Local SEO ranking factors determine whether your business appears in Google’s Local Pack or gets buried beneath competitors. These signals span Google Business Profile optimization, citation consistency, review management, and on-page elements that collectively influence how search engines evaluate local relevance.
For business owners and marketing teams investing in organic visibility, understanding these factors separates thriving local businesses from those struggling to attract nearby customers. The difference between ranking first and fifth in local results can mean thousands of dollars in monthly revenue.
This guide breaks down every ranking factor that matters in 2024, from proximity signals you cannot control to optimization strategies you can implement today. You will learn exactly how to prioritize efforts, avoid common mistakes, and build sustainable local search visibility.

What Are Local SEO Ranking Factors?
Local SEO ranking factors are the specific signals Google uses to determine which businesses appear in location-based search results. These factors evaluate three core dimensions: how close a business is to the searcher, how relevant the business is to the query, and how prominent the business is compared to competitors.
Unlike traditional organic rankings that rely heavily on backlinks and content depth, local search results weigh factors like Google Business Profile completeness, review signals, and NAP consistency across the web. Google’s local algorithm operates somewhat independently from its organic algorithm, which explains why a business might rank well in the Local Pack but poorly in organic results, or vice versa.
How Local Search Differs from Traditional SEO
Traditional SEO focuses primarily on website authority, content relevance, and backlink profiles. Local SEO adds an entirely different layer of signals centered around physical location, business legitimacy, and local reputation.
The Local Pack, those three business listings that appear with a map in search results, uses a distinct ranking system. According to Google’s own documentation, local results are based primarily on relevance, distance, and prominence. This means a small business with strong local signals can outrank national brands with massive domain authority.
Local searches also carry different intent patterns. Someone searching “best Italian restaurant” likely wants nearby options, while “Italian cooking techniques” signals informational intent without location relevance. Understanding this distinction shapes how you approach keyword targeting and content creation.
The technical requirements differ as well. Local SEO demands accurate structured data markup, consistent business information across directories, and active management of your Google Business Profile. These elements barely factor into traditional SEO but become critical for local visibility.
Why Local SEO Matters for Business Growth
Local search drives purchasing decisions at a rate that should command attention from any business serving geographic markets. Most consumers searching for local businesses visit a store within 24 hours, and a significant portion make purchases the same day.
The business impact extends beyond foot traffic. Local Pack visibility builds brand awareness even when users do not click through. Appearing alongside competitors in map results establishes legitimacy and keeps your business top of mind for future needs.
For service area businesses, local SEO often represents the primary customer acquisition channel. Plumbers, electricians, lawyers, and healthcare providers depend on appearing when nearby customers search for their services. Missing from these results means losing business to competitors who invested in local optimization.
The ROI calculation favors local SEO for most small and medium businesses. Unlike paid advertising that stops generating leads when budgets run out, local SEO builds compounding visibility over time. A well-optimized Google Business Profile continues attracting customers months and years after the initial optimization work.

Google Business Profile Ranking Factors
Your Google Business Profile serves as the foundation of local search visibility. This free listing directly controls how your business appears in Google Maps and the Local Pack, making it the single most important asset for local SEO.
Google uses information from your profile to determine relevance to search queries, display business details to potential customers, and evaluate engagement signals that influence rankings. Neglecting your GBP means surrendering control over how Google presents your business to local searchers.
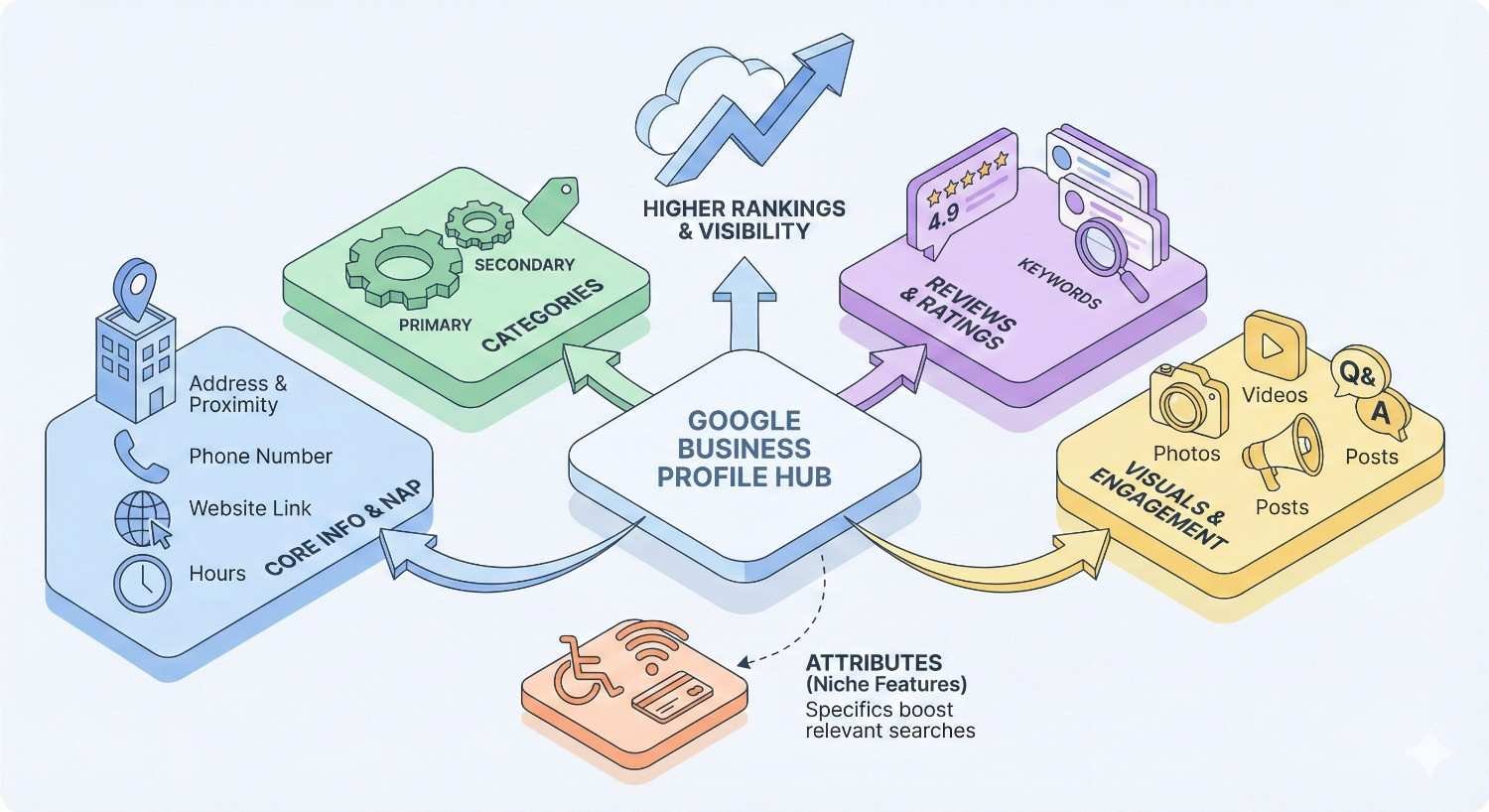
Primary GBP Attributes That Impact Rankings
The core attributes of your Google Business Profile establish baseline relevance and legitimacy. Getting these elements right is non-negotiable for local search success.
Business Name, Address, and Phone (NAP) Accuracy
Your business name in GBP should match your real-world business name exactly. Adding keywords to your business name violates Google’s guidelines and risks suspension, despite the ranking boost some businesses attempt to gain through this tactic.
Address accuracy matters for proximity calculations. Google uses your listed address to determine distance from searchers, so any discrepancy between your GBP address and your actual location creates problems. For businesses that moved locations, updating the address promptly prevents confusion and maintains ranking signals tied to your service area.
Phone number consistency extends beyond GBP to every online mention of your business. Using a local phone number rather than a toll-free number can strengthen local relevance signals, though this varies by industry and business type.
Primary and Secondary Category Selection
Category selection directly influences which searches trigger your business listing. Your primary category carries the most weight, so choosing the most specific accurate category matters significantly.
Google offers hundreds of category options, and specificity typically outperforms broad categories. A “Personal Injury Attorney” category signals more relevance for injury-related searches than the broader “Lawyer” category. Research which categories competitors use and identify the most precise match for your core services.
Secondary categories expand your visibility for related searches without diluting your primary category signal. A restaurant might use “Italian Restaurant” as primary while adding “Catering Service” and “Event Venue” as secondary categories to capture additional relevant searches.
Business Description Optimization
Your 750-character business description provides context about your services, specialties, and unique value proposition. While Google states this description does not directly impact rankings, it influences click-through rates and helps potential customers understand what you offer.
Write descriptions for humans first. Include your primary services, service areas, and differentiating factors naturally. Avoid keyword stuffing, which makes descriptions read poorly and may trigger Google’s spam filters.
Front-load important information since users may not read the entire description. Lead with your core offering and primary service area before expanding into secondary details.
GBP Engagement Signals
Beyond static profile information, Google evaluates how users interact with your listing and how actively you maintain it. These engagement signals indicate business legitimacy and relevance.
Photos and Visual Content
Businesses with photos receive significantly more engagement than those without. Google tracks photo views and uses this engagement data as a quality signal.
Upload high-quality images of your business exterior, interior, products, services, and team. Exterior photos help customers recognize your location, while interior shots set expectations for the experience. For service businesses, before-and-after photos or images of completed work demonstrate capabilities.
Geo-tag photos with your business location metadata when possible. Regularly add new photos to signal an active, operating business. Encourage customers to upload their own photos, which adds authenticity and fresh visual content.
Google Posts and Updates
Google Posts allow you to share updates, offers, events, and news directly on your business profile. These posts appear in your listing and can influence click-through rates.
Post consistently, aiming for at least weekly updates. Share promotions, highlight services, announce events, or provide useful information relevant to your customers. Each post remains visible for seven days before archiving, so regular posting maintains fresh content on your profile.
Include calls to action in posts to drive specific behaviors like calling, visiting your website, or making reservations. Track which post types generate the most engagement and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Q&A Section Management
The Questions and Answers section on your GBP allows anyone to ask questions and anyone to answer them. This creates both opportunity and risk for your business.
Proactively seed common questions and provide authoritative answers. Think about what potential customers frequently ask and address those questions before they are asked by others. This ensures accurate information appears prominently.
Monitor the Q&A section regularly for new questions. Respond quickly to demonstrate attentiveness and prevent incorrect answers from other users. Upvote helpful questions and answers to influence their visibility.
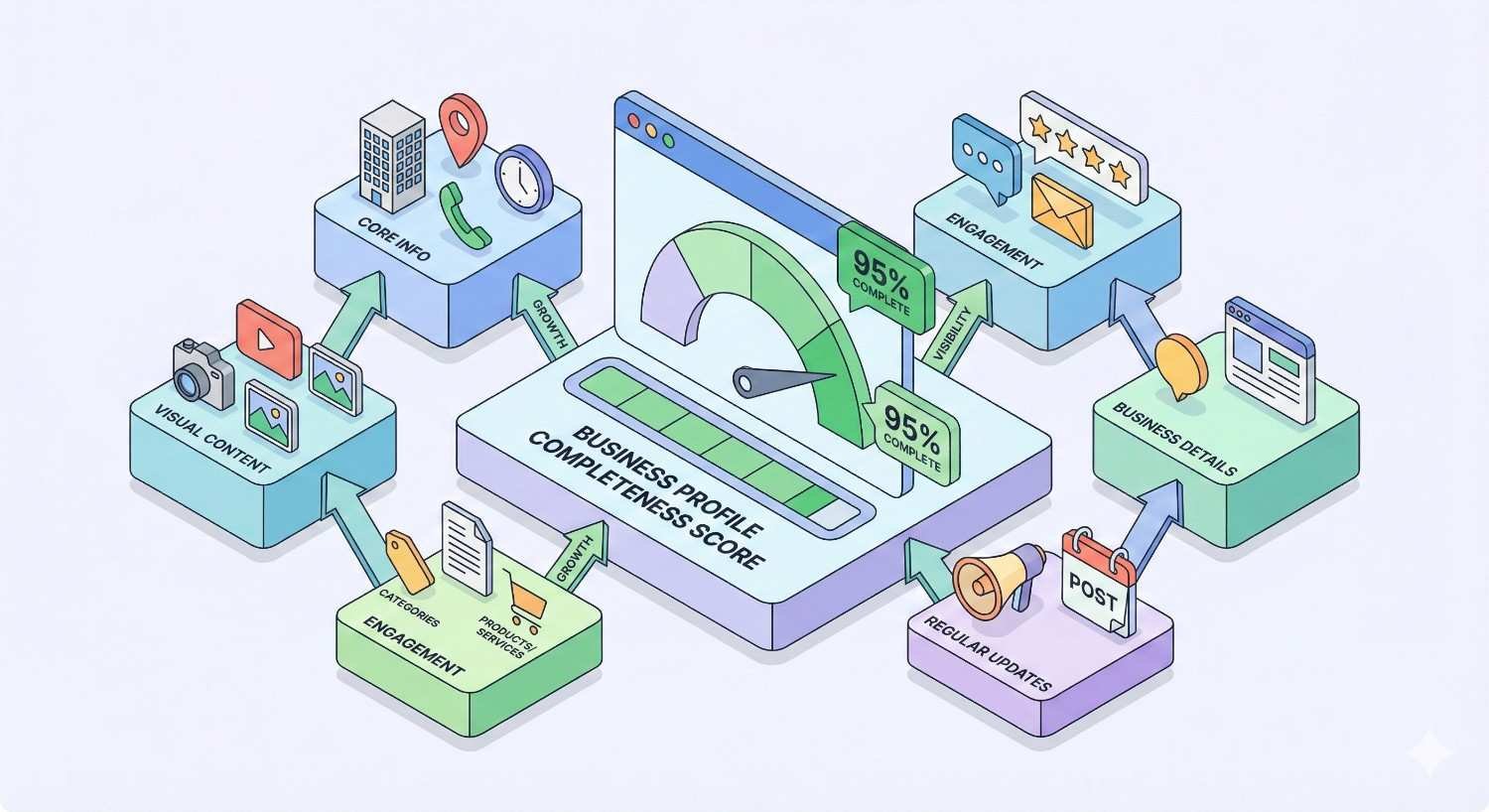
Google Business Profile Completeness Score
Google rewards complete profiles with better visibility. Every empty field represents a missed opportunity to provide relevant information and demonstrate business legitimacy.
Complete every applicable attribute in your profile. This includes business hours, holiday hours, payment methods, accessibility features, amenities, and service options. For restaurants, add menu items. For service businesses, list specific services offered.
The attributes available vary by category, so explore all options Google provides for your business type. Some attributes, like “women-owned” or “veteran-owned,” may resonate with certain customer segments and differentiate your listing.
Keep information current. Outdated hours frustrate customers and signal neglect to Google. Update your profile whenever business details change, and review all information quarterly to catch any inaccuracies.
Proximity Ranking Factors
Proximity measures the distance between the searcher and your business location. This factor operates largely outside your control but understanding how it works helps you set realistic expectations and optimize what you can influence.
Google determines searcher location through IP address, device GPS, and location history. The algorithm then calculates distance to businesses matching the search query and uses this as a primary ranking signal.

How Distance Affects Local Pack Rankings
For searches with explicit location modifiers like “dentist in downtown Chicago,” Google prioritizes businesses within that specified area regardless of where the searcher is located. The searcher could be across the country, but results will focus on downtown Chicago.
For searches without location modifiers, Google assumes local intent and uses the searcher’s current location. This means your rankings literally change based on where the person searching is standing. A business might rank first for someone across the street but not appear at all for someone five miles away.
The weight of proximity varies by query type and competition level. In dense urban areas with many competing businesses, proximity carries enormous weight. In rural areas with fewer options, Google expands the radius and other factors gain importance.
You cannot change your physical location, but you can ensure Google accurately understands where you are located. Verify your address is correct, embed a Google Map on your website, and maintain consistent address information across all online properties.
Service Area Business Considerations
Service area businesses that travel to customers rather than receiving them at a fixed location face unique proximity challenges. Google allows these businesses to hide their address while specifying service areas.
Define your service area accurately in GBP. You can specify cities, postal codes, or a radius around your location. Be realistic about the areas you actually serve rather than claiming an unrealistically large territory.
Service area businesses compete based on the centroid of their service area rather than a specific address. This means a plumber serving a metropolitan area competes differently than one with a storefront. Optimizing for specific neighborhoods through content and citations can help establish relevance in key service areas.
Consider whether a physical location makes sense for your business model. Some service area businesses benefit from establishing a small office or co-working space in their primary service area to strengthen proximity signals.
Multi-Location Proximity Strategies
Businesses with multiple locations can leverage proximity by ensuring each location has its own optimized Google Business Profile. This allows you to capture searches near each physical location.
Each location needs a unique GBP with accurate address, phone number, and location-specific details. Avoid duplicating descriptions across locations. Instead, customize each profile to reflect that specific location’s services, team, and community involvement.
Create dedicated location pages on your website for each physical location. Link these pages to their corresponding GBP listings. This reinforces the connection between your web presence and each physical location.
Strategic location selection for new branches should consider local search competition. Opening in an underserved area with less competition can yield faster local visibility than entering a saturated market.
Relevance Ranking Factors
Relevance measures how well your business matches what the searcher is looking for. Google evaluates relevance through your GBP information, website content, and signals across the web that describe your business.
Strong relevance signals help you rank for searches directly related to your services. Weak relevance signals mean missing opportunities even when proximity and prominence favor your business.
Keyword Optimization for Local Intent
Local keyword optimization differs from traditional keyword targeting. You need to capture searches that combine service terms with location modifiers and implicit local intent.
Research how potential customers search for your services. Tools like Google Keyword Planner, Semrush, and Ahrefs reveal search volumes for terms like “emergency plumber near me” or “family dentist [city name].” Identify the highest-volume terms relevant to your business.
Map keywords to specific pages and GBP elements. Your homepage might target your primary service plus city, while service pages target specific offerings. Your GBP description and posts should naturally incorporate relevant terms without stuffing.
Consider voice search patterns, which tend toward conversational queries. “Where can I get my car fixed nearby” differs from typed searches but represents growing search behavior.
Category and Attribute Alignment
Your GBP categories and attributes must align with the searches you want to rank for. Misalignment between your categories and target keywords creates relevance gaps.
Audit competitor categories to understand what Google considers relevant for your target searches. If competitors ranking for your desired terms use different categories, consider whether your category selection needs adjustment.
Attributes provide additional relevance signals. A restaurant marking “outdoor seating” becomes more relevant for searches including that term. A retailer indicating “curbside pickup” gains relevance for those searches. Complete all applicable attributes to maximize relevance opportunities.
Content Relevance Signals
Your website content reinforces relevance signals from your GBP. Google crawls your site to understand what services you offer, what areas you serve, and how authoritative your content is.
Create dedicated pages for each major service you offer. A law firm should have separate pages for personal injury, family law, and criminal defense rather than lumping everything on one services page. This allows each page to build relevance for specific search terms.
Develop location-specific content that demonstrates expertise in your service areas. Write about local events, community involvement, or area-specific considerations related to your services. This content signals relevance to geographic searches.
Ensure your website clearly states your service areas. Include city and neighborhood names naturally throughout your content, in your footer, and on your contact page. This helps Google understand where you operate.
Prominence Ranking Factors
Prominence reflects how well-known and respected your business is, both online and offline. Google attempts to surface businesses that searchers would recognize and trust, using various signals to evaluate prominence.
Unlike proximity, prominence is something you can actively build over time. Investments in brand building, reputation management, and authority development compound into stronger prominence signals.
Online Reputation and Brand Authority
Your online reputation encompasses reviews, ratings, mentions, and the overall sentiment surrounding your brand across the web. Google aggregates these signals to assess prominence.
Review quantity and quality on Google directly impact prominence. Businesses with more positive reviews signal greater customer validation. But reviews on other platforms also matter. Yelp, Facebook, industry-specific sites, and other review platforms contribute to your overall reputation profile.
Brand mentions across the web, even without links, contribute to prominence. News coverage, blog mentions, social media discussions, and forum references all signal that your business exists in public consciousness.
Domain authority of your website, while more relevant to organic rankings, also influences local prominence. A website with strong backlinks from authoritative sources signals a more prominent business.
Offline Prominence Signals
Google attempts to incorporate offline prominence into local rankings. Well-known businesses that exist prominently in the physical world should, in theory, rank well in local search.
This manifests through signals like branded search volume. When many people search for your business name specifically, Google interprets this as prominence. Building brand awareness through advertising, community involvement, and word-of-mouth indirectly supports local SEO.
Physical signage, local advertising, and community presence generate offline awareness that eventually translates to online signals. Sponsoring local events, participating in community organizations, and maintaining visible storefronts all contribute to prominence over time.
Industry Authority Indicators
Within your specific industry, certain signals indicate authority and expertise. Google may evaluate these industry-specific factors when determining prominence for relevant searches.
Professional certifications, awards, and recognitions signal authority. Display these credentials on your website and GBP. Industry association memberships demonstrate legitimacy and professional standing.
Media coverage in industry publications carries weight. Being quoted as an expert, publishing thought leadership content, or receiving industry awards all build authority signals that support prominence.
Longevity matters as well. Established businesses with years of operation history often outrank newer competitors, all else being equal. Google can verify business age through various signals including domain registration date and historical data.
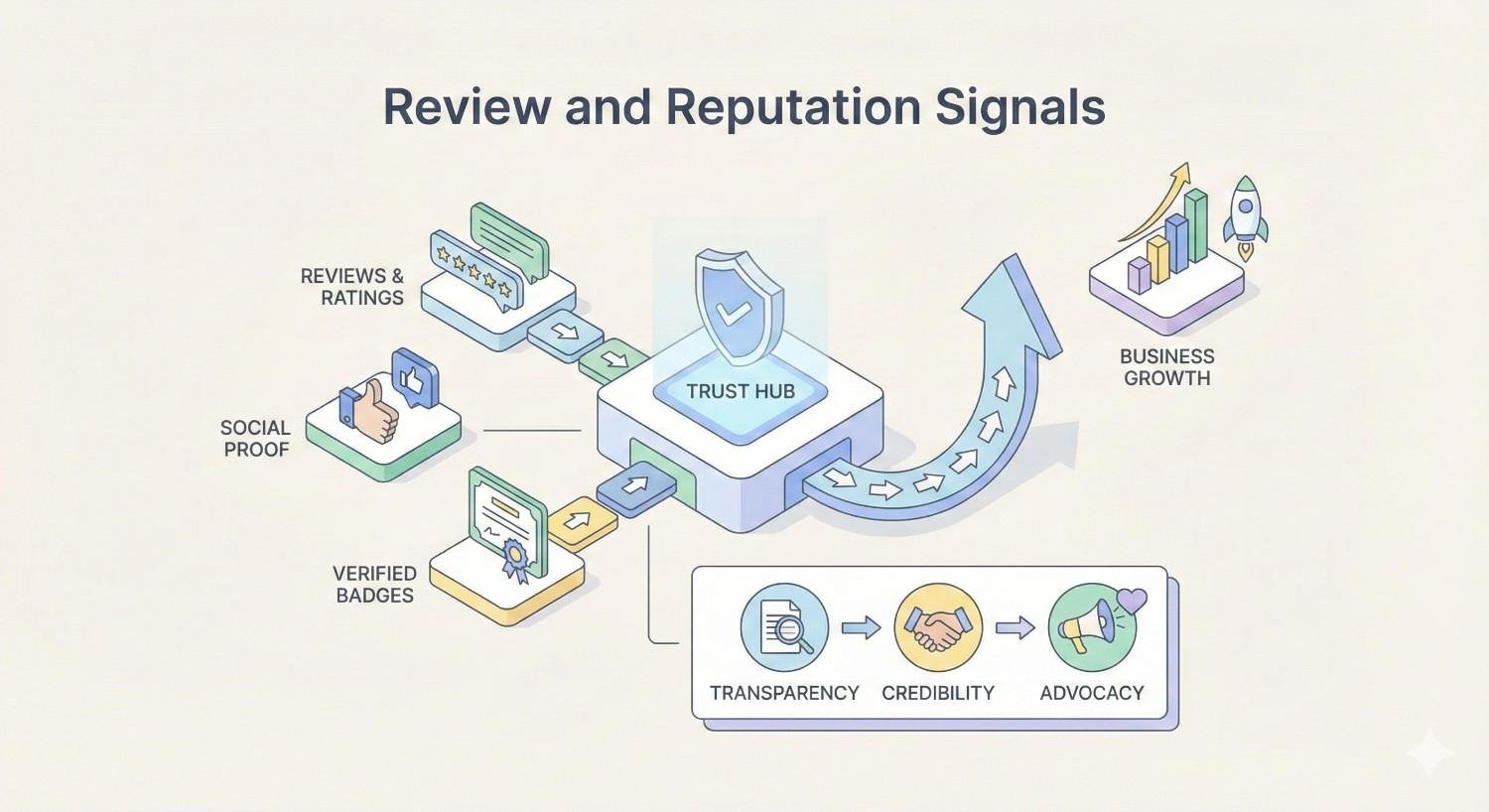
Review and Reputation Signals
Reviews represent one of the most influential and actionable local ranking factors. They directly impact rankings, click-through rates, and conversion rates, making review management essential for local SEO success.
Google has confirmed that reviews factor into local rankings. Beyond the algorithm, reviews shape customer perception and purchasing decisions. A strong review profile delivers compounding benefits across visibility and conversion.
Review Quantity and Velocity
The total number of reviews on your Google Business Profile influences rankings. More reviews generally correlate with better local visibility, though quality and recency also matter.
Review velocity, the rate at which you acquire new reviews, signals ongoing customer activity. A business receiving steady reviews demonstrates continued relevance, while a business whose last review came months ago may appear less active.
Set realistic review acquisition goals based on your transaction volume. A restaurant serving hundreds of customers weekly should accumulate reviews faster than a B2B service provider with fewer clients. Compare your review velocity to competitors to identify gaps.
Implement systematic review requests into your customer journey. Ask satisfied customers for reviews at the point of maximum satisfaction, whether that is after a successful project completion, positive service interaction, or purchase. Make the process easy by providing direct links to your Google review page.
Review Quality and Sentiment
Star ratings matter, but the content of reviews matters more than many businesses realize. Google’s natural language processing analyzes review text to understand sentiment and extract relevant information.
Reviews mentioning specific services help establish relevance for those services. A review stating “best emergency plumbing service in [city]” reinforces relevance for emergency plumbing searches in that location. Encourage customers to mention specific services they received.
Detailed reviews carry more weight than brief star ratings. A thoughtful paragraph describing the customer experience provides more signal than “Great service. 5 stars.” While you cannot control what customers write, you can encourage detailed feedback by asking specific questions when requesting reviews.
Negative reviews happen to every business. How you respond matters more than avoiding them entirely. A professional, helpful response to criticism demonstrates customer service commitment and can actually improve perception among potential customers reading reviews.
Review Diversity Across Platforms
While Google reviews carry the most direct ranking impact, reviews on other platforms contribute to overall prominence and reputation signals. A diverse review profile across multiple platforms signals broader customer validation.
Prioritize platforms relevant to your industry. Restaurants should maintain Yelp and TripAdvisor profiles. Home service businesses benefit from HomeAdvisor and Angi reviews. Healthcare providers should focus on Healthgrades and Zocdoc.
Facebook reviews contribute to your social proof and may influence Google’s understanding of your reputation. Industry-specific directories often display reviews that potential customers consult during their research process.
Do not neglect these secondary platforms, but recognize that Google reviews should remain your primary focus for local SEO purposes. Allocate review acquisition efforts proportionally.
Review Response Strategy
Responding to reviews signals active business management and customer care. Google has indicated that review responses factor into local rankings, though the exact weight remains unclear.
Respond to all reviews, positive and negative. Thank positive reviewers specifically for their feedback. Address negative reviews professionally, acknowledging concerns and offering to resolve issues offline.
Response timing matters. Quick responses demonstrate attentiveness. Aim to respond within 24-48 hours of new reviews appearing.
Avoid defensive or argumentative responses to negative reviews. Future customers reading your responses will judge your professionalism. A calm, helpful response to criticism often impresses potential customers more than the negative review concerns them.
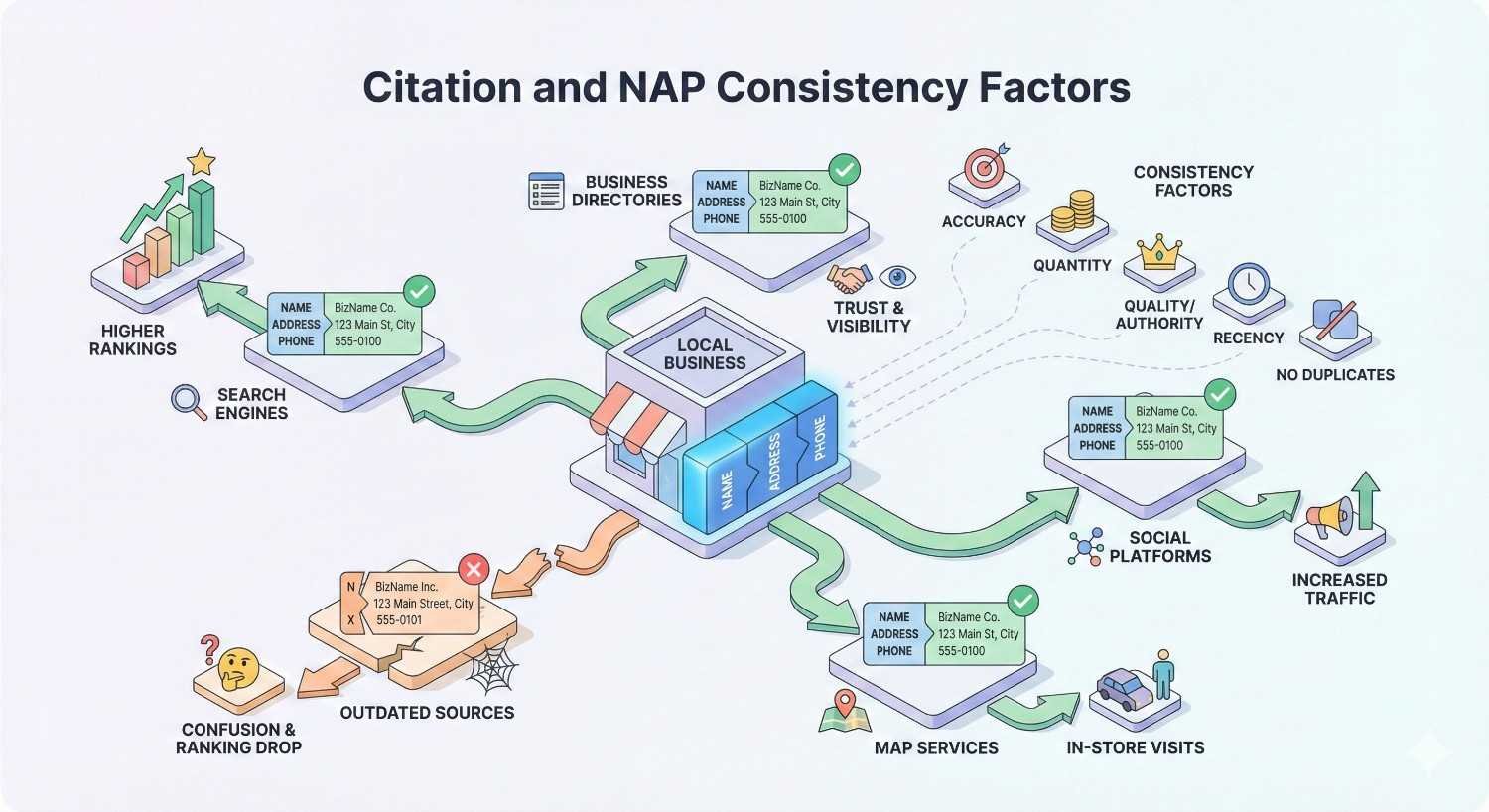
Citation and NAP Consistency Factors
Citations are online mentions of your business name, address, and phone number. They appear in directories, social platforms, data aggregators, and websites across the internet. Consistent citations reinforce your business legitimacy and help Google verify your information.
Inconsistent citations create confusion for search engines and potential customers. Different addresses, phone numbers, or business name variations across the web undermine trust signals and can suppress local rankings.
Structured Citations (Directories)
Structured citations appear in business directories with standardized formats for business information. These directories feed data to search engines and serve as reference points for verifying business details.
Primary Data Aggregators
Data aggregators distribute business information to hundreds of directories and platforms. The major aggregators in the United States include Data Axle, Localeze, Foursquare, and Factual. Ensuring accurate information with these aggregators cascades corrections across their distribution networks.
Submit your business information directly to each major aggregator. Verify existing listings and correct any inaccuracies. This foundational step prevents incorrect information from propagating across the web.
Aggregator updates take time to distribute. After submitting corrections, allow several weeks for changes to appear across downstream directories. Monitor key directories to confirm updates propagated correctly.
Industry-Specific Directories
Every industry has directories that potential customers and search engines consider authoritative. Lawyers should be listed in Avvo and FindLaw. Doctors need profiles on Healthgrades and WebMD. Restaurants belong on Yelp and TripAdvisor.
Identify the top directories for your industry by researching where competitors are listed and where customers in your industry typically search. Prioritize directories that appear in search results for your target keywords.
Complete profiles fully on industry directories. Many allow detailed service descriptions, photos, and additional information beyond basic NAP data. Comprehensive profiles maximize the value of each citation.
Local and Regional Citations
Local directories specific to your city or region provide geographically relevant citations. Chamber of commerce directories, local business associations, city guides, and regional publications all offer citation opportunities.
Search for “[your city] business directory” to identify local citation sources. Many cities have multiple directories run by different organizations. Local newspaper websites often maintain business directories as well.
These local citations reinforce your geographic relevance. A business listed in multiple Austin-specific directories sends stronger local signals than one listed only in national directories.
Unstructured Citations (Mentions)
Unstructured citations are mentions of your business information in content that is not formatted as a directory listing. News articles, blog posts, event pages, and sponsor acknowledgments can all contain unstructured citations.
These mentions contribute to prominence signals even without links. Google can identify your business name and associate mentions with your entity, building awareness of your brand across the web.
Generate unstructured citations through PR efforts, community involvement, and content marketing. Press releases about business news, sponsorship of local events, and contributions to community organizations all create mention opportunities.
NAP Consistency Audit Process
Auditing your citations identifies inconsistencies that may be harming your local rankings. This process should be conducted initially and then periodically to catch new issues.
Use citation audit tools like BrightLocal, Moz Local, or Whitespark to scan for existing citations and identify inconsistencies. These tools check major directories and aggregators, flagging variations in your business information.
Document every variation you find. Common issues include old addresses, outdated phone numbers, inconsistent business name formatting, and duplicate listings. Prioritize corrections based on the authority of the directory.
Correct inconsistencies directly when possible. Many directories allow you to claim and edit listings. For directories without self-service options, contact support to request corrections. Track your correction requests and follow up on those that remain unresolved.

On-Page Local SEO Factors
Your website supports local rankings through on-page optimization that reinforces your location relevance, service offerings, and business legitimacy. While GBP drives Local Pack rankings, your website influences both local and organic visibility.
On-page local SEO connects your web presence to your physical business, helping Google understand what you do and where you do it.
Local Keyword Optimization
Strategic keyword placement signals relevance to local searches. This goes beyond stuffing location names into content and requires thoughtful integration of local terms throughout your site.
Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
Title tags carry significant ranking weight and should include your primary keyword plus location for key pages. A format like “Emergency Plumber in Austin, TX | [Business Name]” clearly signals relevance for local plumbing searches.
Keep title tags under 60 characters to avoid truncation in search results. Front-load important keywords since Google may cut off longer titles.
Meta descriptions do not directly impact rankings but influence click-through rates. Write compelling descriptions that include your location and a clear value proposition. Include a call to action to encourage clicks.
Header Tag Hierarchy
Use header tags to structure content logically while incorporating local keywords naturally. Your H1 should include your primary service and location. H2s and H3s can target secondary keywords and related terms.
Avoid forcing location names into every header. This reads poorly and may trigger over-optimization concerns. Use location modifiers where they fit naturally and provide value to readers.
Local Content Optimization
Body content should naturally reference your service areas without keyword stuffing. Mention neighborhoods, landmarks, and local references that demonstrate genuine local presence.
Write content that serves local searchers specifically. A page about “roof repair in Denver” should address Denver-specific concerns like hail damage, altitude considerations, and local building codes. This specificity signals authentic local expertise.
Include your full address and phone number on every page, typically in the footer. This reinforces NAP consistency and makes contact information easily accessible.
Location Page Best Practices
Location pages serve as landing pages for local searches and connection points between your website and GBP listings. Their structure varies based on whether you have one location or many.
Single Location Websites
For single-location businesses, your homepage often serves as your primary location page. Ensure it clearly communicates your location, services, and contact information.
Create a dedicated contact page with your full address, embedded Google Map, directions from major landmarks, parking information, and hours of operation. This page should be linked from your main navigation.
Consider creating neighborhood or area-specific pages if you serve distinct communities within your broader service area. A dentist in Los Angeles might create pages for specific neighborhoods to capture searches from those areas.
Multi-Location Page Structure
Each location needs its own dedicated page with unique content. Avoid duplicating content across location pages, which creates thin content issues and provides poor user experience.
Include location-specific information on each page: address, phone number, hours, staff members, photos of that location, directions, and any services unique to that location. Write unique descriptions that reflect each location’s character and community.
Implement proper internal linking between location pages and your main service pages. Create a locations index page that links to all individual location pages for easy navigation.
Use consistent URL structures for location pages. Formats like /locations/city-name/ or /city-name/ help users and search engines understand your site architecture.
Schema Markup for Local SEO
Schema markup provides structured data that helps search engines understand your business information. Proper implementation can enhance your search listings with rich results and reinforce your local relevance.
LocalBusiness Schema
LocalBusiness schema tells search engines exactly what type of business you are, where you are located, and how to contact you. This structured data should appear on your homepage and location pages.
Include all relevant properties: business name, address, phone number, hours of operation, geo-coordinates, price range, and accepted payment methods. Use the most specific LocalBusiness subtype available, such as “Dentist” rather than generic “LocalBusiness.”
Validate your schema markup using Google’s Rich Results Test to ensure proper implementation. Errors in schema can prevent search engines from reading your structured data correctly.
Organization Schema
Organization schema provides broader information about your business entity. This complements LocalBusiness schema by establishing your brand identity and corporate structure.
Include your logo, social media profiles, founding date, and parent organization if applicable. This schema helps Google build a complete picture of your business entity.
Review and Aggregate Rating Schema
Review schema can display star ratings in search results, significantly improving click-through rates. Implement aggregate rating schema to show your overall rating based on collected reviews.
Follow Google’s guidelines carefully for review schema. Marking up fake reviews or self-reviews violates guidelines and can result in penalties. Only mark up legitimate customer reviews collected through proper channels.
Internal Linking for Local Authority
Internal links distribute authority throughout your site and help search engines understand content relationships. Strategic internal linking supports local SEO by connecting location pages, service pages, and supporting content.
Link from service pages to relevant location pages and vice versa. A page about “commercial HVAC services” should link to location pages where you offer that service.
Create content that naturally links to your core pages. Blog posts about local topics can link to relevant service and location pages, building internal authority over time.
Use descriptive anchor text that includes relevant keywords. “Our Austin plumbing services” provides more context than “click here” or “learn more.”
Link Building for Local SEO
Links remain a significant ranking factor for local SEO, though the approach differs from traditional link building. Local links from relevant geographic sources carry particular weight for local rankings.
Quality matters more than quantity in local link building. A handful of links from authoritative local sources outweighs dozens of links from irrelevant directories.
Local Link Acquisition Strategies
Focus link building efforts on sources with local relevance. These links signal geographic authority and community connection.
Local news websites offer valuable link opportunities through press coverage, contributed articles, or event sponsorships. Build relationships with local journalists and pitch newsworthy stories about your business.
Local business associations, chambers of commerce, and professional organizations often provide member directories with links. Join relevant organizations and ensure your listing includes a link to your website.
Community involvement generates natural link opportunities. Sponsoring local events, sports teams, or charities typically results in acknowledgment links from event pages and organization websites.
Partner with complementary local businesses for mutual promotion. A wedding photographer might partner with venues, florists, and caterers for reciprocal links and referrals.
Quality vs. Quantity in Local Links
Local link building should prioritize relevance and authority over volume. Ten links from respected local sources provide more value than hundreds of links from low-quality directories.
Evaluate potential link sources based on their local relevance, domain authority, and traffic. A link from your city’s major newspaper carries significant weight. A link from an obscure directory provides minimal value.
Avoid link schemes and paid link networks. Google’s algorithms detect manipulative link patterns, and penalties can devastate local rankings. Build links through legitimate relationships and valuable content.
Anchor Text Optimization
Anchor text, the clickable text of a link, provides context about the linked page. For local SEO, anchor text should naturally incorporate location and service terms without over-optimization.
Vary your anchor text across links. A natural link profile includes branded anchors (your business name), naked URLs, generic phrases (“click here”), and keyword-rich anchors. Over-reliance on exact-match keyword anchors appears manipulative.
When you control anchor text, such as in directory listings or guest posts, use natural variations that include your location and services. “Austin emergency plumber” and “plumbing services in Austin, TX” both provide relevant context.
Local Sponsorships and Partnerships
Sponsorships offer reliable local link opportunities while building community goodwill. Identify sponsorship opportunities that align with your brand and target audience.
Youth sports teams, school programs, community events, and local charities all seek sponsors. Most provide website recognition with links to sponsor sites.
Evaluate sponsorship ROI beyond just the link value. Consider brand exposure, community connection, and potential customer reach. The best sponsorships deliver multiple benefits beyond SEO.
Document your sponsorships and ensure links are implemented correctly. Follow up with organizations if promised links do not appear or contain errors.
Behavioral and User Engagement Signals
Google monitors how users interact with search results and business listings. These behavioral signals indicate whether your listing satisfies searcher intent and provides value.
While the exact weight of behavioral factors remains debated, evidence suggests they influence rankings. More importantly, optimizing for engagement improves conversion rates regardless of ranking impact.
Click-Through Rate from Local Results
Click-through rate measures how often users click your listing when it appears in search results. Higher CTR suggests your listing appeals to searchers and may signal relevance to Google.
Optimize your GBP listing to maximize clicks. Compelling photos, strong review ratings, complete business information, and recent posts all influence whether users click your listing over competitors.
Your business name and category appear prominently in local results. Ensure these accurately represent your business and appeal to your target customers.
Monitor CTR through Google Business Profile Insights. Compare your performance to previous periods and identify opportunities to improve listing appeal.
Dwell Time and Engagement Metrics
When users click through to your website, their subsequent behavior provides quality signals. Users who quickly return to search results may indicate your page did not satisfy their needs.
Create landing pages that immediately address searcher intent. If someone searches for “emergency plumber,” your page should prominently display emergency contact information, not require scrolling through company history.
Page design affects engagement. Clear navigation, readable text, fast loading, and mobile optimization all contribute to positive user experience that keeps visitors engaged.
Include clear calls to action that guide users toward conversion. Phone numbers, contact forms, and appointment scheduling should be easily accessible.
Mobile Engagement Patterns
Most local searches occur on mobile devices. Mobile users have different behavior patterns and expectations than desktop users.
Ensure your website provides excellent mobile experience. Test on actual devices, not just browser simulations. Check that buttons are easily tappable, text is readable without zooming, and forms are simple to complete on small screens.
Mobile users often want immediate action. Click-to-call buttons, directions links, and simple contact forms cater to mobile intent. Reduce friction between search and conversion.
Page speed matters even more on mobile, where connections may be slower. Optimize images, minimize code, and leverage caching to ensure fast mobile loading.
Driving Directions and Click-to-Call
Google tracks when users request directions to your business or click to call from your listing. These actions signal strong purchase intent and business relevance.
Ensure your address is accurate so directions lead customers to the right location. Verify your listing by visiting the location and confirming the map pin placement.
Use a trackable phone number to measure call volume from your GBP listing. This data helps quantify local SEO ROI and identify trends in customer behavior.
Encourage these high-intent actions through your listing optimization. Prominent hours, clear service descriptions, and positive reviews all increase likelihood of direction requests and calls.
Technical SEO Factors for Local Search
Technical SEO ensures search engines can properly crawl, index, and understand your website. Technical issues can undermine all other local SEO efforts by preventing Google from accessing your content.
Address technical fundamentals before investing heavily in content and link building. A technically sound website provides the foundation for local search success.
Mobile-First Optimization
Google uses mobile-first indexing, meaning it primarily uses the mobile version of your site for ranking and indexing. Your mobile site must contain all the content and functionality of your desktop site.
Test your site using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool. Address any issues identified, including text size, tap target spacing, and viewport configuration.
Responsive design adapts your site to different screen sizes automatically. This approach is generally preferred over separate mobile sites, which can create duplicate content and maintenance challenges.
Review your site on multiple devices and browsers. What works on one phone may have issues on another. Test thoroughly to ensure consistent experience.
Page Speed and Core Web Vitals
Page speed directly impacts user experience and serves as a confirmed ranking factor. Slow pages frustrate users and increase bounce rates.
Core Web Vitals measure specific aspects of page experience: Largest Contentful Paint (loading), First Input Delay (interactivity), and Cumulative Layout Shift (visual stability). Google uses these metrics in ranking calculations.
Use Google PageSpeed Insights to analyze your site and identify improvement opportunities. Common issues include unoptimized images, render-blocking resources, and excessive JavaScript.
Prioritize improvements based on impact and effort. Image optimization often provides significant gains with relatively simple implementation. More complex issues like code optimization may require developer resources.
Secure Website (HTTPS)
HTTPS encryption is a confirmed ranking factor and essential for user trust. Sites without HTTPS display security warnings in browsers, deterring potential customers.
Obtain an SSL certificate and implement HTTPS across your entire site. Many hosting providers offer free SSL certificates through Let’s Encrypt.
After implementing HTTPS, ensure all internal links and resources use HTTPS URLs. Mixed content warnings occur when secure pages load insecure resources.
Set up proper redirects from HTTP to HTTPS versions of your pages. Update your GBP listing and citations to use your HTTPS URL.
Crawlability and Indexation
Search engines must be able to crawl your site and index your pages for them to appear in search results. Technical barriers can prevent this entirely.
Check Google Search Console for crawl errors and indexation issues. Address any errors preventing important pages from being indexed.
Review your robots.txt file to ensure you are not accidentally blocking important pages. Verify your XML sitemap is submitted to Google Search Console and includes all pages you want indexed.
Use canonical tags to indicate preferred versions of pages and prevent duplicate content issues. This is particularly important for sites with URL parameters or multiple paths to the same content.
How to Prioritize Local SEO Ranking Factors
With dozens of ranking factors to consider, prioritization becomes essential. Not all factors carry equal weight, and resource constraints require strategic focus.
Effective prioritization considers both impact potential and implementation effort. Start with high-impact, low-effort improvements before tackling complex optimizations.
High-Impact vs. Low-Impact Factors
Research consistently identifies certain factors as most influential for local rankings. Google Business Profile optimization, review signals, and on-page local factors typically top the list.
BrightLocal’s annual Local Search Ranking Factors survey provides industry consensus on factor importance. GBP signals, review signals, and on-page factors consistently rank as top priorities.
Lower-impact factors still matter but should not consume disproportionate resources. Citation building beyond core directories, for example, provides diminishing returns after establishing presence on major platforms.
Focus initial efforts on factors you can control and measure. GBP optimization, review acquisition, and website improvements offer clear action items and trackable results.
Industry-Specific Prioritization
Different industries face different competitive landscapes and customer behaviors. Prioritization should reflect your specific market conditions.
Highly competitive industries like legal services and healthcare require stronger signals across all factors. Less competitive niches may achieve visibility with more basic optimization.
Industries with high review volume, like restaurants and retail, must prioritize review management. Professional services with fewer transactions may focus more on authority building and content.
Analyze what top competitors in your specific market are doing. Identify gaps where you can differentiate and areas where you must match their efforts to compete.
Resource Allocation Framework
Create a prioritized action plan based on your available resources. Small businesses with limited budgets should focus differently than enterprises with dedicated marketing teams.
Start with foundational elements: claim and optimize your GBP, ensure NAP consistency, and fix any technical website issues. These basics must be in place before advanced tactics provide value.
Allocate ongoing resources to review acquisition and GBP maintenance. These require consistent effort rather than one-time optimization.
Budget for periodic audits and updates. Local SEO is not set-and-forget. Algorithm changes, competitor actions, and business changes all require ongoing attention.
Local SEO Ranking Factors by Business Type
Different business models face unique local SEO challenges and opportunities. Strategies that work for retail storefronts may not apply to service area businesses or franchises.
Understanding your business type’s specific considerations helps you focus on relevant factors and avoid wasted effort.
Service Area Businesses (SABs)
Service area businesses travel to customers rather than receiving them at a fixed location. Plumbers, electricians, cleaning services, and mobile businesses fall into this category.
SABs can hide their address in GBP while specifying service areas. This prevents customers from visiting a home office or warehouse while still enabling local visibility.
Without a public address, SABs cannot leverage proximity signals as directly. Compensate by building strong relevance and prominence signals. Create content targeting specific service areas and build citations emphasizing your coverage zones.
Reviews become even more critical for SABs since customers cannot visit a physical location to evaluate the business. Strong review profiles build trust that replaces the credibility of a visible storefront.
Brick-and-Mortar Retail
Retail businesses with physical storefronts benefit from strong proximity signals and foot traffic potential. Your visible presence in the community supports both online and offline prominence.
Optimize for “near me” searches that drive immediate visits. Ensure your hours are accurate, especially during holidays and special events. Nothing frustrates customers more than arriving at a closed store.
Leverage your physical presence for local link building. Host events, participate in community activities, and build relationships with neighboring businesses.
Product inventory integration through Google’s local inventory ads can display specific products available at your location. This feature requires additional setup but can drive highly qualified traffic.
Multi-Location Franchises
Franchises and multi-location businesses must balance brand consistency with local optimization. Each location needs individual attention while maintaining corporate standards.
Create unique GBP listings for each location with location-specific information. Avoid copy-paste descriptions across locations. Each listing should reflect that specific location’s team, services, and community.
Develop location-specific website pages with unique content. Corporate templates can provide structure, but local details must be customized.
Coordinate review management across locations. Establish response guidelines that maintain brand voice while allowing location managers to address specific feedback.
Home-Based Businesses
Home-based businesses face decisions about whether to display their address publicly. Showing a residential address may appear unprofessional, while hiding it limits proximity signals.
Consider your industry norms and customer expectations. Some home-based businesses, like consultants and freelancers, commonly operate without public addresses. Others, like home-based bakeries, may benefit from displaying their location.
If hiding your address, focus heavily on service area optimization and building prominence through other signals. Strong reviews, authoritative content, and local links can compensate for reduced proximity signals.
Evaluate whether a virtual office or co-working space makes sense for your business. These can provide a professional address for GBP while offering meeting space for client interactions.
Measuring Local SEO Performance
Effective measurement enables data-driven optimization and demonstrates ROI to stakeholders. Track the right metrics to understand what is working and where to focus improvement efforts.
Local SEO measurement requires different tools and approaches than traditional SEO tracking. Rankings vary by location, and conversions often happen offline through calls and visits.
Local Pack Tracking Tools
Standard rank tracking tools may not capture local rankings accurately since results vary by searcher location. Specialized local rank tracking provides location-specific data.
Tools like BrightLocal, Whitespark, and Local Falcon track rankings from specific geographic points. This reveals how your visibility changes across your service area.
Track rankings for your priority keywords from multiple locations within your service area. A business might rank first for searchers downtown but fifth for those in the suburbs.
Monitor competitor rankings alongside your own. Understanding the competitive landscape helps contextualize your performance and identify opportunities.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Define KPIs that connect local SEO efforts to business outcomes. Rankings matter, but they should ultimately drive calls, visits, and revenue.
Primary KPIs for local SEO typically include:
GBP Insights metrics: views, searches, actions (calls, direction requests, website clicks)
Local Pack rankings for priority keywords
Website traffic from local searches
Phone calls and form submissions from local landing pages
Review quantity, rating, and sentiment trends
Track these metrics monthly and look for trends over time. Local SEO improvements often take months to materialize, so patience and consistent measurement are essential.
Attribution and ROI Measurement
Connecting local SEO efforts to revenue requires attribution tracking. This can be challenging when conversions happen offline.
Use call tracking to attribute phone calls to specific sources. Dynamic number insertion can show different numbers to visitors from different channels, enabling precise attribution.
Implement conversion tracking for online actions like form submissions, appointment bookings, and chat interactions. Google Analytics and Google Ads provide conversion tracking capabilities.
Survey customers about how they found you. While imprecise, this qualitative data supplements quantitative tracking and reveals the full customer journey.
Calculate ROI by comparing the value of attributed conversions to your local SEO investment. Include both direct costs (tools, services) and indirect costs (time spent on optimization).
Competitive Benchmarking
Regular competitive analysis reveals how your local SEO performance compares to alternatives customers might choose. Benchmarking identifies gaps and opportunities.
Monitor competitor GBP listings for changes in categories, photos, posts, and reviews. Tools like BrightLocal can track competitor review acquisition and ratings over time.
Analyze competitor websites for content gaps and link opportunities. What topics do they cover that you do not? Where are they getting links that you could also pursue?
Track competitor rankings for your priority keywords. When competitors gain or lose positions, investigate what changed to inform your own strategy.
Common Local SEO Ranking Factor Mistakes
Avoiding common mistakes prevents wasted effort and potential penalties. Many businesses unknowingly sabotage their local SEO through well-intentioned but misguided practices.
Learn from others’ errors to accelerate your own progress and avoid setbacks.
NAP Inconsistencies
Inconsistent business information across the web confuses search engines and customers. Even minor variations like “Street” vs. “St.” or different phone number formats can create issues.
Audit your citations regularly and correct inconsistencies promptly. Use a standardized format for your business name, address, and phone number across all platforms.
When your business information changes, update all citations systematically. Create a checklist of everywhere your business is listed and work through it methodically.
Ignoring Review Management
Neglecting reviews means missing one of the most influential ranking factors. Businesses that do not actively request reviews fall behind competitors who do.
Implement a systematic review request process. Train staff to ask satisfied customers for reviews. Use email or SMS follow-ups after transactions.
Respond to all reviews promptly and professionally. Ignoring negative reviews appears dismissive. Ignoring positive reviews misses engagement opportunities.
Keyword Stuffing in GBP
Adding keywords to your business name or stuffing descriptions with repetitive terms violates Google’s guidelines. This tactic may provide short-term gains but risks suspension.
Use your actual business name in GBP. If your legal business name includes location or service terms naturally, that is fine. Adding terms that are not part of your real name is not.
Write descriptions for humans. Include relevant terms naturally but prioritize readability and usefulness over keyword density.
Neglecting Mobile Experience
Poor mobile experience frustrates the majority of local searchers. Slow loading, difficult navigation, and hard-to-use forms drive potential customers to competitors.
Test your site on mobile devices regularly. Use Google’s mobile testing tools to identify issues. Prioritize mobile experience in all website decisions.
Ensure critical actions are easy on mobile. Click-to-call buttons, simple forms, and clear directions should be immediately accessible without scrolling or zooming.
Local SEO Ranking Factors: 2024 Updates and Trends
Local search continues evolving as Google refines its algorithms and user behavior shifts. Staying current with changes helps you adapt strategies and maintain competitive advantage.
Understanding trends also helps you anticipate future developments and position your business accordingly.
Algorithm Changes Affecting Local Search
Google regularly updates its local search algorithms, though major changes are less frequent than in organic search. Recent updates have emphasized review authenticity, spam detection, and user experience signals.
Google has increased enforcement against fake reviews and review gating (selectively soliciting reviews from satisfied customers only). Businesses relying on manipulative review tactics face increased risk.
The integration of AI into search results affects how local information appears. Google’s AI Overviews may summarize local business information, changing how users interact with search results.
Monitor industry news sources like Search Engine Land, Search Engine Journal, and local SEO blogs for algorithm update announcements and analysis.
Emerging Ranking Signals
Several signals appear to be gaining importance in local rankings. While not confirmed by Google, industry testing and observation suggest these factors matter.
Engagement signals from GBP, including photo views, post interactions, and Q&A activity, seem increasingly influential. Active profiles outperform static ones.
Review attributes beyond star ratings, including review text content, reviewer history, and review authenticity signals, appear to carry more weight.
Website experience metrics, particularly Core Web Vitals and mobile usability, continue gaining importance as Google emphasizes page experience.
Future-Proofing Your Local SEO Strategy
Build a local SEO strategy that adapts to changes rather than depending on specific tactics that may become obsolete.
Focus on fundamentals that will always matter: accurate business information, positive customer experiences, quality content, and legitimate authority building. These principles survive algorithm changes.
Diversify your local visibility across multiple platforms. Dependence on Google alone creates risk. Build presence on Yelp, Apple Maps, Bing Places, and industry-specific platforms.
Invest in brand building that transcends search algorithms. Strong brands with loyal customers succeed regardless of ranking fluctuations.
Local SEO Ranking Factors Checklist
Use these checklists to audit your current local SEO status and identify improvement opportunities. Work through each section systematically to ensure comprehensive coverage.
Google Business Profile Checklist
Verify your business and complete verification process
Ensure business name matches your real-world name exactly
Confirm address is accurate and formatted consistently
Add local phone number (not toll-free if possible)
Select the most specific primary category available
Add all relevant secondary categories
Write a complete, keyword-rich business description
Upload high-quality photos of exterior, interior, products, and team
Set accurate business hours including special hours
Complete all applicable attributes for your category
Enable messaging if you can respond promptly
Add products or services with descriptions and prices
Post updates at least weekly
Monitor and respond to Q&A section
On-Page Local SEO Checklist
Include city and service in homepage title tag
Add location to meta descriptions for key pages
Use location naturally in H1 and subheadings
Embed Google Map on contact page
Display full NAP in website footer
Create dedicated pages for each service offered
Develop location pages for each area served
Implement LocalBusiness schema markup
Add Organization schema with logo and social profiles
Create internal links between service and location pages
Ensure mobile-friendly design and functionality
Optimize page speed and Core Web Vitals
Implement HTTPS across entire site
Submit XML sitemap to Google Search Console
Citation and Link Building Checklist
Submit to major data aggregators (Data Axle, Localeze, Foursquare)
Claim and optimize listings on top general directories
Create profiles on industry-specific directories
List in local chamber of commerce and business associations
Audit existing citations for NAP consistency
Correct any inconsistent citations found
Identify local link opportunities (news, sponsors, partners)
Build relationships with complementary local businesses
Pursue local sponsorship opportunities
Monitor for new citation and link opportunities
Technical SEO Checklist
Verify mobile-friendly status with Google’s tool
Test page speed and address issues found
Confirm HTTPS implementation across all pages
Check for crawl errors in Google Search Console
Verify XML sitemap is submitted and error-free
Review robots.txt for unintended blocks
Implement proper canonical tags
Fix any broken links or 404 errors
Ensure proper redirect chains (no chains or loops)
Test structured data with Rich Results Test
Frequently Asked Questions About Local SEO Ranking Factors
What are the top 3 local SEO ranking factors?
The three most influential local SEO ranking factors are Google Business Profile signals, review signals, and on-page optimization. GBP factors include category selection, completeness, and engagement. Reviews encompass quantity, quality, and response management. On-page factors cover local keyword optimization, NAP consistency, and location page quality.
How often do local ranking factors change?
Google updates its local algorithm continuously, though major changes occur a few times per year. Most updates are minor refinements rather than dramatic shifts. The core principles of relevance, proximity, and prominence remain constant even as specific signals evolve. Monitor industry news and your own rankings to detect changes affecting your business.
Do reviews really impact local rankings?
Yes, reviews significantly impact local rankings. Google has confirmed that reviews factor into local search results. Beyond rankings, reviews influence click-through rates and conversion rates. Businesses with more positive reviews consistently outperform those with fewer or lower-rated reviews in local search visibility.
How important is proximity for local SEO?
Proximity is extremely important and largely outside your control. For searches without location modifiers, Google heavily weights distance between the searcher and your business. You cannot change your physical location, but you can ensure Google accurately understands where you are and optimize other factors to compete despite proximity disadvantages.
Can I rank locally without a physical address?
Service area businesses can rank in local search without displaying a public address. Google allows SABs to hide their address while specifying service areas. However, this approach limits proximity signals. SABs must compensate with stronger relevance and prominence signals, including robust review profiles, quality content, and authoritative citations.
How long does local SEO take to work?
Local SEO typically shows initial results within three to six months, with significant improvements taking six to twelve months. Timeline varies based on competition level, starting position, and optimization intensity. Some changes, like GBP optimizations, can impact rankings within weeks. Others, like building review volume and authority, require sustained effort over months.
What is the difference between local SEO and regular SEO?
Local SEO focuses on ranking in location-based searches and Google’s Local Pack, while regular SEO targets organic rankings regardless of location. Local SEO emphasizes Google Business Profile optimization, citations, reviews, and proximity signals. Regular SEO prioritizes content depth, backlinks, and technical optimization. Most local businesses need both approaches working together.
Next Steps: Building Your Local SEO Strategy
Understanding local SEO ranking factors is the first step. Implementing a comprehensive strategy that addresses these factors systematically drives actual results.
DIY Local SEO Action Plan
Start with the highest-impact, lowest-effort improvements. Claim and fully optimize your Google Business Profile if you have not already. This single action can produce noticeable results within weeks.
Audit your NAP consistency across major directories and correct any inconsistencies. Use free tools to identify where your business is listed and spot variations.
Implement a review request system. Simply asking satisfied customers for reviews can dramatically increase your review volume over time.
Optimize your website’s key pages for local search. Add location to title tags, create or improve your contact page, and ensure your NAP appears consistently throughout your site.
Set up Google Search Console and Google Business Profile Insights to track your progress. Review metrics monthly and adjust your approach based on results.
When to Hire a Local SEO Expert
Consider professional help when you lack time to implement strategies consistently, face strong competition requiring advanced tactics, or need faster results than DIY efforts typically produce.
Complex situations also warrant expert assistance. Multi-location businesses, penalty recovery, and competitive markets benefit from experienced guidance.
Evaluate potential providers based on their local SEO specific experience, case studies with measurable results, and transparent reporting practices. Avoid providers promising guaranteed rankings or using tactics that violate Google’s guidelines.
Getting Started with Professional Local SEO Services
Professional local SEO services accelerate results by applying proven strategies systematically. Experienced providers identify opportunities and issues that DIY efforts might miss.
A comprehensive local SEO engagement typically includes GBP optimization, citation building and cleanup, review management strategy, on-page optimization, local link building, and ongoing monitoring and reporting.
Conclusion
Local SEO ranking factors span Google Business Profile optimization, proximity signals, relevance indicators, prominence metrics, reviews, citations, on-page elements, links, behavioral signals, and technical foundations. Mastering these factors requires systematic attention to each area while prioritizing based on your specific business situation and competitive landscape.
The businesses that dominate local search treat local SEO as an ongoing discipline rather than a one-time project. They continuously optimize their GBP, actively manage reviews, maintain citation consistency, and adapt to algorithm changes. This sustained effort compounds into durable competitive advantage.
We help businesses build sustainable local search visibility through comprehensive local SEO strategies. White Label SEO Service provides the expertise and systematic approach needed to improve your local rankings, attract more customers, and grow your business. Contact us to discuss how we can support your local SEO goals.



