backlink profiles rather than during scheduled updates.
Penguin works by devaluing spammy links rather than penalizing entire domains in most cases. However, sites with severely manipulated link profiles can still experience dramatic ranking drops across their entire keyword portfolio.
The algorithm evaluates link quality signals including anchor text distribution, linking domain authority, link velocity, and the relevance between linking and linked content. Patterns that appear unnatural trigger algorithmic suppression.
How Penguin Differs From Other Google Penalties
Penguin is an algorithmic filter, not a manual penalty. This distinction matters for recovery strategy.
Manual penalties come from Google’s human reviewers who identify guideline violations. You’ll receive a notification in Google Search Console explaining the issue. Manual actions require submitting a reconsideration request after fixing problems.
Algorithmic penalties like Penguin happen automatically without notification. Your Search Console won’t show any manual action message. The only indicators are traffic drops correlating with known algorithm update dates.
Panda targets thin, duplicate, or low-quality content. Penguin focuses exclusively on backlink manipulation. A site can be affected by both simultaneously, requiring separate remediation strategies.
Core algorithm updates differ from Penguin because they broadly reassess content quality and relevance rather than specifically targeting link spam. Traffic drops from core updates require content improvements, not link cleanup.
Signs Your Site Has Been Hit by Penguin
Recognizing Penguin symptoms early accelerates recovery. Several patterns indicate algorithmic link penalties.
Sudden traffic drops coinciding with known Penguin update dates strongly suggest algorithmic impact. Cross-reference your Google Analytics data with Moz’s Google Algorithm Update History to identify correlations.
Keyword ranking losses across multiple pages, particularly for competitive commercial terms, indicate potential Penguin filtering. Check if rankings dropped uniformly or if specific pages with aggressive anchor text optimization suffered most.
Organic visibility decline without corresponding manual action notifications points toward algorithmic penalties. If Search Console shows no manual actions but traffic plummeted, Penguin or another algorithm likely caused the drop.
Anchor text over-optimization in your backlink profile raises red flags. If more than 60-70% of your anchors contain exact-match keywords, Penguin may have flagged your site.
Low-quality referring domains dominating your backlink profile suggest vulnerability. Links from link farms, private blog networks, foreign-language spam sites, and irrelevant directories trigger algorithmic filters.
How to Diagnose a Google Penguin Penalty
Accurate diagnosis prevents wasted effort on wrong recovery strategies. Follow this systematic approach to confirm whether Penguin caused your traffic decline.
Checking Google Search Console for Manual Actions
Start by ruling out manual penalties. Log into Google Search Console and navigate to Security & Manual Actions > Manual Actions.
If you see a message about “Unnatural links to your site,” you have a manual penalty requiring a reconsideration request after cleanup. This is actually clearer to address than algorithmic filtering because Google tells you exactly what’s wrong.
No manual action message doesn’t mean you’re penalty-free. It simply means human reviewers haven’t flagged your site. Algorithmic Penguin filtering operates independently and won’t appear here.
Check the Links report in Search Console to see Google’s view of your backlink profile. Compare this data with third-party tools since Google’s data is often incomplete but shows what they’re actually counting.
Review the Performance report for sudden traffic drops. Note specific dates when impressions and clicks declined sharply. These timestamps help correlate with algorithm updates.
Analyzing Traffic Drops Against Penguin Update Dates
Timeline analysis confirms algorithmic impact. Pull your organic traffic data from Google Analytics and overlay it against known Penguin update dates.
Major Penguin updates occurred on:
- April 24, 2012 (Penguin 1.0)
- May 26, 2012 (Penguin 1.1)
- October 5, 2012 (Penguin 1.2)
- May 22, 2013 (Penguin 2.0)
- October 4, 2013 (Penguin 2.1)
- October 17, 2014 (Penguin 3.0)
- September 23, 2016 (Penguin 4.0, real-time integration)
Since Penguin 4.0, the algorithm runs continuously. Traffic drops can occur anytime Google recrawls and reevaluates your backlinks. Look for sudden declines without obvious external causes like seasonality or site changes.
Compare organic traffic patterns with direct and referral traffic. If only organic dropped while other channels remained stable, an algorithm change likely caused the decline.
Segment traffic by landing page to identify which sections suffered most. Pages with aggressive link building often show steeper drops, confirming link-related penalties.
Conducting a Backlink Audit
Comprehensive backlink auditing reveals the scope of your link problems. Use multiple tools since each has different crawl databases.
Export your complete backlink profile from:
- Google Search Console (Links > External Links > Export)
- Ahrefs (Site Explorer > Backlinks)
- SEMrush (Backlink Analytics)
- Majestic (Site Explorer > Backlinks)
Combine and deduplicate these exports. You’ll typically find 20-40% unique links in each tool’s database that others missed.
Analyze key metrics for each linking domain:
- Domain Authority/Domain Rating
- Spam score indicators
- Topical relevance to your site
- Link placement (footer, sidebar, content)
- Anchor text used
Create a master spreadsheet documenting every backlink with these data points. This becomes your working document for categorization and outreach.
Identifying Toxic and Unnatural Links
Not all low-quality links trigger penalties. Focus on patterns that signal manipulation.
Paid links from sites that openly sell links or have “advertise” pages violate guidelines. These often come from low-quality blogs, directories, and article sites.
Private Blog Networks (PBNs) leave footprints including similar site designs, shared hosting, thin content, and links to multiple unrelated sites. PBN links carry high penalty risk.
Exact-match anchor text in high percentages signals manipulation. Natural link profiles show diverse anchors including branded terms, naked URLs, and generic phrases like “click here.”
Irrelevant links from sites completely unrelated to your industry suggest purchased or exchanged links. A plumbing company with links from casino sites raises obvious red flags.
Foreign-language spam sites linking to English content indicate automated link building or negative SEO attacks.
Comment spam and forum signature links from low-quality sites contribute to toxic profiles.
Article directories and press release sites with keyword-stuffed anchors were common pre-Penguin tactics that now trigger penalties.
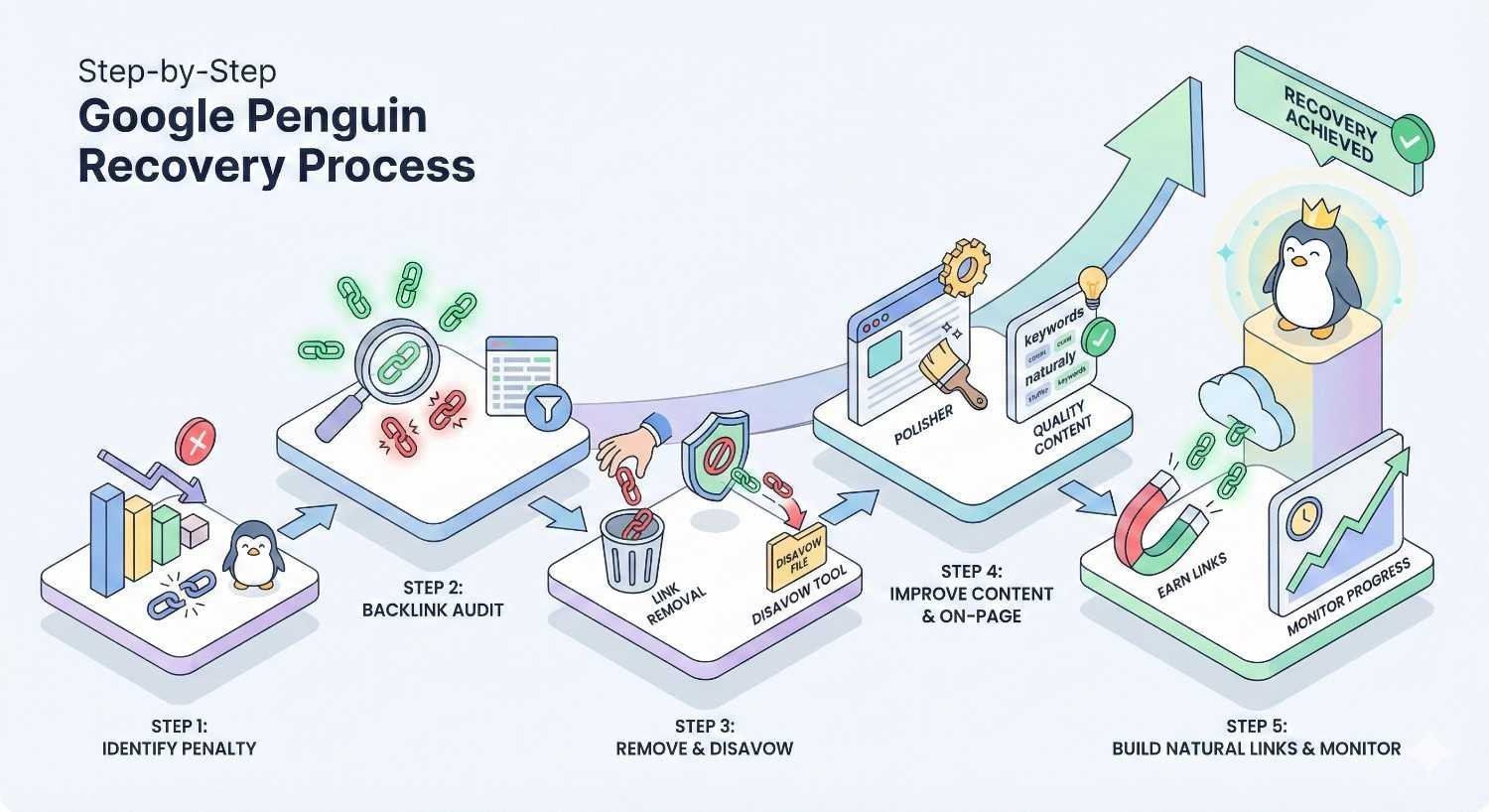
Step-by-Step Google Penguin Recovery Process
Recovery requires methodical execution. Rushing or skipping steps often prolongs the process. Follow this sequence for optimal results.
Step 1 – Export and Audit Your Complete Backlink Profile
Gather backlink data from every available source. Incomplete audits leave toxic links unaddressed, preventing full recovery.
Download exports from Google Search Console, Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Majestic. Each tool crawls the web differently, capturing unique link data.
Combine all exports into a single spreadsheet. Remove exact duplicates but keep variations (different URLs from the same domain count separately).
Add columns for:
- Link status (live, removed, nofollow)
- Domain metrics (DA, spam score)
- Anchor text
- Link type (contextual, sidebar, footer, comment)
- Your categorization (natural, suspicious, toxic)
- Action needed (keep, remove, disavow)
- Outreach status (not contacted, contacted, removed)
Sort by referring domain to group multiple links from the same site. Evaluate domains holistically rather than individual links.
Document your audit methodology. If you later submit a reconsideration request, Google wants to see your systematic approach.
Step 2 – Categorize Links (Natural, Suspicious, Toxic)
Systematic categorization prevents over-disavowing good links while ensuring toxic ones get addressed.
Natural links come from legitimate editorial decisions. Characteristics include:
- Relevant, authoritative sites
- Contextual placement within content
- Varied anchor text
- No payment or exchange involved
- Genuine traffic potential
Keep these links. They help your rankings.
Suspicious links show some warning signs but aren’t definitively manipulative:
- Low-authority but relevant sites
- Slightly over-optimized anchors
- Old directory submissions
- Guest posts on legitimate sites
Evaluate these case-by-case. When uncertain, lean toward keeping links from relevant sites and disavowing irrelevant ones.
Toxic links clearly violate guidelines:
- Obvious link schemes and PBNs
- Paid links from link sellers
- Spam sites and link farms
- Completely irrelevant foreign sites
- Hacked site links
- Excessive exact-match anchors from low-quality sources
These require removal or disavowal.
Create clear criteria for your team. Consistent categorization across thousands of links requires documented standards.
Step 3 – Attempt Manual Link Removal Outreach
Google prefers you remove bad links rather than just disavowing them. Outreach demonstrates good-faith effort.
Find contact information for toxic link sources. Check for:
- Contact pages
- About pages with email addresses
- WHOIS data
- Social media profiles
Send professional removal requests. Keep emails brief and specific:
“Hello, I’m conducting a backlink audit for [yoursite.com] and found a link from your page [URL]. This link doesn’t align with our current SEO strategy. Would you please remove it? Thank you for your help.”
Avoid threatening language about Google penalties. Webmasters respond better to polite requests.
Track all outreach in your spreadsheet:
- Date contacted
- Contact method used
- Response received
- Link removed (yes/no/pending)
Send follow-up emails after 7-10 days if no response. Two contact attempts demonstrate reasonable effort.
Expect low success rates. Many toxic link sources are abandoned sites, spam operations, or unresponsive webmasters. 10-20% removal rates are typical.
Document everything. Screenshots of outreach attempts support reconsideration requests.
Step 4 – Create and Submit a Disavow File
The disavow tool tells Google to ignore specific links when assessing your site. Use it for toxic links you couldn’t remove manually.
Format your disavow file correctly:
- Plain text file (.txt)
- One entry per line
- Use “domain:” prefix to disavow entire domains
- Use full URLs to disavow specific pages
- Add comments with “#” for documentation
Example disavow file:
Copy
# Toxic links identified in audit – June 2024
# PBN sites
domain:spammysite1.com
domain:spammysite2.com
# Paid link sources
domain:buylinkscheap.com
# Specific spam pages
https://example.com/spam-page-with-link
Disavow at the domain level when the entire site is low-quality. Disavow specific URLs when only certain pages are problematic but the domain itself is legitimate.
Submit through Google Search Console’s Disavow Links tool. Upload your file and confirm submission.
Google processes disavow files as they recrawl the disavowed URLs. This isn’t instant. Expect weeks to months before full processing.
Keep your disavow file updated. Add new toxic links discovered in ongoing monitoring.
Step 5 – Submit a Reconsideration Request (If Manual Action)
Reconsideration requests apply only to manual penalties, not algorithmic Penguin filtering. If Search Console shows a manual action, submit a request after completing cleanup.
Write a thorough reconsideration request including:
Acknowledgment of the problem and what caused it. Take responsibility rather than blaming others or claiming ignorance.
Documentation of your cleanup efforts:
- Number of links audited
- Categorization methodology
- Outreach attempts and results
- Links successfully removed
- Disavow file contents
Prevention measures explaining how you’ll avoid future violations:
- New link building policies
- Ongoing monitoring procedures
- Team training completed
Be honest and specific. Vague requests get rejected. Google reviewers want to see genuine effort and understanding.
Submit through Search Console’s Manual Actions section. Click “Request Review” and paste your detailed explanation.
Response times vary from days to weeks. If rejected, address the stated concerns and resubmit. Multiple rejections indicate incomplete cleanup.
Step 6 – Monitor Recovery Progress
Recovery isn’t immediate. Continuous monitoring tracks progress and identifies remaining issues.
Set up tracking for:
- Organic traffic (weekly comparison)
- Keyword rankings (daily or weekly)
- Indexed pages
- New backlinks acquired
- Crawl activity
Watch for gradual ranking improvements. Recovery typically happens incrementally rather than all at once.
Continue auditing new backlinks monthly. Negative SEO attacks or legacy link building can add new toxic links.
Document recovery milestones:
- First ranking improvements
- Traffic returning to pre-penalty levels
- Specific keywords recovered
If recovery stalls, reassess your disavow file. You may have missed toxic links or need to expand your criteria.
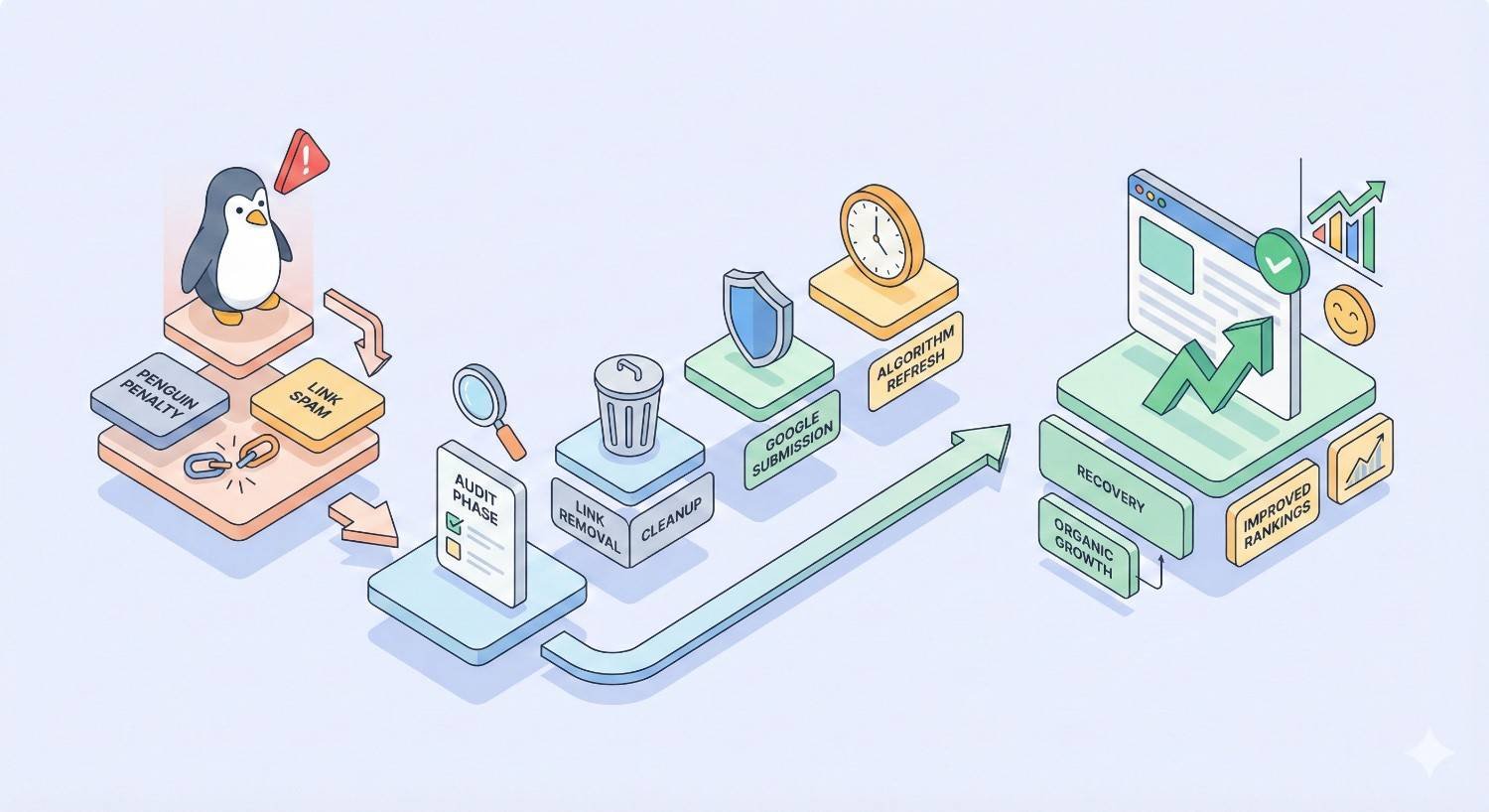
Google Penguin Recovery Timeline: What to Expect
Setting realistic expectations prevents frustration and premature strategy changes. Recovery timelines vary significantly based on penalty severity and cleanup thoroughness.
Algorithmic vs. Manual Penalty Recovery Timeframes
Algorithmic Penguin recovery depends on Google recrawling your site and the disavowed links. Since Penguin 4.0 runs in real-time, recovery can begin within weeks of cleanup completion.
Typical algorithmic recovery timeline:
- Weeks 1-4: Disavow file processing begins
- Weeks 4-8: Initial ranking movements
- Months 2-4: Significant recovery for moderately affected sites
- Months 4-6: Near-complete recovery for most sites
- Months 6-12: Full recovery for severely penalized sites
Manual penalty recovery requires Google reviewer approval. After submitting a reconsideration request:
- Days 1-14: Initial review period
- Days 14-30: Decision communicated
- If approved: Rankings typically return within 2-4 weeks
- If rejected: Address concerns and resubmit
Manual penalties often recover faster once approved because the penalty is explicitly lifted rather than gradually reassessed.
Factors That Influence Recovery Speed
Several variables affect how quickly rankings return.
Penalty severity matters most. Sites with thousands of toxic links and years of manipulation take longer than sites with limited bad links.
Cleanup thoroughness directly impacts recovery. Incomplete audits leaving toxic links active prevent full recovery regardless of time elapsed.
Site authority before the penalty influences recovery potential. Sites with strong content and legitimate link equity recover faster than thin sites built entirely on manipulative links.
Competitive landscape affects visible recovery. Even with penalty lifted, you’re competing against sites that may have improved during your penalty period.
Crawl frequency determines how quickly Google processes changes. High-authority sites get crawled more frequently, accelerating recovery.
Ongoing link building during recovery helps. Building new, high-quality links while cleaning up toxic ones accelerates ranking restoration.
Setting Realistic Expectations for Ranking Restoration
Full recovery to pre-penalty rankings isn’t guaranteed. Several factors affect ultimate outcomes.
Some rankings may never fully return if:
- Competitors strengthened during your penalty
- Your content became outdated
- Search intent shifted
- The manipulative links were your primary ranking factor
Partial recovery is common and still valuable. Recovering 60-80% of lost traffic represents significant business impact.
Focus on sustainable growth rather than exact ranking restoration. Build better content and earn legitimate links rather than trying to recreate pre-penalty positions.
Track business metrics alongside rankings. Traffic, leads, and revenue matter more than specific keyword positions.
Tools for Google Penguin Recovery
The right tools make recovery manageable. Each serves specific functions in the audit and monitoring process.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console provides authoritative data directly from Google. Essential features for recovery include:
Links report shows external links Google has discovered. Export this data as your baseline since it represents what Google actually sees.
Manual Actions section reveals any human-imposed penalties. Check here first to determine your penalty type.
Performance report tracks organic traffic and rankings. Use date comparisons to identify penalty timing and recovery progress.
URL Inspection tool shows how Google sees specific pages. Check if important pages are indexed and identify crawl issues.
Disavow Links tool accepts your disavow file. This is the only way to tell Google to ignore specific links.
Search Console data has limitations. It samples links rather than showing everything, and data can lag by several days.
Backlink Analysis Tools (Ahrefs, SEMrush, Majestic)
Third-party tools provide deeper backlink analysis than Search Console alone.
Ahrefs offers the largest backlink index and excellent toxic link identification. Key features include:
- Comprehensive backlink database
- Domain Rating and URL Rating metrics
- Anchor text analysis
- Link intersect for competitor comparison
- Batch analysis for large link lists
SEMrush combines backlink analysis with broader SEO features:
- Backlink Audit tool with toxicity scoring
- Automated outreach templates
- Integration with other SEMrush tools
- Historical backlink data
Majestic specializes in link analysis with unique metrics:
- Trust Flow and Citation Flow scores
- Topical Trust Flow for relevance assessment
- Historic Index for finding lost links
- Clique Hunter for link scheme detection
Using multiple tools ensures comprehensive coverage. Each has different crawlers finding unique links.
Link Detox and Toxic Link Identification Tools
Specialized tools automate toxic link identification.
Link Detox (LinkResearchTools) provides automated toxicity scoring and disavow file generation. Features include:
- DTOX score for each link
- Automated categorization
- Disavow file creation
- Competitive link risk analysis
Moz Link Explorer includes spam score metrics helping identify risky links. The spam score algorithm evaluates multiple factors correlating with penalized sites.
Kerboo offers link auditing with workflow management for teams handling large-scale cleanups.
These tools accelerate analysis but require human review. Automated scores sometimes flag legitimate links or miss sophisticated spam.
Rank Tracking and Traffic Monitoring Tools
Monitoring tools track recovery progress over time.
Google Analytics remains essential for traffic analysis:
- Organic traffic trends
- Landing page performance
- Conversion tracking during recovery
- Audience behavior changes
Rank tracking tools (Ahrefs, SEMrush, AccuRanker, SERPWatcher) monitor keyword positions:
- Daily or weekly ranking updates
- Historical position data
- SERP feature tracking
- Competitor comparison
Google Looker Studio (formerly Data Studio) creates custom dashboards combining multiple data sources for comprehensive recovery monitoring.
Set up automated alerts for significant ranking changes. Early detection of new problems prevents extended damage.
How to Prevent Future Google Penguin Penalties
Recovery means nothing if you repeat the same mistakes. Implement these practices to maintain clean link profiles permanently.
Building a Natural Link Profile
Natural link profiles share common characteristics that algorithms recognize as legitimate.
Diverse anchor text distribution looks organic. Aim for approximately:
- 30-40% branded anchors (your company name)
- 20-30% naked URLs
- 15-20% generic anchors (“click here,” “learn more”)
- 10-15% partial match keywords
- 5-10% exact match keywords
Varied link types from different sources signal natural acquisition:
- Editorial mentions in articles
- Resource page links
- Social media shares
- Forum discussions (genuine participation)
- Business directory listings (legitimate ones)
Gradual link velocity avoids spikes that trigger scrutiny. Sudden acquisition of hundreds of links looks unnatural regardless of quality.
Topical relevance between linking and linked sites matters. Links from related industries carry more weight and less risk.
Link Building Strategies That Comply With Google Guidelines
Focus on earning links rather than building them artificially.
Content marketing attracts natural links through valuable resources:
- Original research and data studies
- Comprehensive guides and tutorials
- Infographics and visual content
- Tools and calculators
- Expert roundups and interviews
Digital PR earns links from news sites and publications:
- Newsworthy announcements
- Expert commentary on industry trends
- Data-driven stories journalists want to cover
- HARO (Help A Reporter Out) responses
Guest posting on legitimate sites works when done correctly:
- Write for relevant, authoritative publications
- Provide genuine value to their audience
- Use natural anchor text
- Avoid sites that exist primarily for guest posts
Broken link building helps webmasters while earning links:
- Find broken links on relevant sites
- Create content replacing the dead resource
- Suggest your content as a replacement
Relationship building with industry peers generates organic mentions:
- Participate in communities genuinely
- Collaborate on projects
- Share others’ content
- Build real professional relationships
Regular Backlink Monitoring and Maintenance
Ongoing monitoring catches problems before they escalate.
Monthly backlink audits identify new toxic links from:
- Negative SEO attacks
- Scraped content with your links
- Old link building resurfacing
- Hacked sites linking to you
Set up alerts for new backlinks in Ahrefs or SEMrush. Review each new link within days of discovery.
Quarterly comprehensive reviews assess overall profile health:
- Anchor text distribution changes
- Domain authority trends
- Link velocity patterns
- Competitor link gap analysis
Maintain your disavow file by adding newly discovered toxic links. Don’t wait for problems to accumulate.
Document everything for future reference. If questions arise, historical records prove your ongoing diligence.
Avoiding Black Hat SEO Tactics
Understanding what to avoid prevents accidental violations.
Never buy links regardless of how they’re packaged. “Sponsored posts,” “content partnerships,” and “featured placements” that include followed links violate guidelines.
Avoid link exchanges and reciprocal linking schemes. “Link to me and I’ll link to you” arrangements are easily detected.
Don’t use PBNs (Private Blog Networks). Google continuously improves PBN detection, and penalties are severe.
Skip automated link building tools and services promising hundreds of links. These create exactly the patterns Penguin targets.
Reject link schemes from agencies promising quick results. Legitimate SEO takes time. Shortcuts create long-term problems.
Audit agency work if you outsource link building. You’re responsible for links pointing to your site regardless of who built them.
Google Penguin Recovery Case Studies
Real-world examples illustrate recovery timelines and strategies. These composite cases represent typical scenarios.
E-Commerce Site Recovery Example
Situation: An online retailer experienced 75% organic traffic loss following aggressive link building by a previous SEO agency. The backlink profile contained over 15,000 links, with approximately 40% from low-quality directories, article sites, and suspected PBNs.
Diagnosis: Traffic drop correlated with Penguin 4.0 integration. No manual action in Search Console. Anchor text analysis showed 68% exact-match commercial keywords.
Recovery process:
- Complete audit identified 6,200 toxic links
- Outreach campaign contacted 1,800 webmasters
- 340 links successfully removed
- Disavow file submitted with 5,860 entries
- Simultaneous content improvement and legitimate link building
Timeline:
- Month 1-2: Audit and outreach
- Month 3: Disavow submission
- Month 4: First ranking improvements observed
- Month 6: 50% traffic recovery
- Month 9: 80% traffic recovery
- Month 12: Traffic exceeded pre-penalty levels
Key learnings: Combining cleanup with positive link building accelerated recovery. The site emerged stronger by replacing manipulative links with legitimate editorial mentions.
Local Business Penguin Recovery
Situation: A regional service company lost local pack visibility and organic rankings after using a cheap link building service. The profile contained 2,500 links, mostly from irrelevant foreign directories and blog comment spam.
Diagnosis: Rankings dropped for all local keywords within a two-week period. Backlink profile showed obvious manipulation patterns including identical anchor text across hundreds of links.
Recovery process:
- Audit identified 1,800 toxic links
- Limited outreach (most sources were spam sites)
- Comprehensive disavow file submitted
- Focus shifted to local citation building and review generation
Timeline:
- Month 1: Audit and disavow
- Month 2: Local citation cleanup and building
- Month 3: Rankings began returning
- Month 4: Local pack visibility restored
- Month 6: Full recovery achieved
Key learnings: Local businesses often recover faster due to smaller link profiles. Replacing bad links with legitimate local citations provided both recovery and ongoing ranking benefits.
Enterprise Website Recovery Timeline
Situation: A large B2B company discovered their in-house team had engaged in link schemes over several years. The profile contained 85,000 backlinks with significant toxic percentage across multiple subdomains.
Diagnosis: Gradual ranking decline over 18 months suggested ongoing algorithmic suppression rather than single penalty event. Multiple product lines affected differently based on their individual link profiles.
Recovery process:
- Phased audit across all subdomains
- Dedicated team for outreach (contacted 12,000 webmasters)
- 2,400 links removed through outreach
- Segmented disavow files by subdomain
- Complete link building policy overhaul
- Agency partner vetting process implemented
Timeline:
- Months 1-3: Comprehensive audit
- Months 4-6: Outreach campaign
- Month 7: Disavow submission
- Months 8-12: Gradual recovery begins
- Months 12-18: Significant recovery across most products
- Month 24: Near-complete recovery
Key learnings: Enterprise recovery requires organizational change, not just technical fixes. Policy changes and team training prevent recurrence. Larger sites need longer timelines but can achieve full recovery.
When to Hire an SEO Professional for Penguin Recovery
DIY recovery works for some situations. Others require professional expertise. Assess your situation honestly.
DIY vs. Professional Recovery Assessment
Handle recovery yourself if:
- Your backlink profile is under 5,000 links
- You have SEO knowledge and available time
- The penalty appears moderate (less than 50% traffic loss)
- You understand link quality assessment
- Your business can tolerate extended recovery timeline
Hire professionals if:
- Your profile exceeds 10,000 links
- You lack SEO expertise
- Traffic loss exceeds 70%
- Previous recovery attempts failed
- Revenue loss demands fastest possible recovery
- You received a manual penalty
- Multiple algorithm penalties may be involved
Cost-benefit analysis: Professional recovery typically costs $3,000-$15,000 depending on complexity. Calculate your monthly revenue loss from the penalty. If professional recovery saves even 2-3 months, the investment often pays for itself.
What to Look for in a Penguin Recovery Specialist
Not all SEO professionals handle penalty recovery well. Evaluate specialists carefully.
Proven recovery experience matters most. Ask for:
- Case studies with specific metrics
- Client references you can contact
- Examples of successful reconsideration requests
- Timeline expectations based on similar situations
Transparent methodology indicates professionalism:
- Willingness to explain their process
- Clear deliverables and milestones
- Regular reporting and communication
- No guarantees of specific outcomes (recovery can’t be guaranteed)
Technical competence in link analysis:
- Proficiency with multiple backlink tools
- Understanding of Google’s guidelines
- Knowledge of algorithm history and updates
- Ability to distinguish toxic from suspicious links
Red flags to avoid:
- Promises of guaranteed recovery
- Unwillingness to explain methods
- Extremely low prices
- No verifiable case studies
- Pressure tactics or urgency creation
How SEO Agencies Approach Link Penalty Recovery
Professional agencies follow systematic processes refined through multiple recoveries.
Initial assessment includes:
- Complete backlink audit
- Traffic and ranking analysis
- Penalty type determination
- Recovery timeline estimation
- Cost and resource planning
Execution phase typically involves:
- Dedicated analyst for your account
- Proprietary tools and processes
- Scaled outreach capabilities
- Quality control on categorization
- Regular progress reporting
Ongoing support after initial recovery:
- Monitoring for new toxic links
- Disavow file maintenance
- Link building strategy guidance
- Prevention training for your team
Agencies bring efficiency through experience. What takes an inexperienced person weeks, experienced professionals complete in days.
Frequently Asked Questions About Google Penguin Recovery
Is Google Penguin Still Active in 2024?
Yes, Penguin remains active as part of Google’s core algorithm. Since September 2016, Penguin runs continuously in real-time rather than as periodic updates. Google no longer announces Penguin-specific updates because the algorithm constantly evaluates backlink profiles during normal crawling and indexing processes.
Can You Fully Recover From a Penguin Penalty?
Full recovery is possible for most sites that complete thorough cleanup. However, recovery to exact pre-penalty rankings isn’t guaranteed. Competitive landscapes change during penalty periods, and some rankings may have been artificially inflated by the manipulative links. Most sites recover 70-100% of lost traffic with proper remediation.
How Long Does Penguin Recovery Take?
Typical recovery takes 3-6 months for moderately affected sites. Severely penalized sites with extensive toxic link profiles may need 6-12 months. Recovery speed depends on cleanup thoroughness, site authority, crawl frequency, and competitive factors. Manual penalties can recover faster once Google approves the reconsideration request.
Does Disavowing Links Guarantee Recovery?
Disavowing links doesn’t guarantee recovery. The disavow tool tells Google to ignore specified links, but recovery depends on multiple factors including cleanup completeness, remaining link profile quality, and content strength. Disavowing alone without addressing underlying issues or building legitimate links may produce limited results.
What’s the Difference Between Penguin and a Manual Action?
Penguin is an algorithmic filter that automatically suppresses sites with manipulative backlinks. Manual actions are penalties imposed by Google’s human reviewers. Penguin doesn’t generate Search Console notifications; manual actions do. Algorithmic penalties lift automatically when issues are resolved and Google recrawls. Manual penalties require submitting a reconsideration request for review.
Can Negative SEO Cause a Penguin Penalty?
Competitors can attempt negative SEO by building toxic links to your site. Google claims their algorithms can identify and ignore most negative SEO attempts. However, monitoring your backlink profile and proactively disavowing suspicious new links provides protection. If you notice sudden influxes of toxic links you didn’t build, disavow them promptly.
Should I Disavow All Low-Quality Links?
Don’t disavow every low-quality link. Focus on clearly manipulative and toxic links. Some low-quality links occur naturally and don’t harm rankings. Over-disavowing can remove links that actually help your site. Concentrate on links showing clear manipulation patterns: paid links, PBNs, link schemes, and irrelevant spam.
Conclusion
Google Penguin recovery requires systematic diagnosis, thorough backlink auditing, strategic cleanup, and patient monitoring. The process demands attention to detail and commitment to following through completely. Partial efforts produce partial results.
At White Label SEO Service, we’ve guided businesses through successful Penguin recoveries across industries and penalty severities. Our team combines technical expertise with proven processes refined through hundreds of link penalty cases. We understand what works and what wastes time.
Ready to restore your organic visibility and protect your site from future penalties? Contact White Label SEO Service for a comprehensive backlink audit and customized recovery strategy. We’ll assess your situation, provide realistic timelines, and execute the cleanup your site needs to rank again.



