Your service pages are the hardest-working assets on your website, directly connecting search intent to revenue. When optimized correctly, these pages capture high-intent traffic, establish credibility, and convert visitors into qualified leads.
This matters because service pages sit at the intersection of SEO performance and business outcomes. A poorly written service page loses rankings and conversions simultaneously.
This guide covers everything from foundational structure to advanced optimization strategies, giving you a complete framework for service pages that rank and convert.
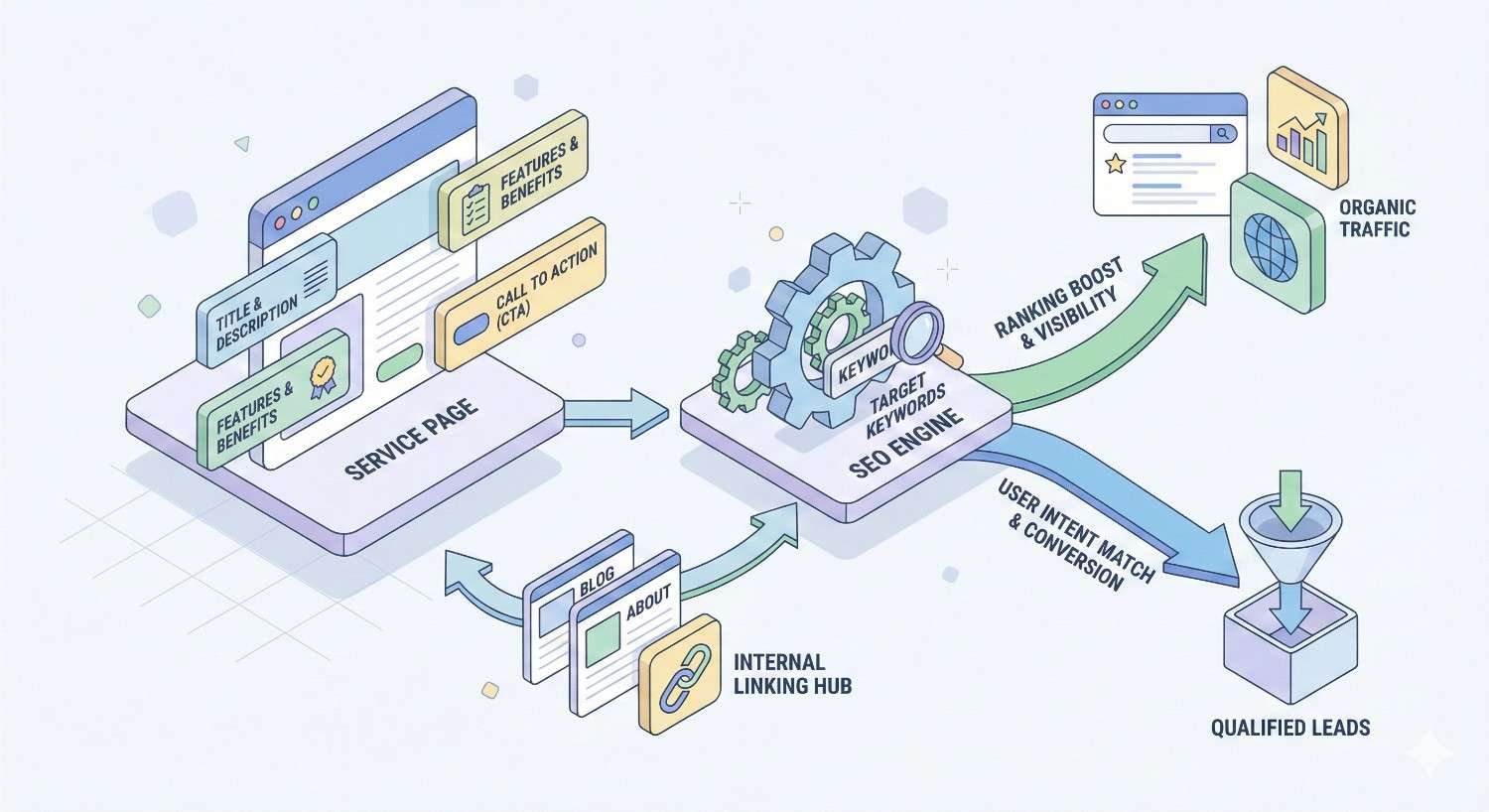
What Is a Service Page and Why It Matters for SEO
A service page is a dedicated webpage that describes a specific service your business offers, targeting users actively searching for that solution. Unlike general website pages, service pages serve a dual purpose: satisfying search engine algorithms and persuading potential customers to take action.
Service pages function as conversion hubs within your website architecture. They capture commercial and transactional search queries, meaning visitors arriving on these pages are typically further along the buying journey than those landing on blog posts or informational content.
From an SEO perspective, service pages build topical authority around your core offerings. Google’s algorithms evaluate whether your site comprehensively covers topics related to your business. Well-optimized service pages signal expertise and relevance, improving your overall domain authority for related searches.
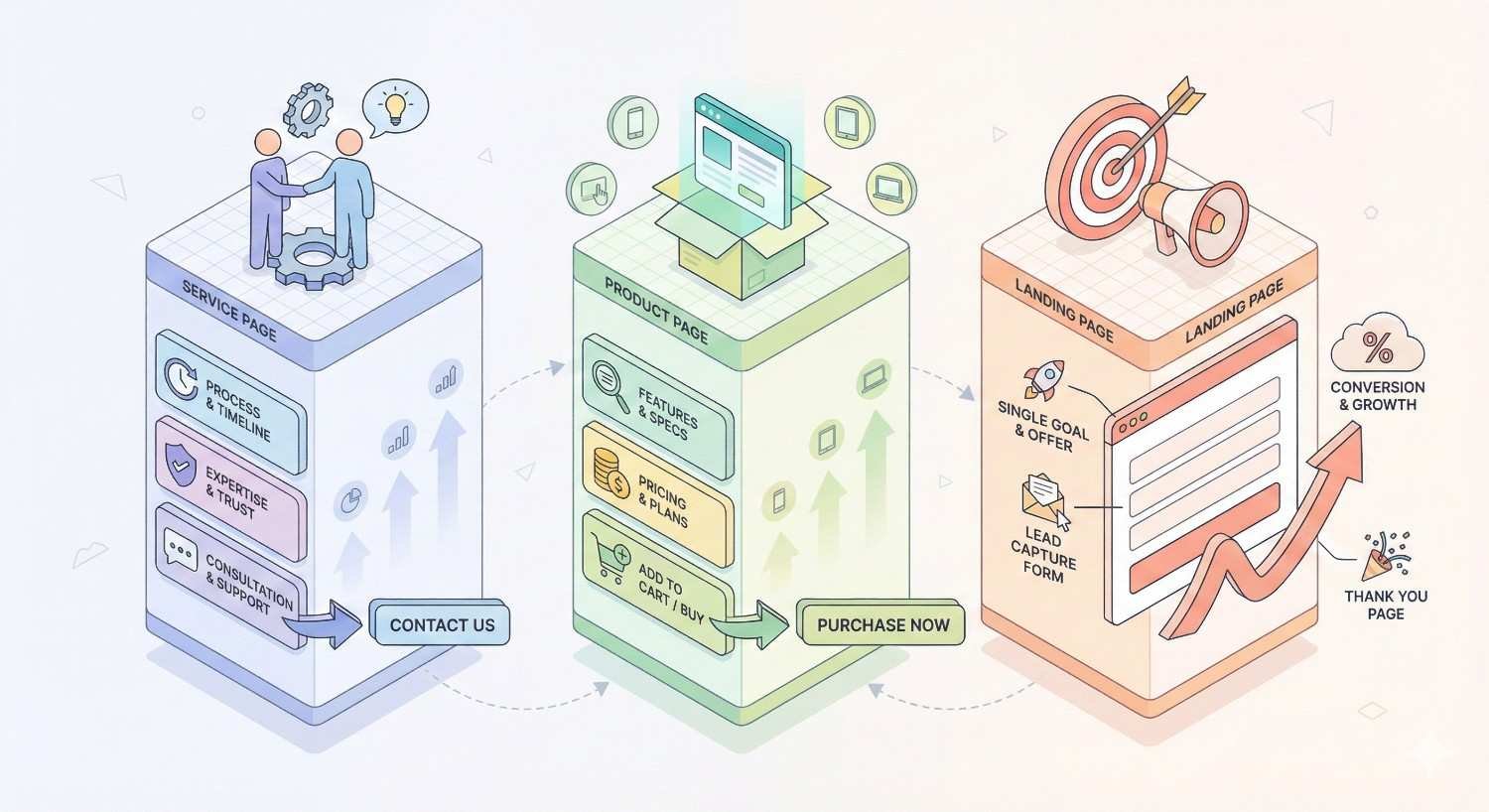
Service Page vs. Product Page vs. Landing Page
Understanding the distinction between these page types prevents strategic confusion and content overlap.
Service pages describe intangible offerings that require explanation, trust-building, and often customization. They typically target broader keyword clusters and serve multiple user intents. A service page for “SEO consulting” needs to explain methodology, showcase expertise, and address various client scenarios.
Product pages focus on tangible items with specific attributes like price, specifications, and availability. The content structure emphasizes features, comparisons, and purchase facilitation. Users arriving on product pages often have clearer purchase intent.
Landing pages are campaign-specific destinations designed for a single conversion goal. They strip away navigation and distractions, focusing entirely on one action. Landing pages typically receive paid traffic rather than organic visitors.
The key difference lies in intent breadth. Service pages must satisfy multiple search intents and user questions within a single page, while landing pages optimize for one specific conversion path.
How Service Pages Drive Organic Visibility and Conversions
Service pages generate organic visibility through strategic keyword targeting and comprehensive content coverage. When someone searches “digital marketing agency services” or “plumbing repair near me,” properly optimized service pages appear in results.
According to BrightEdge research, organic search drives 53% of all website traffic, making service page optimization essential for sustainable lead generation. These pages capture users with commercial intent, meaning they’re actively evaluating solutions rather than casually browsing.
The conversion impact compounds over time. Unlike paid advertising that stops generating leads when budgets pause, well-ranked service pages continue attracting qualified traffic indefinitely. This creates predictable lead flow and reduces customer acquisition costs.
Service pages also support the entire website’s SEO performance through internal linking. They serve as hub pages that connect to related content, case studies, and supporting resources, distributing link equity throughout your site architecture.
Understanding Service Page Search Intent
Search intent determines whether your service page satisfies user needs or sends visitors back to search results. Misaligned intent causes high bounce rates, poor engagement metrics, and declining rankings.
Google’s algorithms have become sophisticated at identifying intent signals. Pages that match user expectations receive ranking boosts, while mismatched content gets filtered out regardless of technical optimization.
Commercial vs. Transactional Intent in Service Searches
Commercial intent searches indicate users are researching and comparing options before making decisions. These queries include terms like “best,” “top,” “reviews,” “vs,” and “comparison.” Users want information to inform their choice, not immediate purchase options.
Examples include:
- “best SEO agencies for small business”
- “web design services comparison”
- “accounting firm reviews”
Service pages targeting commercial intent should emphasize differentiation, social proof, and educational content that positions your offering favorably against alternatives.
Transactional intent searches signal readiness to take action. These queries include terms like “hire,” “get quote,” “pricing,” “near me,” and specific service names. Users have already decided they need the service and are selecting a provider.
Examples include:
- “hire SEO consultant”
- “web design services pricing”
- “emergency plumber near me”
Service pages targeting transactional intent should prioritize clear calls-to-action, pricing transparency, and friction-free contact methods.
Most service pages need to address both intent types since visitors arrive at different decision stages. Structure your content to satisfy researchers early in the page while providing clear conversion paths for ready buyers.
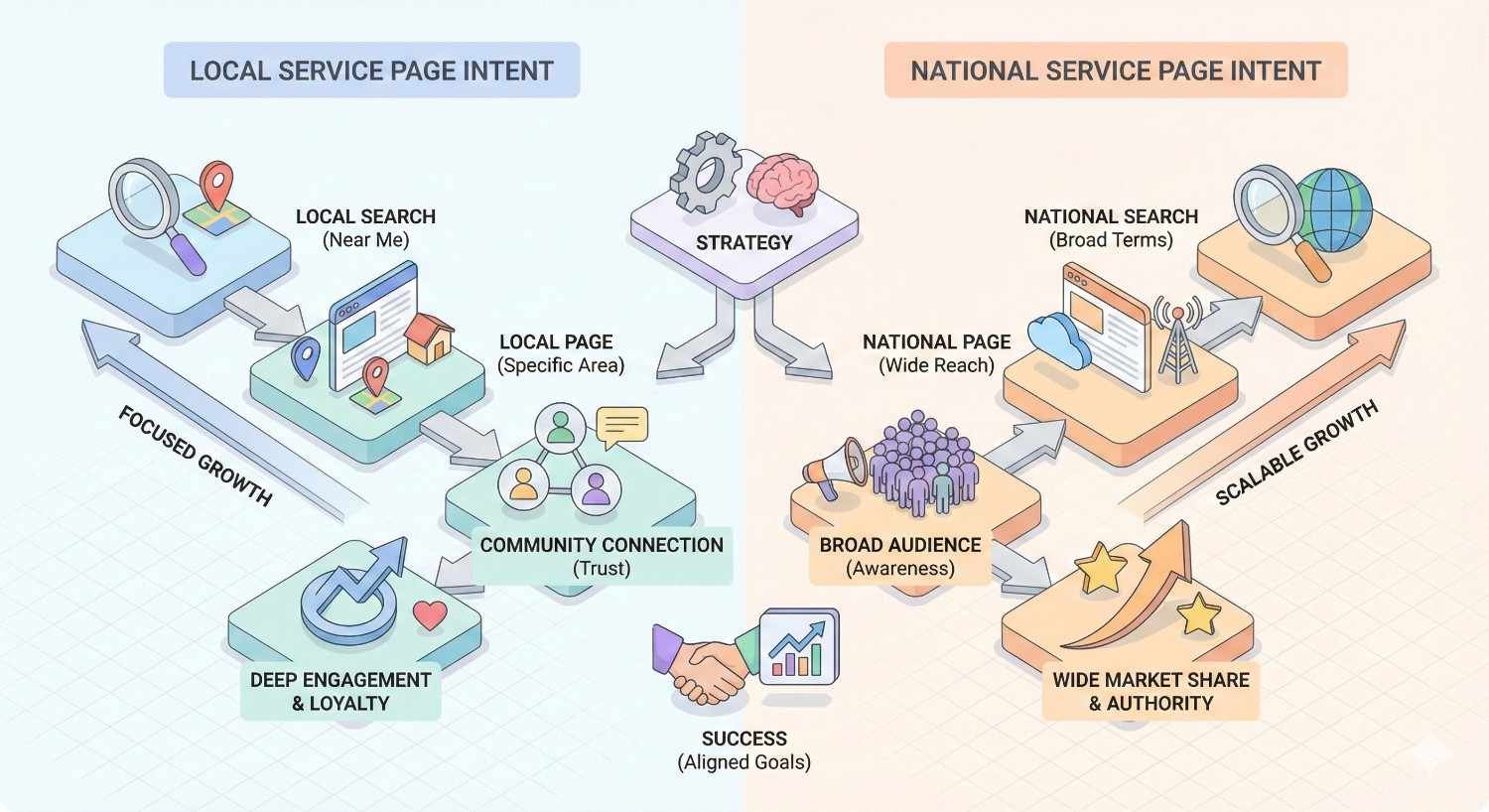
Local vs. National Service Page Intent
Geographic intent fundamentally changes service page strategy and content requirements.
Local service searches include location modifiers or trigger Google’s local pack results. Users searching “dentist in Chicago” or “HVAC repair near me” expect location-specific information, service area details, and local trust signals.
Local service pages require:
- Geographic keywords in titles, headers, and content
- Service area specifications
- Local business schema markup
- Google Business Profile integration
- Location-specific testimonials and case studies
- NAP (Name, Address, Phone) consistency
National service searches target broader audiences without geographic constraints. Users searching “enterprise SEO services” or “SaaS marketing agency” evaluate providers regardless of location.
National service pages require:
- Industry-specific expertise signals
- Scalability and capacity indicators
- Remote service delivery explanations
- Broader competitive differentiation
- National or industry-recognized credentials
Some businesses need both approaches, creating location-specific service pages for local markets while maintaining broader service pages for national visibility.
Mapping User Journey Stages to Service Content
Users arrive at service pages from different journey stages, each requiring specific content elements.
Awareness stage visitors recognize they have a problem but haven’t identified solutions. They search for symptoms, challenges, or general information. Service page content should acknowledge pain points and introduce your service as a solution category.
Consideration stage visitors understand available solutions and are evaluating options. They compare features, methodologies, and providers. Service page content should differentiate your approach, explain your process, and provide comparison frameworks.
Decision stage visitors have selected their preferred solution type and are choosing a specific provider. They evaluate pricing, credentials, and trust factors. Service page content should reduce risk perception, showcase social proof, and facilitate easy contact.
Effective service pages address all three stages through strategic content organization. Lead with problem acknowledgment, transition to solution explanation, and conclude with conversion facilitation.
Essential Components of High-Performing Service Pages
High-performing service pages share common structural elements that satisfy both search algorithms and user expectations. Missing components create gaps that competitors exploit.
Service Description and Value Proposition
Your service description must clearly explain what you offer, who it’s for, and why it matters. Vague descriptions confuse visitors and fail to differentiate your offering.
Start with a clear, jargon-free explanation of the service. Assume visitors have basic familiarity with the problem but limited knowledge of solutions. Define technical terms when necessary.
Your value proposition answers “why choose this service from this provider?” It should communicate:
- The primary benefit or outcome clients receive
- What makes your approach different or better
- Who the ideal client is for this service
Avoid generic value propositions like “quality service” or “customer satisfaction.” Instead, specify measurable outcomes: “Increase organic traffic by 40-60% within 12 months through data-driven SEO strategies.”
Place your value proposition prominently, ideally within the first 100 words of page content. Users decide within seconds whether to continue reading or return to search results.
Process and Methodology Explanation
Explaining your process builds trust and reduces perceived risk. Potential clients want to understand what happens after they contact you.
Break your service delivery into clear phases or steps:
- Initial consultation or discovery
- Assessment or audit
- Strategy development
- Implementation
- Monitoring and optimization
- Reporting and communication
For each phase, briefly explain what happens, what the client provides, and what they receive. This transparency demonstrates professionalism and sets accurate expectations.
Methodology explanation also differentiates your service. If you use proprietary frameworks, specific tools, or unique approaches, highlight these elements. They become competitive advantages that competitors cannot easily replicate.
Pricing and Package Information
Pricing transparency has become increasingly important for service page conversions. Gartner research indicates that B2B buyers spend only 17% of their journey meeting with potential suppliers, meaning most evaluation happens through website content.
Consider these pricing display approaches:
Starting prices work well for customized services: “SEO packages starting at $2,500/month.” This qualifies leads while acknowledging variability.
Package tiers suit standardized offerings: Bronze, Silver, Gold packages with clear feature differentiation. This simplifies decision-making and enables self-selection.
Price ranges provide guidance without commitment: “Most clients invest $5,000-$15,000 for this service.” This sets expectations while preserving flexibility.
Request quote approaches work for highly customized services but should include factors that influence pricing. Help visitors understand what affects cost even if you don’t display specific numbers.
If competitors hide pricing, displaying yours becomes a differentiation advantage. Transparency builds trust and attracts qualified leads who understand investment requirements.
Social Proof and Trust Signals
Social proof reduces perceived risk and validates your claims. Include multiple proof types throughout your service page.
Client testimonials should be specific and results-focused. “Great service!” provides minimal value. “Increased our organic traffic by 127% in 8 months” demonstrates concrete outcomes.
Case studies provide detailed proof of capability. Link to full case studies from your service page, including brief summaries with key metrics.
Client logos create instant credibility through association. Display recognizable brands you’ve served, with permission.
Certifications and credentials validate expertise. Industry certifications, partner badges, and professional memberships signal competence.
Awards and recognition provide third-party validation. Industry awards, media mentions, and rankings demonstrate market recognition.
Statistics and metrics quantify your track record. “500+ clients served” or “10 years in business” establish experience.
Distribute social proof throughout the page rather than concentrating it in one section. This reinforces credibility as users scroll through content.
Clear Calls-to-Action and Conversion Elements
Every service page needs clear, compelling calls-to-action that guide visitors toward conversion. Weak or missing CTAs waste qualified traffic.
Primary CTA should be prominent and specific. “Get Your Free SEO Audit” outperforms “Contact Us.” Action-oriented language with clear value propositions increases click-through rates.
Secondary CTAs capture visitors not ready for primary conversion. Offer downloadable resources, newsletter subscriptions, or consultation scheduling as alternatives.
CTA placement matters significantly. Include CTAs:
- Above the fold (visible without scrolling)
- After major content sections
- Within the page conclusion
- As sticky elements on longer pages
Form design affects conversion rates. Request only essential information initially. Long forms with unnecessary fields create friction and reduce submissions.
Contact alternatives accommodate different preferences. Some visitors prefer phone calls, others prefer email, and some want chat. Provide multiple contact methods.
FAQ Section for Service-Specific Questions
FAQ sections serve dual purposes: answering common questions and capturing long-tail search traffic. They also qualify for FAQ rich snippets in search results.
Identify questions through:
- Sales team feedback on common inquiries
- Customer service logs
- Keyword research for question-based queries
- Competitor FAQ analysis
- “People Also Ask” boxes in search results
Structure FAQs with clear questions as headers (H3 or H4) and concise, direct answers. Avoid lengthy responses that bury the actual answer.
Prioritize questions that:
- Address common objections
- Clarify service scope
- Explain pricing factors
- Describe the client experience
- Differentiate from competitors
Update FAQs regularly based on new questions that emerge from client interactions.
Service Page Content Structure and Hierarchy
Content structure affects both user experience and search engine understanding. Logical hierarchy helps visitors find information quickly while signaling topic relationships to algorithms.
Above-the-Fold Content Strategy
Above-the-fold content determines whether visitors continue engaging or bounce. This visible area without scrolling must accomplish several objectives simultaneously.
Headline (H1) should clearly state the service and include your primary keyword. “Professional SEO Services for Growing Businesses” immediately communicates the page topic.
Subheadline expands on the headline with your value proposition or key differentiator. This supporting text provides context and encourages continued reading.
Hero image or video visually represents your service or outcomes. Avoid generic stock photos that could appear on any competitor’s site.
Primary CTA should be visible above the fold. Visitors ready to convert shouldn’t need to scroll to find contact options.
Trust indicators like client logos, ratings, or credentials provide immediate credibility signals.
The above-the-fold area should answer: “What is this service, who is it for, and why should I care?” within seconds of page load.
Organizing Service Features and Benefits
Features describe what your service includes. Benefits explain why those features matter to clients. Effective service pages connect both.
Feature-benefit pairing creates compelling content:
- Feature: “Monthly performance reports”
- Benefit: “Stay informed about ROI without manual tracking”
Organize features logically through:
Categorization groups related features together. For an SEO service: Technical SEO, Content Strategy, Link Building, Analytics.
Priority ordering places most important or differentiating features first. Lead with what matters most to your target audience.
Visual formatting makes features scannable. Use bullet points, icons, or comparison tables for easy consumption.
Avoid feature lists without context. Each feature should connect to a client outcome or problem solved.
Supporting Content Sections (Case Studies, Testimonials)
Supporting content sections provide evidence for claims made in primary service descriptions.
Case study summaries should include:
- Client industry or type
- Challenge or objective
- Solution implemented
- Measurable results
- Timeline
Link to full case studies for visitors wanting detailed information. Keep summaries brief and results-focused.
Testimonial placement works best when contextually relevant. Place testimonials about specific service aspects near related content sections.
Before/after comparisons visually demonstrate transformation. Screenshots, metrics comparisons, or visual representations of improvement create compelling proof.
Video testimonials increase credibility through authenticity. Clients speaking about their experience carry more weight than written quotes.
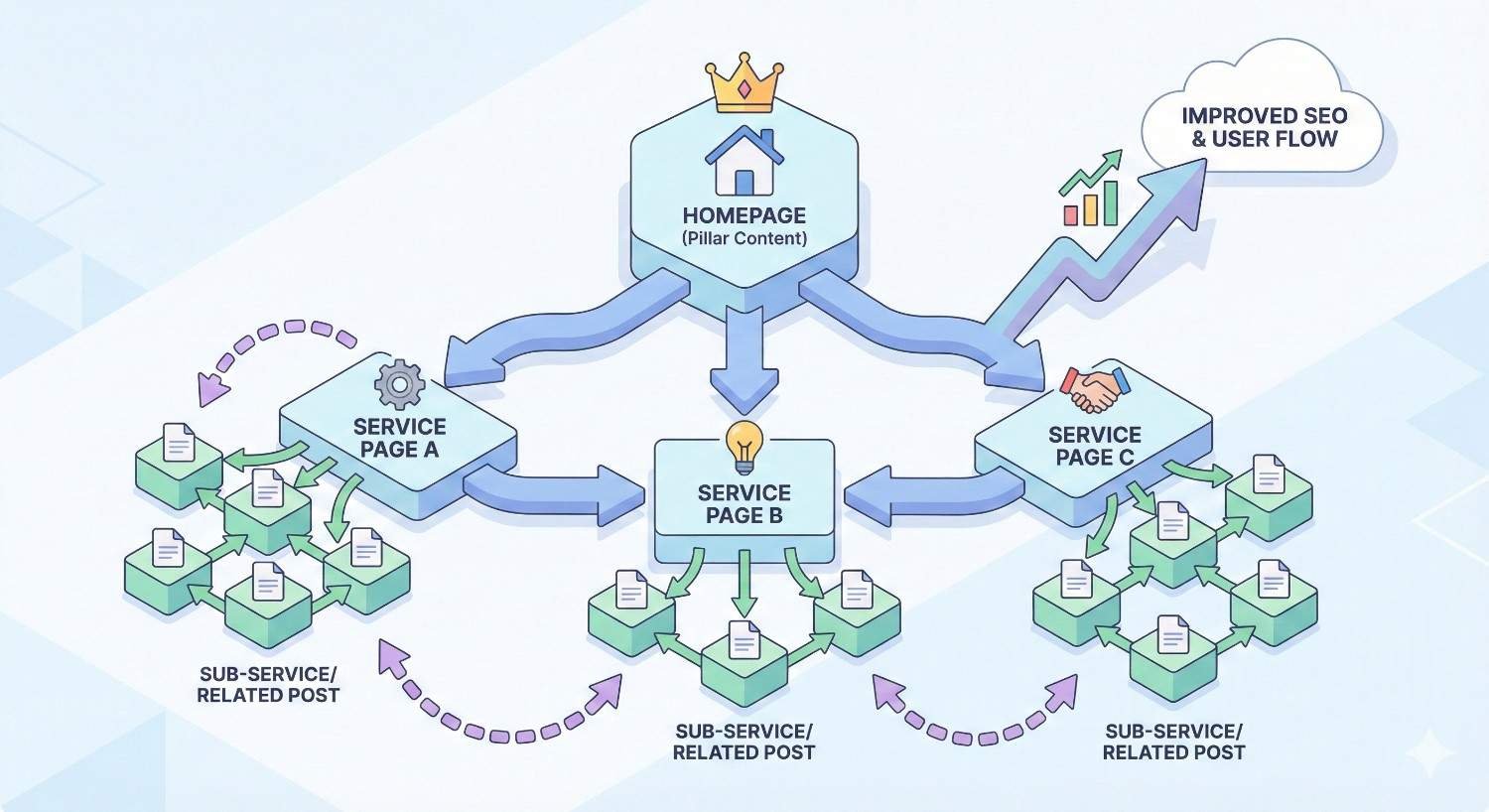
Internal Linking Architecture for Service Pages
Internal linking distributes page authority and guides users through your site. Service pages should connect strategically to related content.
Link to supporting content:
- Related blog posts that expand on topics mentioned
- Case studies demonstrating service outcomes
- Resource pages with tools or guides
- FAQ pages with additional questions
Link from supporting content:
- Blog posts should link to relevant service pages
- Case studies should link to services used
- Resource pages should reference applicable services
Link between related services:
- Cross-sell opportunities (SEO services linking to content marketing)
- Service hierarchies (parent services linking to specialized sub-services)
- Complementary offerings that clients often purchase together
Use descriptive anchor text that indicates the linked page’s topic. “Learn more about our technical SEO audits” outperforms “click here.”
Writing Service Descriptions That Rank and Convert
Service descriptions must satisfy two audiences: search algorithms evaluating relevance and humans making purchase decisions. Balancing these requirements creates content that ranks and converts.
Balancing SEO Keywords with Persuasive Copywriting
Keyword integration should feel natural, not forced. Modern search algorithms understand context and penalize obvious keyword stuffing.
Primary keyword placement:
- H1 headline (exact match or close variation)
- First paragraph (within first 100 words)
- At least one H2 subheading
- Meta title and description
- Image alt text
Secondary keyword integration:
- H2 and H3 subheadings
- Throughout body content naturally
- FAQ questions and answers
Semantic keyword usage:
- Related terms and synonyms throughout
- Industry terminology where appropriate
- Question phrases that users search
Write for humans first, then review for keyword opportunities. If a sentence sounds awkward with a keyword inserted, find a different placement or use a variation.
Persuasive copywriting techniques that support SEO:
- Clear, benefit-focused headlines
- Scannable formatting with subheadings
- Specific claims with supporting evidence
- Action-oriented language
- Emotional connection to pain points
Addressing Pain Points and Solutions
Pain point content creates emotional connection and demonstrates understanding. Visitors should recognize their situation in your descriptions.
Identify pain points through:
- Customer interviews and feedback
- Sales call recordings and notes
- Support ticket analysis
- Competitor review mining
- Industry forum discussions
Structure pain point content:
- Acknowledge the problem specifically
- Validate the frustration or challenge
- Explain why common solutions fail
- Introduce your approach as the solution
- Describe the transformed outcome
Example structure: “Struggling to generate consistent leads from your website? You’re not alone. Many businesses invest in SEO without seeing results because they focus on rankings instead of revenue. Our approach connects search visibility directly to lead generation, ensuring every optimization decision supports your business goals.”
Pain point content also captures search traffic. Users often search for problems before searching for solutions.
Differentiating Your Service from Competitors
Differentiation prevents commoditization and justifies pricing. Without clear differentiation, visitors compare solely on price.
Differentiation categories:
Methodology differentiation: Unique processes, frameworks, or approaches that competitors don’t use.
Specialization differentiation: Focus on specific industries, business sizes, or problem types.
Results differentiation: Superior outcomes, faster timelines, or better guarantees.
Experience differentiation: Team credentials, years in business, or client portfolio.
Technology differentiation: Proprietary tools, exclusive partnerships, or advanced capabilities.
Service differentiation: Better communication, more transparency, or superior support.
Identify your strongest differentiators and emphasize them throughout service page content. Generic claims like “experienced team” or “quality service” don’t differentiate because every competitor makes them.
Using Semantic Keywords and Related Terms
Semantic SEO involves using related terms, synonyms, and contextually relevant language that helps search engines understand topic depth.
Semantic keyword sources:
- Google’s “related searches” at bottom of results
- “People Also Ask” questions
- Keyword research tool suggestions
- Competitor content analysis
- Wikipedia and industry glossaries
Integration approaches:
Natural variation: Instead of repeating “SEO services” throughout, use “search engine optimization,” “organic search strategy,” “SEO solutions,” and “search visibility services.”
Contextual terms: Include terms that naturally appear in comprehensive coverage. An SEO service page should mention “rankings,” “traffic,” “keywords,” “backlinks,” “content,” and “technical optimization.”
Entity mentions: Reference relevant brands, tools, concepts, and industry terms. Mentioning “Google Search Console,” “Core Web Vitals,” or “E-E-A-T” signals topical expertise.
Semantic richness helps pages rank for variations and long-tail queries beyond primary keywords.
Technical SEO for Service Pages
Technical optimization ensures search engines can crawl, understand, and rank your service pages effectively. Technical issues can undermine even excellent content.
Title Tag and Meta Description Optimization
Title tags and meta descriptions directly influence click-through rates from search results.
Title tag best practices:
- Include primary keyword near the beginning
- Keep under 60 characters to avoid truncation
- Include brand name (typically at end)
- Make it compelling and specific
- Differentiate from other pages on your site
Example: “Professional SEO Services | Data-Driven Growth | Brand Name”
Meta description best practices:
- Include primary keyword within first 100 characters
- Keep under 160 characters total
- Include a clear call-to-action
- Highlight unique value proposition
- Match search intent
Example: “Increase organic traffic and leads with our proven SEO services. Custom strategies, transparent reporting, measurable results. Get your free audit today.”
Test different title and description variations. Google Search Console shows click-through rates that indicate which versions perform best.
Header Tag Hierarchy and Keyword Placement
Header tags (H1-H6) create content hierarchy that helps both users and search engines understand page structure.
H1 tag rules:
- One H1 per page only
- Include primary keyword
- Clearly describe page topic
- Match user search intent
H2 tags represent major sections. Include secondary keywords and semantic variations. Each H2 should cover a distinct subtopic.
H3-H4 tags break down H2 sections into smaller components. Use for detailed breakdowns, lists, or supporting points.
Hierarchy logic:
- H2s should be subtopics of H1
- H3s should be subtopics of their parent H2
- Never skip levels (H1 → H3 without H2)
Keyword placement in headers signals topic relevance, but prioritize clarity over keyword insertion. Awkward headers hurt user experience.
Schema Markup for Service Pages (Service, LocalBusiness)
Schema markup helps search engines understand page content and can generate rich snippets in search results.
Service schema describes your service offering:
json
Copy
{
“@type”: “Service”,
“name”: “SEO Services”,
“description”: “Professional search engine optimization services”,
“provider”: {
“@type”: “Organization”,
“name”: “Your Company”
},
“areaServed”: “United States”,
“serviceType”: “SEO”
}
LocalBusiness schema applies to location-based services:
json
Copy
{
“@type”: “LocalBusiness”,
“name”: “Your Company”,
“address”: {
“@type”: “PostalAddress”,
“streetAddress”: “123 Main St”,
“addressLocality”: “City”,
“addressRegion”: “State”
},
“telephone”: “+1-555-555-5555”
}
FAQ schema enables FAQ rich snippets:
json
Copy
{
“@type”: “FAQPage”,
“mainEntity”: [{
“@type”: “Question”,
“name”: “Question text?”,
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: “Answer text”
}
}]
}
Validate schema implementation using Google’s Rich Results Test tool.
URL Structure and Slug Optimization
URL structure affects both SEO and user experience. Clean, descriptive URLs perform better than complex strings.
URL best practices:
- Include primary keyword
- Keep short (under 75 characters)
- Use hyphens between words
- Lowercase only
- Avoid parameters when possible
- Create logical hierarchy
Good examples:
- /services/seo/
- /seo-services/
- /services/technical-seo-audit/
Poor examples:
- /services/page?id=123
- /Our_SEO_Services_Page/
- /services/seo-search-engine-optimization-services-for-business/
URL hierarchy should reflect site architecture. If you have service categories, use folder structure: /services/category/specific-service/
Image Optimization and Alt Text for Service Visuals
Images enhance service pages but require optimization for SEO and performance.
Image optimization checklist:
- Compress files without visible quality loss
- Use appropriate formats (WebP, JPEG, PNG)
- Implement lazy loading for below-fold images
- Specify width and height attributes
- Use descriptive file names (seo-audit-process.jpg, not IMG_1234.jpg)
Alt text best practices:
- Describe image content accurately
- Include relevant keywords naturally
- Keep under 125 characters
- Don’t start with “image of” or “picture of”
- Provide context for screen readers
Example: “SEO consultant reviewing website analytics dashboard with client”
Images should support content, not replace it. Search engines cannot fully understand images, so surrounding text should convey key information.
Service Page Content Length and Depth
Content length debates persist in SEO, but the answer depends on topic complexity, competition, and user needs.
How Much Content Is Enough?
There’s no universal word count requirement. The right length covers the topic comprehensively without padding.
Factors determining appropriate length:
Competitive analysis: Review top-ranking pages for your target keywords. If competitors average 2,000 words, you likely need similar depth to compete.
Topic complexity: Simple services require less explanation than complex offerings. A basic cleaning service needs less content than enterprise software implementation.
User intent: Transactional searches often prefer concise pages with clear CTAs. Informational searches expect comprehensive coverage.
Question coverage: List all questions users might have about your service. Your content should answer them all.
According to Backlinko’s analysis, the average first-page Google result contains approximately 1,447 words. However, this varies significantly by industry and query type.
Start with comprehensive coverage, then edit for conciseness. It’s easier to trim excess than to identify gaps.
Balancing Comprehensiveness with User Experience
Comprehensive content shouldn’t sacrifice usability. Long pages require careful formatting to remain accessible.
Formatting for long content:
- Clear heading hierarchy for scanning
- Short paragraphs (2-4 sentences)
- Bullet points for lists
- Visual breaks between sections
- Table of contents for very long pages
- Jump links to specific sections
Content prioritization:
- Most important information first
- Progressive disclosure (overview → details)
- Clear section labels
- Scannable summaries before deep dives
Mobile considerations:
- Even shorter paragraphs
- Larger tap targets for links
- Collapsible sections for lengthy content
- Fast loading despite content volume
Test page engagement metrics. High bounce rates or low time-on-page may indicate content overwhelm rather than insufficient information.
When to Create Sub-Service Pages
Complex services often benefit from hierarchical page structures with parent and child pages.
Create sub-service pages when:
- Individual components have significant search volume
- Services require detailed explanation beyond parent page scope
- Different audience segments need different information
- Pricing or processes vary significantly between components
Example structure:
- /seo-services/ (parent page)
- /seo-services/technical-seo/
- /seo-services/content-strategy/
- /seo-services/link-building/
- /seo-services/local-seo/
Parent page role: Overview of full service offering, links to sub-services, general trust signals, primary conversion path.
Child page role: Detailed coverage of specific component, targeted keywords, specialized case studies, component-specific FAQs.
This architecture captures more search traffic while providing appropriate depth for each topic.

Local SEO Optimization for Service Pages
Local service businesses require additional optimization strategies to capture geographic searches and appear in local pack results.
Location-Specific Service Page Strategies
Businesses serving multiple locations need strategic approaches to location pages.
Single location businesses should integrate location signals throughout their main service pages:
- City/region mentions in content
- Local landmarks or references
- Service area specifications
- Local testimonials
Multi-location businesses have several options:
Location landing pages: Create pages for each service area (/services/seo-services-chicago/). Include location-specific content, testimonials, and case studies.
Service + location combinations: For businesses with many locations and services, create matrices carefully to avoid thin content.
Hub and spoke model: Main service page links to location-specific versions with unique content for each area.
Avoid creating duplicate content across location pages. Each page needs unique elements beyond just changing the city name.
Google Business Profile Integration
Google Business Profile (GBP) directly impacts local search visibility and should connect to your service pages.
GBP optimization for service pages:
- List all services in GBP service section
- Link GBP to relevant service pages
- Maintain consistent service descriptions
- Add service-specific photos
- Respond to reviews mentioning specific services
Service page GBP connections:
- Embed Google Maps showing location
- Display GBP reviews on service pages
- Link to GBP for directions/contact
- Match service names between website and GBP
GBP posts can promote specific services and link directly to service pages, driving traffic and signaling relevance.
Local Keywords and Geographic Modifiers
Local keyword strategy extends beyond adding city names to existing content.
Geographic modifier types:
- City names: “SEO services Chicago”
- Neighborhoods: “web design Lincoln Park”
- Regions: “digital marketing Northern California”
- Service areas: “plumbing services Cook County”
- Landmarks: “near downtown,” “by the airport”
Local keyword research:
- Use location filters in keyword tools
- Analyze local competitor keywords
- Review Google Suggest for local variations
- Check “near me” search volumes
Integration approaches:
- Title tags with location
- H1 and H2 headers with geographic terms
- Natural mentions throughout content
- Location-specific case studies
- Local client testimonials
Balance keyword optimization with natural readability. Forced location mentions hurt user experience.
NAP Consistency and Local Citations
NAP (Name, Address, Phone) consistency across the web affects local search rankings.
Service page NAP requirements:
- Display full business name exactly as registered
- Include complete address with suite/unit numbers
- Show phone number in consistent format
- Match information across all pages
Citation building for service pages:
- List services in relevant directories
- Ensure NAP matches website exactly
- Include service-specific categories
- Add service descriptions where allowed
Inconsistent NAP information confuses search engines and reduces local ranking potential. Audit existing citations regularly.
Service Page Content for Different Business Models
Different business models require adapted service page approaches based on audience expectations and decision processes.
B2B Service Pages vs. B2C Service Pages
B2B and B2C audiences have fundamentally different needs and decision processes.
B2B service page characteristics:
- Longer decision cycles requiring more information
- Multiple stakeholders influencing decisions
- ROI and business outcome focus
- Case studies with measurable results
- Detailed methodology explanations
- Integration and implementation details
- Security and compliance information
B2C service page characteristics:
- Shorter decision cycles
- Individual decision-makers
- Emotional benefits alongside practical ones
- Social proof from similar customers
- Pricing transparency expectations
- Simpler language and explanations
- Immediate availability signals
Content length differences: B2B pages typically require more depth to address stakeholder questions. B2C pages often benefit from conciseness with clear paths to conversion.
Agency and Consultancy Service Pages
Professional service firms face unique challenges in demonstrating intangible value.
Agency service page requirements:
- Team expertise and credentials
- Process transparency
- Portfolio and case studies
- Client relationship approach
- Communication and reporting methods
- Scalability and capacity
Differentiation strategies:
- Specialization in specific industries or service types
- Proprietary methodologies or frameworks
- Notable client relationships
- Award recognition and certifications
- Thought leadership content
Trust building elements:
- Team bios with credentials
- Client testimonials with attribution
- Detailed case studies with metrics
- Industry association memberships
- Media mentions and speaking engagements
SaaS and Software Service Pages
Software service pages blend product and service elements, requiring hybrid approaches.
SaaS service page elements:
- Feature explanations with benefits
- Use case scenarios
- Integration capabilities
- Pricing tiers and comparisons
- Free trial or demo offers
- Implementation and onboarding process
- Support and training options
Technical considerations:
- System requirements
- Security and compliance certifications
- API documentation links
- Uptime and performance guarantees
Conversion optimization:
- Free trial CTAs prominently placed
- Demo request options
- Self-service signup paths
- Sales contact for enterprise
Professional Services (Legal, Medical, Financial)
Regulated industries require careful attention to compliance and trust signals.
Professional service page requirements:
- Credentials and licensing information
- Professional association memberships
- Compliance and regulatory adherence
- Confidentiality assurances
- Experience and track record
Trust signals specific to professional services:
- Attorney bar admissions and specializations
- Medical board certifications
- Financial licenses and registrations
- Continuing education and training
- Professional liability insurance
Content restrictions:
- Avoid guarantees where prohibited
- Include required disclaimers
- Follow advertising regulations
- Maintain client confidentiality in examples
YMYL considerations: Google applies higher standards to “Your Money or Your Life” content. Professional service pages need exceptional E-E-A-T signals.
Conversion Rate Optimization for Service Pages
Traffic without conversions wastes SEO investment. Conversion rate optimization ensures service pages generate leads and revenue.
CTA Placement and Messaging Strategy
Strategic CTA placement captures visitors at decision moments throughout the page.
Placement best practices:
- Above the fold for immediate visibility
- After problem/solution sections when motivation peaks
- Following social proof when trust is established
- At page conclusion as final prompt
- Sticky CTAs on longer pages
Messaging optimization:
- Action verbs: “Get,” “Start,” “Schedule,” “Download”
- Specific outcomes: “Get Your Free Audit” vs. “Contact Us”
- Urgency when appropriate: “Limited Availability”
- Value emphasis: “No Obligation Consultation”
CTA testing variables:
- Button color and size
- Copy variations
- Placement positions
- Surrounding context
- Form length
Track CTA performance through click-through rates and conversion rates. Small improvements compound significantly over time.
Form Design and Lead Capture Optimization
Form design directly impacts conversion rates. Every additional field reduces submissions.
Form optimization principles:
- Request minimum necessary information
- Use clear field labels
- Provide helpful error messages
- Show progress for multi-step forms
- Optimize for mobile completion
Field prioritization:
- Essential: Name, email, phone (choose based on follow-up method)
- Helpful: Company, role, service interest
- Optional: Budget, timeline, detailed requirements
Progressive profiling: Capture basic information initially, then gather additional details through follow-up interactions.
Form placement: Test inline forms vs. modal popups vs. dedicated landing pages. Different audiences prefer different approaches.
Trust Elements and Risk Reversal
Trust elements reduce perceived risk and increase conversion willingness.
Trust signal types:
- Security badges and certifications
- Money-back guarantees
- Free consultations or trials
- Privacy policy links
- Client testimonials near forms
- Industry certifications
Risk reversal strategies:
- “No obligation” language
- Free initial assessments
- Satisfaction guarantees
- Easy cancellation policies
- Transparent pricing
Placement strategy: Position trust elements near conversion points where hesitation occurs. Testimonials near forms, guarantees near pricing, security badges near payment.
A/B Testing Service Page Elements
Systematic testing improves conversion rates over time through data-driven optimization.
High-impact test elements:
- Headlines and value propositions
- CTA copy and design
- Form length and fields
- Social proof placement
- Pricing presentation
- Page layout and structure
Testing methodology:
- Test one variable at a time
- Ensure statistical significance before conclusions
- Run tests for adequate duration
- Document results for future reference
Tools for testing:
- Google Optimize (free)
- VWO
- Optimizely
- Unbounce
Prioritize tests based on potential impact and traffic volume. High-traffic pages yield faster results.
Content Refresh and Maintenance Strategy
Service pages require ongoing maintenance to maintain rankings and conversion performance.
When and How to Update Service Page Content
Regular updates signal freshness and ensure accuracy.
Update triggers:
- Service changes or additions
- Pricing updates
- New case studies or testimonials
- Industry changes affecting services
- Ranking declines for target keywords
- Conversion rate drops
- Competitor improvements
Update types:
Minor updates: Fix errors, update statistics, add recent testimonials. Minimal effort, ongoing maintenance.
Moderate updates: Add new sections, expand existing content, update examples. Quarterly or semi-annual.
Major updates: Restructure page, rewrite significant portions, add new features. Annual or when performance significantly declines.
Update process:
- Audit current performance metrics
- Identify gaps or outdated elements
- Research competitor changes
- Plan and prioritize updates
- Implement changes
- Monitor impact
Monitoring Service Page Performance Metrics
Track metrics that indicate page health and identify improvement opportunities.
SEO metrics:
- Keyword rankings for target terms
- Organic traffic volume and trends
- Click-through rate from search results
- Impressions for target queries
Engagement metrics:
- Bounce rate
- Time on page
- Scroll depth
- Pages per session
Conversion metrics:
- Form submissions
- Phone calls (if tracked)
- Chat initiations
- Conversion rate
Tools for monitoring:
- Google Search Console for search performance
- Google Analytics for engagement and conversions
- Rank tracking tools for keyword positions
- Heatmap tools for user behavior
Set up regular reporting cadences to catch issues early.
Seasonal and Market-Driven Content Updates
Some services have seasonal patterns or market-driven demand fluctuations.
Seasonal considerations:
- Tax services peak before filing deadlines
- HVAC services peak in extreme weather
- Retail services peak during holidays
- B2B services may slow during summer
Seasonal content strategies:
- Update messaging to reflect seasonal needs
- Adjust CTAs for urgency during peak periods
- Add seasonal FAQs or content sections
- Promote seasonal offers or packages
Market-driven updates:
- Industry regulation changes
- Technology advancements
- Economic condition shifts
- Competitive landscape changes
Stay informed about industry developments that affect service relevance or positioning.
Handling Service Changes and Deprecations
Services evolve, and pages must reflect current offerings accurately.
Service changes:
- Update all affected pages promptly
- Redirect old URLs if service names change
- Update internal links pointing to changed services
- Notify existing clients of changes
Service deprecation:
- Decide whether to remove or redirect page
- 301 redirect to most relevant alternative
- Update internal links
- Remove from navigation and sitemaps
- Consider maintaining page with “no longer offered” notice if it has significant backlinks
New service launches:
- Create comprehensive page before launch
- Build internal links from related content
- Promote through existing channels
- Monitor initial performance closely
Multi-Service Page Architecture
Businesses offering multiple services need strategic page architecture to maximize SEO coverage without creating confusion.
Parent Service Pages vs. Child Service Pages
Hierarchical structures organize services logically for users and search engines.
Parent page functions:
- Overview of service category
- Links to specific service pages
- General trust signals and credentials
- Category-level keywords
Child page functions:
- Detailed coverage of specific service
- Targeted long-tail keywords
- Service-specific case studies
- Specialized FAQs
Example hierarchy:
Copy
/digital-marketing-services/ (parent)
├── /digital-marketing-services/seo/ (child)
├── /digital-marketing-services/ppc/ (child)
├── /digital-marketing-services/social-media/ (child)
└── /digital-marketing-services/content-marketing/ (child)
Parent pages should provide enough value to rank independently while clearly directing users to specific services.
Service Category Hub Pages
Hub pages organize related services and build topical authority.
Hub page elements:
- Category overview and benefits
- Links to all services in category
- Comparison or selection guidance
- Category-level testimonials
- Cross-service case studies
Hub page SEO benefits:
- Targets broader category keywords
- Distributes link equity to child pages
- Demonstrates comprehensive coverage
- Creates logical site architecture
Content depth: Hub pages need substantial content, not just link lists. Provide value that justifies the page’s existence.
Cross-Linking Between Related Services
Strategic internal linking strengthens topical relationships and guides user journeys.
Cross-linking opportunities:
- Complementary services often purchased together
- Services that address related problems
- Upsell and cross-sell paths
- Service comparison contexts
Implementation approaches:
- “Related services” sections on each page
- Contextual links within content
- “Clients also purchased” recommendations
- Service bundle suggestions
Anchor text strategy:
- Use descriptive, keyword-rich anchor text
- Vary anchor text naturally
- Avoid over-optimization with exact match anchors
Avoiding Keyword Cannibalization
Keyword cannibalization occurs when multiple pages compete for the same keywords, diluting ranking potential.
Identification methods:
- Search site:yourdomain.com “keyword” to see competing pages
- Review Search Console for pages ranking for same queries
- Analyze which page Google prefers for target terms
Prevention strategies:
- Clear keyword targeting for each page
- Distinct search intents addressed
- Proper internal linking hierarchy
- Canonical tags when appropriate
Resolution approaches:
- Consolidate competing pages into one comprehensive page
- Differentiate targeting (one page for “SEO services,” another for “local SEO services”)
- Use canonical tags to indicate preferred page
- Adjust internal linking to favor primary page
Document keyword targets for each service page to prevent future conflicts.
Service Page Content for Competitive Markets
Highly competitive markets require advanced strategies to achieve visibility and differentiation.
Differentiation Strategies in Saturated Niches
When competitors offer similar services, differentiation becomes critical for both rankings and conversions.
Differentiation approaches:
Niche specialization: Focus on specific industries, business sizes, or problem types. “SEO for SaaS companies” faces less competition than “SEO services.”
Methodology differentiation: Develop and name proprietary processes. Unique frameworks become competitive moats.
Results differentiation: Guarantee specific outcomes or showcase superior results. Data-backed claims stand out.
Experience differentiation: Emphasize unique team backgrounds, credentials, or perspectives.
Content differentiation: Create more comprehensive, better-organized, more useful content than competitors.
Analyze competitor positioning to identify gaps and opportunities for differentiation.
Niche-Specific Service Page Approaches
Industry-specific service pages capture targeted traffic and demonstrate specialized expertise.
Niche page benefits:
- Less competitive keywords
- Higher relevance signals
- Better conversion rates from qualified traffic
- Demonstrated industry expertise
Niche page requirements:
- Industry-specific terminology and context
- Relevant case studies and examples
- Understanding of industry challenges
- Compliance with industry regulations
Example niche pages:
- /seo-services-for-healthcare/
- /seo-services-for-ecommerce/
- /seo-services-for-law-firms/
Each niche page should contain unique content, not just the main service page with industry name inserted.
Building Topical Authority Through Service Content
Topical authority signals comprehensive expertise that improves rankings across related queries.
Authority building strategies:
Content depth: Cover topics more thoroughly than competitors. Answer every question users might have.
Content breadth: Create supporting content around service topics. Blog posts, guides, and resources demonstrate expertise.
Internal linking: Connect service pages to supporting content, creating topic clusters.
External signals: Earn backlinks, mentions, and citations that validate expertise.
Consistency: Regularly publish and update content in your topic area.
Topical authority compounds over time. Early investment in comprehensive coverage pays dividends as authority builds.
Competitor Analysis for Service Page Optimization
Systematic competitor analysis reveals opportunities and benchmarks for improvement.
Analysis elements:
Content analysis:
- Word count and depth
- Topics and subtopics covered
- Content structure and formatting
- Unique value propositions
SEO analysis:
- Target keywords
- Title tags and meta descriptions
- Header structure
- Schema markup usage
Conversion analysis:
- CTA placement and messaging
- Form design
- Trust signals used
- Pricing presentation
Gap identification:
- Topics competitors miss
- Questions left unanswered
- Weak differentiation claims
- Poor user experience elements
Use competitor insights to create superior pages, not to copy approaches.
Measuring Service Page SEO Success
Measurement enables optimization. Track metrics that connect SEO efforts to business outcomes.
Key Performance Indicators for Service Pages
Select KPIs that align with business objectives and provide actionable insights.
Visibility KPIs:
- Keyword rankings for target terms
- Search impressions
- Share of voice vs. competitors
- Featured snippet appearances
Traffic KPIs:
- Organic sessions
- New vs. returning visitors
- Traffic growth rate
- Traffic by device type
Engagement KPIs:
- Bounce rate
- Average session duration
- Pages per session
- Scroll depth
Conversion KPIs:
- Form submissions
- Phone calls
- Chat initiations
- Conversion rate
- Cost per lead (compared to other channels)
Revenue KPIs:
- Leads generated
- Pipeline value
- Closed revenue attributed to organic
- Customer lifetime value from organic leads
Prioritize KPIs based on business model and goals. Not all metrics matter equally.
Tracking Rankings for Service Keywords
Rank tracking provides visibility into SEO progress and competitive positioning.
Tracking best practices:
- Monitor primary and secondary keywords
- Track local and national rankings separately
- Include competitor rankings for context
- Note SERP feature presence (featured snippets, local pack)
Tracking frequency:
- Weekly for active optimization campaigns
- Monthly for maintenance monitoring
- Daily during major algorithm updates
Tools for rank tracking:
- Semrush
- Ahrefs
- Moz
- SE Ranking
- AccuRanker
Rankings fluctuate naturally. Focus on trends rather than daily movements.
Conversion Tracking and Attribution
Connect SEO efforts to business outcomes through proper tracking setup.
Tracking implementation:
- Goal tracking in Google Analytics
- Event tracking for micro-conversions
- Phone call tracking with dynamic numbers
- CRM integration for lead quality analysis
Attribution considerations:
- First-touch attribution credits initial discovery
- Last-touch attribution credits final conversion
- Multi-touch attribution distributes credit across touchpoints
Reporting approaches:
- Organic traffic to conversion rate
- Assisted conversions from organic
- Revenue attributed to organic channel
- Comparison to other acquisition channels
Proper attribution demonstrates SEO ROI and justifies continued investment.
Using Search Console Data for Service Page Insights
Google Search Console provides direct data about search performance.
Key Search Console reports:
Performance report:
- Queries driving impressions and clicks
- Click-through rates by query
- Average position trends
- Page-level performance
Coverage report:
- Indexing status
- Crawl errors
- Valid pages vs. excluded
Enhancements reports:
- Schema markup validation
- Mobile usability issues
- Core Web Vitals status
Actionable insights:
- Identify high-impression, low-CTR queries for title/description optimization
- Find queries where you rank positions 5-15 for quick win opportunities
- Discover new keyword opportunities from query data
- Identify technical issues affecting specific pages
Review Search Console data weekly during active optimization, monthly for maintenance.
Common Service Page Content Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding common mistakes prevents wasted effort and poor performance.
Thin Content and Duplicate Service Descriptions
Thin content fails to satisfy user needs and signals low quality to search engines.
Thin content indicators:
- Pages under 300 words with no unique value
- Generic descriptions that could apply to any competitor
- Missing answers to common user questions
- No supporting evidence or examples
Duplicate content issues:
- Same description across multiple service pages
- Location pages with only city name changed
- Copied content from other websites
- Template content without customization
Solutions:
- Audit existing pages for depth and uniqueness
- Expand thin pages with comprehensive coverage
- Create unique content for each service variation
- Consolidate pages that cannot be differentiated
Over-Optimization and Keyword Stuffing
Aggressive optimization backfires, hurting both rankings and user experience.
Over-optimization signs:
- Keyword density exceeding natural language patterns
- Exact-match keywords forced into awkward sentences
- Every heading containing target keyword
- Unnatural anchor text in internal links
Consequences:
- Google penalties for manipulation
- Poor user experience and high bounce rates
- Reduced trust and credibility
- Lower conversion rates
Balanced approach:
- Write naturally first, optimize second
- Use semantic variations instead of exact repetition
- Prioritize readability over keyword density
- Test content with real users for naturalness
Neglecting Mobile Experience
Mobile traffic dominates most industries. Poor mobile experience loses visitors and rankings.
Mobile optimization requirements:
- Responsive design that adapts to screen sizes
- Touch-friendly buttons and links
- Readable text without zooming
- Fast loading on mobile networks
- Easy form completion on small screens
Common mobile issues:
- Text too small to read
- Buttons too close together
- Horizontal scrolling required
- Slow loading from large images
- Pop-ups blocking content
Testing approaches:
- Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test
- Real device testing across phone types
- Mobile usability report in Search Console
- User testing with mobile participants
Missing or Weak Conversion Elements
Traffic without conversion capability wastes SEO investment.
Common conversion failures:
- No clear call-to-action
- CTA buried below the fold
- Contact information hard to find
- Forms with too many required fields
- No phone number for phone-preferring visitors
Conversion element checklist:
- Primary CTA visible above fold
- Multiple CTAs throughout long pages
- Phone number prominently displayed
- Contact form with minimal fields
- Trust signals near conversion points
- Clear next steps after form submission
Audit service pages specifically for conversion capability, not just content quality.
Service Page Content Writing Checklist
Use this checklist to ensure comprehensive service page optimization.
Pre-Writing Research and Planning
- Identify primary and secondary target keywords
- Analyze top-ranking competitor pages
- Document user questions and pain points
- Define unique value proposition
- Outline content structure and sections
- Gather case studies and testimonials
- Collect relevant statistics and data
- Determine appropriate content length
Content Creation and Optimization Checklist
- Write compelling H1 with primary keyword
- Create clear value proposition in first paragraph
- Structure content with logical H2/H3 hierarchy
- Include comprehensive service description
- Explain process and methodology
- Address pricing or investment expectations
- Integrate social proof throughout
- Add FAQ section with common questions
- Use semantic keywords naturally
- Include internal links to related content
- Add external links to authoritative sources
- Write for target audience reading level
- Ensure mobile-friendly formatting
Technical SEO Implementation Checklist
- Optimize title tag (under 60 characters, keyword included)
- Write compelling meta description (under 160 characters)
- Create clean URL slug with keyword
- Implement appropriate schema markup
- Optimize images with descriptive alt text
- Compress images for fast loading
- Verify mobile responsiveness
- Check page speed and Core Web Vitals
- Ensure proper canonical tag
- Add to XML sitemap
- Verify indexability
Post-Publication Monitoring and Optimization
- Submit URL to Google Search Console
- Monitor indexing status
- Track keyword rankings weekly
- Review Search Console performance data
- Analyze user engagement metrics
- Track conversion rates
- Gather user feedback
- Plan content updates based on performance
- Build internal links from new content
- Monitor competitor changes
Conclusion
Service page content writing combines SEO fundamentals with conversion optimization to create pages that attract qualified traffic and generate leads. The strategies covered here provide a complete framework for building service pages that perform.
Success requires ongoing attention. Search algorithms evolve, competitors improve, and user expectations change. Regular monitoring and updates keep your service pages competitive and effective.
We at White Label SEO Service specialize in creating high-performing service pages that drive sustainable organic growth. Contact us to discuss how we can help optimize your service pages for better rankings and conversions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long should a service page be for optimal SEO performance?
Service page length depends on topic complexity and competition. Analyze top-ranking competitors for your target keywords to establish benchmarks. Most effective service pages range from 1,000 to 2,500 words, covering topics comprehensively without unnecessary padding.
Should I create separate service pages for each location I serve?
Create location-specific pages only if you can provide unique, valuable content for each. Pages with only city names changed create duplicate content issues. Include location-specific testimonials, case studies, and relevant local information to justify separate pages.
How often should I update my service page content?
Review service pages quarterly for accuracy and performance. Update immediately when services, pricing, or processes change. Refresh content annually with new statistics, case studies, and examples even if core services remain unchanged.
What schema markup should I use for service pages?
Implement Service schema for all service pages. Add LocalBusiness schema for location-based services. Include FAQ schema if your page has a question-and-answer section. Use Organization schema to establish entity relationships.
How do I measure if my service page SEO is working?
Track keyword rankings, organic traffic, and conversions from organic sources. Use Google Search Console for search performance data and Google Analytics for engagement and conversion metrics. Compare month-over-month and year-over-year trends.
Should I include pricing on my service pages?
Pricing transparency generally improves conversion rates and qualifies leads. If exact pricing isn’t possible, provide ranges, starting prices, or factors that influence cost. Visitors increasingly expect pricing information before contacting businesses.
How do I differentiate my service page from competitors?
Identify unique aspects of your methodology, specialization, results, or experience. Develop proprietary frameworks or processes. Include specific case studies with measurable outcomes. Focus on depth and quality that competitors don’t match.



