Most websites need a comprehensive technical SEO audit every quarter, though high-traffic e-commerce sites benefit from monthly reviews while static small business sites can audit annually. The right frequency depends on your site’s complexity, content velocity, and business objectives.
Technical SEO forms the foundation of your organic visibility. Without regular audits, crawl errors, broken redirects, and Core Web Vitals failures accumulate silently, eroding your rankings before you notice the damage.
This guide covers optimal audit schedules by business type, warning signs requiring immediate attention, essential audit components, and how to build a sustainable technical SEO monitoring system.
What Is a Technical SEO Audit?
A technical SEO audit is a systematic evaluation of your website’s infrastructure, examining how search engines crawl, index, and render your pages. Unlike content audits that focus on keywords and topics, technical audits diagnose the underlying architecture that determines whether your content can rank at all.
Think of it as a health checkup for your website. You’re checking vital signs: server response times, mobile rendering, security certificates, and the thousands of signals that tell Google whether your site deserves visibility.
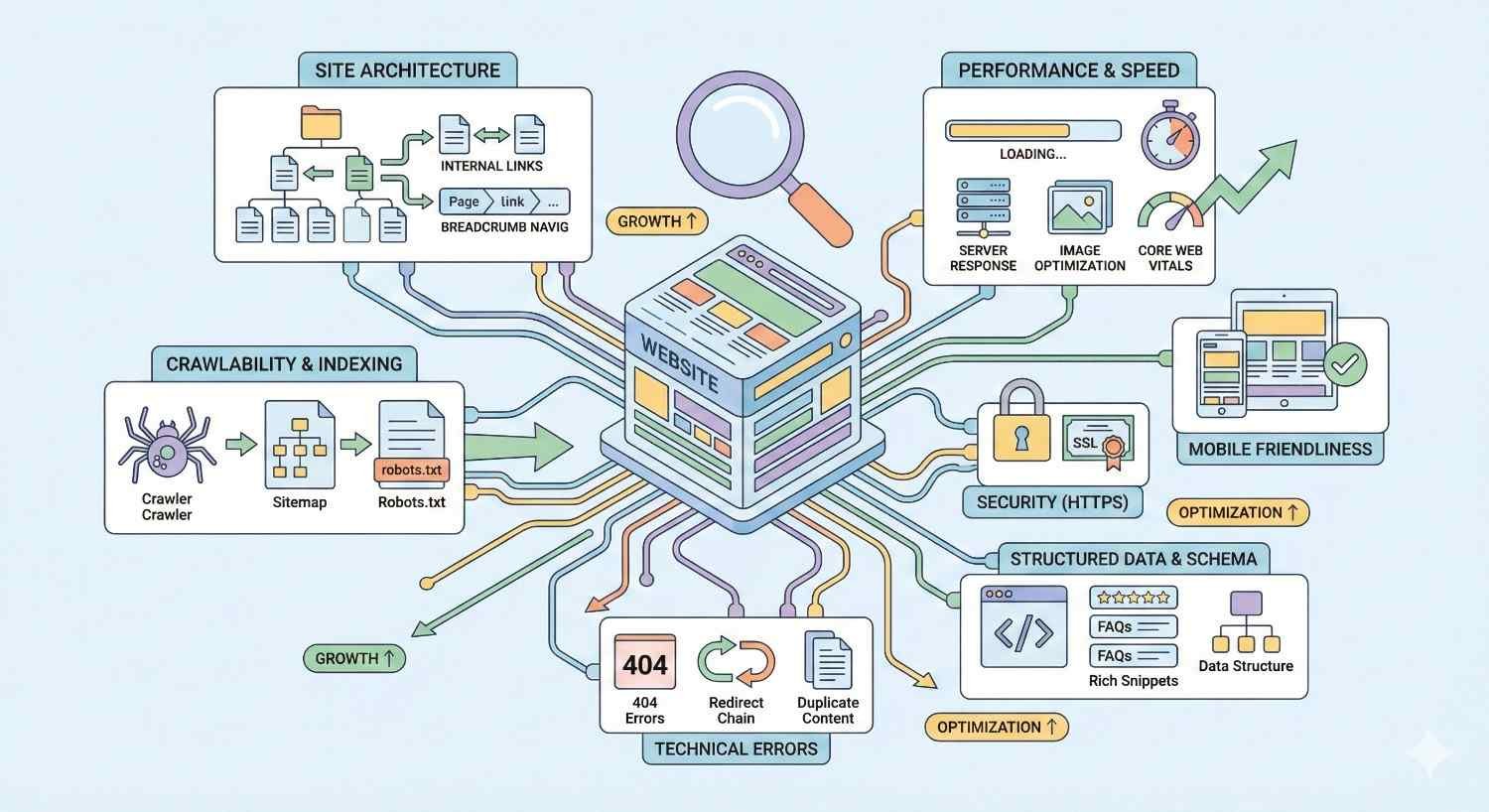
Core Components of a Technical SEO Audit
A thorough technical audit examines multiple interconnected systems. Crawlability analysis reveals whether search engine bots can access your pages efficiently. Indexability checks confirm your important pages appear in search results while thin or duplicate content stays out.
Site speed assessment measures load times across devices and connection types. Mobile usability testing ensures responsive design works correctly. Security verification confirms HTTPS implementation and identifies vulnerabilities.
Structured data validation checks schema markup accuracy. Internal linking analysis maps how authority flows through your site. Each component affects the others, creating a complex system requiring regular evaluation.
Why Technical Audits Matter for Organic Performance
Technical issues create invisible barriers between your content and search visibility. A single misconfigured robots.txt file can deindex your entire site. Slow page speeds push mobile users away before they see your content. Broken canonical tags split ranking signals across duplicate URLs.
Google’s documentation confirms that technical accessibility is a prerequisite for ranking. Your content strategy and link building efforts deliver diminished returns when technical problems prevent proper crawling and indexing.
Regular audits catch problems early. A redirect chain that adds 200 milliseconds today becomes a 2-second delay after six months of accumulated changes. Proactive monitoring prevents small issues from compounding into ranking disasters.
How Often Should You Run a Technical SEO Audit?
The optimal audit frequency balances thoroughness against resource constraints. Auditing too rarely allows problems to accumulate. Auditing too frequently wastes time on unchanged elements. Your ideal schedule depends on how quickly your site changes and how much organic traffic matters to your business.
Standard Audit Frequency Recommendations
Most SEO professionals recommend quarterly comprehensive audits as the baseline for active websites. This cadence catches seasonal issues, accommodates CMS update cycles, and aligns with typical business planning periods.
Between quarterly deep dives, monthly spot checks on critical metrics prevent surprises. Weekly automated monitoring catches urgent issues like server errors or sudden indexing drops. This layered approach provides coverage without overwhelming your team.
Quarterly Audits for Most Businesses
Quarterly audits work well for businesses publishing content regularly but not daily. This includes most B2B companies, professional services firms, and mid-sized e-commerce operations with stable product catalogs.
A quarterly schedule allows enough time for meaningful changes to occur while catching issues before they cause significant damage. You’ll identify patterns across seasons, spot gradual performance degradation, and maintain consistent technical health.
Plan audits at the start of each quarter. This timing lets you address findings before peak business periods and align technical improvements with content and marketing initiatives.
Monthly Audits for High-Traffic or E-commerce Sites
Sites with substantial organic traffic or frequent content changes need monthly comprehensive audits. E-commerce platforms adding products daily, news publishers, and large content sites fall into this category.
High-traffic sites face greater risk from technical problems. A crawl error affecting 1% of pages matters more when you have 100,000 URLs than when you have 100. Monthly audits catch issues before they affect significant traffic volumes.
E-commerce sites also experience constant change: new products, price updates, inventory fluctuations, promotional pages. Each change introduces potential technical problems requiring faster detection cycles.
Annual Audits for Small or Static Websites
Small business websites with minimal content changes can audit annually. A local service provider with 10-20 static pages and no blog doesn’t generate enough change to justify quarterly reviews.
Annual audits should coincide with broader business planning. Review technical health alongside your marketing strategy refresh. Even static sites need periodic checks for security updates, hosting changes, and accumulated minor issues.
However, annual audits require robust monitoring between reviews. Set up automated alerts for critical failures so you’re not waiting twelve months to discover your site dropped from search results.
Factors That Determine Your Technical SEO Audit Frequency
No universal schedule fits every website. Your optimal frequency emerges from evaluating multiple factors specific to your situation. Consider each element below when establishing your audit cadence.
Website Size and Complexity
Larger sites require more frequent audits. A 50-page brochure site behaves predictably. A 50,000-page e-commerce catalog with faceted navigation, user-generated content, and dynamic filtering creates exponentially more opportunities for technical problems.
Complexity compounds the challenge. Sites with multiple subdomains, international versions, or complex JavaScript frameworks need closer monitoring. Each architectural layer adds potential failure points.
Evaluate your site’s technical debt honestly. Legacy systems, accumulated workarounds, and undocumented customizations increase audit frequency requirements.
Rate of Content Publication
Content velocity directly impacts audit needs. Publishing five articles weekly introduces more potential issues than publishing five articles monthly. Each new page creates opportunities for broken links, duplicate content, or indexing problems.
Track your publication rate across all content types: blog posts, product pages, landing pages, and user-generated content. Higher velocity demands more frequent technical reviews.
Consider seasonal variations too. If you publish heavily before holidays, schedule audits immediately after peak periods to catch accumulated issues.
Platform and CMS Updates
WordPress, Shopify, and other platforms release updates regularly. Each update can affect technical SEO elements: URL structures, schema markup, caching behavior, or mobile rendering.
Schedule audits after major platform updates. A WordPress core update or theme change warrants immediate technical review. Plugin updates affecting SEO functionality require the same attention.
Document your update schedule and align audit timing accordingly. If your platform updates monthly, your audit schedule should account for post-update verification.
Traffic Volume and Business Goals
Higher traffic volumes justify more frequent audits because problems affect more users and revenue. A 10% traffic drop matters more when you’re receiving 100,000 monthly visitors than 1,000.
Business goals also influence frequency. If organic search drives 60% of your leads, technical SEO deserves more attention than if it drives 10%. Align audit investment with channel importance.
Calculate the cost of technical problems in your context. Understanding potential revenue impact helps justify appropriate audit frequency and resources.
Industry Competitiveness
Competitive industries require tighter technical optimization. When competitors audit monthly, quarterly reviews leave you perpetually behind. Technical SEO becomes a differentiator when content and links reach parity.
Monitor competitor technical performance. Tools like Screaming Frog can crawl competitor sites, revealing their technical sophistication. Match or exceed their audit frequency to maintain competitive position.
Industries with rapid change, like technology or finance, also demand more frequent audits. Algorithm updates and search feature changes affect these sectors disproportionately.
Previous Technical Issues and Site Health
Sites with history of technical problems need closer monitoring. If you’ve experienced indexing issues, migration failures, or Core Web Vitals problems, increase audit frequency until you establish consistent health.
Track issue recurrence patterns. Some problems resurface predictably: redirect chains accumulating, sitemap bloat, or crawl budget waste. Schedule audits to catch recurring issues before they impact performance.
New sites also warrant increased frequency during their first year. Establishing technical foundations requires more attention than maintaining mature, stable architecture.
Algorithm Updates and Search Engine Changes
Google releases thousands of algorithm updates annually, with several major core updates each year. Each update can shift technical SEO priorities or expose previously hidden issues.
Schedule audits after confirmed core updates. Google’s Search Status Dashboard tracks update rollouts. Post-update audits identify whether changes affected your site and what adjustments you need.
Stay informed about search engine announcements. New ranking factors, like page experience signals, require audit scope expansion. Your audit checklist should evolve with search engine requirements.
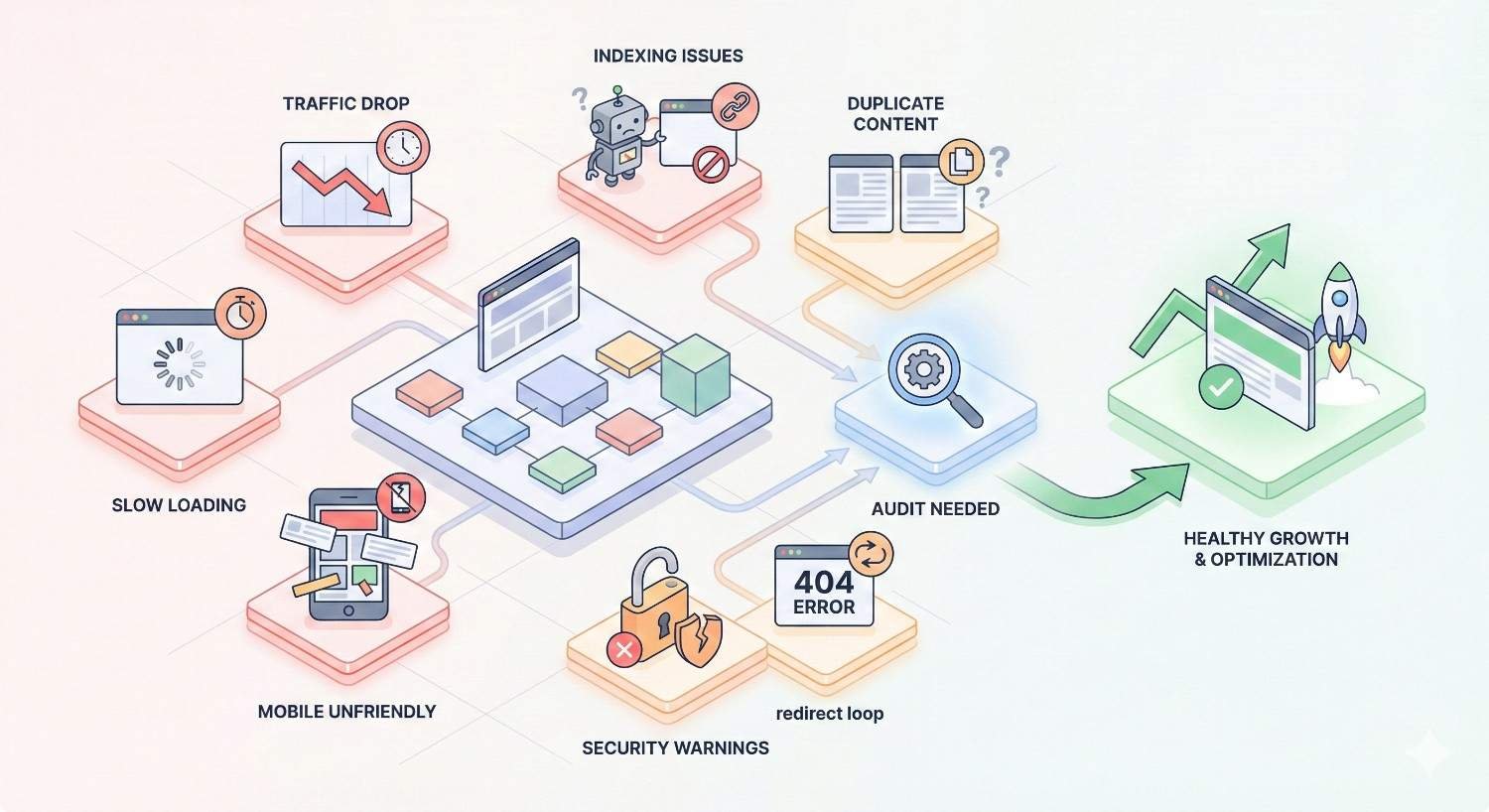
Signs You Need an Immediate Technical SEO Audit
Some situations demand immediate audits regardless of your regular schedule. These warning signs indicate potential serious problems requiring urgent attention.
Sudden Traffic Drops
Unexplained traffic declines warrant immediate investigation. Check Google Search Console for manual actions, security issues, or coverage errors first. If those appear clean, conduct a full technical audit.
Distinguish between gradual decline and sudden drops. Gradual decline often indicates content or competitive issues. Sudden drops, especially affecting specific page types or sections, typically signal technical problems.
Compare traffic patterns across page categories. If product pages dropped while blog posts remained stable, focus your audit on product page technical elements.
Indexing Issues or Coverage Errors
Google Search Console’s Coverage report reveals indexing problems. Spikes in “Excluded” pages, new “Error” categories, or declining “Valid” counts all trigger immediate audits.
Pay attention to specific error types. “Crawled – currently not indexed” suggests quality or duplicate content issues. “Discovered – currently not indexed” indicates crawl budget problems. Each error type points toward different technical causes.
Monitor index coverage trends, not just snapshots. A site maintaining 95% indexation that drops to 85% needs immediate attention even if absolute numbers seem acceptable.
Core Web Vitals Failures
Core Web Vitals affect rankings and user experience. Failing thresholds in Google Search Console’s Core Web Vitals report demands immediate audit and remediation.
Focus on the specific metrics failing. Largest Contentful Paint problems indicate image or server issues. Cumulative Layout Shift points to CSS or ad loading problems. First Input Delay suggests JavaScript execution issues.
Test both mobile and desktop experiences. Mobile failures matter more for most sites given Google’s mobile-first indexing approach.
Site Migration or Redesign
Any site migration requires pre-migration audits, post-migration verification, and ongoing monitoring for several months afterward. Migrations create more technical SEO problems than any other single event.
Document everything before migration: URL structures, redirect maps, canonical tags, internal links, and indexation status. Post-migration audits compare current state against this baseline.
Plan for extended monitoring after migrations. Problems often emerge weeks or months later as search engines fully process changes.
Major Platform or Infrastructure Changes
Hosting changes, CDN implementations, server migrations, and major plugin updates all warrant immediate technical audits. Infrastructure changes affect site speed, availability, and crawlability.
Test thoroughly in staging environments before production deployment. Post-deployment audits verify that production behavior matches staging expectations.
Monitor server logs after infrastructure changes. Unusual crawl patterns, error rates, or response times indicate problems requiring investigation.
Manual Actions or Security Issues
Manual actions from Google require immediate response. Check Search Console’s Security & Manual Actions section regularly. Any notification demands immediate audit and remediation.
Security issues affect both rankings and user trust. Hacked content, malware, or phishing warnings devastate organic performance. Address security problems before any other technical work.
After resolving manual actions or security issues, request reconsideration and monitor recovery. Full recovery can take weeks or months depending on issue severity.
What to Check in Each Technical SEO Audit
Comprehensive audits examine multiple technical dimensions. Use this checklist to ensure thorough coverage across all critical areas.
Crawlability and Indexability
Verify that search engines can access and index your important pages. Check robots.txt for unintended blocks. Review meta robots tags for noindex directives. Examine X-Robots-Tag HTTP headers.
Analyze crawl stats in Google Search Console. Look for crawl errors, response code distributions, and crawl request trends. Identify pages receiving insufficient crawl attention.
Test JavaScript rendering. Use Google’s URL Inspection tool to compare rendered HTML against source HTML. JavaScript-dependent content may not be indexed properly.
Site Speed and Core Web Vitals
Measure page speed across representative page types. Test homepage, category pages, product pages, and blog posts separately. Each template may have different performance characteristics.
Use PageSpeed Insights for field data from real users. Lab data from Lighthouse provides diagnostic details. Both perspectives matter for complete understanding.
Prioritize Core Web Vitals metrics: LCP, FID (or INP), and CLS. These directly affect rankings and user experience. Address failures before optimizing already-passing metrics.
Mobile Usability and Responsiveness
Test mobile rendering across device sizes. Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test provides basic verification. Manual testing on actual devices reveals issues automated tools miss.
Check for mobile-specific problems: touch targets too close together, content wider than screen, illegible font sizes. These issues affect both rankings and conversions.
Verify mobile and desktop content parity. Google’s mobile-first indexing means mobile content determines rankings. Missing mobile content won’t rank regardless of desktop presence.
URL Structure and Redirects
Audit URL patterns for consistency and clarity. Identify parameter-heavy URLs, session IDs in URLs, or inconsistent formatting. Clean URL structures improve crawlability and user experience.
Map all redirects. Identify redirect chains exceeding two hops. Find redirect loops. Locate soft 404s returning 200 status codes. Each redirect problem wastes crawl budget and dilutes link equity.
Check for mixed content issues. HTTP resources on HTTPS pages create security warnings and potential ranking problems.
XML Sitemaps and Robots.txt
Verify sitemap accuracy. Sitemaps should include only indexable, canonical URLs. Remove redirecting URLs, noindexed pages, and non-canonical versions.
Check sitemap size limits. Individual sitemaps shouldn’t exceed 50,000 URLs or 50MB uncompressed. Large sites need sitemap index files organizing multiple sitemaps.
Review robots.txt for accuracy. Confirm intended blocks are working. Verify you’re not accidentally blocking CSS, JavaScript, or images that search engines need for rendering.
Structured Data and Schema Markup
Validate structured data using Google’s Rich Results Test. Check for errors and warnings across all schema types implemented.
Verify schema accuracy. Product schema should reflect actual prices and availability. Review schema should represent real customer feedback. Inaccurate schema can trigger manual actions.
Identify schema opportunities. Pages eligible for rich results without implemented schema represent quick wins. Prioritize high-traffic pages for schema implementation.
HTTPS and Security
Confirm complete HTTPS implementation. All pages should load via HTTPS. HTTP versions should redirect to HTTPS. Mixed content warnings indicate incomplete migration.
Check SSL certificate validity and expiration. Expired certificates break site access entirely. Set calendar reminders for renewal dates.
Review security headers. HSTS, Content-Security-Policy, and X-Frame-Options headers improve security posture. While not direct ranking factors, security affects user trust.
Duplicate Content and Canonicalization
Identify duplicate content across your site. Check for www vs. non-www versions, HTTP vs. HTTPS, trailing slash variations, and parameter-based duplicates.
Verify canonical tag implementation. Every page should have a self-referencing canonical or point to the preferred version. Canonical tags should be consistent with other signals like internal links and sitemaps.
Address near-duplicate content. Product variations, location pages, and filtered views often create near-duplicates requiring consolidation or canonical management.
Internal Linking Architecture
Map internal link distribution. Identify orphan pages with no internal links. Find pages with excessive links diluting their value. Ensure important pages receive proportional link equity.
Check anchor text patterns. Internal anchor text should be descriptive and varied. Avoid generic anchors like “click here” or over-optimized exact-match anchors.
Analyze click depth. Important pages should be reachable within three clicks from homepage. Deep pages receive less crawl attention and link equity.
Continuous Monitoring vs. Periodic Audits
Effective technical SEO combines scheduled comprehensive audits with ongoing automated monitoring. Neither approach alone provides complete coverage.
Setting Up Ongoing Technical Monitoring
Configure automated monitoring for critical metrics. Track indexation counts, crawl errors, Core Web Vitals, and uptime continuously. Set thresholds triggering alerts when metrics exceed acceptable ranges.
Monitor Google Search Console daily. The Performance report reveals traffic changes quickly. The Coverage report shows indexing problems. The Core Web Vitals report tracks page experience.
Implement log file monitoring for crawl behavior insights. Server logs reveal how search engines actually interact with your site, often exposing issues invisible to other tools.
Tools for Real-Time Technical SEO Tracking
Google Search Console provides free, authoritative data directly from Google. No third-party tool matches its accuracy for indexation and search performance data.
Screaming Frog enables scheduled crawls with change detection. Configure weekly crawls comparing against baselines to identify new issues automatically.
Uptime monitoring services like Pingdom or UptimeRobot catch availability problems immediately. Downtime affects both users and search engine crawling.
When Continuous Monitoring Replaces Scheduled Audits
Mature monitoring systems can reduce comprehensive audit frequency. If automated tools catch 90% of issues in real-time, quarterly audits become verification exercises rather than discovery processes.
However, monitoring never fully replaces human analysis. Automated tools miss context-dependent issues, strategic problems, and emerging best practices. Periodic human review remains essential.
Consider continuous monitoring as extending time between audits, not eliminating them. Monthly monitoring might enable quarterly audits to become semi-annual for stable sites.
Combining Automated Alerts with Manual Reviews
Build a tiered response system. Automated alerts handle urgent issues requiring immediate attention. Scheduled reviews address accumulated minor issues and strategic improvements.
Define alert thresholds carefully. Too sensitive triggers alert fatigue. Too lenient misses important problems. Calibrate based on your site’s normal variation patterns.
Document alert responses. Track which alerts led to real problems versus false positives. Refine thresholds based on historical accuracy.
How Technical Audits Fit Into Your Overall SEO Strategy
Technical SEO doesn’t exist in isolation. Effective strategies coordinate technical work with content development and authority building for maximum impact.
Technical SEO as the Foundation
Technical health enables other SEO efforts. The best content can’t rank if search engines can’t crawl it. Strong backlinks provide limited value if they point to broken pages.
Prioritize technical foundations before scaling content production. Fixing a site-wide indexing problem delivers more impact than publishing ten new articles on a broken site.
Think of technical SEO as infrastructure investment. It doesn’t directly generate traffic but enables everything that does.
Coordinating Technical, Content, and Link Building Efforts
Align technical audits with content calendars. Schedule audits before major content launches to ensure new pages deploy on solid foundations.
Coordinate with link building campaigns. Verify target pages are indexable and fast-loading before acquiring links. Technical problems waste link building investment.
Share audit findings across teams. Content teams need to know about duplicate content issues. Development teams need to understand SEO requirements. Cross-functional communication improves outcomes.
Prioritizing Technical Fixes Based on Business Impact
Not all technical issues deserve equal attention. Prioritize fixes affecting high-traffic pages, high-converting pages, or large page categories.
Calculate potential impact before allocating resources. A Core Web Vitals fix affecting your top 10 landing pages matters more than fixing orphan pages receiving no traffic.
Balance quick wins against strategic improvements. Some fixes take minutes and deliver immediate results. Others require significant development resources but provide lasting benefits.

Technical SEO Audit Frequency by Business Type
Different business models face different technical challenges. Adjust your audit frequency based on your specific situation.
Startups and New Websites
New sites need frequent audits during their first year. Monthly comprehensive audits help establish solid foundations and catch problems before they compound.
Focus on fundamentals: indexation, crawlability, and basic on-page elements. New sites don’t need advanced technical optimization until basics are solid.
Reduce frequency as the site matures and stabilizes. After 12 months of consistent technical health, transition to quarterly audits.
SMEs and Growing Businesses
Growing businesses typically benefit from quarterly comprehensive audits with monthly spot checks. This cadence balances thoroughness against resource constraints.
Pay attention to scaling challenges. What worked at 100 pages may break at 1,000 pages. Audit frequency should increase during rapid growth periods.
Align audits with business planning cycles. Quarterly audits fit naturally with quarterly business reviews, enabling integrated planning.
E-commerce and Transactional Sites
E-commerce sites need monthly comprehensive audits minimum. Product catalog changes, inventory updates, and promotional pages create constant technical flux.
Focus on product page technical health. These pages drive revenue directly. Indexation problems, slow load times, or structured data errors directly impact sales.
Schedule additional audits around peak seasons. Pre-holiday audits ensure technical readiness. Post-holiday audits catch problems introduced during high-activity periods.
Enterprise and Large-Scale Websites
Enterprise sites with hundreds of thousands of pages need continuous monitoring supplemented by monthly comprehensive audits. Scale creates unique challenges requiring dedicated technical SEO resources.
Segment audits by site section. Audit product pages one month, blog content the next, support documentation the following month. Rotating focus ensures complete coverage over time.
Invest in automated testing integrated with deployment pipelines. Catch technical problems before they reach production rather than discovering them in audits.
Agencies Managing Multiple Client Sites
Agencies need scalable audit processes. Standardize audit procedures across clients while customizing frequency based on individual client needs.
Prioritize clients by risk and value. High-traffic clients or those with complex sites need more frequent attention. Stable, simple sites can follow standard quarterly schedules.
Build audit efficiency through templates and automation. Consistent processes enable junior team members to conduct audits while senior staff focus on strategic recommendations.
Common Technical SEO Audit Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced practitioners make avoidable errors. Learn from common mistakes to improve your audit effectiveness.
Auditing Too Infrequently
The most common mistake is simply not auditing often enough. Technical problems accumulate silently. By the time you notice traffic drops, damage has compounded for months.
Set calendar reminders for scheduled audits. Treat them as non-negotiable appointments. Skipping “just this once” often becomes a pattern.
If resources are limited, conduct lighter audits more frequently rather than comprehensive audits rarely. Catching major issues quickly matters more than exhaustive analysis.
Ignoring Mobile and Core Web Vitals
Desktop-focused audits miss critical mobile issues. Google’s mobile-first indexing means mobile experience determines rankings. Desktop performance is secondary.
Core Web Vitals directly affect rankings. Ignoring page experience metrics leaves ranking potential unrealized. Prioritize CWV in every audit.
Test on actual mobile devices, not just emulators. Real-world mobile experience often differs from simulated testing.
Failing to Prioritize Fixes
Comprehensive audits generate long issue lists. Without prioritization, teams either feel overwhelmed or address easy issues while ignoring impactful ones.
Score issues by impact and effort. High-impact, low-effort fixes come first. Low-impact, high-effort fixes may never be worth addressing.
Limit active fix lists to manageable numbers. Better to complete five important fixes than start twenty and finish none.
Not Tracking Changes Over Time
Single-point audits miss trends. Without historical comparison, you can’t distinguish new problems from longstanding issues or measure improvement.
Maintain audit archives. Compare current findings against previous audits. Track which issues recur and which stay fixed.
Build dashboards tracking key metrics over time. Visualizing trends reveals patterns invisible in individual audit reports.
Tools and Resources for Technical SEO Audits
The right tools make audits more efficient and thorough. Build a toolkit covering all audit dimensions.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console is essential and free. It provides authoritative data about how Google sees your site: indexation status, crawl stats, Core Web Vitals, and search performance.
Check Search Console at least weekly. The Performance report shows traffic trends. The Coverage report reveals indexing problems. The Enhancements reports track structured data and page experience.
Use the URL Inspection tool for page-level diagnostics. It shows exactly how Google crawls, renders, and indexes specific URLs.
Screaming Frog and Crawling Tools
Screaming Frog SEO Spider is the industry-standard crawling tool. It identifies broken links, redirect chains, duplicate content, and dozens of other technical issues.
Configure custom extractions for site-specific checks. Extract schema markup, track specific elements, or identify pages missing required components.
Schedule regular crawls with change detection. Automated comparison against previous crawls highlights new issues requiring attention.
PageSpeed Insights and Core Web Vitals Tools
PageSpeed Insights combines lab testing with field data from real users. It provides both diagnostic information and actual user experience metrics.
Web Vitals Chrome extension enables real-time CWV monitoring during manual testing. See metrics as you browse your site.
Chrome DevTools provides detailed performance analysis. The Performance panel reveals exactly what’s slowing page loads.
Log File Analysis Tools
Server logs reveal how search engines actually crawl your site. Log analysis shows crawl frequency, response codes, and bot behavior invisible to other tools.
Tools like Screaming Frog Log File Analyser or Botify process large log files efficiently. They identify crawl waste, discover uncrawled pages, and reveal bot behavior patterns.
Combine log analysis with crawl data for complete pictures. Logs show what bots do; crawlers show what they should find.
All-in-One SEO Platforms
Platforms like Semrush, Ahrefs, and Moz combine multiple audit capabilities. They provide crawling, rank tracking, backlink analysis, and competitive intelligence in unified interfaces.
These platforms suit teams needing comprehensive toolsets without managing multiple subscriptions. They sacrifice some depth for breadth and convenience.
Evaluate platforms based on your specific needs. Some excel at technical auditing while others focus on content or links. Choose based on your priorities.
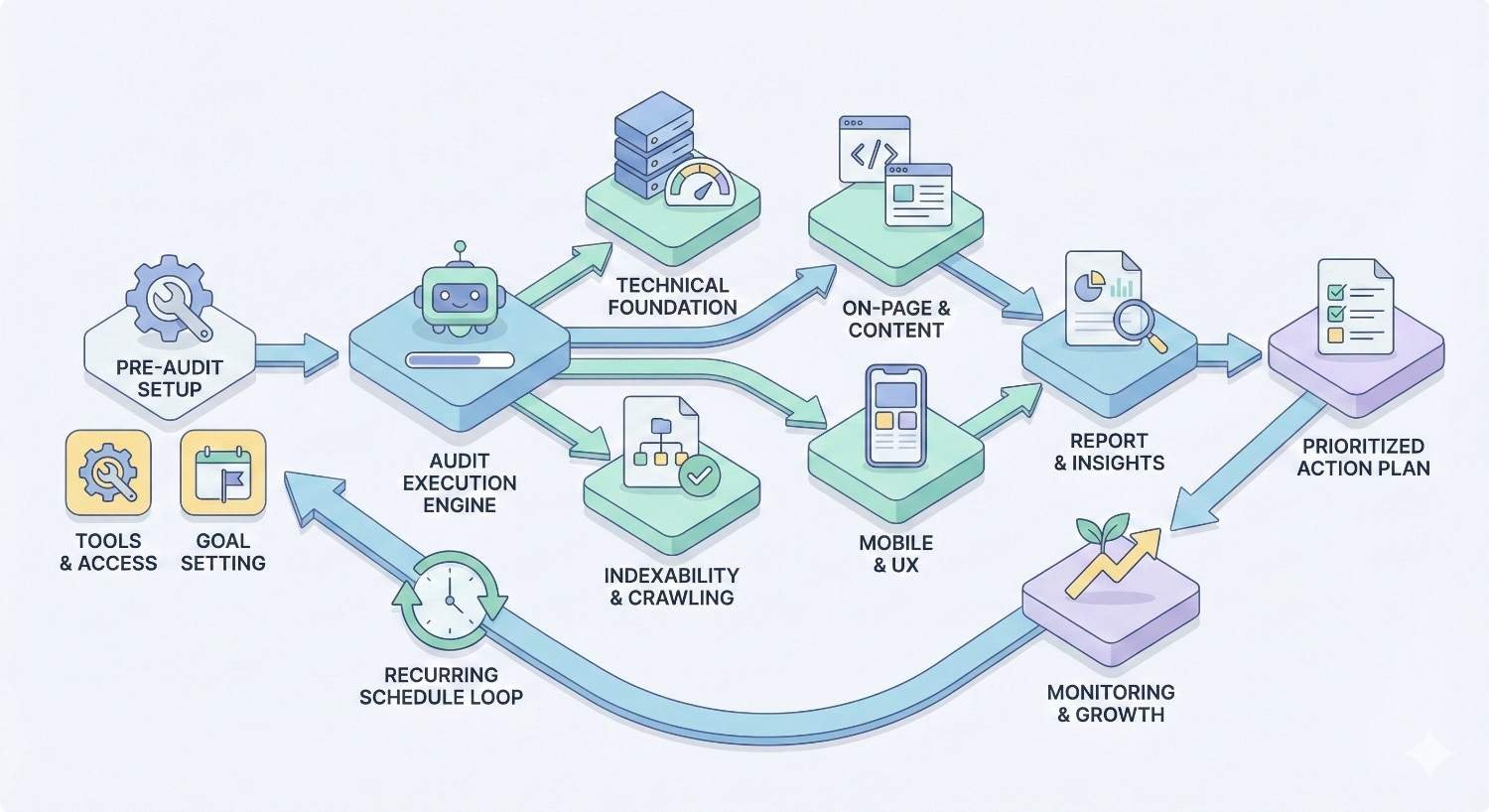
Creating a Technical SEO Audit Schedule
Sustainable technical SEO requires systematic scheduling. Build processes ensuring consistent attention without overwhelming your team.
Building Your Audit Calendar
Map audit activities across the year. Schedule comprehensive quarterly audits on specific dates. Plan monthly spot checks between major audits. Set weekly monitoring review times.
Align with business calendars. Avoid scheduling audits during peak business periods when teams lack bandwidth for fixes. Plan pre-season audits ensuring readiness for important periods.
Build buffer time for remediation. Audits without fix time are pointless. Schedule implementation sprints following each audit.
Assigning Responsibilities and Ownership
Designate clear ownership for technical SEO. Someone must be accountable for audit completion and issue resolution. Shared responsibility often means no responsibility.
Define roles clearly. Who conducts audits? Who prioritizes findings? Who implements fixes? Who verifies completion? Each step needs an owner.
Establish escalation paths for critical issues. When audits reveal urgent problems, teams need clear processes for rapid response.
Documenting and Tracking Technical Issues
Maintain centralized issue tracking. Spreadsheets work for small sites. Project management tools suit larger operations. Whatever system you use, use it consistently.
Document issue details thoroughly. Include discovery date, affected URLs, severity assessment, recommended fix, assigned owner, and resolution status. Incomplete documentation leads to repeated work.
Track issue lifecycle from discovery through verification. Closed issues should include resolution date and verification that fixes worked.
Measuring the Impact of Technical Improvements
Connect technical fixes to business outcomes. Track traffic, rankings, and conversions for pages affected by technical improvements. Demonstrate ROI to justify continued investment.
Measure before and after. Baseline metrics before fixes enable meaningful comparison. Without baselines, you can’t prove impact.
Report results to stakeholders. Technical SEO competes for resources with other initiatives. Demonstrating value ensures continued support.
How We Help Businesses Maintain Technical SEO Health
Technical SEO requires specialized expertise and consistent attention. Many businesses lack internal resources for comprehensive technical management.
Our Approach to Technical SEO Audits
We conduct thorough technical audits examining every dimension affecting search performance. Our audits go beyond automated tool outputs to provide strategic recommendations prioritized by business impact.
Each audit includes detailed findings, clear explanations of issues and their effects, and actionable remediation plans. We translate technical complexity into business language stakeholders understand.
We customize audit scope and frequency based on your specific situation. Enterprise sites need different approaches than small business websites. Our recommendations reflect your reality.
Ongoing Monitoring and Performance Tracking
Beyond periodic audits, we provide continuous monitoring catching issues before they impact performance. Automated alerts notify us of critical problems requiring immediate attention.
Regular reporting keeps you informed of technical health trends. Monthly summaries highlight key metrics, resolved issues, and emerging concerns. You maintain visibility without needing technical expertise.
We track the impact of technical improvements, demonstrating ROI and informing future priorities. Data-driven decision making ensures resources focus where they matter most.
Strategic Technical SEO as Part of Full-Service Growth
Technical SEO integrates with our broader organic growth services. We coordinate technical work with content strategy and authority building for maximum combined impact.
Our team handles technical complexity so you can focus on your business. Whether you need comprehensive management or targeted support for specific challenges, we adapt to your needs.
Conclusion
Technical SEO audit frequency depends on your website’s size, complexity, and rate of change. Most businesses benefit from quarterly comprehensive audits supplemented by monthly monitoring, while high-traffic e-commerce sites need monthly deep dives and static small sites can audit annually.
The key is establishing consistent processes catching problems before they compound. Automated monitoring extends human audit capabilities, but periodic expert review remains essential for strategic optimization.
We help businesses worldwide build and maintain technical SEO foundations supporting sustainable organic growth. Contact White Label SEO Service to discuss your technical SEO audit needs and establish the right monitoring cadence for your situation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I audit my website for technical SEO issues?
Most websites benefit from quarterly comprehensive technical SEO audits. High-traffic or frequently updated sites should audit monthly, while small static sites can audit annually. Supplement scheduled audits with continuous automated monitoring for critical metrics.
What triggers the need for an immediate technical SEO audit?
Sudden traffic drops, indexing errors in Google Search Console, Core Web Vitals failures, site migrations, major platform updates, or security warnings all require immediate audits. Don’t wait for scheduled reviews when these warning signs appear.
Can I rely on automated tools instead of manual technical SEO audits?
Automated tools catch many issues but miss context-dependent problems and strategic opportunities. Use automation for continuous monitoring and initial issue detection, but conduct periodic manual reviews for comprehensive analysis and prioritization.
What’s the difference between a technical SEO audit and a full SEO audit?
Technical audits focus on infrastructure: crawlability, indexability, site speed, and architecture. Full SEO audits also examine content quality, keyword targeting, backlink profiles, and competitive positioning. Technical audits are one component of comprehensive SEO analysis.
How long does a technical SEO audit take to complete?
Small sites with under 100 pages can be audited in a few hours. Mid-sized sites need one to two days. Enterprise sites with hundreds of thousands of pages may require weeks for comprehensive analysis. Complexity and tool availability affect timelines significantly.
Should I audit my website after every Google algorithm update?
Major core updates warrant post-update audits to identify any negative impacts. Minor daily updates don’t require individual responses. Monitor Search Console for performance changes after confirmed updates and audit if you notice significant ranking or traffic shifts.
What are the most critical elements to check in every technical SEO audit?
Prioritize indexation status, crawl errors, Core Web Vitals, mobile usability, and redirect health in every audit. These elements most directly affect search visibility. Expand scope to include structured data, security, and internal linking as resources allow.