Link building penalties can devastate your organic traffic overnight, erasing months of SEO progress and costing your business thousands in lost revenue. Whether you’re dealing with a manual action from Google or an algorithmic devaluation, understanding how these penalties work is essential for protecting your search visibility.
The stakes have never been higher. Google’s spam detection systems have grown increasingly sophisticated, and practices that worked five years ago now trigger severe ranking drops. For business owners and marketing teams investing in SEO, one wrong link building decision can undo years of careful optimization work.
This guide covers everything you need to know about link penalties: what causes them, how to identify warning signs, proven prevention strategies, and step-by-step recovery processes if you’ve already been hit.
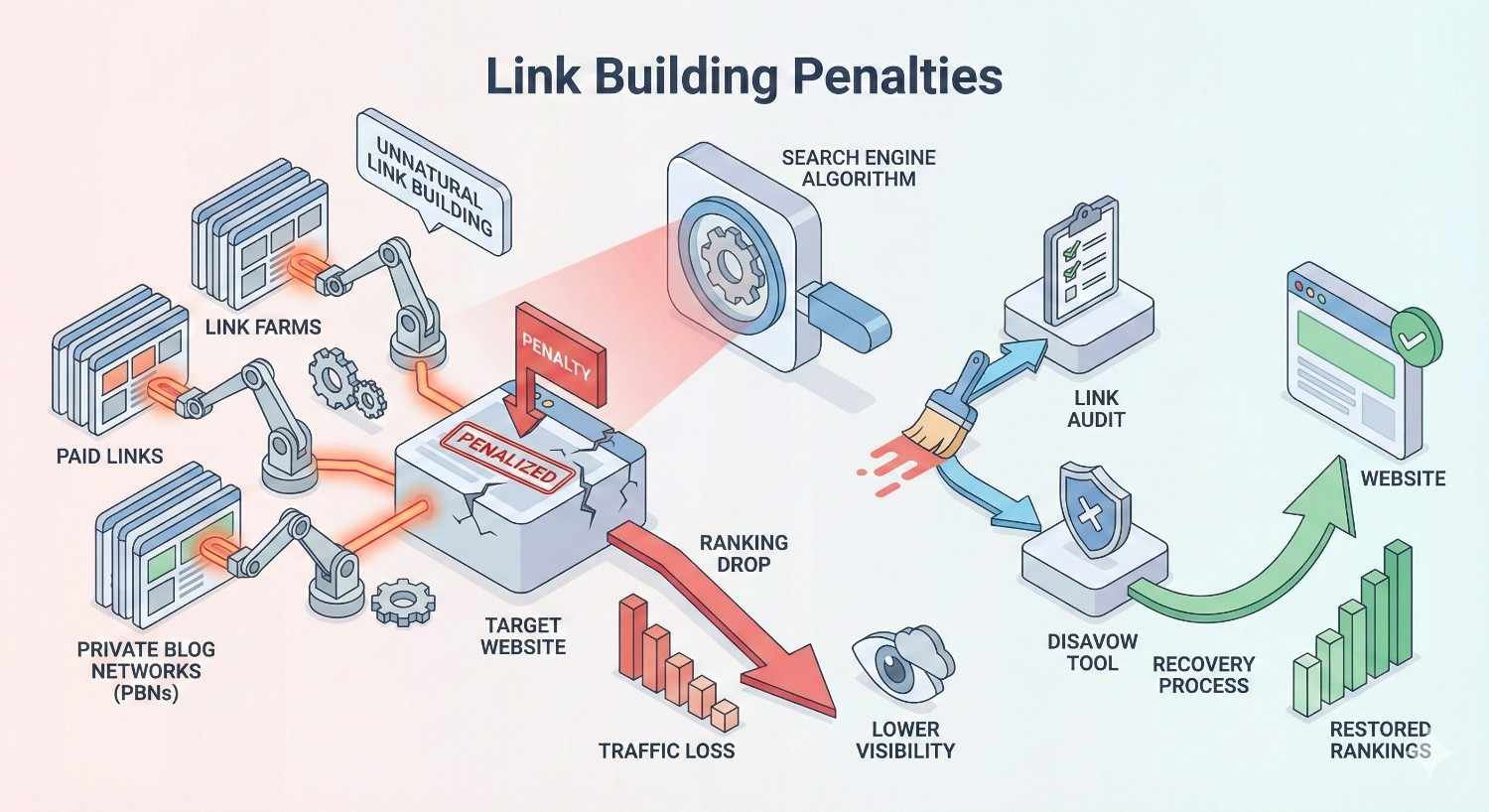
What Are Link Building Penalties?
Link building penalties are negative actions Google takes against websites that violate its guidelines regarding link acquisition and manipulation. These penalties directly impact your search rankings, organic traffic, and ultimately your business revenue.
Google views links as votes of confidence between websites. When you artificially inflate these votes through manipulative practices, you’re essentially trying to game the system. Google’s response ranges from devaluing specific links to removing your entire site from search results.
Manual Actions vs. Algorithmic Penalties
Manual actions occur when a Google employee reviews your site and determines you’ve violated their webmaster guidelines. You’ll receive a notification in Google Search Console explaining the issue. These penalties require you to fix the problem and submit a reconsideration request before recovery can begin.
Algorithmic penalties happen automatically when Google’s systems detect unnatural link patterns. The Penguin algorithm specifically targets link spam. Unlike manual actions, you won’t receive any notification. Your rankings simply drop, and you’re left to diagnose the cause yourself.
The key difference matters for recovery. Manual actions have a clear path forward: fix the issue, document your changes, and request reconsideration. Algorithmic penalties require you to clean up your link profile and wait for Google to recrawl and reassess your site during future algorithm updates.
How Google Identifies Unnatural Links
Google uses multiple signals to detect manipulative link building. Their systems analyze link velocity, anchor text distribution, source quality, and contextual relevance at scale.
Machine learning models identify patterns that indicate paid or artificial links. These include sudden spikes in backlinks, unusually high percentages of exact-match anchor text, links from irrelevant websites, and connections to known link networks.
Google also employs manual reviewers who investigate suspicious patterns flagged by automated systems. They examine whether links appear editorial in nature or seem designed purely to manipulate rankings.
The sophistication of detection continues improving. Google’s SpamBrain system now uses AI to identify both spammy links and the sites that generate them, making traditional manipulation tactics increasingly risky.
The Real Cost of Link Penalties (Traffic, Rankings, Revenue)
A link penalty doesn’t just hurt your rankings. It impacts every metric tied to organic search performance.
Traffic drops can exceed 90% for severe penalties. Sites that relied heavily on organic search for leads and sales see immediate revenue impacts. E-commerce businesses report losing thousands of dollars daily during penalty periods.
Recovery takes time. Even after addressing the issues, algorithmic recovery can take 3-6 months or longer. Manual action recovery depends on Google’s review timeline, which typically ranges from 2-4 weeks but can extend further for complex cases.
Beyond direct losses, penalties damage your domain’s long-term authority. Rebuilding trust with Google requires sustained effort over months or years. The opportunity cost of diverting resources to recovery instead of growth compounds these losses.
Types of Link Building Penalties
Understanding the specific type of penalty you’re facing determines your recovery strategy. Google categorizes link-related issues differently, and each requires a distinct approach.
Manual Link Penalties
Manual penalties appear in your Google Search Console under the Security & Manual Actions section. Google provides specific information about the violation type.
Unnatural Links to Your Site
This penalty targets incoming backlinks that violate Google’s guidelines. Common triggers include purchased links, link exchanges, and links from low-quality directories or article networks.
The notification typically states that Google has detected “a pattern of unnatural, artificial, deceptive, or manipulative links pointing to your site.” You’ll need to identify and address these problematic backlinks to recover.
Unnatural Links from Your Site
This penalty focuses on outbound links from your website. Selling links that pass PageRank, participating in link schemes, or having excessive affiliate links without proper attributes can trigger this action.
Google expects you to remove or nofollow the problematic outbound links and demonstrate that you’ve stopped the practice.
Partial Match Penalties
Not all manual actions affect your entire site. Partial penalties target specific pages or sections where Google detected violations. Your homepage might rank normally while affected pages disappear from results entirely.
Partial penalties often indicate localized issues, such as a specific landing page with purchased links or a blog section with spammy guest posts.
Algorithmic Link Penalties
Algorithmic penalties operate differently from manual actions. They’re applied automatically based on signals Google’s systems detect.
Penguin Algorithm Updates
Google’s Penguin algorithm specifically targets link spam. Originally launched in 2012, Penguin now runs in real-time as part of Google’s core algorithm.
Penguin devalues spammy links rather than penalizing entire sites in most cases. However, severe manipulation can still result in significant ranking drops across your domain.
Core Algorithm Link Devaluations
Google’s core algorithm updates often include link-related adjustments. These updates can change how Google evaluates link quality, relevance, and authority.
A site that maintained stable rankings might suddenly drop after a core update if Google’s systems determine its link profile no longer meets quality thresholds.
Spam Update Impacts
Google releases dedicated spam updates targeting various manipulation tactics. These updates specifically address link spam, among other issues.
Google’s December 2024 spam update targeted sites using manipulative link practices, resulting in ranking drops for affected domains.
Site-Wide vs. Partial Penalties
The scope of a penalty significantly affects both impact and recovery difficulty.
Site-wide penalties affect your entire domain. All pages lose rankings, and organic traffic drops across the board. These typically result from systematic violations, such as site-wide footer links or domain-level participation in link schemes.
Partial penalties target specific URLs, subdirectories, or sections. A blog with spammy guest posts might be penalized while your product pages remain unaffected. Partial penalties are generally easier to recover from since the scope of cleanup is limited.
Identifying whether you’re facing a site-wide or partial penalty helps prioritize your recovery efforts and set realistic timeline expectations.
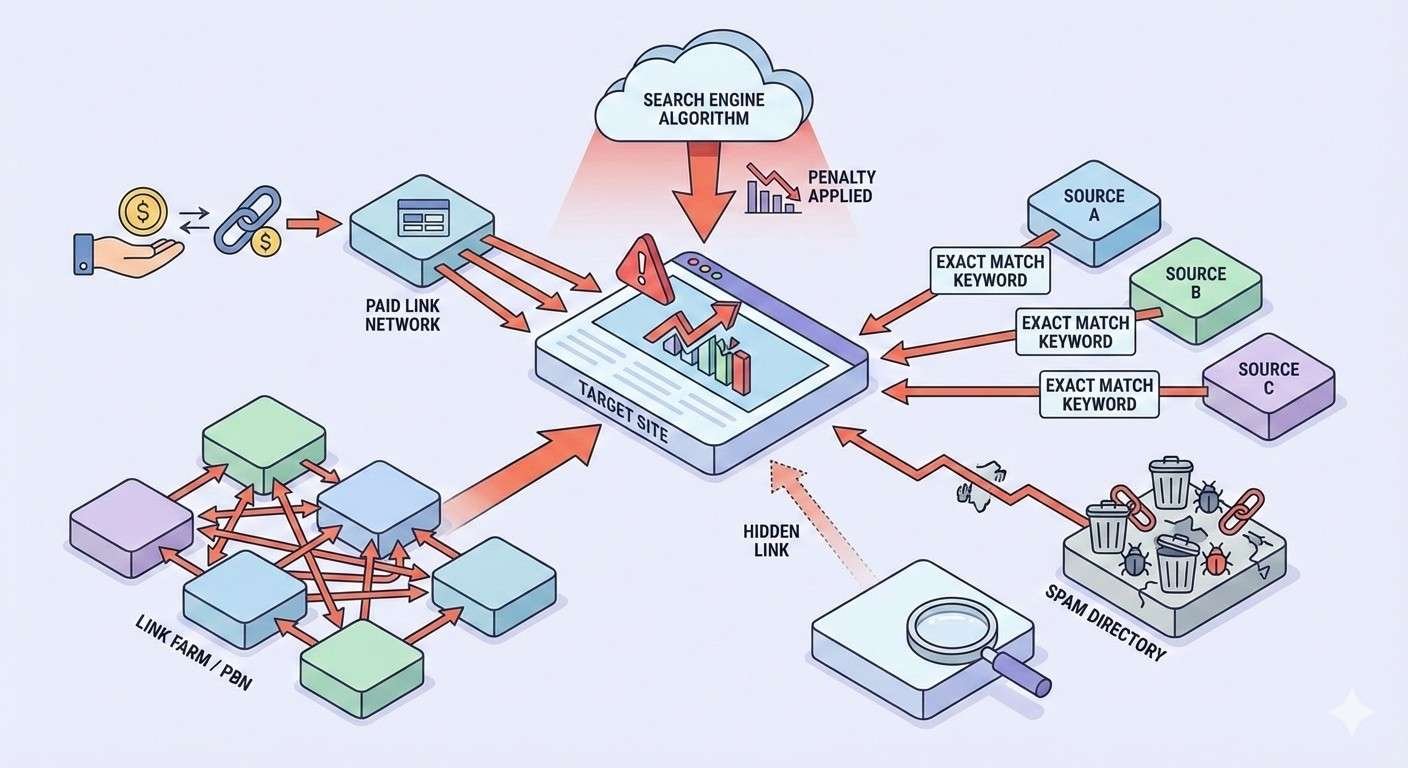
Link Building Practices That Trigger Penalties
Knowing what triggers penalties helps you avoid them. Google’s guidelines explicitly prohibit certain practices, while others fall into gray areas that carry significant risk.
Paid Links and Link Schemes
Link schemes represent the most common penalty trigger. Google defines these as any links intended to manipulate PageRank or a site’s ranking.
Buying or Selling Links That Pass PageRank
Purchasing links for SEO purposes directly violates Google’s guidelines. This includes paying for links, exchanging products or services for links, and sending free items in exchange for links.
The key factor is whether the link passes PageRank. Paid links with proper rel=”sponsored” or rel=”nofollow” attributes don’t violate guidelines because they don’t pass ranking signals.
Excessive Link Exchanges
Reciprocal linking at scale triggers penalties. While occasional natural link exchanges between related sites are normal, systematic “link to me and I’ll link to you” arrangements are manipulative.
Google specifically calls out “excessive link exchanges” and “partner pages exclusively for the sake of cross-linking” as violations.
Large-Scale Guest Posting Campaigns
Guest posting for links has become increasingly risky. Google targets “large-scale article marketing or guest posting campaigns with keyword-rich anchor text links.”
The issue isn’t guest posting itself but using it primarily as a link building tactic. Guest posts should provide genuine value to the host site’s audience, not serve as link vehicles.
Low-Quality Link Sources
The quality of linking domains matters as much as quantity. Links from certain source types almost always cause problems.
Private Blog Networks (PBNs)
PBNs are networks of websites created specifically to build links. Google actively identifies and devalues these networks.
Even well-disguised PBNs carry risk. Google’s systems detect patterns in hosting, registration, content quality, and linking behavior that reveal network connections.
Link Farms and Spam Directories
Link farms exist solely to sell or exchange links. Spam directories accept any submission regardless of quality. Both provide zero editorial value and signal manipulation to Google.
These sources often have obvious characteristics: thin content, excessive outbound links, no real traffic, and domains with spam-related histories.
Automated Link Building Tools
Tools that automatically create links across forums, comments, profiles, and directories violate guidelines. The scale and pattern of automated links make them easy for Google to detect.
Even tools marketed as “safe” or “white hat” often produce link patterns that trigger algorithmic filters.
Forum and Comment Spam
Dropping links in forum signatures, blog comments, and discussion threads rarely provides value. Google has long devalued these link types, and excessive use can trigger penalties.
Contextual, relevant participation in communities is fine. Mass-posting links across unrelated discussions is spam.
Manipulative Anchor Text Patterns
Anchor text distribution provides strong signals about link naturalness. Over-optimization is a common penalty trigger.
Exact-Match Anchor Text Over-Optimization
Natural link profiles contain diverse anchor text. When a high percentage of your backlinks use exact-match keywords, it signals manipulation.
A site selling “blue widgets” shouldn’t have 50% of its backlinks using “blue widgets” as anchor text. Natural profiles include brand names, URLs, generic phrases, and varied keyword references.
Keyword-Stuffed Anchor Text
Anchor text like “best cheap blue widgets for sale online” screams manipulation. Natural editorial links rarely use keyword-stuffed phrases.
Google’s algorithms specifically look for anchor text patterns that appear optimized rather than natural.
Unnatural Anchor Text Distribution
Beyond exact-match issues, the overall distribution matters. Natural profiles typically show:
- Brand name anchors: 30-40%
- URL anchors: 20-30%
- Generic anchors (click here, learn more): 15-25%
- Keyword variations: 15-25%
- Exact-match keywords: 5-10%
Significant deviation from natural patterns raises flags.
Link Velocity Red Flags
How quickly you acquire links matters. Unnatural velocity patterns indicate manipulation.
Sudden Link Spikes
Acquiring hundreds of links in a week when you normally get a few per month signals artificial activity. Unless you’ve published viral content or received major press coverage, sudden spikes appear manipulative.
Google’s systems track link acquisition over time. Anomalies trigger closer examination.
Unnatural Growth Patterns
Consistent, steady link growth that never varies also appears unnatural. Real websites experience fluctuations based on content publishing, seasonal trends, and marketing activities.
A perfectly linear growth curve suggests automated or purchased links rather than organic acquisition.
Inconsistent Link Acquisition
Patterns that don’t match your content or marketing activities raise questions. Getting links to pages with no content updates, during periods of no marketing activity, or from unrelated industries suggests manipulation.
Hidden and Deceptive Links
Attempting to hide links from users while making them visible to search engines is a clear violation.
Hidden Text and Links
Using CSS to hide links, matching text color to background color, or positioning links off-screen violates guidelines. Google considers this deceptive.
Modern detection easily identifies these techniques. The risk far outweighs any potential benefit.
Cloaking and Redirects
Showing different content to search engines than to users is cloaking. Using redirects to send users to different pages than search engines see is equally problematic.
Both practices can result in severe penalties, including complete removal from search results.
Widget and Footer Link Schemes
Embedding links in widgets, templates, or footers that appear across many sites creates unnatural link patterns. These site-wide links from a single source appear manipulative.
Google specifically mentions “widely distributed links in the footers or templates of various sites” as a violation.
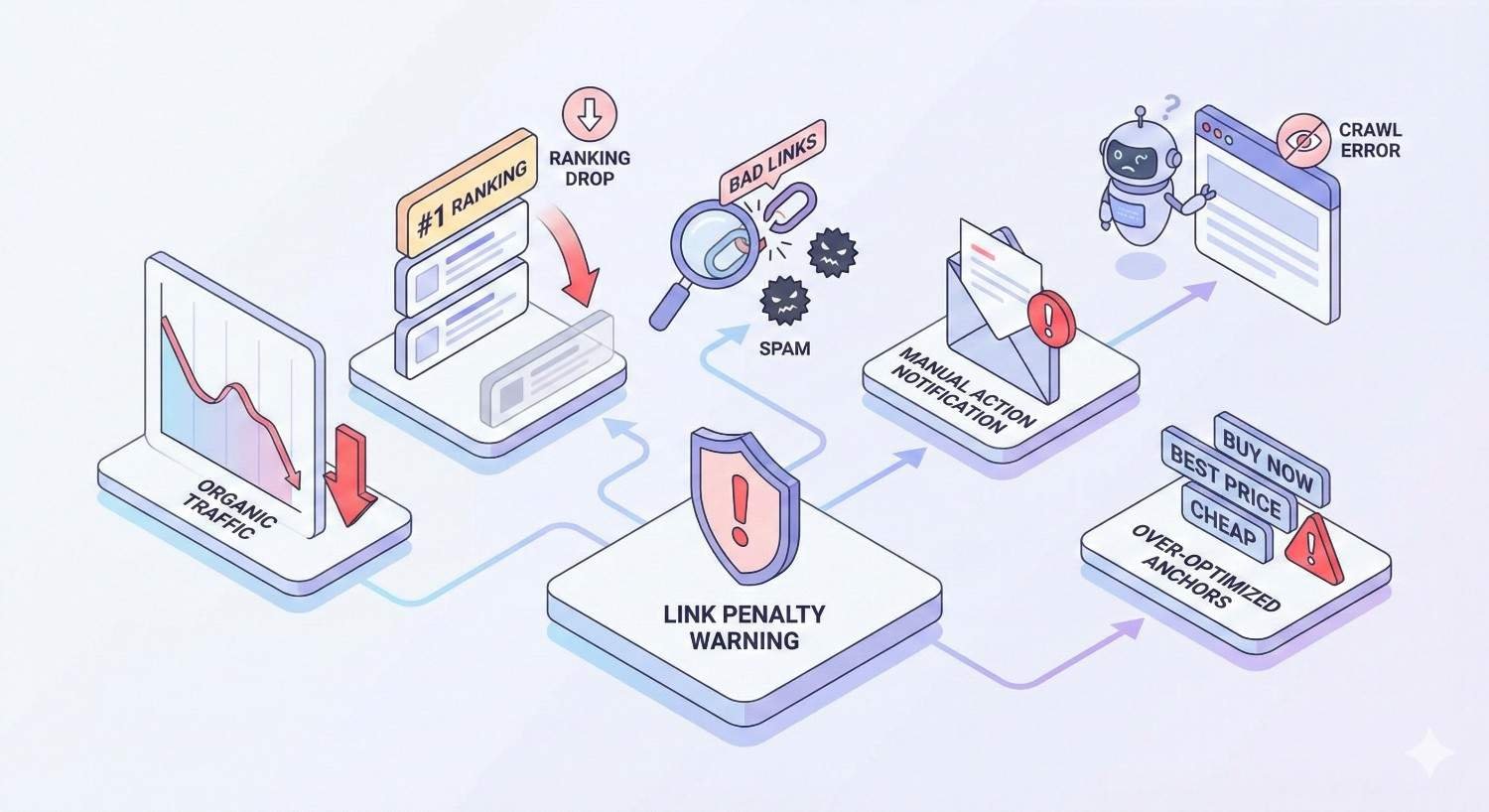
Warning Signs You May Have a Link Penalty
Early detection allows faster response. Recognizing penalty indicators helps you address issues before they cause lasting damage.
Sudden Traffic and Ranking Drops
The most obvious sign is a significant, sudden drop in organic traffic. Check Google Analytics for sharp declines that don’t correlate with seasonal patterns or site changes.
Ranking drops across multiple keywords simultaneously often indicate penalties. Use rank tracking tools to monitor position changes and identify patterns.
Not all drops indicate penalties. Algorithm updates, technical issues, and competitor improvements can also cause declines. Investigation is necessary to determine the cause.
Manual Action Notifications in Google Search Console
Google Search Console displays manual actions under Security & Manual Actions > Manual Actions. Check this section regularly.
If you have a manual action, Google provides specific information about the violation. This is the clearest indicator of a penalty and includes guidance on what needs to be fixed.
Set up email notifications in Search Console to receive alerts about new manual actions immediately.
Algorithmic Update Correlation
Track Google algorithm updates and compare timing to your traffic changes. Tools like Semrush Sensor and Moz’s Google Algorithm Update History help identify update dates.
If your traffic dropped within days of a confirmed algorithm update, the update likely affected your site. Research what the update targeted to understand potential issues.
Unnatural Link Profile Patterns
Audit your backlink profile for warning signs:
- High percentage of links from low-quality domains
- Excessive exact-match anchor text
- Links from irrelevant industries or topics
- Sudden acquisition of many links
- Links from known spam sources
These patterns don’t guarantee a penalty but indicate elevated risk.
Competitor Negative SEO Attacks
Competitors sometimes attempt to harm rivals by building spammy links to their sites. While Google claims to handle most negative SEO automatically, severe attacks can cause problems.
Monitor for sudden influxes of low-quality links you didn’t build. Unusual anchor text patterns, links from foreign-language spam sites, or connections to adult or gambling content may indicate an attack.
How to Audit Your Link Profile for Penalty Risks
Regular audits help identify problems before they trigger penalties. A systematic approach ensures thorough analysis.
Using Google Search Console for Link Analysis
Google Search Console provides your most authoritative link data. Navigate to Links > External Links to see domains linking to your site.
Export the full list for analysis. Google shows the top linking sites, top linked pages, and top linking text. This data comes directly from Google’s index.
While Search Console doesn’t show every link, it represents what Google considers most important. Discrepancies between Search Console data and third-party tools can indicate which links Google is ignoring.
Third-Party Link Analysis Tools
Multiple tools provide comprehensive backlink analysis. Each offers different data and features.
Ahrefs Link Audit
Ahrefs maintains one of the largest backlink indexes. Their Site Explorer shows referring domains, anchor text distribution, and link growth over time.
The Backlink Audit feature identifies potentially harmful links based on multiple quality signals. You can export data for further analysis or disavow file creation.
SEMrush Backlink Audit
SEMrush’s Backlink Audit tool automatically scores links based on toxicity markers. It integrates with Google Search Console for more complete data.
The tool categorizes links by risk level and provides specific reasons why each link might be problematic.
Moz Link Explorer
Moz provides Domain Authority and Spam Score metrics that help evaluate link quality. Their Link Explorer shows your complete backlink profile with quality indicators.
Spam Score specifically identifies characteristics associated with penalized or banned sites.
Majestic Trust Flow Analysis
Majestic’s Trust Flow and Citation Flow metrics measure link quality and quantity. High Citation Flow with low Trust Flow indicates many low-quality links.
Their topical Trust Flow shows whether your links come from relevant industries, helping identify off-topic link building.
Identifying Toxic and Risky Links
Not all low-quality links cause penalties, but identifying risky links helps prioritize cleanup efforts.
Link Quality Metrics to Evaluate
Consider multiple factors when assessing link risk:
- Domain Authority/Rating of linking site
- Spam Score or toxicity indicators
- Relevance to your industry
- Traffic and engagement on linking site
- Editorial context of the link
- Anchor text used
No single metric determines toxicity. Evaluate links holistically.
Red Flag Link Patterns
Certain characteristics strongly indicate problematic links:
- Links from sites with no real content
- Links from pages with hundreds of outbound links
- Links from sites in unrelated languages
- Links from known link networks
- Links with exact-match commercial anchor text
- Links from sites penalized by Google
Spam Score Interpretation
Spam Score (Moz) and similar metrics indicate risk level but aren’t definitive. A high Spam Score doesn’t guarantee a link is harmful, and a low score doesn’t guarantee safety.
Use spam scores as one input among many. Manual review of flagged links provides better accuracy than relying solely on automated scores.
Analyzing Anchor Text Distribution
Export your anchor text data and calculate percentages for each category:
- Brand anchors
- URL anchors
- Generic anchors
- Partial-match keyword anchors
- Exact-match keyword anchors
Compare your distribution to natural benchmarks. Significant over-optimization in keyword categories indicates risk.
Visualizing anchor text distribution in a chart helps identify imbalances quickly.
Documenting Your Link Inventory
Create a comprehensive spreadsheet documenting:
- Linking domain
- Specific linking URL
- Target page on your site
- Anchor text used
- Link quality assessment
- Risk level (low, medium, high)
- Action needed (keep, remove, disavow)
This documentation supports recovery efforts and reconsideration requests. It also provides a baseline for ongoing monitoring.
How to Avoid Link Building Penalties
Prevention is far easier than recovery. Building a penalty-proof link strategy requires understanding guidelines and implementing sustainable practices.
Follow Google’s Webmaster Guidelines
Google’s guidelines explicitly state what’s allowed and prohibited. Familiarity with these rules is essential.
Link Scheme Guidelines
Google’s link schemes documentation lists specific violations:
- Buying or selling links for ranking purposes
- Excessive link exchanges
- Large-scale guest posting with keyword-rich anchors
- Automated link building
- Requiring links as part of Terms of Service
- Text advertisements that pass PageRank
- Advertorials or native advertising with PageRank-passing links
- Low-quality directory or bookmark site links
- Forum comments with optimized links
- Widely distributed footer or template links
Quality Guidelines for Links
Google wants links that represent genuine editorial endorsements. The key question: would this link exist if search engines didn’t?
Links should provide value to users, come from relevant sources, and appear naturally within content. Anything that exists primarily to influence rankings violates the spirit of the guidelines.
Best Practices Documentation
Google’s Search Essentials (formerly Webmaster Guidelines) provides comprehensive guidance. Review these documents regularly as Google updates them.
Understanding the principles behind the rules helps you evaluate gray-area situations where specific guidance doesn’t exist.
Build Natural, Editorial Links
The safest links are those you earn through genuine value. Focus on creating reasons for others to link to you.
Content-Driven Link Acquisition
Create content that naturally attracts links:
- Original research and data
- Comprehensive guides and resources
- Unique tools and calculators
- Expert analysis and insights
- Visual content and infographics
Content that provides genuine value earns links without manipulation.
Digital PR and Outreach
Legitimate outreach to journalists, bloggers, and industry publications can earn editorial links. The key is providing genuine value, not just requesting links.
Pitch stories, offer expert commentary, and build relationships. Links should be a byproduct of valuable contributions, not the primary goal.
Creating Linkable Assets
Develop resources others want to reference:
- Industry statistics and benchmarks
- Free tools that solve problems
- Comprehensive glossaries or guides
- Original research and surveys
- Interactive content and calculators
These assets attract links naturally over time.
Earning Links Through Value
Focus on being genuinely useful to your industry. Answer questions, solve problems, and contribute meaningfully to conversations.
When you consistently provide value, links follow naturally. This approach takes longer but builds sustainable authority.
Diversify Your Link Profile
Natural link profiles show diversity across multiple dimensions. Intentionally building variety reduces risk.
Varied Link Sources
Acquire links from different types of sites:
- Industry publications
- News sites
- Blogs and personal sites
- Educational institutions
- Government resources
- Business directories
- Social platforms
Over-reliance on any single source type appears unnatural.
Natural Anchor Text Mix
Actively manage anchor text diversity. When you can influence anchor text (such as in guest posts or partnerships), vary your approach:
- Use brand name frequently
- Include natural URL references
- Allow generic phrases
- Limit exact-match keywords
Let some links use whatever anchor text the publisher chooses naturally.
Different Link Types (dofollow, nofollow, UGC, sponsored)
Natural profiles include various link attributes. Not every link should be dofollow.
Nofollow links from social media, forums, and user-generated content are normal. Sponsored links from paid placements should use appropriate attributes. A profile with only dofollow links appears manipulated.
Geographic and Topical Diversity
Links should come from relevant geographic regions and topically related sites. A US-based business with most links from foreign sites raises questions.
Topical relevance matters too. Links from your industry carry more weight and appear more natural than random off-topic links.
Use Proper Link Attributes
Google provides specific attributes for different link types. Using them correctly protects you from penalties.
When to Use rel=”nofollow”
Use nofollow when you don’t want to vouch for the linked content or when the link wasn’t editorially placed. Common uses include:
- User-generated content you haven’t verified
- Links in comments or forums
- Links you’re unsure about
- Paid links (though sponsored is preferred)
rel=”sponsored” for Paid Links
Any link you paid for should use rel=”sponsored”. This includes:
- Paid advertisements
- Sponsored content
- Affiliate links
- Paid placements
Using sponsored tells Google the link is commercial, preventing it from passing PageRank while avoiding penalties.
rel=”ugc” for User-Generated Content
Links in user-generated content like comments, forum posts, and community contributions should use rel=”ugc”.
This attribute tells Google the link came from users rather than the site owner, providing appropriate context.
Proper Implementation Guidelines
Attributes can be combined: rel=”nofollow sponsored” or rel=”ugc nofollow”. Implement them in the HTML anchor tag.
Audit your site to ensure proper attributes are applied consistently. Many CMS platforms have settings to automatically add appropriate attributes to user-generated links.
Maintain Natural Link Velocity
How quickly you acquire links should match your content and marketing activities.
Gradual Link Growth
Build links steadily over time rather than in bursts. Consistent, gradual growth appears natural and sustainable.
Plan link building activities to spread acquisition across months rather than concentrating efforts in short periods.
Consistent Acquisition Patterns
Your link velocity should correlate with your activities. Publishing major content should generate more links. Quiet periods should show slower acquisition.
Patterns that don’t match your actual marketing activities appear artificial.
Avoiding Sudden Spikes
Unless you have a legitimate reason (viral content, major press coverage), avoid acquiring many links quickly.
If you do experience a natural spike, document the cause. This documentation helps if Google questions the pattern.
Vet Link Opportunities Carefully
Not every link opportunity is worth pursuing. Evaluate potential links before acquiring them.
Domain Authority and Trust Signals
Check the linking site’s authority metrics. While not perfect indicators, very low authority sites rarely provide value and may indicate spam.
Look for signs of legitimate operation: real content, actual traffic, genuine engagement, and professional presentation.
Relevance and Topical Alignment
Links from relevant sites carry more weight and less risk. A link from an industry publication makes sense. A link from an unrelated site raises questions.
Prioritize opportunities that align with your business and audience.
Traffic and Engagement Metrics
Sites with real traffic and engagement are more likely to be legitimate. Use tools like SimilarWeb or SEMrush to estimate traffic.
Sites with no traffic despite having content often exist solely for link building.
Red Flags to Avoid
Decline opportunities that show warning signs:
- Sites that openly sell links
- Pages with excessive outbound links
- Content that exists only to place links
- Sites with no clear purpose or audience
- Domains with spam-related histories
- Requests for specific anchor text
Monitor Your Link Profile Regularly
Ongoing monitoring catches problems early. Establish regular review processes.
Monthly Link Audits
Review new backlinks monthly. Identify any suspicious additions and investigate their source.
Track changes in anchor text distribution, referring domain quality, and overall profile health.
New Link Monitoring
Set up alerts for new backlinks using tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush. Immediate notification of new links helps you identify problems quickly.
Investigate unexpected links, especially from low-quality sources or with suspicious anchor text.
Disavow File Maintenance
If you maintain a disavow file, review and update it regularly. Add newly identified toxic links and remove entries for domains that have improved.
Keep documentation of why each domain was disavowed for future reference.
What should I do if I already have a penalty?
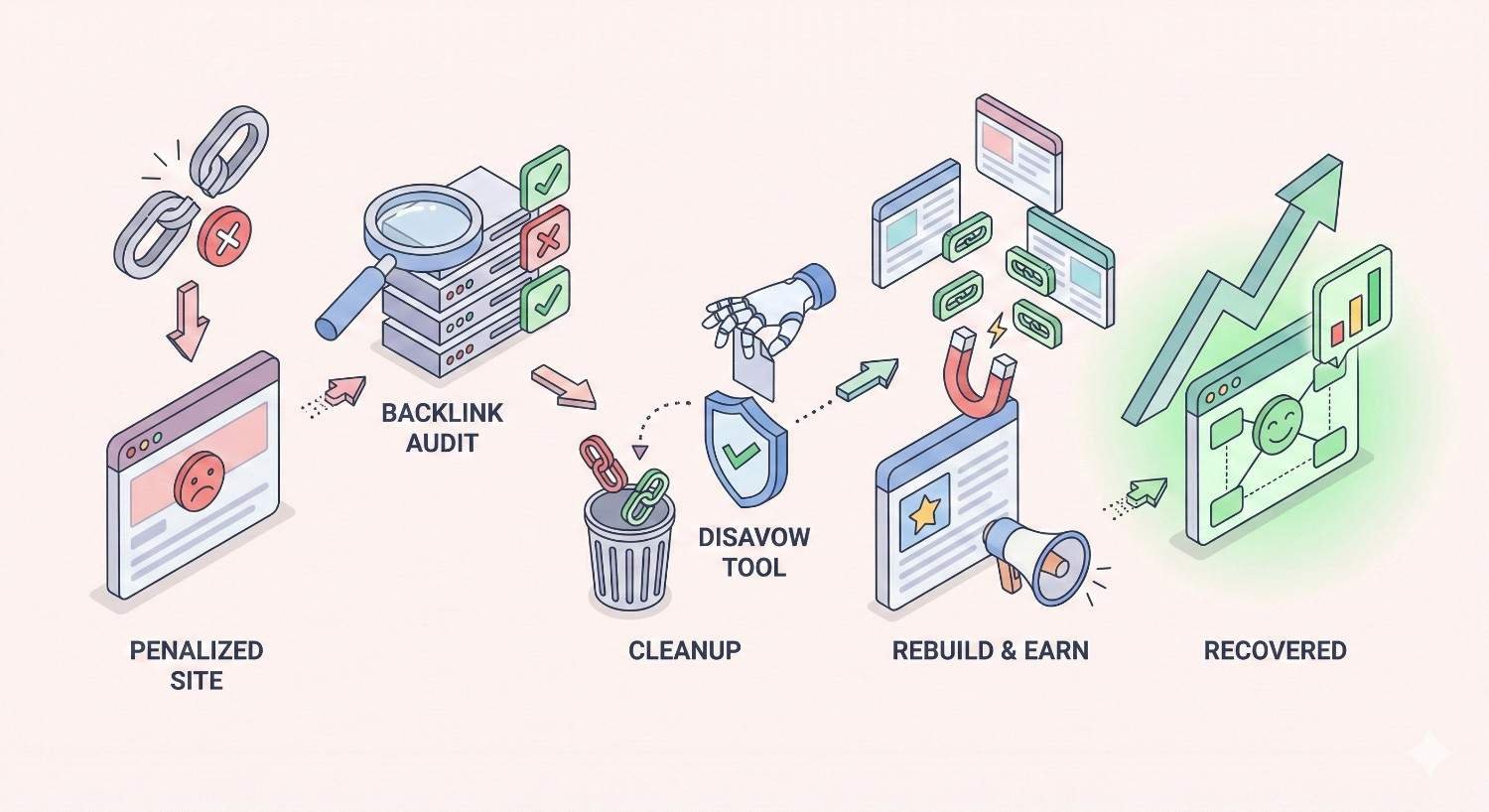
How to Recover from a Link Penalty
If you’re already facing a penalty, systematic recovery is essential. The process differs based on penalty type but follows similar principles.
Step 1: Identify the Penalty Type
Before taking action, confirm what you’re dealing with.
Manual Action Recovery Process
Check Google Search Console for manual actions. If present, Google tells you exactly what’s wrong. Read the notification carefully to understand the specific violation.
Manual actions require you to fix the issue and submit a reconsideration request. Recovery doesn’t happen until Google reviews and approves your request.
Algorithmic Penalty Recovery Process
If no manual action exists but you’ve experienced significant drops correlating with algorithm updates, you’re likely facing algorithmic issues.
Algorithmic recovery doesn’t require a reconsideration request. Instead, you must clean up your link profile and wait for Google to recrawl and reassess your site.
Step 2: Conduct a Comprehensive Link Audit
Thorough analysis identifies all problematic links.
Export Complete Link Profile
Gather data from multiple sources:
- Google Search Console (most authoritative)
- Ahrefs
- SEMrush
- Moz
- Majestic
Combine and deduplicate the data for a complete picture.
Categorize Links by Risk Level
Review each linking domain and categorize:
- Safe: High-quality, relevant, editorial links
- Neutral: Average quality, no obvious issues
- Suspicious: Quality concerns, needs investigation
- Toxic: Clear violations, should be addressed
Focus removal efforts on toxic and suspicious categories.
Document Toxic Links
Create detailed documentation of problematic links:
- Linking URL
- Your target page
- Anchor text
- Why it’s problematic
- Action taken (removal request, disavow)
This documentation supports reconsideration requests and provides an audit trail.
Step 3: Remove or Disavow Harmful Links
Address identified toxic links through removal or disavowal.
Manual Link Removal Outreach
Contact webmasters to request link removal. While time-consuming and often unsuccessful, demonstrating removal efforts strengthens reconsideration requests.
Send polite, professional emails explaining the situation. Track all outreach attempts and responses.
Creating a Disavow File
The disavow file tells Google to ignore specific links when assessing your site. Format the file correctly:
Copy
# Disavow file for example.com
# Updated: [Date]
# Toxic domains
domain:spamsite1.com
domain:spamsite2.com
# Specific URLs
http://example.com/spammy-page
Include comments explaining your reasoning.
Submitting to Google Search Console
Upload your disavow file through the Google Disavow Tool. Select your property and upload the text file.
Google processes the file during future crawls. Effects aren’t immediate.
Disavow Best Practices and Warnings
Use disavow carefully:
- Only disavow links you’re confident are harmful
- Don’t disavow legitimate links
- Review the file before submission
- Keep records of what you’ve disavowed and why
Incorrect disavow usage can harm your rankings by removing valuable link signals.
Step 4: Submit a Reconsideration Request (Manual Actions)
For manual actions, you must request Google’s review after addressing issues.
What to Include in Your Request
Your reconsideration request should cover:
- Acknowledgment of the violation
- Explanation of what caused the problem
- Detailed description of actions taken
- Evidence of cleanup efforts
- Commitment to following guidelines
Documentation Requirements
Provide supporting documentation:
- Spreadsheet of toxic links identified
- Record of removal outreach attempts
- Copy of your disavow file
- Timeline of cleanup activities
Thorough documentation demonstrates serious effort.
Writing an Effective Reconsideration Request
Be honest, specific, and thorough. Acknowledge mistakes without making excuses. Explain exactly what you did to fix the problem.
Show that you understand why the violation occurred and how you’ll prevent recurrence. Generic or vague requests often fail.
Response Timeline Expectations
Google typically responds within 2-4 weeks, though complex cases may take longer. You’ll receive notification in Search Console.
If rejected, Google usually explains why. Address the feedback and resubmit.
Step 5: Wait for Algorithmic Recovery
Algorithmic penalties don’t have reconsideration requests. Recovery happens when Google recrawls and reassesses.
Algorithm Update Cycles
Major algorithm updates occur several times per year. Core updates typically happen quarterly. Spam updates occur as needed.
Your site may not recover until a relevant update processes your cleaned-up link profile.
Recovery Timeline Expectations
Algorithmic recovery typically takes 3-6 months minimum. Some sites take longer depending on severity and cleanup thoroughness.
Patience is essential. Continued improvement efforts during the waiting period help.
Monitoring Recovery Signals
Track key metrics during recovery:
- Organic traffic trends
- Keyword rankings
- Indexed pages
- Crawl activity
Gradual improvement indicates recovery is progressing.
Step 6: Rebuild with Clean Link Building
After recovery, rebuild your link profile using safe practices.
Establishing New Link Acquisition Strategy
Develop a sustainable strategy focused on:
- Content-driven link earning
- Legitimate outreach and PR
- Building genuine relationships
- Creating linkable assets
Avoid any tactics that contributed to the original penalty.
Building Authority Safely
Focus on quality over quantity. A few high-quality editorial links provide more value than many low-quality links.
Build authority gradually through consistent value creation and legitimate promotion.
Long-Term Monitoring and Maintenance
Implement ongoing monitoring to prevent future issues:
- Regular link audits
- New link alerts
- Anchor text tracking
- Quality assessments
Early detection of problems prevents penalties from recurring.
Link Building Penalties vs. Link Devaluation
Not all negative link outcomes are penalties. Understanding the difference helps you respond appropriately.
Understanding the Difference
Penalties actively suppress your rankings as punishment for violations. Devaluation simply ignores links, removing their positive impact without additional punishment.
Penalties require cleanup and potentially reconsideration. Devaluation means the links just don’t help you anymore.
How Google Devalues Links Without Penalizing
Google’s systems can identify and ignore manipulative links without penalizing the target site. The Penguin algorithm often devalues rather than penalizes.
Devalued links simply don’t pass PageRank. Your rankings may drop because you lost link value, but you’re not being punished.
Impact on Rankings and Traffic
Devaluation impacts are typically less severe than penalties. You lose the benefit of devalued links but don’t face additional suppression.
Traffic drops from devaluation tend to be proportional to how much those links contributed to your rankings.
Strategic Response to Devaluation
If you suspect devaluation rather than penalty:
- Don’t panic about cleanup
- Focus on building new quality links
- Replace lost link value with legitimate acquisition
- Monitor for actual penalty signs
Aggressive disavowing isn’t necessary for devaluation since the links are already being ignored.
Common Link Building Penalty Myths
Misconceptions about penalties lead to poor decisions. Understanding reality helps you respond appropriately.
“All Paid Links Cause Penalties”
Not all paid links violate guidelines. Links with proper rel=”sponsored” attributes are compliant. Advertising that doesn’t pass PageRank is acceptable.
The violation is paying for links that pass ranking signals without disclosure, not all commercial link relationships.
“Nofollow Links Protect You Completely”
Nofollow indicates you don’t vouch for the link, but it doesn’t make manipulative practices acceptable. Massive nofollow link schemes can still raise flags.
Nofollow is appropriate for certain link types, not a loophole for manipulation.
“Disavowing Links Hurts Your Rankings”
Disavowing legitimate links can hurt rankings by removing valuable signals. However, disavowing truly toxic links doesn’t hurt you since those links weren’t helping anyway.
The risk is incorrect disavowing, not the tool itself.
“Negative SEO Always Causes Penalties”
Google claims to handle most negative SEO automatically. While severe attacks can cause problems, Google’s systems are designed to identify and ignore obviously artificial negative links.
Don’t assume every ranking drop is negative SEO. Investigate thoroughly before concluding you’re under attack.
“You Can’t Recover from a Penguin Penalty”
Many sites have successfully recovered from Penguin-related issues. Recovery requires thorough cleanup and patience, but it’s absolutely possible.
The key is addressing the root cause completely and building a clean link profile going forward.
How Long Does Link Penalty Recovery Take?
Setting realistic expectations helps you plan appropriately and avoid frustration.
Manual Action Recovery Timeline
Manual action recovery depends on:
- How quickly you complete cleanup
- Quality of your reconsideration request
- Google’s review queue
Typical timeline: 4-8 weeks from cleanup completion to recovery, assuming your request is approved on the first attempt.
Algorithmic Penalty Recovery Timeline
Algorithmic recovery requires waiting for relevant algorithm updates to process your changes.
Typical timeline: 3-6 months minimum, potentially longer for severe cases or if cleanup is incomplete.
Factors That Affect Recovery Speed
Several factors influence recovery time:
- Severity of the original violation
- Thoroughness of cleanup
- Quality of new link building
- Overall site quality and authority
- Algorithm update timing
Sites with strong fundamentals beyond links often recover faster.
Setting Realistic Expectations
Plan for recovery to take longer than you hope. Build contingency into your projections.
Use the recovery period productively by improving other aspects of your site and building legitimate links.
Protecting Your Site from Negative SEO Link Attacks
While relatively rare, negative SEO attacks do occur. Preparation and monitoring help you respond effectively.
What Is Negative SEO?
Negative SEO involves competitors attempting to harm your rankings through manipulative tactics. Link-based attacks involve building spammy links to your site.
Other forms include content scraping, fake reviews, and hacking, but link attacks are most common.
How to Detect Negative SEO Attacks
Watch for warning signs:
- Sudden influx of low-quality backlinks
- Links with inappropriate anchor text
- Links from foreign-language spam sites
- Connections to adult, gambling, or pharmaceutical spam
- Patterns that don’t match your marketing activities
Regular monitoring catches attacks early.
Responding to Toxic Link Attacks
If you identify an attack:
- Document everything thoroughly
- Continue monitoring to track the attack’s scope
- Consider proactive disavowing of clearly malicious links
- Focus on building positive signals to counteract negative ones
Don’t panic. Most attacks have limited impact if addressed appropriately.
Proactive Monitoring and Protection
Implement ongoing protection:
- Set up new link alerts
- Review backlinks weekly during active attacks
- Maintain relationships with your legitimate link sources
- Keep documentation of your link building activities
Preparation makes response faster and more effective.
When to Use the Disavow Tool Defensively
Proactive disavowing makes sense when:
- You can clearly identify attack links
- The attack is significant in scale
- Links are obviously malicious (spam anchor text, known bad neighborhoods)
Don’t disavow speculatively. Only disavow links you’re confident are harmful.
Safe Link Building Strategies for Long-Term Growth
Sustainable link building focuses on earning links through genuine value. These strategies build authority without penalty risk.
Content Marketing and Link Earning
Creating valuable content naturally attracts links over time.
Original Research and Data Studies
Conduct surveys, analyze data, or compile industry statistics. Original research gets cited and linked by others writing about your topic.
Publish findings with clear methodology and shareable data visualizations.
Comprehensive Resource Guides
Create the definitive resource on topics in your industry. Comprehensive guides become reference materials that others link to.
Update guides regularly to maintain relevance and link value.
Visual Content and Infographics
Visual content gets shared and embedded, generating links. Create infographics, charts, and diagrams that communicate complex information clearly.
Provide embed codes to make linking easy.
Tools and Calculators
Free tools that solve problems attract links naturally. Calculators, generators, and interactive tools provide ongoing value that earns links.
Promote tools to relevant audiences who will use and share them.
Digital PR and Media Outreach
Legitimate media relationships generate high-quality editorial links.
Journalist Outreach Strategies
Build relationships with journalists covering your industry. Provide expert commentary, data, and story ideas.
Be helpful without expecting immediate links. Relationships generate coverage over time.
HARO and Source Requests
Respond to journalist queries through Help A Reporter Out (HARO) and similar platforms. Providing expert quotes can earn links from major publications.
Respond quickly with concise, valuable information.
Press Release Distribution
Newsworthy announcements can generate coverage and links. Focus on genuinely newsworthy content, not promotional fluff.
Distribute through legitimate channels and follow up with relevant journalists.
Brand Mention Monitoring
Track mentions of your brand that don’t include links. Reach out to request link additions to existing mentions.
Tools like Google Alerts, Mention, and BrandWatch help identify opportunities.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
Business relationships naturally generate link opportunities.
Industry Partnerships
Partner with complementary businesses on content, events, or initiatives. Partnerships often include mutual promotion and linking.
Focus on genuine collaboration that benefits both parties.
Co-Marketing Initiatives
Joint webinars, research projects, and content collaborations generate links from partner promotion.
Choose partners with relevant audiences and complementary expertise.
Supplier and Vendor Relationships
Business relationships often include directory listings, case studies, and testimonials that generate links.
Leverage existing relationships for legitimate link opportunities.
Association and Organization Memberships
Industry associations, chambers of commerce, and professional organizations often link to members.
Active participation increases visibility and link opportunities.
Broken Link Building
Finding broken links on relevant sites and offering your content as a replacement is a legitimate outreach strategy.
Identify broken links using tools like Ahrefs or Check My Links. Create or identify content that could replace the broken resource. Reach out to webmasters offering your content as an alternative.
Success rates are low, but the links earned are legitimate and valuable.
Unlinked Brand Mentions
When others mention your brand without linking, you have a natural outreach opportunity.
Monitor mentions using brand tracking tools. Reach out politely to request link additions. Most site owners are happy to add links to mentions they’ve already made.
Expert Contributions and Interviews
Sharing expertise through interviews, podcasts, and expert roundups generates links naturally.
Accept interview requests and pitch yourself as an expert source. Provide genuine value in your contributions.
Local and Industry Citations
Business directories, industry listings, and local citations provide foundational links.
Focus on legitimate, relevant directories. Avoid mass submission to low-quality directories.
Tools for Link Penalty Prevention and Monitoring
The right tools make link management more efficient and effective.
Google Search Console
Your most important tool for link monitoring. Search Console shows:
- Top linking sites
- Top linked pages
- Anchor text data
- Manual actions
Check Search Console regularly and set up email notifications.
Link Analysis Platforms
Comprehensive backlink tools provide deeper analysis:
- Ahrefs: Large index, detailed metrics, historical data
- SEMrush: Integrated SEO suite, toxicity scoring
- Moz: Domain Authority, Spam Score, Link Explorer
- Majestic: Trust Flow, Citation Flow, topical analysis
Use multiple tools for complete coverage since each has different data.
Automated Monitoring Tools
Set up automated alerts for:
- New backlinks
- Lost backlinks
- Anchor text changes
- Referring domain changes
Tools like Ahrefs Alerts, SEMrush, and Linkody provide automated monitoring.
Anchor Text Analysis Tools
Dedicated anchor text analysis helps identify over-optimization:
- Ahrefs anchor text report
- SEMrush anchor text analysis
- Majestic anchor text breakdown
Regular analysis catches distribution problems early.
Penalty Risk Assessment Tools
Some tools specifically assess penalty risk:
- SEMrush Backlink Audit toxicity scores
- Moz Spam Score
- Link Detox (specialized penalty analysis)
Use these as screening tools, not definitive judgments.
When to Hire Professional Help for Link Penalties
Some situations benefit from expert assistance. Knowing when to seek help saves time and improves outcomes.
Signs You Need Expert Assistance
Consider professional help when:
- You’ve received a manual action and don’t know how to respond
- Recovery attempts have failed
- The penalty is severe and business-critical
- You lack time or expertise for thorough analysis
- The situation is complex or unclear
Professional assistance often accelerates recovery.
What Professional Link Audits Include
Comprehensive professional audits typically cover:
- Complete backlink profile analysis
- Toxic link identification and categorization
- Anchor text distribution analysis
- Competitor comparison
- Risk assessment and prioritization
- Actionable recommendations
- Disavow file creation
Quality audits provide clear direction for recovery.
Penalty Recovery Services
Specialized recovery services handle:
- Link audit and analysis
- Removal outreach campaigns
- Disavow file management
- Reconsideration request preparation
- Ongoing monitoring and maintenance
Look for providers with documented recovery success.
Choosing the Right SEO Partner
Evaluate potential partners based on:
- Documented experience with penalty recovery
- Transparent methodology
- Realistic timeline and outcome expectations
- Clear communication and reporting
- References from similar situations
Avoid providers promising quick fixes or guaranteed results.
Conclusion
Link building penalties represent one of the most significant risks to your organic search performance, but they’re entirely preventable with the right approach. Understanding what triggers penalties, recognizing warning signs early, and implementing sustainable link building practices protects your investment in SEO.
The path forward is clear: focus on earning links through genuine value rather than manipulating rankings through artificial means. Build content worth linking to, develop real relationships in your industry, and maintain vigilant monitoring of your link profile.
We help businesses build penalty-proof link strategies that drive sustainable organic growth. Contact White Label SEO Service to discuss how we can protect and strengthen your search visibility for the long term.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if I have a link penalty?
Check Google Search Console for manual actions under Security & Manual Actions. If no manual action exists but you’ve experienced sudden traffic drops correlating with algorithm updates, you may have an algorithmic penalty. Audit your link profile for toxic links and unnatural patterns.
Can I recover from a Google link penalty?
Yes, recovery is possible for both manual and algorithmic penalties. Manual actions require cleanup and a successful reconsideration request. Algorithmic penalties require cleaning your link profile and waiting for Google to reassess during future updates. Recovery typically takes 3-6 months.
Should I disavow all low-quality links?
No. Only disavow links you’re confident are harmful. Disavowing legitimate links removes valuable ranking signals. Focus on clearly toxic links: spam sites, link networks, and obviously manipulative sources. When in doubt, leave the link alone.
How many backlinks can trigger a penalty?
There’s no specific number. Penalties result from patterns and proportions, not absolute counts. A site with 100 backlinks where 50 are spammy faces more risk than a site with 10,000 backlinks where 100 are spammy. Quality and proportion matter more than quantity.
Do nofollow links protect me from penalties?
Nofollow links don’t pass PageRank, but they don’t make manipulative practices acceptable. Massive nofollow link schemes can still raise flags. Use nofollow appropriately for user-generated content and paid links, not as a loophole for manipulation.
How often should I audit my backlink profile?
Conduct comprehensive audits quarterly and monitor new links monthly. Set up automated alerts for new backlinks so you can identify problems quickly. More frequent monitoring is appropriate during active link building campaigns or after penalty recovery.
Can competitors hurt my rankings with negative SEO?
While negative SEO attacks occur, Google’s systems are designed to identify and ignore obviously artificial negative links. Most attacks have limited impact. Monitor your backlinks regularly, and if you identify a clear attack, document it and consider proactive disavowing of obviously malicious links.



